Domain logic & Applied logic
As mentioned earlier , The business logic in domain driven design is divided into two parts ( layer ): Domain logic and application logic :

- Domain logic consists of the core domain rules of the system , Application logic implements application specific use cases
Although the definition is clear , But it may not be easy to implement . You may not be able to decide which code should be in the application layer , What code should be in the domain layer . This section attempts to explain the differences
Multiple application tiers
When the system is large ,DDD Helps handle complexity . especially , If you develop multiple applications in a domain , Then the separation of domain logic and application logic becomes much more important .
Suppose you are building a system with multiple applications
A web application , use ASP.NET Core MVC structure , Show users your product . Such websites can see products without certification . Users can only perform certain operations ( For example, add products to the shopping cart ) Will log in to the website .
A background management program , Use Angular UI structure ( Use REST APIs). This application is used by the company's office staff to manage the system ( Such as editing product description )
A mobile application , Compared with the website , It has simpler UI. It can go through REST APIs Or other technology ( Such as TCP Socket ) Communicate with the server .
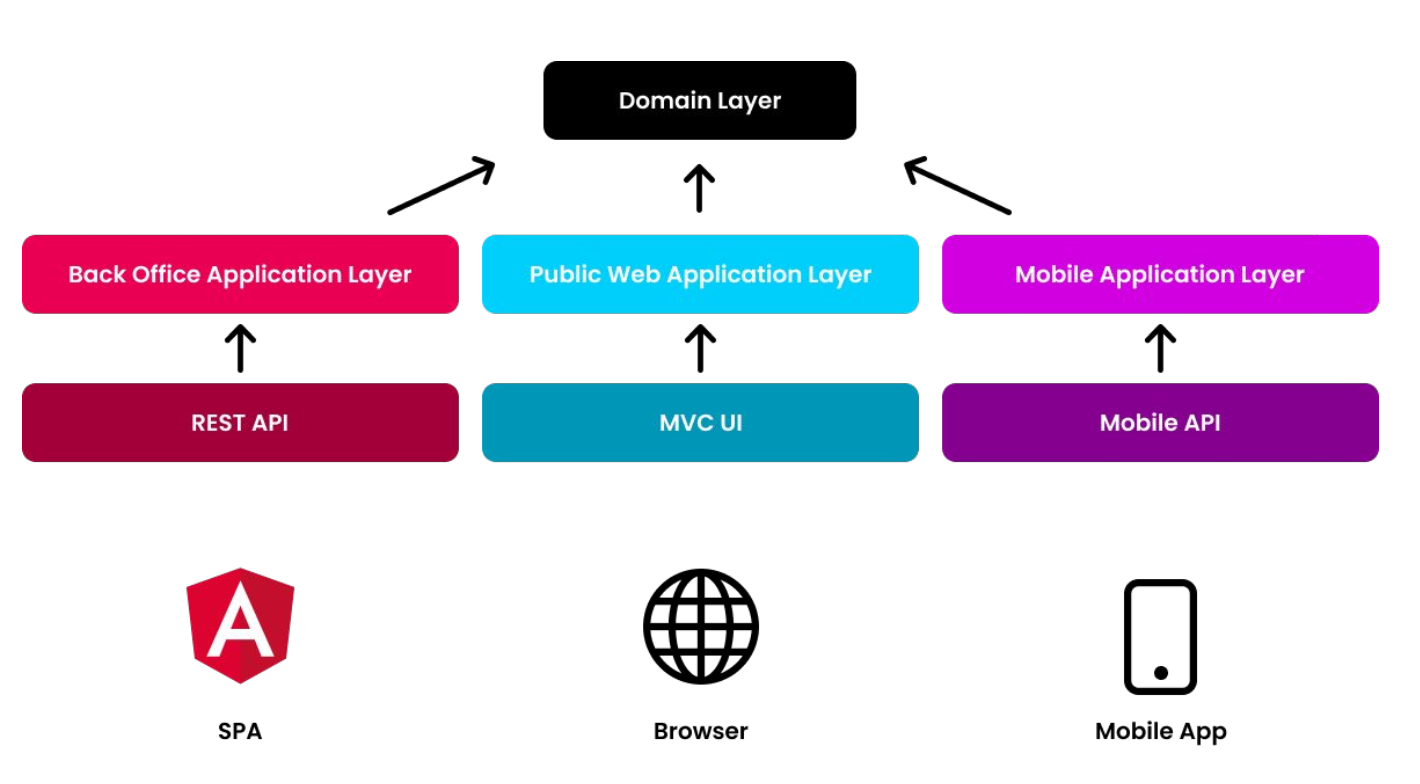
Each application has different requirements 、 Different use cases ( Application service method )、 Different dto、 Different authentication and authorization rules …… etc.
Mixing all this logic into a single application layer will make your services contain too much logic , Make code harder to develop 、 Maintenance and testing , And lead to potential bug
If there are multiple applications in a domain :
- For each application / Client type creates a separate application layer , And implement application specific business logic in these separate layers .
- Use a single domain layer to share core domain logic .
This design makes it more important to distinguish between domain logic and application logic .
For a clearer understanding of the implementation , You can create different projects for each application type (.csproj). for example :
Background management application :
IssueTracker.Admin.Application & IssueTracker.Admin.Application.ContractsPublic website application :
IssueTracker.Public.Application & IssueTracker.Public.Application.ContractsMobile application :
IssueTracker.Mobile.Application & IssueTracker.Mobile.Application.Contracts
Case study
This section contains some examples of application services and domain services , To discuss how to decide to place business logic in these services
Example : Create a new organization in the domain service
public class OrganizationManager : DomainService
{
// Omit dependency injection
public async Task<Organization> CreateAsync(string name)
{
if(await _organizationRepository.AnyAsync(x => x.Name == name))
{
throw new BusinessException("IssueTracking:DuplicateOrganizationName");
}
await _authorizationService.CheckAsync("OrganizationCreationPermissin");
Logger.LogDebug($"Creating organization {name} by {_currentUser.UserName}");
var organization = new Organization();
await _emailSender.SendAsync(
"[email protected]",
"New Organization",
"A new organization created with name: " + name
);
return organization;
}
}
Let's take a step-by-step look at CreateAsync Method , To discuss whether the code should be placed in domain services
correct : It first checks for duplicate organization names , And throw an exception in this case . This is related to the core domain rules , We do not allow duplicate names
error : Domain services should not perform authorization . to grant authorization It should be done in the application layer .
error : It records a message containing the user name of the current user . Domain services should not depend on the current user . Even if there are no users in the system , Domain services should also be available . The current user ( conversation ) It should be an and expression / Concepts related to application layer .
error : It sends information about the creation of this new organization E-mail . We think this is also a use case specific business logic . You may want to create different types of e-mail in different use cases , Or in some cases, you don't need to send email .
Example : Create a new organization in the application service
public class OrganizationAppService : ApplicationService
{
// Omit dependency injection
[UnitOfWork]
[Authorize("OrganizationCreationPermissin")]
public async Task<Organization> CreateAsync(CreateOrganizationDto input)
{
await _paymentService.ChargeAsync(
CurrentUser.Id,
GetOrganizationPrice()
);
var organization = await _organizationManager.CreateAsync(input.Name);
await _organizationManager.InsertAsync(organization);
await _emailSender.SendAsync(
"[email protected]",
"New Organization",
"A new organization created with name: " + input.Name
);
return organization; //!!!
}
private double GetOrganizationPrice()
{
return 42.0; // Or get it from somewhere else
}
}
Let's take a step-by-step look at CreateAsync Method , To discuss whether code parts should be placed in application services
correct : The application service method should be a unit of work ( Business ).ABP Of The unit of work The system makes this automatic ( You don't even need to add
[UnitOfWork]attribute ).correct : to grant authorization It should be done at the application layer . here , It is through the use of
[Authorize]Property to completecorrect : Call payment ( Infrastructure services ) To charge for this operation ( Creating an organization is a paid service in our business )
correct : The application service method is responsible for saving changes to the database .
correct : We can send E-mail Notify the system administrator
error : Do not return entities from application services . It's back to a DTO.
Discuss : Why don't we move the payment logic to domain services ?
You may want to know why the payment code is not OrganizationManager in . This is a It's very important Thing , We don't want to Missed payment .
However , Just being important is not enough to treat code as core business logic . We may have other use cases , Create a new... In these use cases Organization There is no charge . such as :
Administrator users can use background applications to create new organizations , Without paying anything
Data import for background work / Integrate / Synchronization systems may also need to create organizations that do not have any payment operations .
As you can see , Payment is not necessary to create an effective organization . It is use case specific application logic .
Example : Additions and deletions operation
public class IssueAppService
{
private readonly IssueManager _issueManager;
public IssueAppService(IssueManager issueManager)
{
_issueManager = issueManager;
}
public async Task<IssueDto> GetAsync(Guid id)
{
return _issueManager.GetAsync(id);
}
public async Task CreateAsync(IssueCreationDto input)
{
return _issueManager.CreateAsync(input);
}
public async Task UpdateAsync(UpdateIssueDto input)
{
return _issueManager.UpdateAsync(input);
}
public async Task DeleteAsync(Guid id)
{
return _issueManager.DeleteAsync(id);
}
}
The application service itself does nothing , Instead, you delegate all your work to domain services . It will even dto Pass to IssueManager
- Don't just be simple without any domain logic CRUD Operate to create domain services .
- Never deliver to domain services dto Or return from the domain service dto.
Application services can directly use the repository to query 、 establish 、 Update or delete data , Unless some domain logic needs to be performed during these operations . under these circumstances , establish Domain Service Method , But only for those methods that are really needed
If you are more interested in Domain Driven Design and building large enterprise systems , The following books are recommended as reference books :
- "Domain Driven Design" by Eric Evans
- "Implementing Domain Driven Design" by Vaughn
Vernon - "Clean Architecture" by Robert C. Martin
The end