当前位置:网站首页>Redis configuration and optimization of NoSQL
Redis configuration and optimization of NoSQL
2022-06-11 14:02:00 【Be a super hard worker】
1、 Relational database and non relational database
1.1、 Relational database
characteristic :
It's a structured database , Create in a relational model ( Two dimensional table model ) On the basis of , Record oriented .
SQL sentence ( Standard data query language ): The language of relational databases , Used to perform retrieval and operation of data in relational database .
Mainstream relational databases :oracle、 MySQL、 SQL server、Microsoft Access、 DB2、 PostgreSQL
---------------------
Use requirement :
First create the database and table, and then design the table structure
Then, when storing data, store it according to the table structure
If the data does not match the table structure, the storage will fail 1.2、 Non relational database
NoSQL (NoSQL = Not only SQL )
In addition to the mainstream relational databases , They are all non relational .
There is no need to build a database and table in advance to define the data storage table structure
Each record can have different data types and number of fields ( For example, the text in wechat group chat 、 picture 、 video 、 Music, etc ).
Mainstream NoSQL database :Redis、 MongBD、 Hbase、 Memcached
1.3、 difference
1.3.1、 Data storage mode ( The main difference )
Relational database : Table format 、 Stored in rows and columns of the data table 、 Data table Association collaborative storage , Easy to extract data
Non relational database : Block combination 、 Stored in a data set ( Similar documents 、 Key value pairs or graph structures )
1.3.2、 scaling ( Maximum difference )
sql database : Vertical expansion , There is an upper limit to the promotion space
nosql database : It's scale out , Based on distributed storage 、 By adding more database servers ( node ) Share the load
1.3.3、 Support for transactional
sql database : Easy to rollback transactions , Stable performance
Nosql database : The value lies in the scalability of operations and big data processing ,( Transaction operation is also available , But the stability is no better than )
1.4、 summary
summary :
Relational database :
example - > Database one > surface (table) -- > Record line (row)、 Data field (0o1 1mn) .
Non relational database :
example > database > aggregate (collection)- > Key value pair (key value)
Non relational databases do not need to build databases and collections manually ( surface ).2、Redis brief introduction
2.1、 brief introduction
Redis ( Remote dictionary server ) :
Open source 、 Use C language-written NoSQL database
Run based on memory and support persistence
Single process model 、 One server can start more than one Redis process , The processing speed depends on the execution efficiency of the main process
Redis While improving the concurrent processing ability, it will give the server CPU Cause a lot of pressure
That is, in the actual production environment , You need to decide how many... To open according to the actual needs redis process .
If the requirements for high concurrency are higher , You may consider starting multiple processes on the same server .
if cpu Resources are tight , A single process can be used 2.2、 advantage
It has very high data reading and writing speed : The speed of data reading can be as high as 110000 Time /s, Data write speed can be as high as 81000 Time /s.
Support rich data types : Support key-values、Strings、lists、Hashes、Sets And SortedSets And so on .
Support data persistence : The data in memory can be saved on disk , When you restart, you can load it again for use .
Atomicity :redis All operations are atomic .
Support data backup : namely master-salve Mode data backup
2.3、 application
Memory based databases , Is a high-performance cache
Apply to session cache 、 queue 、 Ranking List 、 Counter 、 The hottest article recently 、 The hottest comment recently 、 Publish, subscribe, etc
It is suitable for data with high real-time requirements 、 Data storage is characterized by expiration and obsolescence 、 There is no need for persistence or only weak consistency 、 A scenario with simple logic
2.4、 Fast
Redis Is a pure memory structure , Avoid disk I/o Wait for time-consuming operations .
Is a pure memory structure , Avoid disk I/O Wait for time-consuming operations .
The core module of command processing is single thread , Reduced lock competition , And the cost of creating and destroying threads frequently , Reduces the consumption of thread context switching
Adopted 1/0 Multiplexing mechanism , Adults have improved concurrency efficiency .3、Redis Installation and deployment
1)# Close the firewall and SElinux
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
setenforce 0
2)# install gcc gcc-c++ compiler
yum install -y gcc gcc-c++ make
3)# Switch to /opt Catalog , Upload the downloaded installation package and unzip it
cd /opt/
tar zxvf redis-5.0.7.tar.gz
4)# Enter the directory and compile and install
cd /opt/redis-5.0.7/
make
make PREFIX=/usr/local/redis install
# because Redis The source package directly provides Makefile file , So after unpacking the package , You don't have to do it first ./configure To configure , It can be executed directly make And make install Command to install
5)# perform install_server.sh Script
cd /opt/redis-5.0.7/utils
./install_server.sh # Enter all the way , The guide asks you to enter the path
# The path needs to be entered manually
Please select the redis executable path [] /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-server
Selected config:
Port : 6379 # The default listening port is 6379
Config file : /etc/redis/6379.conf # Profile path
Log file : /var/log/redis_6379.log # Log file path
Data dir : /var/lib/ redis/6379 # Data file path
Executable : /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-server # Executable file path
Cli Executable : /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-cli # Client command tools
6)# Optimize the path and check whether the port is open
# hold redis The executable program file of is put into the directory of path environment variable to facilitate system identification
ln -s /usr/local/redis/bin/* /usr/local/bin/
# When install_server.sh The script is finished ,Redis The service has started , The default listening port is 6379
netstat -natp | grep redis
7)# Modify the configuration file
vim /etc/redis/6379.conf
bind 127.0.0.1 192.168.200.50 #70 That's ok , Add the listening host address
port 6379 #93 That's ok ,Redis Default listening port
daemonize yes #137 That's ok , Enable daemons
pidfile /var/run/redis_6379.pid #159 That's ok , Appoint PID file
loglevel notice #167 That's ok , The level of logging
logfile /var/log/redis_6379.log #172 That's ok , Specify log text
8) # restart redis Check the listening address
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 restart # restart
ss -antp|grep redis
9)##Redis Service control
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 stop # stop it
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 start # start-up
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 restart # restart
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 status # state
4、Redis Common commands for multiple databases
4.1、 increase ( data )
set: Storing data , The command format is set key value
get: get data , The command format is get key
127.0.0.1:6379> set teacher zhangsan
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get teacher
"zhangsan"
# keys The command can take the list of key values that conform to the rules , Usually, it can be combined with +、? And so on .
127.0.0.1:6379> set k1 1
127.0.0.1:6379> set k2 2
127.0.0.1:6379> set k3 3
127.0.0.1:6379> set v1 4
127.0.0.1:6379> set v5 5
127.0.0.1:6379> set v22 54.1、 increase ( data )
set: Storing data , The command format is set key value
get: get data , The command format is get key
127.0.0.1:6379> set teacher zhangsan
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get teacher
"zhangsan"
# keys The command can take the list of key values that conform to the rules , Usually, it can be combined with +、? And so on .
127.0.0.1:6379> set k1 1
127.0.0.1:6379> set k2 2
127.0.0.1:6379> set k3 3
127.0.0.1:6379> set v1 4
127.0.0.1:6379> set v5 5
127.0.0.1:6379> set v22 5
4.2、 Delete
#del The command can delete the specified... Of the current database key.
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
127.0.0.1:6379> del v5
127.0.0.1:6379> get v54.3、 Change
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# rename The command is to have key. Rename . ( Cover )
Command format : rename. Source key, The goal is key.
Use rename Command to rename , No matter the goal key Rename whether it exists , And source key The value of will override the target key Value .
In the actual process , First use exists Command view target key Whether there is , Then decide whether to carry out rename command , To avoid overwriting important data .
# renamenx The function of the command is to modify the existing key Rename , And check whether the new name exists , If target key If it exists, it will not be renamed .( No coverage )
Command format : renamenx Source key The goal is key
4.4、 check
# View all keys in the current database
127.0.0.1:6379> KEYS *
# View the current database to v Initial data
127.0.0.1:6379> KEYS v*
# View the current database to v Data with any bit after the beginning
127.0.0.1:6379> KEYS v
# View the current database to v start v Data with any two digits after the beginning
127.0.0.1:6379> KEYS v??
#dbsize The function of the command is to view the current database key Number of .
127.0.0.1:6379> dbsize
4.5、 sentence
#exists The command can determine whether the key value exists .
127.0.0.1:6379> exists teacher # Judge teacher Does the key exist
(integer) 1 # 1 Express teacher The key exists
127.0.0.1:6379> exists tea
(integer) 0 #0 Express tea The key doesn't exist
# type Command can be obtained key Corresponding value Value type .
127.0.0.1:6379> type k1
string
4.6、 set up ( password )
# Use config set requirepass yourpassword Command set password
127.0.0.1:6379> config set requirepass 123456.
# Use config get requirepass life Let me check the password (- Once you set the password , You have to verify the password first , Otherwise, all operations are not available )
127.0.0.1:6379> auth 123456 ## Input password
127.0.0.1:6379> config get requirepass ## Check the password
1) "requirepass"
2) "123456"
## Empty password
127.0.0.1:6379> config set requirepass ' '
4.6、 Cheku
Redis Support multiple databases ,Redis By default, include 16 A database , The database name is in numbers 0-15 Named in turn .
Multiple databases are independent of each other , Mutual interference .
# Switching between multiple databases
Command format : select Serial number
Use redis-cli Connect Redis After the database , The default sequence number is 0 The database of .
# Switch to serial number 10 The database of
127.0.0.1:6379> select 10
# Switch to serial number 0 The database of
127.0.0.1:6379[15]> select 0
4.7、 Move ( Database data )
# Moving data between multiple databases
Format : move Key value serial number 
4.8、 clear ( Empty data )
# Clear the data in the database
IFLUSHDB: Clear the current database data
FLUSHALL : Clear all database data , Use with caution ! ( Delete library , Don't use it. !!!!!!!!!!!!!)5、Redis Command tool
-----------------------------Redis Command tool ----------------------------------------------
redis-server: Used to start Redis Tools for
redis-benchmark: Used to detect Redis The operating efficiency of the machine
redis-check-aof: Repair AOF Persistent files
redis-check-rdb: Repair RDB Persistent files
redis-cli: Redis Command line tools
----------------------------redis-cli Command line tools -------------------------------------------
grammar : redis-cli -h host -p port -a password
h: Specify the remote host
p : Appoint Redis The port number of the service
-a: Specified password , The database password is not set and can be omitted -a Options
If you don't add any options to indicate , Then use 127.0.0.1:6379 Connect... On this computer Redis database
redis-cli -h 192.168.80.10 -p 6379
--------------------- redis-benchmark Testing tools ---------------------------------------------
redis -benchmark It's official Redis Performance testing tools , Can effectively test Redis Service performance .
Basic test Syntax : redis-benchmark [ Options ] [ Option value ].
-h: Specify the server host name .
-p: Specify the server port .
-s: Specify the server socket
-c: Specify the number of concurrent connections .
-n: Specify the number of requests .
-d: Specify... In bytes SET/GET Data size of value .
-k:1=keep alive 0=reconnect
-r:SET/GET/INCR Use random key, SADD Use random values .
-P: To transmit through pipes <numreq> request .
-q: Forced exit redis. Show only query/sec value .
--CSV: With CSV Format output .
-1: Generate a cycle , Perform tests permanently .
-t: Run only comma separated list of test commands .
# towards IP The address is 192.168.80.10、 Port is 6379 Of Redis Server send 100 Multiple concurrent connections and 100000 Requests to test performance
redis -benchmark -h 192.168.80.200 -p 6379 -c 100 -n 1 00000
# The test access size is 100 Byte packet performance
redis-benchmark -h 192.168.10.161 -p 6379 -q -d 100
# Test on this machine Redis The service is in progress set_ And 1push Performance during operation
redis-benchmark -t set, 1push -n 100000 -q6、Redis High availability
Reids High availability ratio web High availability in the server means more , In addition to ensuring normal service ( Such as the separation of master and slave 、 Fast disaster recovery technology ), Also need to consider the expansion of data capacity 、 Data security will not be lost .
Redis in , High availability technology mainly includes persistence 、 Master slave copy 、 Sentinels and clusters
----------------------------------------
● Persistence : Persistence is the simplest high availability method ( Sometimes it's not even classified as a highly available means ), The main function is data backup , Store data on hard disk , Ensure that data is not lost due to process exit
● Master slave copy : Master slave replication is highly available Redis The basis of , Sentinels and clusters are highly available based on master-slave replication . Master-slave replication mainly realizes multi machine backup of data , And load balancing and simple fault recovery for read operations . defects : Failure recovery cannot be automated ; Write operations are not load balanced ; Storage capacity is limited by a single machine
● sentry : On the basis of master-slave replication , Sentinels achieve automated recovery from malfunctions . defects : Write operations are not load balanced ; Storage capacity is limited by a single machine
●Cluster colony : By clustering ,Redis It solves the problem that write operation cannot be load balanced , And storage capacity is limited by single machine , A relatively complete high availability scheme has been realized 7、Redis Persistence
Save the memory data to the hard disk according to a certain policy , Achieve the purpose of data persistence
Support type :RDB 、AOF
●RDB Persistence : Save the data records in memory to disk regularly .
●AOF Persistence (append only file) : Write the operation log to the file by appending , Be similar to MySQL Of binlog.
--------------------------
Main stream :AOF( Better real-time )7.1、RDB Persistence
RDB Persistence : Save a snapshot of the data generated in the current process in memory to the hard disk within a specified time interval ( Also called snapshot persistence )
Compress storage with binary , The saved file suffix is rdb
When Redis On reboot , Can read snapshot file recovery data .

7.1.1、 The trigger condition
Manual and automatic triggering
(1) Manual trigger
save Command and bgsave Commands can be generated RDB file .
save command : Blocking Redis Server process , until RDB Until the file is created , During blocking , The server cannot process any command requests .
bgsave command : Create a subprocess , The child process is responsible for creating RDB file , The parent process ( namely Redis The main process ) Then continue processing the request .
remarks :
bgsave During command execution , Only fork Child process will block the server , And for save command , The whole process blocks the server , therefore save It's basically abandoned , Online environment should be eliminated save Use .
--------------------------------------------------
(2) Automatic triggering
In auto trigger RDB Persistence ,Redis Will also choose bgsave instead of save To persist .
save m n
The most common case of automatic triggering In the configuration file save m n, Designated as m Within seconds n The next change , Will trigger bgsave.
---------------------------
#### Auto trigger profile
vim /etc/ redis/6379. conf
--219 That's ok -- Here are three save When any condition is satisfied , Will cause bgsave Call to
save 900 1 : When the time comes 900 seconds , If redis The data happened, at least 1 Changes , execute bgsave
save 300 10 : When the time comes 300 seconds , If redis The data happened, at least 10 Changes , execute bgsave
save 60 10000 : When the time comes 60 seconds , If redis The data happened, at least 10000 Changes , execute bgsave
--254 That's ok -- Appoint RDB file name
dbfilename dump.rdb
--264 That's ok -- Appoint RDB Document and AOF File directory
dir /var/lib/redis/6379
--242 That's ok -- Open or not RDB File compression
rdbcompression yes
#### Other automatic trigger mechanisms
except savemn outside , There are other situations that trigger bgsave:
● In the master-slave replication scenario , If full replication is performed from a node , Then the master node will execute bgsave command , And will rdb The file is sent to the slave node .
● perform shutdown On command , Automatic execution rdb Persistence .7.1.2、 Execute the process

(1) Redis The parent process first judges : Is it currently being implemented save, or bgsave/bgrewriteaof Can be inherited by child processes. , If it's being executed bgsave The command returns directly to .
bgsave/bgrewriteaof Cannot be executed at the same time , Mainly based on performance considerations : Two concurrent subprocesses perform a large number of disk writes at the same time , May cause serious performance problems
(2) Parent process execution fork Action create subprocess , In this process, the parent process is blocked ,Redis Cannot execute any command from the client
(3) The parent process fork after ,bgsave Command return "Background saving started" Information doesn't block the parent process anymore , And can respond to other commands
(4) Subprocess creation RDB file , Generate a temporary snapshot file according to the memory snapshot of the parent process , After the completion of the original file for atomic replacement
(5) The child process sends a signal to the parent to indicate completion , Parent process update statistics 7.1.3、 Load on startup
RDB File loading is performed automatically when the server starts , There is no special order . But because of AOF Higher priority , So when AoF On ,Redis Will load first
AOF File to recover data : Only when A0F closed , Will be in Redis Detect when the server starts RDB file , And automatically load . The server loads RDB Blocked during file , Until it is loaded .
Become a stop .
Redis load RDB When you file , Would be right RDB Check the file , If the file is corrupted , Error will be printed in the log ,Redis Qi Action failed .7.2、AOF Persistence
take Redis Each write performed 、 The delete command is recorded in a separate log file , The query operation will not record ;
When Redis Execute again on restart AOF Command in the file to recover data .
And RDB comparison ,AOF Better real-time , So it has become a mainstream persistence solution .

7.2.1、 Turn on AOF
Redis The server is turned on by default RDB, close AOF: To turn on A0F, You need to configure... In the configuration file :
vim /etc/ redis/6379. conf
--700 That's ok -- modify , Turn on AOF
appendonly yes
--704 That's ok -- Appoint AOF File name .
appendfilename "appendonly.aof"
--796 That's ok -- Whether to ignore the last instruction that may have problems
aof- load-truncated yes7.2.2、 Execute the process
AOF The implementation process includes
Order to append (append): take Redis The writing of Append command to buffer aof_ buf:
File is written to (write) Synchronize with files (sync): According to different synchronization strategies, we will aof_buf The contents of the file are synchronized to the hard disk ;
File rewriting (rewrite): Rewrite regularly A0F file , Achieve the purpose of compression .
(1) Order to append (append)
Redis First append the write command to the buffer , Instead of writing directly to a file , It is mainly to avoid writing commands to the hard disk directly every time , Cause the hard disk IO Become Redis The bottleneck of the load .
The format of the command append is Redis The protocol format of the command request , It's a plain text format , Good compatibility 、 High readability 、 Easy to handle 、 It is easy to operate and avoid secondary overhead .
stay AOF In file , Except for the specified database select command ( Such as select 0 For the selection 0 The database ) By Redis Added , The others are written commands sent by the client .
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(2) File is written to (write) Synchronize with files (sync)
Redis Provides a variety of AOF Cache synchronization strategy , The policy involves the operating system write Functions and fsync function , The explanation is as follows :
In order to improve the efficiency of file writing , In modern operating systems , When the user calls write Function to write data to a file , The operating system usually temporarily stores data to - - In a memory buffer , When the buffer is filled or exceeds the specified time limit , To write the buffer data to the hard disk . This kind of operation improves the efficiency , But it also brings security issues : If the computer goes down , Data in the memory buffer will be lost ; So the system also provides fsync、fdatasync And so on , It can force the operating system to write the data in the buffer to the hard disk immediately , So as to ensure the security of data .
AOF There are three synchronization methods for the cache synchronization file policy , They are :
vim /etc/ redis/6379. conf
●appendfsync always:
Command write aof_ buf Call the system immediately after fsync The operation is synchronized to AOF file ,fsync After completion, the thread returns . In this case , Every time you have a write command, you have to synchronize to AOF file , Hard disk I0 Become a performance bottleneck ,Redis Only about a few hundred TPs write in , It's seriously reduced Redis Performance of : Even with solid state drives (ssD) , It can only process tens of thousands of commands per second , And it will greatly reduce ssD Life span of .
●appendfsync no:
Command write aof__buf After calling the system write operation , incorrect AOF File do fsync Sync : Synchronization is the responsibility of the operating system , Usually the synchronization period is 30 second . In this case , The timing of file synchronization is uncontrollable , And there will be a lot of data piled up in the buffer , Data security cannot be guaranteed .
●appendfsync everysec:
Command write aof_ buf After calling the system write operation ,write After completion, the thread returns ; fsync The synchronization file operation is called once per second by a dedicated thread .everysec It's a compromise between the two strategies ,
It's a balance between performance and data security , So it is Redis Default configuration , It's also our recommended configuration .
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(3) File rewriting (rewrite)
Over time ,Redis More and more write commands are executed by the server ,AOF The files will get bigger and bigger : Too much AOF Files will not only affect the normal operation of the server , It can also cause data recovery to take too long .
File rewriting refers to periodic rewriting AOF file , Reduce AOF Volume of file . It should be noted that ,AOF heavy To write is to put Redis In process data is converted to write commands , Sync to the new AOF file : Not to the old AOF File for any read 、 Write operation !
Another thing to note about file rewriting is : about AOr In terms of persistence , File rewriting is highly recommended , But it's not necessary ; Even if there is no file rewriting , Data can also be persisted
And in Redis Import at startup : So in some reality , Automatic file rewriting is turned off , And then through the timing task, at a certain time of the day .
# The reason why file rewriting can be compressed AOF file , The reason lies in :
● Expired data is no longer written to the file
● Invalid commands are no longer written to the file : If some data is set repeatedly (set mykey v1, set mykey v2)、 Some data has been deleted (set myset v1, del myset) etc. .
● Multiple commands can be combined into one : Such as sadd myset vl, sadd myset v2,sadd myset v3 Can be combined into sadd myset vl v2 v3.
From the above, we can see that , Because after rewriting AOF There are fewer orders to execute , File rewriting can reduce the space occupied by the file , It can also speed up recovery .
# Trigger of file rewriting , It can be divided into manual trigger and automatic trigger :
● Manual trigger : Call directly bgrewriteaof command , The execution of the order is related to bgsave Some similar : All are fork The subprocess does the specific work , And only in fork Time blocking .
● Automatic triggering : By setting auto-aof-rewrite-min-size Options and auto-aof-rewrite-percentage Option to automate BGREWRITEAOF.
Only when auto-aof-rewrite-min-size and auto-aof -rewrite-percentage When both options are met , Will automatically trigger AOF rewrite , namely bgrewriteaof operation .
vim /etc/ redis/ 6379. conf
--729--
●auto-aof-. rewrite-percentage 100
At present AOF file size ( namely aof_ current_ size) Is the last time the log was rewritten AOF file size (aof_ base_ size) At twice , happen BGREWRITEAOF operation
●auto-aof- rewrite-min-size 64mb
At present AOF File execution BGREWRITEAOF The minimum value of the command , Avoid starting Reids Due to the small file size, frequent BGREWRITEAOF
About the file rewriting process , There are two points to note : (1) Rewriting by the parent process fork The subprocess goes on : (2) During rewrite Redis Write commands executed , Need to be added to the new A0F In file , So Redis Introduced aof_ rewrite_ _buf cache .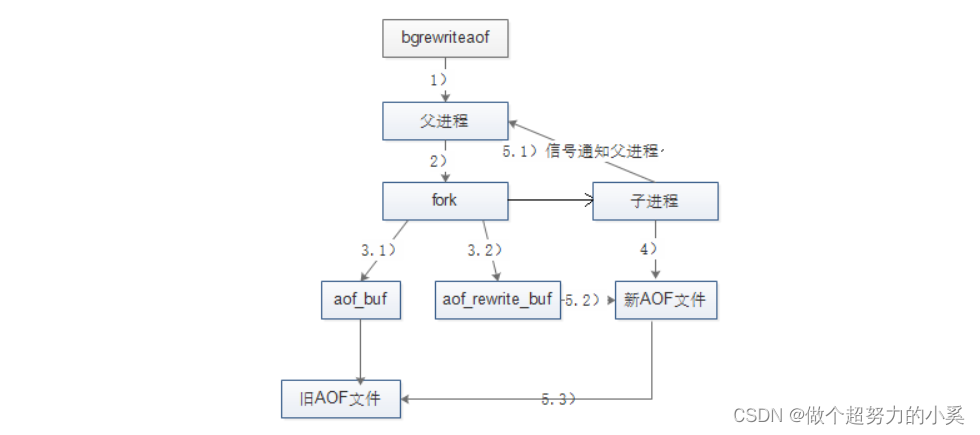
(1) Redis The parent process first determines whether there is currently executing bgsave/bgrewriteaof Can be inherited by child processes. , If there is one bgrewriteaof The command returns directly to , If there is bgsave Orders wait bgsave Execute after the execution is completed . (2) Parent process execution fork Action create subprocess , In this process, the parent process is blocked . (3.1) The parent process fork after ,bgrewriteaof Command return "Background append only file rewrite started" Information doesn't block the parent process anymore , And can respond to other commands .Redis All write commands for are still written to AOF buffer , And according to appendfsync Policy synced to hard disk , Keep the original AOF The right mechanism . (3.2) because fork The operation uses copy on write technology , Child processes can only share fork Memory data during operation . Because the parent process is still responding to commands , therefore Redis Use AOF Rewrite buffer (aof_rewrite_ buf) Save this data , Prevent new AOF This data is lost during file generation . in other words ,bgrewriteaof perform period ,Redis At the same time, the write command of aof_ buf and aof_ rewirte buf Two buffers . (4) Sub process according to memory snapshot , Write to the new... According to the command merge rule AOF file . (5.1) The subprocess writes a new AOF After the document , Signal the parent process , Parent process update statistics , The details can be obtained through info persistence see . (5.2) The parent process put AOF The data in the rewrite buffer is written to the new AOF file , This guarantees new AOF The database state saved by the file is consistent with the current state of the server . (5.3) Use the new AOF File replace old file , complete AOF rewrite .
7.3、RDB And AOF Advantages and disadvantages
●RDB Persistence advantage :RDB The files are compact , Small volume , Network transmission is fast , Suitable for full replication : Recovery speed ratio AOF Much faster , The impact on performance is relatively small
shortcoming : Real time persistence is not possible , Need to meet a specific format , Compatibility is poor ( The old version of Redis Not compatible with the new version of RDB file )
about RDB Persistence , On the one hand is bgsave It's going on fork In operation Redis The main process will block , On the other hand , Sub process writing data to the hard disk will also bring IO pressure .●AOF Persistence
advantage : Support second level persistence 、 Compatibility is good. ,
shortcoming : The file is big 、 Slow recovery 、 Great impact on performance .
about AOF Persistence , The frequency of writing data to the hard disk is greatly increased (everysec Second level under strategy ),IO More stressful , It may even cause AOF Additional blocking problem .
AOF Document rewriting and RDB Of bgsave similar , There will be fork The blocking and the subprocess's Io The pressure problem . relatively speaking , because AOF Write data to the hard disk more often , So right. Redis The performance of the main process will be affected more .8、Redis Performance management
see Redis Memory usage
192.168.9.236: 7001> info memory or redis-cli info memory

8.2、 Memory fragmentation rate
8.2.1、 produce
mem_ fragmentation_ ratio: Memory fragmentation rate .mem_ fragmentation_ ratio = used_ memory rss / used_ memory used_ memory_ rss: yes Redis Xiang Cao Memory for system application . used_ memory: yes Redis in The memory occupied by the data . used_ memory_ peak:redis Peak memory usage .
Redis It has its own memory manager , In order to improve the efficiency of memory use , To manage the application and release of memory .
Redis When the value in is deleted , Did not release memory directly , Give it back to the operating system , It was handed over Redis There is a memory manager inside .
Redis When applying for memory in , First, check whether there is enough memory available in your memory manager .
Redis This mechanism of , Improved memory usage , But it will make Redis Some of them are not in use , But not free memory , Caused memory fragmentation .
# Track memory fragmentation rate for understanding Redis The resource performance of an instance is very important :
● The memory fragmentation rate is 1 To 1.5 Between is normal , This value indicates that the memory fragmentation rate is relatively low , Also explain Redis No memory swap occurred .
● The memory fragmentation rate exceeds 1.5, explain Redis It consumes the physical memory 150%, among 508 It's the memory fragmentation rate .
● The memory fragmentation rate is lower than 1 Of , explain Redis Memory allocation exceeds physical memory , The operating system is swapping memory . Need to increase available physical memory or reduce Redis Memory footprint .8.2.2、 solve
If your Redis The version is 4.0 Following , Need to be in redis-cli Enter... On the tool shutdown save command , Give Way Redis The database performs a save operation and closes Redis service , Restart the server again .Redis After the server restarts ,Redis Will return unused memory to the operating system , The fragmentation rate will come down .
Redis4.0 Version start , It can be done without restarting , Online defragmentation of memory .
config set activedefrag yes # Automatic debris removal , The memory will clean up automatically .
memory purge # Manual debris removal 8.3、 Memory usage
redis The memory usage of the instance exceeds the maximum available memory , The operating system will start memory and memory swap Space exchange . # Ways to avoid memory swapping : ● Select the installation for the cache data size Redis example ● Use as much as possible Hash Data structure storage ● Set up key The expiration time of
8.4、 Internal recovery key
Memory cleaning strategy , Ensure reasonable distribution redis Limited memory resources .
When the set maximum threshold is reached , You need to select one key Recycling strategy for , By default, the recycling policy is to prohibit deletion .
Modify... In configuration file jmaxmemory-policy Property value :
vim /etc/ redis/6379.conf
-598--
maxmemory-policy noenviction
●volatile-iru: Use LRU The algorithm eliminates the data from the data set with the expiration time set ( Remove the least recently used key, Set... For TTL Of key)
●volatile-ttl: Select the data that is about to expire from the data set with expiration time ( Remove recently expired key)
●volatile-random: Randomly select data from the data set with expiration time set ( In setting up the TTL Of key Randomly remove )
●allkeys-lru: Use LRU Algorithms eliminate data from all data sets ( Remove the least used key, For all key)
●allkeys-random: Select any data from the data set ( Remove randomly key)
●noenviction: Ban data obsolescence ( Don't delete until it's full )边栏推荐
- Unity detects whether the object is within the viewing cone of the camera
- Two small things, feel the gap with the great God
- couldn‘t upgrade db schema: insert into ACT_GE_PROPERTY values (‘common.sche[已解决]
- CVPR 2022 | 神经辐射场几何编辑方法NeRF-Editing
- Check box select all or deselect all
- How to quickly compress the size of video?
- 强大的全文本搜索工具——AnyTXT Searcher
- Just after the college entrance examination, I was confused and didn't know what to do? Tell me what I think
- SQL must know and know
- Some transformation thoughts of programmers after they are 35 years old
猜你喜欢

JSP implementation of performance appraisal system for bank counter business

Three level classification display

NoSQL之Redis配置与优化

CVPR 2022 | 神经辐射场几何编辑方法NeRF-Editing

Energy storage operation and configuration analysis of high proportion wind power system (realized by Matlab)

Can't understand kotlin source code? Starting with the contracts function~

代码对比工具,我就用这6个

三级分类展示

LNMP deployment

cadence SPB17.4 - group operation(add to group, view group list, delete group)
随机推荐
Ecplise cannot connect to SQL Server
Terraformer导入云上资源
AGV robot RFID sensor ck-g06a and Siemens 1200plc Application Manual
VIM secondary replacement
Business practice of volcano engine cloud database VEDB in bytes
Unity detects whether the object is within the viewing cone of the camera
Xiaomi 9-wire brush ROM
Check box select all or deselect all
Bs-xx-007 registered residence management system based on JSP
Work summary: it took a long time to write SQL because of Cartesian product problem (Cartesian product summary attached)
Hashicopy之nomad应用编排方案06(配置task)
create_engine mysql connector加密方式报错
Sqlmap detection SQL lab range
复选框 全选or取消全选
Kubernetes binary installation (v1.20.15) (VI) deploying worknode nodes
在启牛开的证券账户安全吗?如何申请低佣金的股票账户?
[signal de-noising] chromatographic baseline estimation and de-noising based on sparsity (beads) with matlab code and papers
Terraformer importing cloud resources
Ali, tell me about the application scenarios of message oriented middleware?
Network information system emergency response