当前位置:网站首页>Basic tutorial of scala -- 16 -- generics
Basic tutorial of scala -- 16 -- generics
2022-07-04 18:52:00 【Empty.】
Scala Basic course –16– Generic
Chapter goal
- Master generic methods , class , The use of traits
- Learn about Generic upper and lower bounds
- Understand covariance , Inversion , Unchanging usage
- Master the list to reorder cases
1. Generic
Generic means Refers to a specific data type , stay Scala in , For generics [ data type ] Express . In actual development , Generics are generally used in combination with arrays or collections , besides , There are three other common uses of generics :
- Generic methods
- Generic classes
- Generic characteristics
1.1 Generic methods
Generic methods refer to Define generics on method declarations , namely : The parameter type of this method is determined by generics . When a method is called , Specify specific data types .
Format
def Method name [ Generic names ](..) = {
//...
}
demand
Define methods getMiddleElement(), Used to get the intermediate elements of an array of any type .
- Train of thought : Implement directly without considering generics ( be based on Array[Int] Realization )
- Train of thought two : Add generic support .
Reference code
// Case study : Generic method demonstration .
// details : Generic methods call methods Specify specific data types .
object ClassDemo01 {
// demand : Use a method to get the middle element of an array of any type
// Train of thought : Implement directly without considering generics ( be based on Array[Int] Realization )
//def getMiddleElement(arr: Array[Int]) = arr(arr.length / 2)
// Train of thought two : Add generic support
def getMiddleElement[T](arr: Array[T]) = arr(arr.length / 2)
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// Calling method
println(getMiddleElement(Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)))
println(getMiddleElement(Array("a", "b", "c")))
}
}
1.2 Generic classes
Generic classes refer to Define generics on class declarations , namely : The parameter types of members in this class are determined by generics . When you create an object , Specify specific data types .
Format
class class [T](val Variable name : T)
demand
- Define a Pair Generic classes , This class contains two fields , And the types of the two fields are not fixed .
- Create different types of Pair Generic class object , And print .
Reference code
// Case study : Generic - Demonstrate the use of generic classes .
// Generic classes : When creating objects , Specify specific data types .
object ClassDemo02 {
//1. Achieve one Pair Generic classes
//2. Pair Class contains two fields , And the types of the two fields are not fixed
class Pair[T](var a:T, var b:T)
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//3. Create different types of generic class objects , And print
var p1 = new Pair[Int](10, 20)
println(p1.a, p1.b)
var p2 = new Pair[String]("abc", "bcd")
println(p2.a, p2.b)
}
}
1.3 Generic characteristics
Generic traits refer to Define generics on the declaration of traits , namely : The parameter types of members in this trait are determined by generics . When defining subclasses or sub singleton objects of generic characteristics , Specify specific data types .
Format
trait Trait A[T] {
// Members of traits
}
class class B extends Trait A[ Specify the specific data type ] {
// Members in class
}
demand
- Define generic attributes Logger, This class has a variable a and show() Method , They all use Logger Generics of traits .
- Define singleton object ConsoleLogger, Inherit Logger Trait .
- Print the singleton object ConsoleLogger Members of the .
Reference code
// Case study : Demonstrate generic characteristics .
object ClassDemo03 {
//1. Define generic attributes Logger, There is one in this category a Variables and show() Method , It's all used Logger Generics of traits .
trait Logger[T] {
// Defining variables
val a:T
// Define methods .
def show(b:T) = println(b)
}
//2. Define singleton object ConsoleLogger, Inherit Logger Trait .
object ConsoleLogger extends Logger[String]{
override val a: String = " Zhang San "
}
//main Method , As the main entrance to the program .
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//3. Print the singleton object ConsoleLogger Members of the .
println(ConsoleLogger.a)
ConsoleLogger.show("10")
}
}
2. Up and down
We are using generics ( Method , class , Trait ) when , If you want to limit which class the generic type must inherit from 、 Or it must be the parent of which class . here , You need to use it Upper and lower bounds of generics .
2.1 upper bound
Use T <: Type name Represents adding a upper bound , Indicates that generic parameters must be derived from this class ( Or itself ) Inherit .
Format
[T <: type ]
for example : [T <: Person] It means , Generic T Data type of Must be Person Type or Person Subtypes of
demand
- Define a Person class
- Define a Student class , Inherit Person class
- Define a generic method demo(), The method receives one Array Parameters .
- limit demo Methodical Array The element type can only be Person perhaps Person Subclasses of
- Test call demo() Method , Pass in different element types Array
Reference code
// Case study : Demonstrate the upper and lower bounds of generics upper bound .
object ClassDemo04 {
//1. Define a Person class
class Person
//2. Define a Student class , Inherit Person class
class Student extends Person
//3. Define a demo Generic methods , The method receives one Array Parameters ,
// limit demo Methodical Array The element type can only be Person perhaps Person Subclasses of
def demo[T <: Person](arr: Array[T]) = println(arr)
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//4. Test call demo, Pass in different element types Array
//demo(Array(1, 2, 3)) // This will report an error , Because it can only pass in Person Or its subtype .
demo(Array(new Person()))
demo(Array(new Student()))
}
}
2.2 Lower bound
Use T >: data type Represents adding a Lower bound , Indicates that generic parameters must be from the type itself or the parent type of the type .
Format
[T >: type ]
Be careful :
- for example : [T >: Person] It means , Generic T Data type of Must be Person Type or Person The father type of
- If a generic has an upper bound 、 There is also a lower bound . The lower bound is written before , The upper bound is written after . namely : [T >: type 1 <: type 2]
demand
- Define a Person class
- Define a Policeman class , Inherit Person class
- Define a Superman class , Inherit Policeman class
- Define a demo Generic methods , The method receives one Array Parameters ,
- limit demo Methodical Array The element type can only be Person、Policeman
- Test call demo, Pass in different element types Array
Reference code
// Case study : Demonstrate the upper and lower bounds of generics Lower bound .
// If you are setting generics , It involves the existing upper bound , There is also a lower bound , It must be : The lower bound is in front , The upper bound is behind .
object ClassDemo05 {
//1. Define a Person class
class Person
//2. Define a Policeman class , Inherit Person class
class Policeman extends Person
//3. Define a Superman class , Inherit Policeman class
class Superman extends Policeman
//4. Define a demo Generic methods , The method receives one Array Parameters ,
// limit demo Methodical Array The element type can only be Person、Policeman
// Lower bound upper bound
def demo[T >: Policeman <: Policeman](arr: Array[T]) = println(arr)
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//5. Test call demo, Pass in different element types Array
//demo(Array(new Person))
demo(Array(new Policeman))
//demo(Array(new Superman)) // Will report a mistake , Because it can only pass in : Policeman Class gets its parent type , and Superman yes Policeman Subtypes of , So no .
}
}
3. Covariance 、 Inversion 、 Non variable
stay Spark Covariance is widely used in the source code of 、 Inversion 、 Non variable , Learning this knowledge is of great significance to our future reading spark The source code is very helpful .
- Non variable : class A And the class B There is a parent-child relationship , however Pair[A] and Pair[B] Not between
Any relationship. - Covariance : class A And the class B There is a parent-child relationship , Pair[A] and Pair[B] There are also
Father and sonRelationship . - Inversion : class A And the class B There is a parent-child relationship , however Pair[A] and Pair[B] Between
Children and parentsRelationship .
Here's the picture :
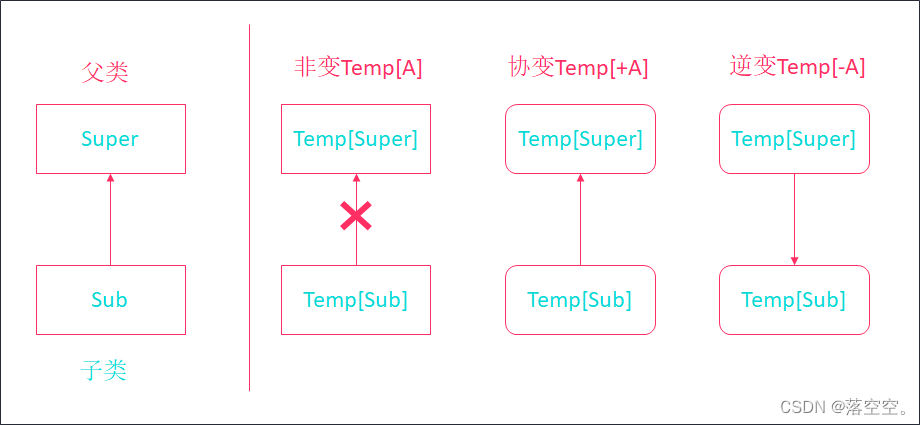
3.1 Non variable
Grammar format
class Pair[T]{
}
- The default generic class is
Immutable - namely : type B yes A Subtypes of ,Pair[A] and Pair[B] Without any affiliation
3.2 Covariance
Grammar format
class Pair[+T]
- type B yes A Subtypes of ,Pair[B] Think of it as Pair[A] Subtypes of
- The direction of the parameterized type is consistent with that of the type .
3.3 Inversion
Grammar format
class Pair[-T]
- type B yes A Subtypes of ,Pair[A] Conversely, it can be considered as Pair[B] Subtypes of
- The direction of parameterized types is opposite to that of types
3.4 Example
demand
- Define a Super class 、 And one. Sub Class inherits from Super class
- Use covariance 、 Inversion 、 Immutable defines three generic classes
- Create generic class objects to demonstrate covariance 、 Inversion 、 Non variable
Reference code
// Case study : Demonstrate non change , Covariance , Inversion .
object ClassDemo06 {
//1. Define a Super class 、 And one. Sub Class inherits from Super class
class Super // Parent class
class Sub extends Super // Subclass
//2. Use covariance 、 Inversion 、 Immutable defines three generic classes
class Temp1[T] // Non variable
class Temp2[+T] // Covariance
class Temp3[-T] // Inversion .
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//3. Create generic classes to demonstrate covariance 、 Inversion 、 Non variable
// Demonstrate non change .
val t1:Temp1[Sub] = new Temp1[Sub]
//val t2:Temp1[Super] = t1 // Compiler error , Because non change is : Super and Sub There is a parent-child relationship , however Temp1[Super] and Temp1[Sub] There is no relationship between .
// Demonstrate covariance
val t3:Temp2[Sub] = new Temp2[Sub]
val t4:Temp2[Super] = t3 // Don't complain , Because covariance is : Super and Sub There is a parent-child relationship , therefore Temp2[Super] and Temp2[Sub] There is also a father son relationship .
//Temp2[Super] It's the father type , Temp2[Sub] It's a subtype .
// Demonstrate inverter
val t5:Temp3[Super] = new Temp3[Super]
val t6:Temp3[Sub] = t5 // Don't complain , Because inversion is : Super and Sub There is a parent-child relationship , therefore Temp3[Super] and Temp3[Sub] There is also a relationship between son and father .
//Temp3[Super] It's a subtype , Temp3[Sub] It's the father type .
}
}
4. Case study : List to reorder
4.1 demand
Known under the current project data There is one in the folder 1.txt text file , The contents of the document are as follows :
11 6 5 3 22 9 3 11 5 1 2After reordering the above data , Re write to data Under folder 2.txt In the text file , The content is as follows :
1 2 3 5 6 9 11 22
4.2 Purpose
Investigate Generic , list , flow Related content .
4.3 Reference code
import java.io.{
BufferedWriter, FileWriter}
import scala.io.Source
// Case study : List to reorder , And write the file .
object ClassDemo07 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//1. Define the data source object .
val source = Source.fromFile("./data/1.txt")
//2. Read all data from the specified file ( String form )
val list1:List[String] = source.mkString.split("\\s+").toList
//3. hold List[String] List to List[Int]
val list2:List[Int] = list1.map(_.toInt)
//4. hold List[Int] convert to Set[Int], De duplication of list elements .
val set:Set[Int] = list2.toSet
//5. hold Set[Int] Turn into List[Int], And then in ascending order
val list3:List[Int] = set.toList.sorted
//println(list3)
//6. Rewrite the data to data Under folder 2.txt In file .
val bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("./data/2.txt"))
for(i <- list3) {
bw.write(i.toString)
bw.newLine() // Don't forget to add new lines
}
//7. Release resources
bw.close()
}
}
st[Int] convert to Set[Int], De duplication of list elements .
val set:Set[Int] = list2.toSet
//5. hold Set[Int] Turn into List[Int], And then in ascending order
val list3:List[Int] = set.toList.sorted
//println(list3)
//6. Rewrite the data to data Under folder 2.txt In file .
val bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(“./data/2.txt”))
for(i <- list3) {
bw.write(i.toString)
bw.newLine() // Don't forget to add new lines
}
//7. Release resources
bw.close()
}
}
边栏推荐
- 蓝桥:合根植物
- Digital "new" operation and maintenance of energy industry
- Nature Microbiology | 可感染阿斯加德古菌的六种深海沉积物中的病毒基因组
- 爬虫(6) - 网页数据解析(2) | BeautifulSoup4在爬虫中的使用
- .NET ORM框架HiSql实战-第二章-使用Hisql实现菜单管理(增删改查)
- 【Go语言刷题篇】Go完结篇|函数、结构体、接口、错误入门学习
- android使用SQLiteOpenHelper闪退
- [cloud voice suggestion collection] cloud store renewal and upgrading: provide effective suggestions, win a large number of code beans, Huawei AI speaker 2!
- Wireshark抓包TLS协议栏显示版本不一致问题
- Tutorial on the use of Huawei cloud modelarts (with detailed illustrations)
猜你喜欢
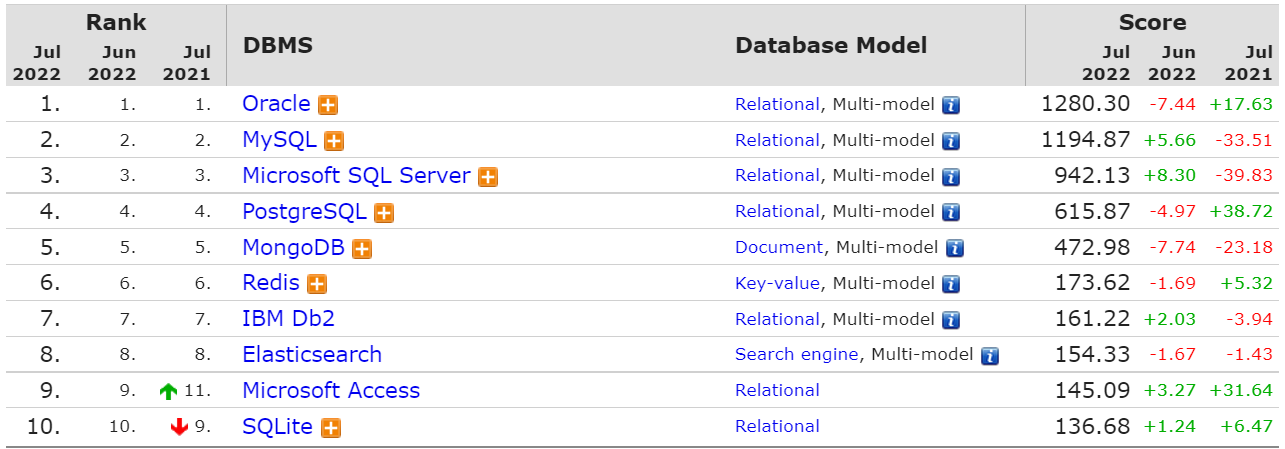
DB engines database ranking in July 2022: Microsoft SQL Server rose sharply, Oracle fell sharply
Scala基础教程--13--函数进阶

Weima, which is going to be listed, still can't give Baidu confidence
Scala基础教程--17--集合
基于NCF的多模块协同实例
力扣刷题日记/day8/7.1

Just today, four experts from HSBC gathered to discuss the problems of bank core system transformation, migration and reconstruction

What types of Thawte wildcard SSL certificates provide
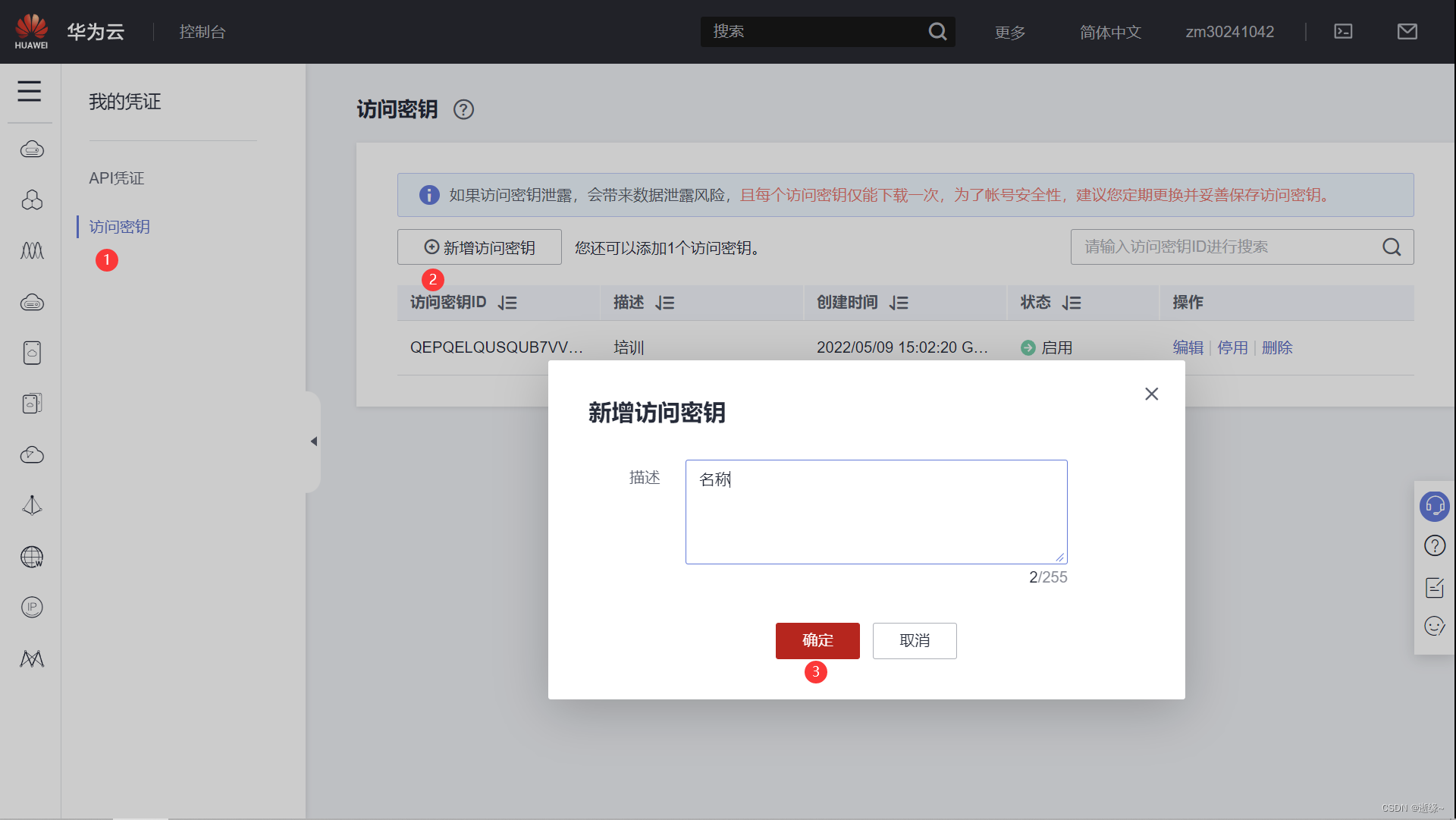
华为云ModelArts的使用教程(附详细图解)
Unity makes revolving door, sliding door, cabinet door drawer, click the effect of automatic door opening and closing, and automatically play the sound effect (with editor extension code)
随机推荐
大厂面试总结大全二
基于unity的愤怒的小鸟设计
NBA赛事直播超清画质背后:阿里云视频云「窄带高清2.0」技术深度解读
78 year old professor Huake impacts the IPO, and Fengnian capital is expected to reap dozens of times the return
未来几年中,软件测试的几大趋势是什么?
一种将Tree-LSTM的强化学习用于连接顺序选择的方法
Reptile elementary learning
MySQL common add, delete, modify and query operations (crud)
Li Kou brush question diary /day1/2022.6.23
The block:usdd has strong growth momentum
File processing examples of fopen, FREAD, fwrite, fseek
mysql5.7安装教程图文详解
能源行业的数字化“新”运维
TorchDrug教程
Uni app and uviewui realize the imitation of Xiaomi mall app (with source code)
同事悄悄告诉我,飞书通知还能这样玩
提升复杂场景三维重建精度 | 基于PaddleSeg分割无人机遥感影像
Wireshark packet capturing TLS protocol bar displays version inconsistency
字节跳动Dev Better技术沙龙成功举办,携手华泰分享Web研发效能提升经验
An example of multi module collaboration based on NCF