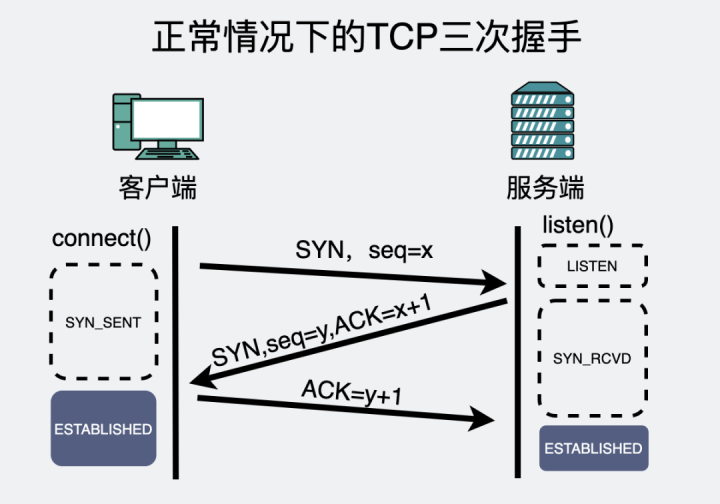
We all know ,TCP It's a
Connection oriented 、 reliable 、 Transport layer based on byte stream
Communication protocol .
What's mentioned here "
Connection oriented
", It means the need for Establishing a connection , Use connections , Release the connection .
Establishing a connection
It means what we know
TCP Three handshakes
.
and
Use connections
, Is sent through a 、 A form of confirmation , Conduct
The data transfer
.
And that is
Release the connection
, That's what we're used to
TCP Four waves
.
TCP Four waves
You should know better , But you've seen it
Three waves
Do you ? also
Two waves
Well ?
Have seen ? that
Four handshakes
Well ?
Today's topic , I don't want to be just curious , I don't want to engage in cold knowledge .
Let's start with four waves , Get some practical knowledge .
TCP Four waves
In a brief review TCP Four waves .
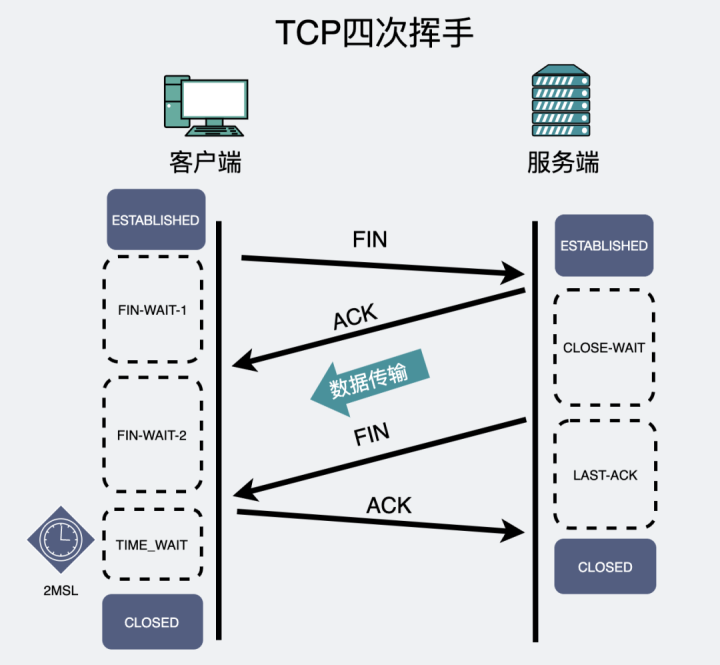
Under normal circumstances . As long as the data transmission is over ,
Whether it's the client or the server , Can take the initiative to wave four times
, Release the connection .
Just like the picture , hypothesis , The four waves were initiated by the client , Then it is
The initiative
. The server passively receives the wave request from the client , It's called
Passive party
.
Client and server , In limine , It's all in ESTABLISHED state .
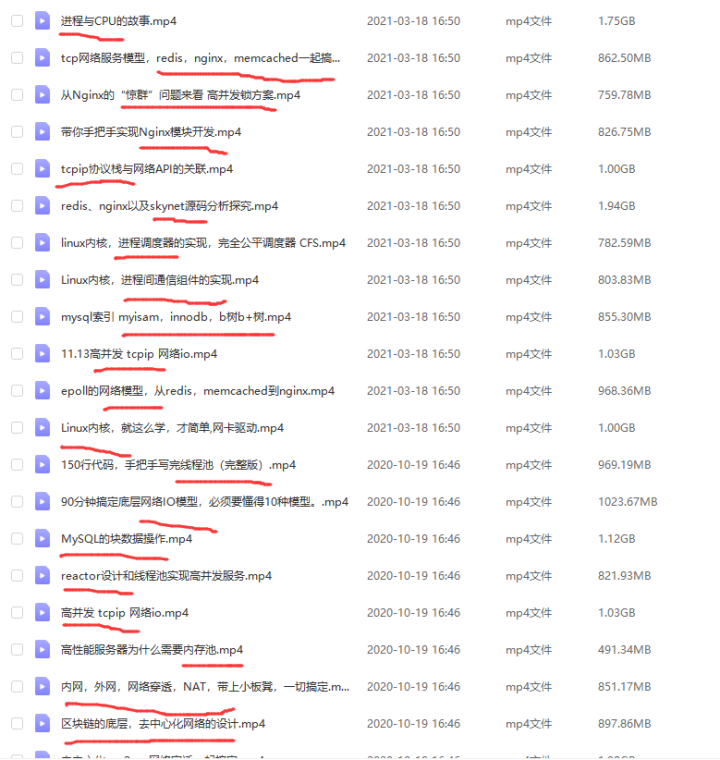
First wave
: In general , The active party performs close() or shutdown() Method , Will send a FIN Message comes out , Express "
I don't send data anymore
".
Second wave
: After receiving the request from the active party FIN After the message , The passive side immediately responds to a ACK, intend " I received your FIN 了 , I know you don't send data anymore ".
What is mentioned above is
The initiative
No more sending data . But if at this time ,
Passive party
There are still data to send , Then keep sending . Be careful , Although between the second and third wave , The passive side can send data to the active side , But it is not certain whether the active party can receive it normally , This will be said later .
Third wave
: After the passive side senses the second wave , Will do a series of finishing work , Finally, a close(), At this time, there will be a third wave FIN-ACK.
Fourth wave
: The active party returns a ACK, It means received .
The first wave and the third wave , It's all triggered by our initiative in the application ( For example, call close() Method ), That is what we need to pay attention to when writing code .
Second and fourth wave , The kernel protocol stack automatically helps us complete , We can't touch this place when we write code , So you don't need to care too much .
In addition, whether active or passive , Each side sent out a FIN And a ACK . Also received a FIN And a ACK .
Let's pay attention to this , I'll mention later .
FIN Be sure to execute the program close() or shutdown() Can it be sent out ?
not always
. In general , Through to socket perform close() or shutdown() Method will emit FIN. But actually , As long as the application exits , Whether it's
Take the initiative
sign out , still
passive
sign out ( For some inexplicable reason kill 了 ),
Metropolis
issue FIN.
FIN Refer to " I no longer send data ", therefore shutdown() Turn off reading and don't send to each other FIN, Turn off writing before sending FIN.
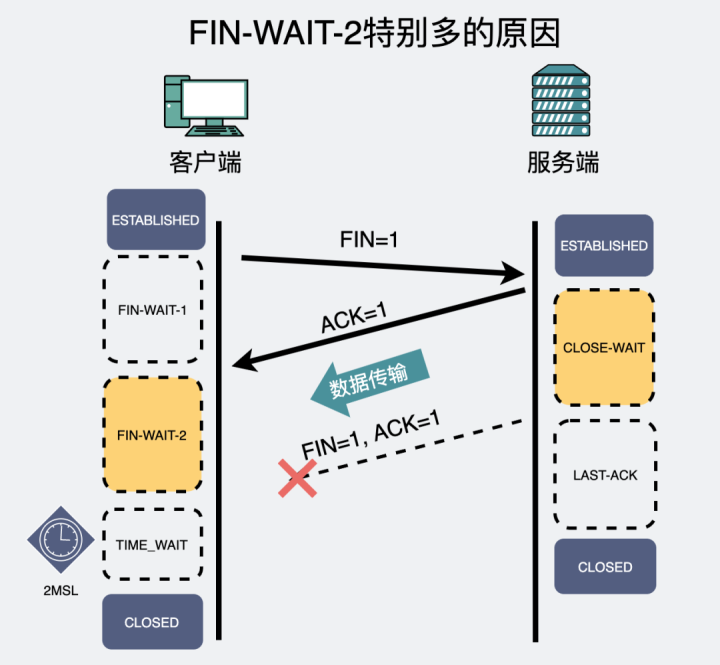
If on the machine FIN-WAIT-2 There are many states , What is it for?
According to the four waves above , It can be seen that ,FIN-WAIT-2 yes
The initiative
The state over there .
Programs in this state , I've been waiting for
Third wave
Of FIN. The third wave needs to be executed by the passive party in the code close() issue .
So when the machine FIN-WAIT-2 There are many states , Well, generally speaking , There will be a lot of... On another machine CLOSE_WAIT. There are a lot of CLOSE_WAIT The machine that you're using , Why are you reluctant to call close() Close the connection .
therefore , If on the machine FIN-WAIT-2 There are many states , Generally, it is because the opposite end does not execute close() Method send out the third wave .
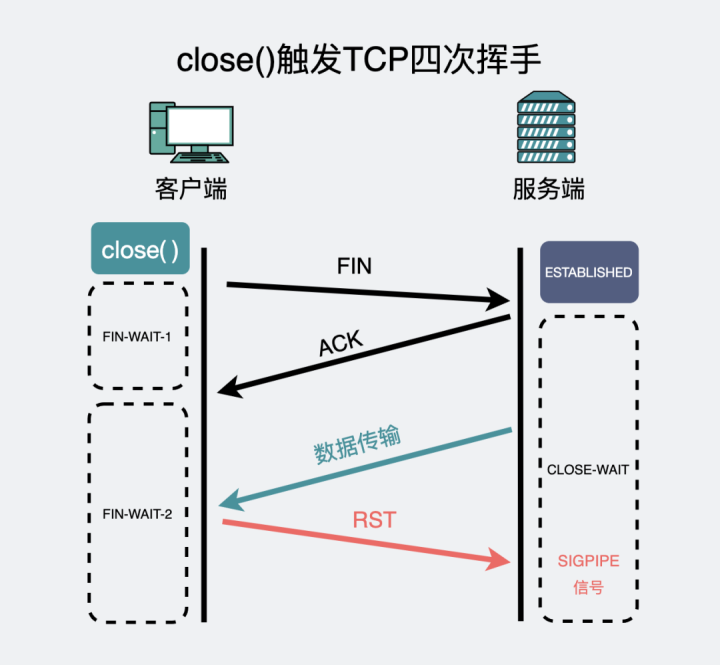
The active party is close Data received later , What will happen to
An article I wrote before 《 Code execution send After success , Is the data sent out ?》 in , From the perspective of source code ,
In general
, The program takes the initiative to execute close() When ;
As we all know ,TCP yes
Full duplex communication
, It means sending data at the same time , It can also receive data .
Close() The meaning is , At the same time
Turn off sending and receiving
Message functionality .
in other words , although
Theoretically
, Between the second and third wave , The passive side can transmit data to the active side .
But if The four waves of the active side are through close() The trigger , The active party will not receive this message . And there will be another RST. Just end the connection .
【 Article Welfare 】 In addition, Xiaobian also sorted out some C++ Back-end development interview questions , Teaching video , Back end learning roadmap for free , You can add what you need :
Click to join the learning exchange group ~
Group file sharing
Xiaobian strongly recommends C++ Back end development free learning address :
C/C++Linux Server development senior architect /C++ Background development architect
Between the second and third wave , Can't transfer data ?
Neither . Mentioned earlier Close() The meaning is , At the same time
Turn off sending and receiving
Message functionality .
If you can do it
Just turn off sending messages
,
Do not turn off receiving messages
The function of , Then you can continue to receive messages . such half-close The function of , By calling shutdown() Method can do .
int shutdown(int sock, int howto); among howto The mode is disconnected . There are the following values :
SHUT_RD: Turn off reading . At this time, the application layer should no longer try to receive data , In the kernel protocol stack, even if the receive buffer receives data, it will be discarded .
How do you know the opposite end socket Yes close still shutdown
No matter
Take the initiative
The closing party calls close() still shutdown(), For the passive side , Only one received FIN.
passive
The closing party
I was confused
," How do I know if the other party wants me to continue sending data ?"

Actually , There's no need to get tangled up , Send it when it's time .
Between the second wave and the third wave , If
passive
The closing party wants to send data , So at the code level , It's the execution of send() Method .
int send( SOCKET s,const char* buf,int len,int flags);send() Will copy the data to the local computer
Send buffer
. If there is no problem with the send buffer , Can be copied in , So normally ,send()
commonly
Will return success .

then
Passive party
The kernel protocol stack sends data to
Take the initiative
The closing party .
If the last time
Take the initiative
The closing party calls shutdown(socket_fd, SHUT_WR). At this time ,
Active Closing Party
No more messages sent , But it can receive
Passive party
The news of , As usual , All's well that ends well .
If the last time
Take the initiative
The closing party calls close(). that
The initiative
Upon receipt of
Passive party
The data will be directly
discarded
, Then go back to one RST.
For the second case .
Passive party
Kernel protocol stack
received RST, Will close the connection . But the kernel connection is closed , The application layer doesn't know ( Unless notified ).
At this point, the passive side
application layer
Next steps , does
Read or write
.
If it is written , Then the program will produce SIGPIPE The signal , Application layer code can capture and process signals , If you don't deal with , By default, the process will terminate , Abnormal exit .
To sum up
, When the passive closing side recv() return EOF when , Explain that the active party passes close() or shutdown(fd, SHUT_WR) Launched the first wave .
If the passive party performs
two
send().
The second time send() when . If the initiative is through shutdown(fd, SHUT_WR) The first wave initiated , At this time send() Will still succeed . If the active party passes close() The first wave initiated , Then there will be SIGPIPE The signal , The process terminates by default , Abnormal exit . If you don't want to quit abnormally , Remember to capture and process this signal .
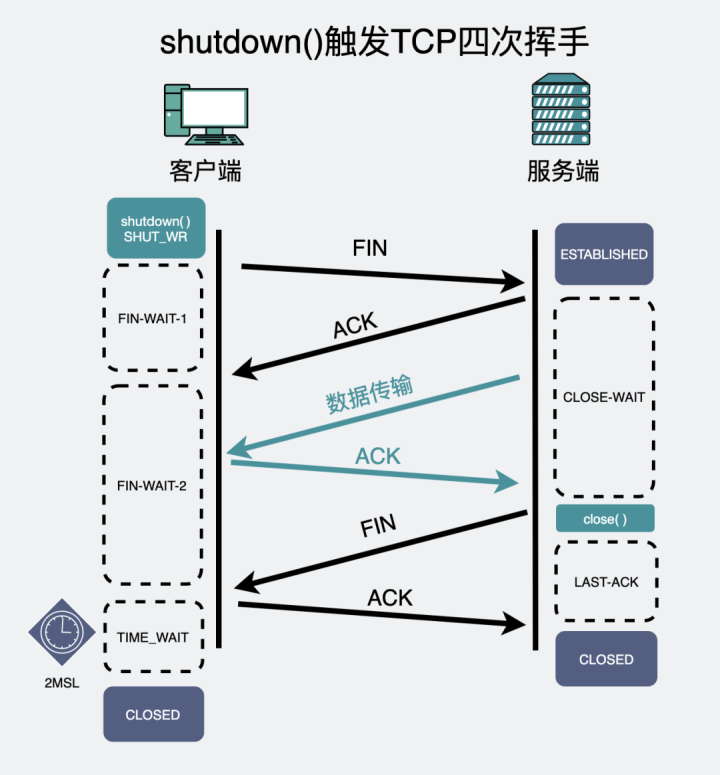
If the passive side doesn't wave for the third time , What will happen?
Third wave , By
Passive party
Actively triggered , For example, call close().
If it's due to a code error or some other reason , The passive side just doesn't perform the third wave .
Now , The active party will use... When waving for the first time close() still shutdown(fd, SHUT_WR) , There are different behaviors .
If it is shutdown(fd, SHUT_WR) , It indicates that the active party actually only turns off write , But you can also read , At this time, it will always be in FIN-WAIT-2, Die waiting for the third wave of the passive side .
If it is close(), It means that the active party's reading and writing are turned off , At this time, you will be in FIN-WAIT-2 A span , This time is by net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout control , It's usually 60s, This value coincides with 2MSL equally .
After that time , The state does not become `TIME-WAIT`, It's directly becoming `CLOSED`.
# cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_fin_timeout
60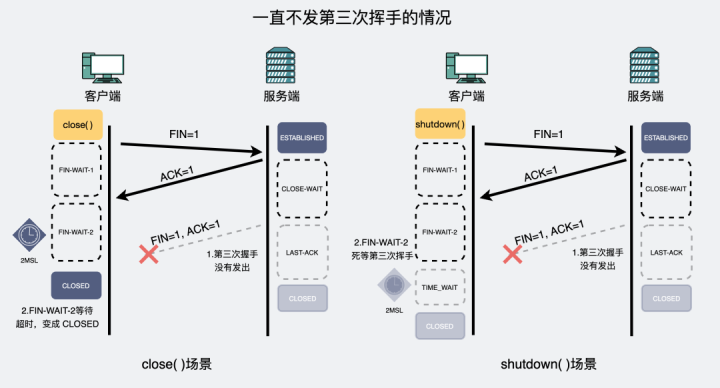
TCP Three waves
After four waves , Is it possible to wave three times ?
it is possible that .
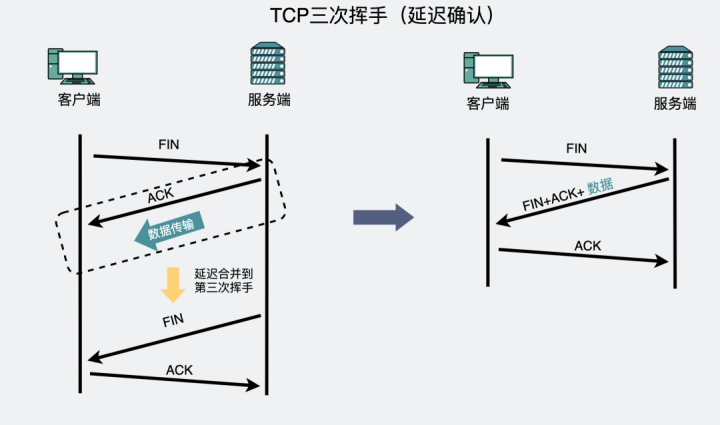
We know ,TCP Wave your hand four times , Between the second and third wave , It is possible to have data transmission . The purpose of the third wave is to tell the active party ," The passive party has no data to send ".
therefore , After the first wave , If the passive party has no data, send it to the active party . The second and third wave is
There may be
Merge transmitted . So there are three waves .
If you have data to send , Can't it be three waves
What is mentioned above is
No data to send
The situation of , If second 、 Between the third wave
There's data
To send , Can't it become three waves ?
Not at all
.TCP There is also a feature called
Delay confirmation
. It can be simply understood as :
The receiver does not need to reply immediately after receiving the data ACK Confirmation package .
On this basis ,
Not every time you send a packet, you can receive one
ACK
Confirmation package , Because the receiver can merge confirmation .
And this merger is confirmed , Put it in your hand four times , You can wave your hand a second time 、 Third wave , And the data transmission between them are combined to send . So there are three waves .
TCP Two waves
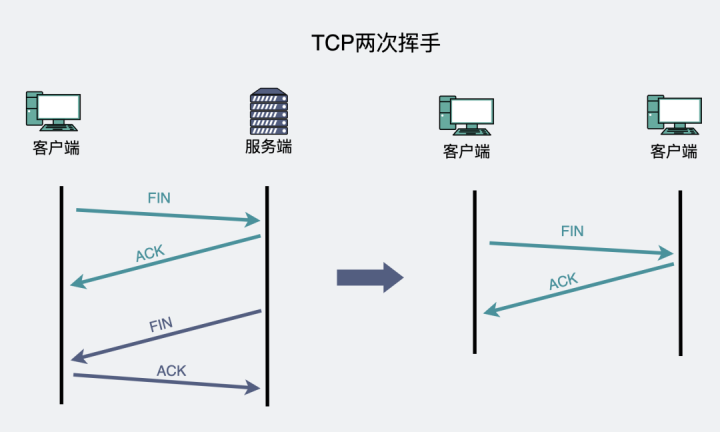
Mentioned in the previous four waves , When it was closed, both sides
Sent out a FIN And received a ACK
.
Under normal circumstances TCP Both ends of the connection , It's different
IP+ port
The process of .
But if TCP Both ends of the connection ,
IP+ port
In the same case , So when you close the connection , It did the same
One end sent out a FIN, Also received a ACK
, It's just that these two ends are actually the same socket .
And this kind of two ends
IP+ port
The same connection , It's called
TCP Self join
.
Yes , You read that right , I didn't type wrong, either .
The same socket You can really connect yourself , Form a connection .
One socket Can establish a connection ?
It's mentioned above that , Same client socket, Initiate a connection request to yourself . The connection can be established successfully . Such a connection , It's called
TCP Self join
.
Let's try to reproduce .
Note that I did the experiment on the following system . stay mac Most of them can't be reproduced .
# cat /etc/os-release
NAME="CentOS Linux"
VERSION="7 (Core)"
ID="centos"
ID_LIKE="rhel fedora"
VERSION_ID="7"
PRETTY_NAME="CentOS Linux 7 (Core)" adopt nc The command can simply create a
TCP Self join
# nc -p 6666 127.0.0.1 6666 above -p You can specify the source port number . That is, a port number is specified as 6666 To connect to 127.0.0.1:6666 .
# netstat -nt | grep 6666
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6666 127.0.0.1:6666 ESTABLISHED The whole process , There is no server involved
. You can grab a bag and have a look .
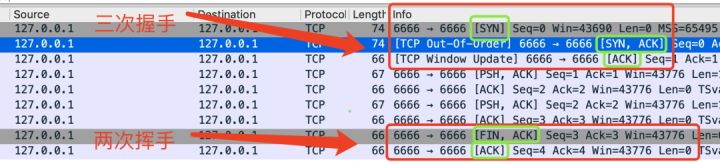
You can see ,
same socket, When you connect yourself , The handshake is three times . Waving is twice .
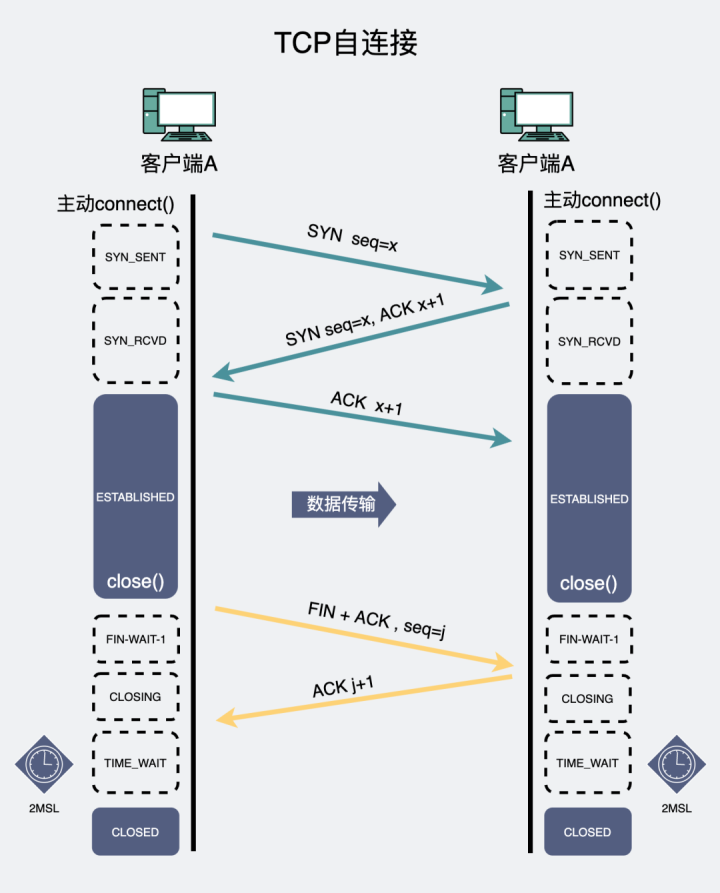
In the picture above , Both sides are the same client , Drawing it into two is to facilitate everyone to understand the transfer of state .
We can take the handshake state of the self connection
In contrast
Under normal circumstances TCP Three handshakes .
Look at the state diagram of self connection , Let's look at the following questions .
【 Article Welfare 】 In addition, Xiaobian also sorted out some C++ Back-end development interview questions , Teaching video , Back end learning roadmap for free , You can add what you need :
Click to join the learning exchange group ~
Group file sharing
Xiaobian strongly recommends C++ Back end development free learning address :
C/C++Linux Server development senior architect /C++ Background development architect
After the first handshake from one end , If you receive the first handshake SYN package ,TCP How the connection state will change ?
After the first handshake , The connection state becomes SYN_SENT state . If you receive the first handshake at this time SYN package , Then the connection status will change from SYN_SENT The state becomes SYN_RCVD.
// net/ipv4/tcp_input.c
static int tcp_rcv_synsent_state_process()
{
// SYN_SENT State, , received SYN package
if (th->syn) {
// The state is set to SYN_RCVD
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_SYN_RECV);
}
} After a second handshake from one end , If you receive a second handshake SYN+ACK package ,TCP How the connection state will change ?
Second, after shaking hands , The connection state changes to SYN_RCVD 了 , At this point, if you receive a second handshake SYN+ACK package . The connection status will change to ESTABLISHED.
// net/ipv4/tcp_input.c
int tcp_rcv_state_process()
{
// Omit a lot of logic from the front , If you can get here, you think there must be ACK
if (true) {
// Judge this ack Is it legal
int acceptable = tcp_ack(sk, skb, FLAG_SLOWPATH | FLAG_UPDATE_TS_RECENT) > 0;
switch (sk->sk_state) {
case TCP_SYN_RECV:
if (acceptable) {
// Status from SYN_RCVD To ESTABLISHED
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_ESTABLISHED);
}
}
}
} After the first wave at one end , Received the bag waving for the first time ,TCP How the connection state will change ?
After the first wave , The state at one end will become FIN-WAIT-1. Under normal circumstances , Waiting for the second wave ACK. But in fact, I waited A first wave FIN package , At this time, the connection state will change to CLOSING.
// net/
static void tcp_fin(struct sock *sk)
{
switch (sk->sk_state) {
case TCP_FIN_WAIT1:
tcp_send_ack(sk);
// FIN-WAIT-1 State, , received FIN, To CLOSING
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_CLOSING);
break;
}
} This is sort of
Hide the plot
了 .
CLOSING see little of , Except in
Self connection closed
Outside , It usually appears in TCP Both ends
Simultaneous closure
In case of connection .
be in CLOSING When in state , Just get another ACK, You can get into TIME-WAIT state , And then wait for 2MSL, The connection is completely disconnected . This is a little different from the normal four waves . You can slide to the beginning of the article TCP Wave four times and compare .
Code recurrence from connection
Maybe people will doubt , Is this nc The software itself bug.
Then we can try strace Look what's done inside it .
# strace nc -p 6666 127.0.0.1 6666
// ...
socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP) = 3
fcntl(3, F_GETFL) = 0x2 (flags O_RDWR)
fcntl(3, F_SETFL, O_RDWR|O_NONBLOCK) = 0
setsockopt(3, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, [1], 4) = 0
bind(3, {sa_family=AF_INET, sin_port=htons(6666), sin_addr=inet_addr("0.0.0.0")}, 16) = 0
connect(3, {sa_family=AF_INET, sin_port=htons(6666), sin_addr=inet_addr("127.0.0.1")}, 16) = -1 EINPROGRESS (Operation now in progress)
// ... Nothing more than to create a client socket Handle , Then execute... On this handle bind, The port number that binds it is 6666, And then 127.0.0.1:6666 launch connect Method .
We can try to use C Language to reproduce again .
The following code , Only for reproducing problems . Skipping directly does not affect reading at all .
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <strings.h>
int main()
{
int lfd, cfd;
struct sockaddr_in serv_addr, clie_addr;
socklen_t clie_addr_len;
char buf[BUFSIZ];
int n = 0, i = 0, ret = 0 ;
printf("This is a client \n");
/*Step 1: Create client side socket The descriptor cfd*/
cfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if(cfd == -1)
{
perror("socket error");
exit(1);
}
int flag=1,len=sizeof(int);
if( setsockopt(cfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &flag, len) == -1)
{
perror("setsockopt");
exit(1);
}
bzero(&clie_addr, sizeof(clie_addr));
clie_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
clie_addr.sin_port = htons(6666);
inet_pton(AF_INET,"127.0.0.1", &clie_addr.sin_addr.s_addr);
/*Step 2: Client side usage bind Binding client's IP And port */
ret = bind(cfd, (struct sockaddr* )&clie_addr, sizeof(clie_addr));
if(ret != 0)
{
perror("bind error");
exit(2);
}
/*Step 3: connect Link server side IP And port number */
bzero(&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(6666);
inet_pton(AF_INET,"127.0.0.1", &serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr);
ret = connect(cfd,(struct sockaddr *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
if(ret != 0)
{
perror("connect error");
exit(3);
}
/*Step 4: Write data to the server */
while(1)
{
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin);
write(cfd, buf, strlen(buf));
n = read(cfd, buf, sizeof(buf));
write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, n);// Write on the screen
}
/*Step 5: close socket The descriptor */
close(cfd);
return 0;
} Save as client.c file , Then execute the following command , You will find that the connection is successful .
# gcc client.c -o client && ./client
This is a client
# netstat -nt | grep 6666
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6666 127.0.0.1:6666 ESTABLISHED explain , This is not nc Of bug. in fact , This is also a case allowed by the kernel .
Self connected solutions
Self connection is generally less common , But it's not difficult to solve .
The solution is simple , As long as you can ensure that the ports of the client and server are inconsistent .
in fact , When we write code, we usually don't specify the port of the client , The system will randomly assign a range of ports to the client . And this range , You can query through the following command
# cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range
32768 60999 That is, as long as our server port is not 32768-60999 In this range , For example, set to 8888. You can avoid this problem .
Another solution , You can refer to golang Implementation of standard network library , After the connection is established, judge IP Whether the and port are consistent , If you encounter self connection , Then disconnect and try again .
func dialTCP(net string, laddr, raddr *TCPAddr, deadline time.Time) (*TCPConn, error) {
// If it is self connected , We'll try again here
for i := 0; i < 2 && (laddr == nil || laddr.Port == 0) && (selfConnect(fd, err) || spuriousENOTAVAIL(err)); i++ {
if err == nil {
fd.Close()
}
fd, err = internetSocket(net, laddr, raddr, deadline, syscall.SOCK_STREAM, 0, "dial", sockaddrToTCP)
}
// ...
}
func selfConnect(fd *netFD, err error) bool {
// Determine whether the port 、IP Agreement
return l.Port == r.Port && l.IP.Equal(r.IP)
} Four handshakes
aforementioned TCP Self connection is a scenario where the client connects itself . Can different clients be interconnected ?
The answer is
Tolerable
, There is a situation called
TCP Open at the same time
.
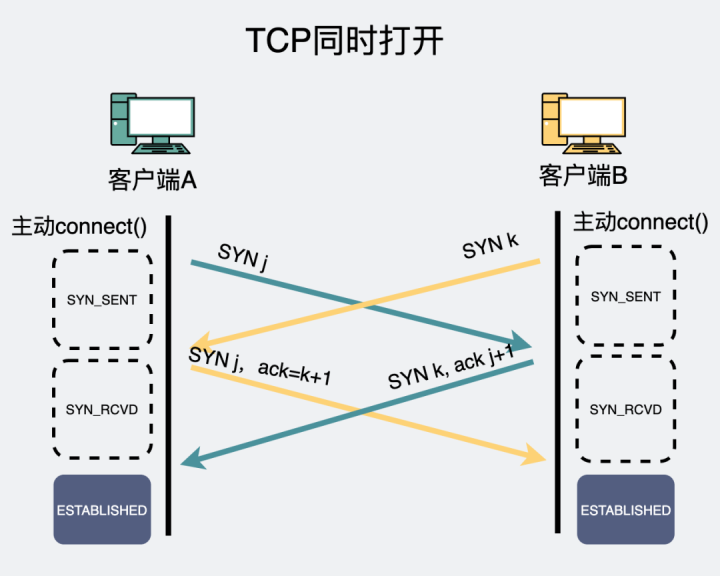
You can compare ,
TCP Open at the same time
Change of state during handshake , Follow TCP Self connection is very much like .
such as SYN_SENT State, , I got another one SYN, In fact, it is equivalent to self connection , After the first handshake , Received the first handshake request again . The result is to become SYN_RCVD.
stay SYN_RCVD Received in status SYN+ACK, It's equivalent to self connection , After the second handshake , Received a second handshake request , The result is to become ESTABLISHED.
Their source code is actually the same piece of logic .
Reappear TCP Open at the same time
Respectively in
Two consoles
Next , Execute the following two lines respectively .
while true; do nc -p 2224 127.0.0.1 2223 -v;done
while true; do nc -p 2223 127.0.0.1 2224 -v;done The meaning of the above two commands is also relatively simple , Two clients request each other to connect to each other's port number , If it fails, keep trying again .
What you see after execution is , It will fail madly at first , retry . After a while , Connection established .
# netstat -an | grep 2223
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:2224 127.0.0.1:2223 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:2223 127.0.0.1:2224 ESTABLISHED The following results are obtained during packet capture .
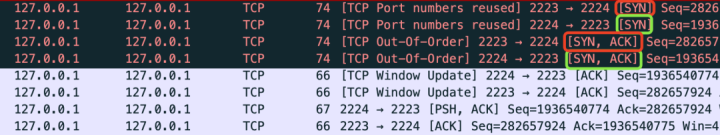
You can see , It takes four interactions to establish the connection . So it can be said that this is through
" Four handshakes "
Established connection .
And more importantly , There are only two clients involved ,
There is no server
.
See here , I wonder if everyone is like me , A new wave of cognition , Yes socket With a new understanding .
In the old idea , Establishing a connection , There must be a client and a server , And the server has to execute a listen() And a accept(). But in fact , None of this is necessary .
So next time , The interviewer asked you
" No, listen(), TCP Can you establish a connection ?"
, I think you should know how to answer .
But here's the problem , There are only two clients , No, listen() , Why can we establish TCP Connect ?
If you're interested , We'll have a chance to fill this hole again .
summary
Four waves
in , Whether the program is actively executed close(), Or the process was killed , It's possible to wave for the first time FIN package . If on the machine FIN-WAIT-2 There are many states , Generally, it is because the opposite end does not execute close() Method send out the third wave .
The same socket I even myself , Will produce
TCP Self join
, The self connected wave is
Two waves
.
No, listen, A connection can also be established between two clients . This situation is called
TCP Open at the same time
, It consists of
Four handshakes
produce .
Reference material

Recommend a zero sound education C/C++ Free open courses developed in the background , Personally, I think the teacher spoke well , Share with you :
C/C++ Background development senior architect , The content includes Linux,Nginx,ZeroMQ,MySQL,Redis,fastdfs,MongoDB,ZK, Streaming media ,CDN,P2P,K8S,Docker,TCP/IP, coroutines ,DPDK Etc , Learn now
original text :
See you for a long time !TCP Two waves , Have you ever seen ? What about the four handshakes ?
原网站版权声明
本文为[InfoQ]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/185/202207041608463488.html