当前位置:网站首页>Explain factor analysis in simple terms, with case teaching (full)
Explain factor analysis in simple terms, with case teaching (full)
2022-06-25 12:05:00 【Halosec_ Wei】
1、 effect
Factor analysis is based on the idea of dimension reduction , In the case of no or less loss of original data information as far as possible , The complex variables are aggregated into a few independent common factors , These common factors can reflect the main information of many variables , While reducing the number of variables , It also reflects the internal relationship between variables . Generally, factor analysis has three functions : One is to reduce the dimension of factors , Second, calculate the factor weight , Third, calculate the weighted calculation factor to summarize the comprehensive score .
2、 Input / output description
Input :2 Two or more quantitative variables ( Assuming that N A variable ).
Output : The minimum dimension reduction is 1 dimension ( A variable , Generally used for comprehensive evaluation ), Maximum dimension reduction N A variable ( Generally used for data desensitization ), At the same time, the composition weight of each variable after dimension reduction can be obtained , Used to represent the data retention of the original variable .
3、 Case example
According to the region 2021 Annual gross domestic product 、 Per capita disposable income and other indicators , Quantitatively evaluate the ranking of economic development level of multiple provinces, cities and regions or the weight of each index .
4、 Case data

Factor analysis data
5、 Case operation

Step1: New projects ;
Step2: Upload data ;
Step3: Select the corresponding data to open and preview , Click start analysis after confirmation ;
step4: choice 【 Factor analysis 】;
step5: View the corresponding data format ,【 Factor analysis 】 The input data is required to be put into [ ration ] The independent variables X( Number of variables ≥2).
step6: Select the number of principal components 、 Factor rotation mode ( Be careful : In factor analysis, it tends to describe the correlation between the original variables , Therefore, in general, the number of principal components selected in factor analysis is the independent variable X Number , The feature root selection is based on the set threshold , The number of principal components larger than the corresponding limit is taken as the number of selected principal components , The default is 1.)
step7: Click on 【 To analyze 】, Complete the operation .
6、 Output results
Output results 1:KMO Inspection and Bartlett The test of

*p<0.05,**p<0.01,***p<0.001
Chart description :KMO The results of the inspection show that ,KMO The value of is 0.775, meanwhile ,Bartlett Result display of spherical inspection , Significance P The value is 0.000***, The level is significant , Rejection of null hypothesis , That is to say, there is correlation between the variables , The results of factor analysis are valid , The reliability of the results was average .
Output results 2: Variance interpretation table

Chart description :
The above table is the explanation table of total variance , It mainly depends on the contribution rate of factors to variable interpretation ( It can be understood as how many factors are needed to express the variable as 100%), Generally speaking, it should be expressed to 90% That's all , Otherwise, adjust the number of factors . Variance explanation table , The contribution rate of cumulative interpretation of the first two factors reached 94.296%( Generally, it is greater than 90% that will do ), It shows that the first two factors can be used to evaluate the economic development level of provinces, cities and regions . The first three factors are more effective , The contribution rate of cumulative interpretation reaches 98.921%.
Output results 3: Gravel map

Chart description : When the broken line suddenly becomes smooth from steep , The number of principal components corresponding to steep to stable is the number of reference extracted principal components . It can be seen from the picture that , Start with the third principal component , The eigenvalues of the principal components begin to decrease slowly , The contribution to the cumulative interpretation of the factors reached 90% Under the circumstances , We can choose to keep the three principal components .
Output results 4: Factor load factor table

Chart description : The above table is the factor load factor table , The importance of hidden variables in each factor can be analyzed . The first factor and GDP 、 total imports and exports 、 Budgetary revenues 、 The four variables of current assets of industrial enterprises are highly correlated , Can be summed up as “ Local development status ”; The second factor is highly correlated with the variable of per capita disposable income , Can be summed up as “ People's affluence ”.
Output results 5: Factor load matrix thermodynamic diagram

Chart description : The above figure shows the thermodynamic diagram of load matrix , The importance of hidden variables in each factor can be analyzed , The darker the color of the heat map, the greater the correlation . The first factor and GDP 、 total imports and exports 、 Budgetary revenues 、 The four variables of current assets of industrial enterprises are highly correlated , The second factor is highly correlated with the variable of per capita disposable income .
Output results 6: Factor load quadrant analysis


Chart description : The factor load graph reduces the dimension of multiple factors into two or three factors , The spatial distribution of factors is presented by quadrant diagram . Make a two-dimensional factor load quadrant when two factors are retained . Three dimensional factor load quadrants are made when three factors are retained .
Output results 7: Composition matrix

Chart description : The formula of the model :
F1=0.236× GDP ( One hundred million yuan )+0.057× Per capita disposable income ( element )+0.192× total imports and exports ( Thousand dollars )+0.214× Budgetary revenues ( One hundred million yuan )+0.23× Current assets of industrial enterprises ( One hundred million yuan )
F2=0.244× GDP ( One hundred million yuan )+1.348× Per capita disposable income ( element )+0.618× total imports and exports ( Thousand dollars )+0.552× Budgetary revenues ( One hundred million yuan )+0.298× Current assets of industrial enterprises ( One hundred million yuan )
F3=0.063× GDP ( One hundred million yuan )+0.821× Per capita disposable income ( element )+4.519× total imports and exports ( Thousand dollars )+2.024× Budgetary revenues ( One hundred million yuan )+1.681× Current assets of industrial enterprises ( One hundred million yuan )
F4=-3.888× GDP ( One hundred million yuan )+0.164× Per capita disposable income ( element )+0.517× total imports and exports ( Thousand dollars )-0.199× Budgetary revenues ( One hundred million yuan )+5.176× Current assets of industrial enterprises ( One hundred million yuan )
F5=-1.375× GDP ( One hundred million yuan )+0.605× Per capita disposable income ( element )+0.94× total imports and exports ( Thousand dollars )+8.783× Budgetary revenues ( One hundred million yuan )-1.017× Current assets of industrial enterprises ( One hundred million yuan )
From above, we can get : F=(0.669/1.0)×F1+(0.274/1.0)×F2+(0.046/1.0)×F3+(0.006/1.0)×F4+(0.005/1.0)×F5
Output results 8: Factor weight analysis

Chart description : The weight calculation result of the factor shows , factor 1 The weight for 66.9%、 factor 2 The weight for 27.396%、 factor 3 The weight for 4.625%、 factor 4 The weight for 0.576%、 factor 5 The weight for 0.503%.
Output results 9: Comprehensive score table

Chart description : According to the comprehensive score , Guangdong Province has the highest comprehensive score , That is to say, the economic development level of Guangdong Province ranks first , The second is Jiangsu Province .
7、 matters needing attention
- Factor analysis requires strong collinearity or correlation between variables , Otherwise, it can't pass KMO Inspection and Bartlett Spherical test ;
- Factor analysis is a generalization of principal component analysis , Relative to principal component analysis , Prefer to describe the correlation between original variables ( Focus on analyzing the output results 4、 Output results 5、 Output results 6).
- Factor analysis usually needs to integrate their own professional knowledge , And the software results , Even if the eigenvalue is less than 1, The principal components can also be extracted ;
- KMO The value is null There is no possible cause for :
(1) Too little sample size will easily lead to too high correlation coefficient , It is generally expected that the analysis sample size is greater than 5 Times the number of analysis items ;
(2) The correlation between the analysis items is too high or too low .
8、 Model theory
Factor analysis is a method of reducing multidimensional variables to a few common factors according to the correlation between variables , Then the multidimensional variable statistical analysis method is analyzed . The basic idea is to divide the original variables into two parts : One part is the linear combination of common factors , Condensing represents most of the information in the original variables ; The other part is the special factor which has nothing to do with the common factor , It reflects the linear combination of common factors and original variables The gap between .p Dimension variable
x =[x1 ,…,xi ,…,xp ]T The factor analysis model is :

Or as

among f =[f 1 ,f 2 ,…,f m ]T namely by carry take Of Male common because Son towards The amount , generation surface 了 primary beginning change The amount in No can straight Pick up view measuring but customer view save stay Of m (m <p) Three mutually independent common influencing factors ;A=(aik) Is the factor load matrix , matrix Elements aik by change The amount x i Yes Male common because Son fk The load of , It reflects the correlation coefficient between the two , The greater the absolute value , The more relevant ;
For multidimensional variables x The key to establish the factor analysis model is to solve the factor load matrix A And the common factor vector f , The steps are as follows :
1) In order to eliminate the influence of different dimensions of variables , To contain n individual p Samples of dimensional variables X=[x1 ,x2 ,…,xn ] Standardize . After standardization , The mean value of each variable is 0, The variance of 1. For the convenience of expression, the standardized variables are still used X Express , Its elements are

2) Find the covariance matrix of the sample S , Its elements are
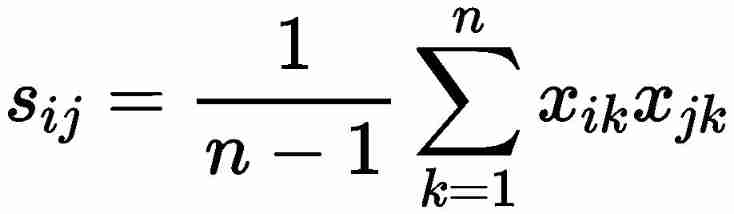
3) For the sample covariance matrix S Do eigenvalue decomposition , obtain p Eigenvalues λ1 ≥λ2≥…≥λp ≥0, The corresponding eigenvalue vector is γ1 , γ2 ,…,γp , Before taking it m The eigenvector of the largest eigenvalue estimates the factor load matrix . At the same time, in order to ensure the variance of each component of the common factor vector by 1, Divide it by the corresponding standard deviation λj . The corresponding eigenvector in the factor load matrix γj Then multiply by λj . Therefore, the factor load matrix
![]()
The parameter m Determined by the cumulative variance contribution rate of common factors , namely

It is generally believed , At present m The cumulative variance contribution rate of common factors exceeds 90% when , It can be considered that before m The linear combination of common factors can basically restore the original variable information .
Common factor vector f , That is, the specific score of the original variable on the common factor can be estimated by regression method
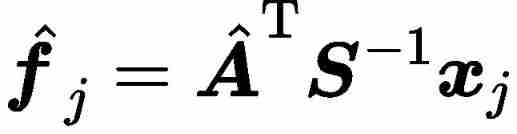
Go through the above steps , After obtaining the factor load matrix and the common factor vector , Then we can get that the special factor vector of the original variable is

9、 reference
[1] Gao Huixuan . Apply multivariate statistical analysis [M]. Beijing : Peking University press ,2005.
[2] Wenxu , Wang Hao , David , etc. . Identification method of abnormal data of bus load based on factor analysis [J]. Journal of Chongqing University ,2021,44(8):91-102.
10、 Learning Websites
边栏推荐
- A detour taken by a hardware engineer
- Kotlin学习笔记
- Encapsulation of practical methods introduced by webrtc native M96 basic base module (MD5, Base64, time, random number)
- R语言使用nnet包的multinom函数构建无序多分类logistic回归模型、使用summary函数获取模型汇总统计信息
- Architects reveal the difference between working in Alibaba, Tencent and meituan
- quarkus saas动态数据源切换实现,简单完美
- ThingsPanel 發布物聯網手機客戶端(多圖)
- The cloud native data lake has passed the evaluation and certification of the ICT Institute with its storage, computing, data management and other capabilities
- 设置图片的透明度从左到右渐变
- Old ou, a fox friend, has had a headache all day. The VFP format is always wrong when it is converted to JSON format. It is actually caused by disordered code
猜你喜欢

为什么ping不通网站 但是却可以访问该网站?

Nacos installation and use

揭秘GaussDB(for Redis):全面对比Codis

一款好用的印章设计工具 --(可转为ofd文件)

Why can't you Ping the website but you can access it?

黑马畅购商城---3.商品管理

VFP uses Kodak controls to control the scanner to solve the problem that the volume of exported files is too large

Specific meanings of node and edge in Flink graph

使用php脚本查看已开启的扩展

Explain websocket protocol in detail
随机推荐
quarkus saas动态数据源切换实现,简单完美
R语言dist函数计算dataframe数据中两两样本之间的距离返回样本间距离矩阵,通过method参数指定距离计算的方法、例如欧几里得距离
依概率收敛
Idea local launch Flink task
Comment TCP gère - t - il les exceptions lors de trois poignées de main et de quatre vagues?
VFP develops a official account to receive coupons, and users will jump to various target pages after registration, and a set of standard processes will be sent to you
R语言caTools包进行数据划分、scale函数进行数据缩放、e1071包的naiveBayes函数构建朴素贝叶斯模型
图片打标签之获取图片在ImageView中的坐标
Record the process of submitting code to openharmony once
黑马畅购商城---2.分布式文件存储FastDFS
黑马畅购商城---1.项目介绍-环境搭建
VFP uses Kodak controls to control the scanner to solve the problem that the volume of exported files is too large
Actual combat summary of Youpin e-commerce 3.0 micro Service Mall project
What should I do to dynamically add a column and button to the gird of VFP?
一個硬件工程師走過的彎路
plt.gca()画框及打标签
开哪家证券公司的账户是比较好,比较安全的
设置图片的透明度从左到右渐变
ThingsPanel 发布物联网手机客户端(多图)
The idea of mass distribution of GIS projects