当前位置:网站首页>TCP experimental verification
TCP experimental verification
2022-07-26 03:13:00 【GSX_ MI】
1. understand CLOSE_WAIT state
- When the client and the server are doing TCP When communication , If the client calls close Function to close the corresponding file descriptor , At this point, the underlying operating system of the client will send a message to the server FIN request , After receiving the request, the server will ACK Respond to .
- But if the server receives a message from the client FIN After the request , Server side does not call close Function to close the corresponding file descriptor , Then the server will not send to the client FIN request , It is equivalent to only completing the first two of the four waves , At this point, the connection status of the client and the server will change to FIN_WAIT_2 and CLOSE_WAIT.
(1) Write a simple one TCP Socket to simulate this phenomenon , In fact, we only need to write server-side code , Some network tools are used to act as clients to send connection requests to our servers .
(2) The initialization of the server requires the creation of sockets 、 Binding and listening , Then the main thread can call accept Function gets the established connection from the bottom layer . After obtaining the connection, the main thread creates a new thread to provide services for the connection , The new thread only needs to execute an endless loop logic .
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <pthread.h>
const int port = 8081;
const int num = 5;
void* Routine(void* arg)
{
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
int fd = *(int*)arg;
delete (int*)arg;
while (1){
std::cout << "socket " << fd << " is serving ........ " << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return nullptr;
}
int main()
{
// Create a listening socket
int listen_sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (listen_sock < 0){
std::cerr << "socket error" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// binding
struct sockaddr_in local;
memset(&local, 0, sizeof(local));
local.sin_port = htons(port);
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
if (bind(listen_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0){
std::cerr << "bind error" << std::endl;
return 2;
}
// monitor
if (listen(listen_sock, num) < 0){
std::cerr << "listen error" << std::endl;
return 3;
}
// Start the server
struct sockaddr_in peer;
memset(&peer, 0, sizeof(peer));
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
for (;;){
int sock = accept(listen_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, &len);
if (sock < 0){
std::cerr << "accept error" << std::endl;
continue;
}
std::cout << "get a new link: " << sock << std::endl;
int* p = new int(sock);
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, Routine, (void*)p);
}
return 0;
}
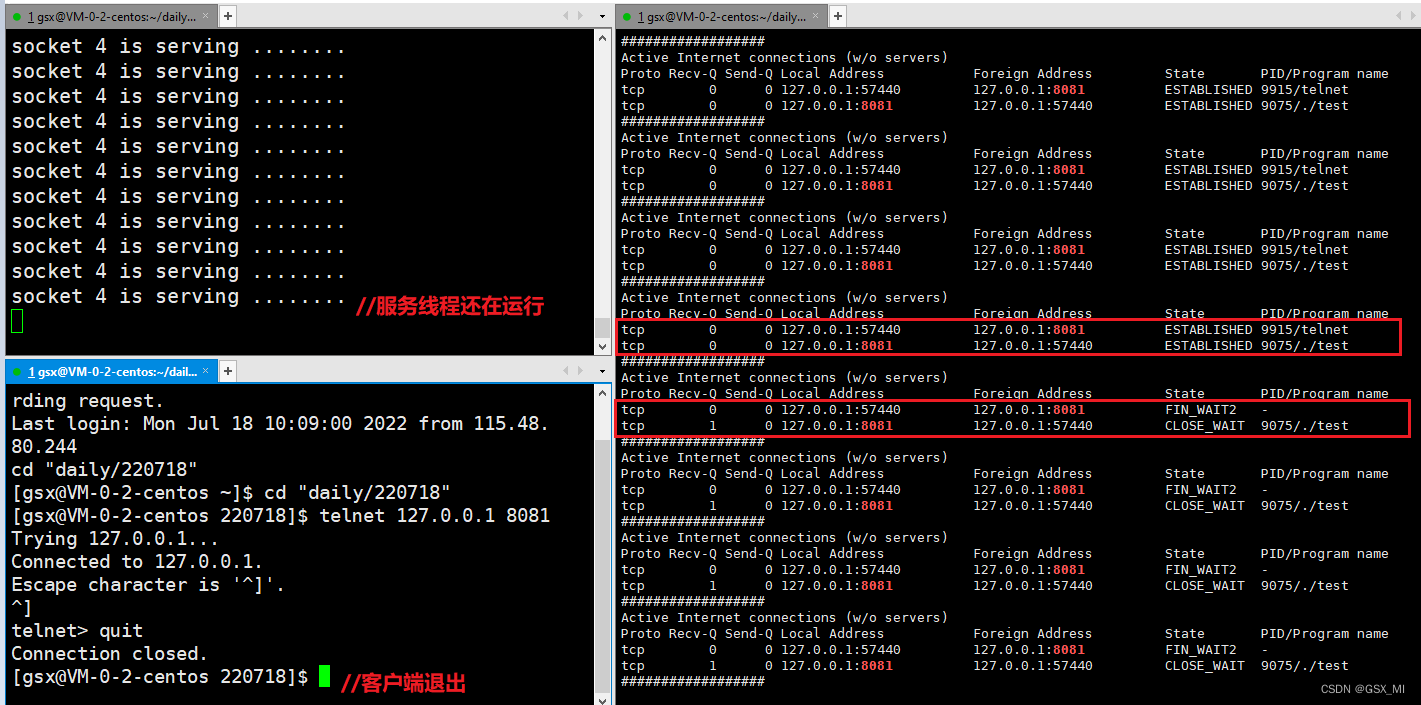
(3) Run the server , And use telnet Tools to connect to our server , Through the following monitoring script, you can see that the two statuses are ESTABLISHED The connection of , One is the client and the other is the server .
[[email protected] 220718]$ while :; do sudo netstat -ntp|head -2&&sudo netstat -ntp | grep 8081; sleep 1; echo "##################"; done

(4) Give Way telnet sign out , This is equivalent to the client sending a disconnect request to the server , But at this time, the server side does not call close The function closes the corresponding file descriptor and is still processing authentication , So when telnet after , The status of the connection maintained by the client will change to FIN_WAIT_2, The status of the connection maintained by the server will change to CLOSE_WAIT.
2. understand TIME_WAIT state
(1) When the client and the server are doing TCP When communication , Client calls close Function to close the corresponding file descriptor , If the server also calls after receiving close Function is closed , At this time, both parties will normally complete four waves .
- However, the party who initiated the four waves initiatively did so after the four waves , Will not enter immediately CLOSED state , But into a brief TIME_WAIT Status waits for a certain amount of time , Only in the end will we enter CLOSED state .
- The party who actively disconnects enters TIME_WAIT state .
(2) because telnet After exiting, the server does not call close Close the corresponding file descriptor , Therefore, the status of the client maintenance connection of the client maintenance stays at FIN_WAIT_2 state , The state of the server maintenance connection stays at CLOSE_WAIT state .
- Let the client and the server continue to wave twice after completion , You need to call on the server side close Function to close the corresponding file descriptor . Although the server code does not call close function , But because the life cycle of the file descriptor follows the process , When the process exits , The file descriptors corresponding to the process will be closed automatically .
- So it just needs to be in telnet Just let the server process exit after exiting , The file descriptor corresponding to the server process will be closed automatically , At this point, the server bottom layer TCP Will send... To the client FIN request , Complete the remaining two waves .
(3) After four waves, the connection maintained by the client will enter TIME_WAIT state , The connection maintained by the server will immediately enter CLOSED state .
3. solve TIME_WAIT Caused by state bind The way to fail
(1) The party who actively disconnects , Will enter TIME_WAIT state . If the server process exits when a client is connected to the server , It is equivalent to the server actively launching four waves , At this point, the connection maintained by the server will enter after four waves TIME_WAIT state .
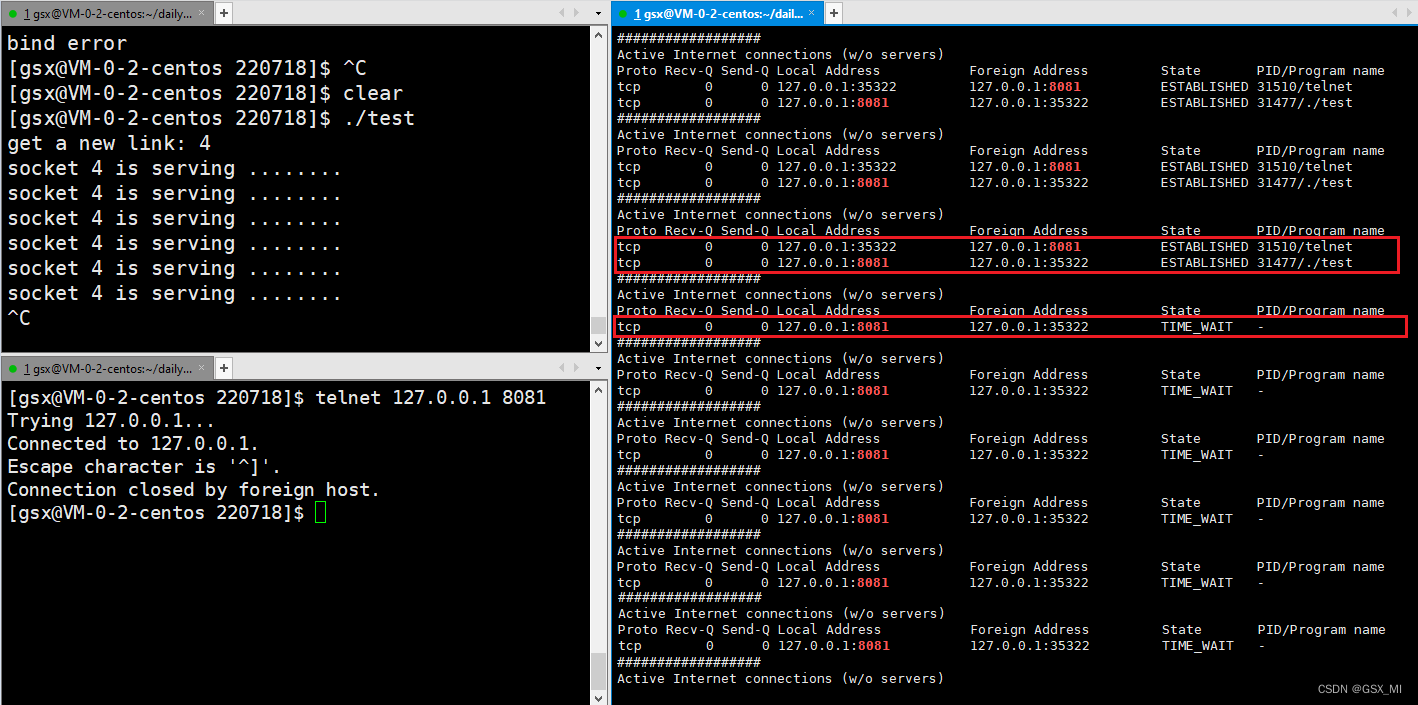
(2) When the connection is in TIME_WAIT period , If the server wants to restart again , There will be binding failure .

- because stay TIME_WAIT period , This connection has not been completely released , This means that the port number bound to the server is still occupied , At this point, the server wants to continue binding the port number to start , Just wait TIME_WAIT end .
- But when the server crashes, the most important thing is actually to restart the server immediately , If you want to crash the server after TIME_WAIT It can also be restarted immediately , You need to make the server call socket Function to create a socket , Continue to call setsockopt Function to set port reuse , This is also the recommended practice when writing server code .
(3)setsockopt function
function : int setsockopt(int sockfd, int level, int optname, const void *optval, socklen_t optlen);
Parameters :
- sockfd: The file descriptor corresponding to the socket that needs to be set .
- level: The hierarchy of options to be set . For example, setting options in the socket layer corresponds to SOL_SOCKET.
- optname: Options to be set . The available values of this option are the same as those set level Parameters are related to .
- optval: Pointer to the new value of the storage option to be set .
- optlen: The length of the new value to be set .
Return value : Set successfully returned 0, Setting failed to return -1, At the same time, the error code will be set .
What we need to set here is the listening socket , Set the port multiplexing option on the socket layer for listening sockets SO_REUSEADDR, Setting this option to a non-zero value means that port multiplexing is enabled , Indicates that it is allowed to create the same port number but IP Multiple with different addressessocket The descriptor
- int opt = 1;
- setsockopt(listen_sock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &opt, sizeof(opt));
(4) When the server crashes, we can restart the server immediately , Instead of waiting TIME_WAIT end .


(5) Even if the corresponding processes of both sides of the communication exit , But there is still a problem on the server side TIME_WAIT State connection , This also further illustrates Process management and connection management are two relatively independent units . The connection is made by TCP Self managing , Connection is not necessarily It will close with the exit of the process .
4. understand Listen Second parameter of
(1) Writing TCP Server code for socket , After socket creation and binding , Need to call listen Function to set the created socket to listen , After that, the server can call accept Function to get the established connection . among listen The first parameter of the function is the socket that needs to be set to listen , and listen The second parameter of is usually set to 5, Let's explore the meaning of the second parameter .
(2) The following is an experiment to illustrate listen The specific meaning of the second parameter of :
- Write first TCP Server side code of socket , When the server initializes, it creates sockets in turn 、 binding 、 monitor , But the server does not call after initialization accept Function to get the connection established at the bottom .
- For verification purposes , There will be listen The second parameter of the function is set to 2.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <pthread.h>
const int port = 8081;
const int num = 2;
int main()
{
// Create a listening socket
int listen_sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (listen_sock < 0){
std::cerr << "socket error" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
int opt = 1;
setsockopt(listen_sock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &opt, sizeof(opt));
// binding
struct sockaddr_in local;
memset(&local, 0, sizeof(local));
local.sin_port = htons(port);
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
if (bind(listen_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0){
std::cerr << "bind error" << std::endl;
return 2;
}
// monitor
if (listen(listen_sock, num) < 0){
std::cerr << "listen error" << std::endl;
return 3;
}
// Start the server
for (;;){
sleep(1);
// Do not call accept Get the connection
}
return 0;
}
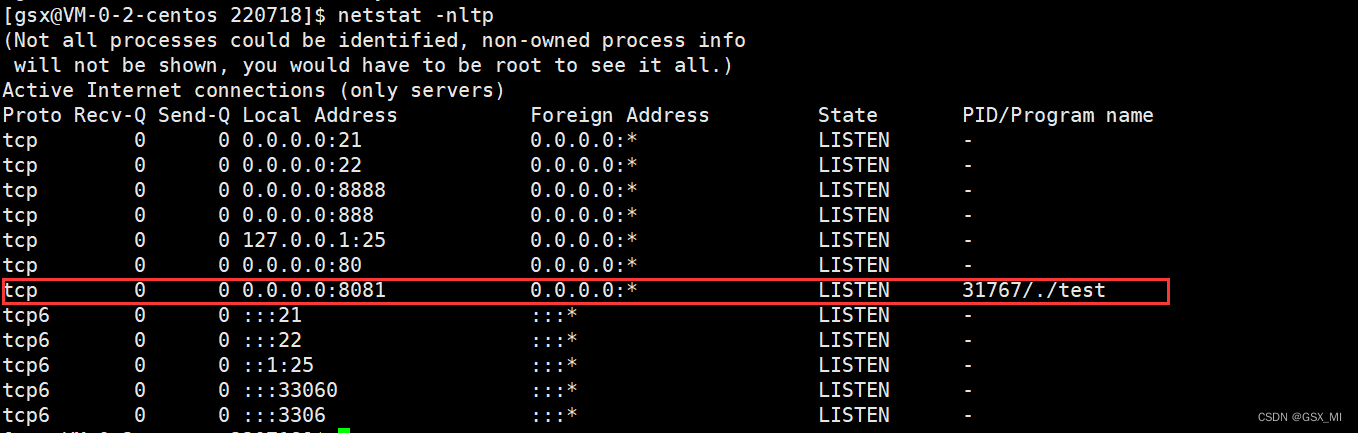
① Run the program , Use netstat -nltp command , see server In a listening state
② use Postman Send a connection request to our server .
In order to make the experimental phenomenon more obvious , It's best not to use a browser for testing , Because the browser will resend the connection request if no response is received .

③Postman After the connection request is initiated , At this point, you can see the following command , At this point, a new connection is added to the server , The connection is currently in ESTABLISHED state .
sudo netstat -ntp | head -2&&sudo netstat -ntp | grep 8081

④ use Postman Launch a second 、 Third connection request .

⑤ The server side will also add a corresponding second 、 The third connection has been established , Because the server did not call accept Function to get the established connection , So now the number of connections that have been established on the server side is 3.

⑥ Continue to use Postman Send a fourth connection request to the server .
 At this time, the server does not continue to add. The status is ESTABLISHED The connection of , Instead, a new status is added SYN_RCVD The connection of .
At this time, the server does not continue to add. The status is ESTABLISHED The connection of , Instead, a new status is added SYN_RCVD The connection of .

⑦ A new status has been added on the server SYN_RCVD The connection of , This means that the server does not respond to the connection request just sent by the client
- Reuse Postman Make a connection request to the server , No more connections in any state will be added to the server .
- And for the status just now is SYN_RCVD The connection of , Because the server does not reply to it for a long time , After three failed handshakes, the connection will be automatically released .

⑧ Summary of experiments
- No matter how many clients make connection requests to the server , Finally, at most three connections on the server side will be established successfully .
- When a fourth connection request is sent , The server just received a message from the client SYN request , But did not respond to it .
- When more connection requests are sent , The server will directly reject these connection requests .
(3)Listen Second parameter of
① actual TCP Two connection queues are used for connection management :
- Full connection queue (accept queue ). The full connection queue is used to save the data in ESTABLISHED state , But not called by the upper layer accept Remove the connection .
- Semi connected queues . The semi connected queue is used to save the data in SYN_SENT and SYN_RCVD State connection , That is, the connection of three handshakes has not been completed .
② The length of the full connection queue is actually affected by listen The influence of the second parameter , commonly TCP The length of the full connection queue is equal to listen Add one to the value of the second parameter .
③ Because we set up listen The value of the second parameter is 2, At this point, the length of the full connection queue on the server side is 3, Therefore, only three servers are allowed to be in ESTABLISHED State connection .
(4) Why does the bottom layer maintain the connection queue ?
- Generally, the role of connection queue will only be reflected when the server is under great pressure , If the server pressure itself is not great , Once the underlying connection is established successfully , The upper layer will immediately read and process the connection .
- When the server starts, it usually creates multiple service threads in advance to provide services for the client , The main thread is from the bottom accept After connecting, you can hand it over to these service threads for processing .
- If few clients make connection requests to the server , Once the connection is established at the bottom, it will be immediately connected by the main line accept Come up and give it to the service thread for processing .
- However, if a large number of clients make connection requests to the server , When each service thread is serving a connection , After the bottom layer establishes a connection, the main thread cannot get it , At this point, the established connections at the bottom will be put into the connection queue , Only when a service thread is idle , The main thread will get the established connection from the connection queue .
- Without this connection queue , So when the server-side service threads are providing services , Connection requests from other clients will be directly rejected .
- But it is possible that when the connection request is rejected , A service thread has finished providing services , At this point, the service thread cannot immediately get a connection to provide services , So the service thread must be idle for some time , Until another client sends a connection request .
- If the connection queue is set , When a service thread has finished providing services , If there are established connections in the connection queue , Then the main thread can immediately obtain a connection from the connection queue and hand it to the service thread for processing , At this point Ensure that the server is almost fully loaded .
(5) Why can't the connection queue be too long
- The full connection queue cannot be too long , The system is generally set to 5
- Although maintaining the connection queue can keep the server almost fully working , But the connection queue cannot be set too long .
- If the queue is too long , This means that the connection at the end of the queue needs to wait a long time to get the service , At this point, the request of the client will be delayed .
- Besides , The server maintains the connection at a cost , The longer the connection queue is set , The more cost the system will have to pay to maintain this queue .
- But instead of maintaining a long connection , Cause the client to wait too long , And take up a lot of temporarily unused resources , It is better to save some resources for the server , Let the server provide services for clients faster . Right server Efficiency and resource consumption .
- Therefore, although the connection queue needs to be maintained , But the connection queue cannot be maintained too long
5.SYN Flood attack
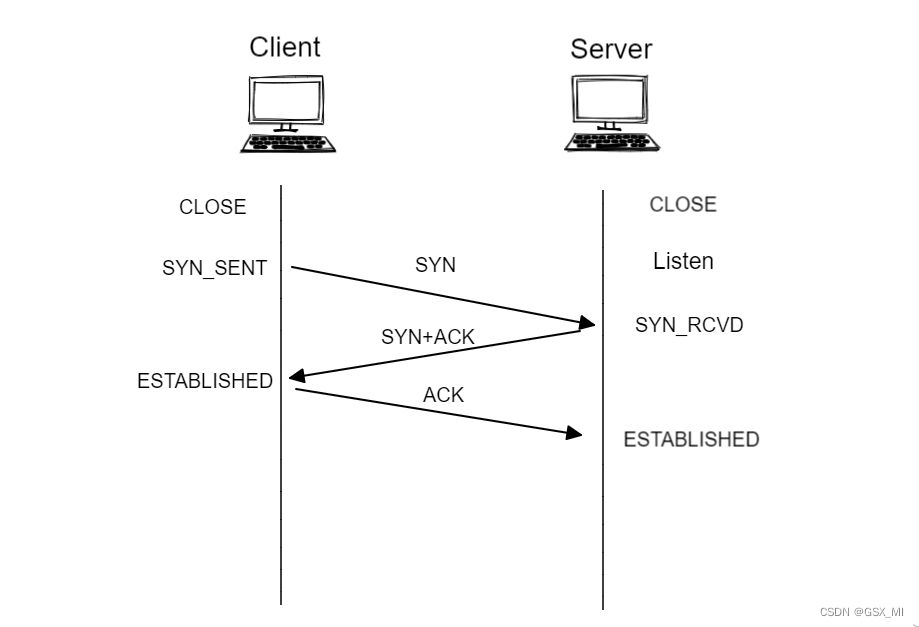
(1) The process of normal connection establishment :
- When the client sends a connection establishment request to the server , The server will SYN+ACK Respond to , And put the connection into the semi connection queue (syns queue) among .
- When the server sends SYN+ACK After receiving the client response , The connection will be moved from the semi connection queue to the full connection queue (accept queue) among .
- At this point, the upper layer can call accept function , Get the established connection from the full connection queue

(2) Connection establishment exception :
- However, if the client suddenly crashes or drops the line after initiating the connection establishment request , Then the server sends SYN+ACK There will be no corresponding ACK The reply .
- In this case, the server will retry ( Send... Again SYN+ACK To the client ) And wait for a while , Eventually, the server will fail to receive ACK Answer and discard the connection , This length of time is called SYN timeout.
- stay SYN timeout Within time , This connection will always be maintained in the semi connection queue .
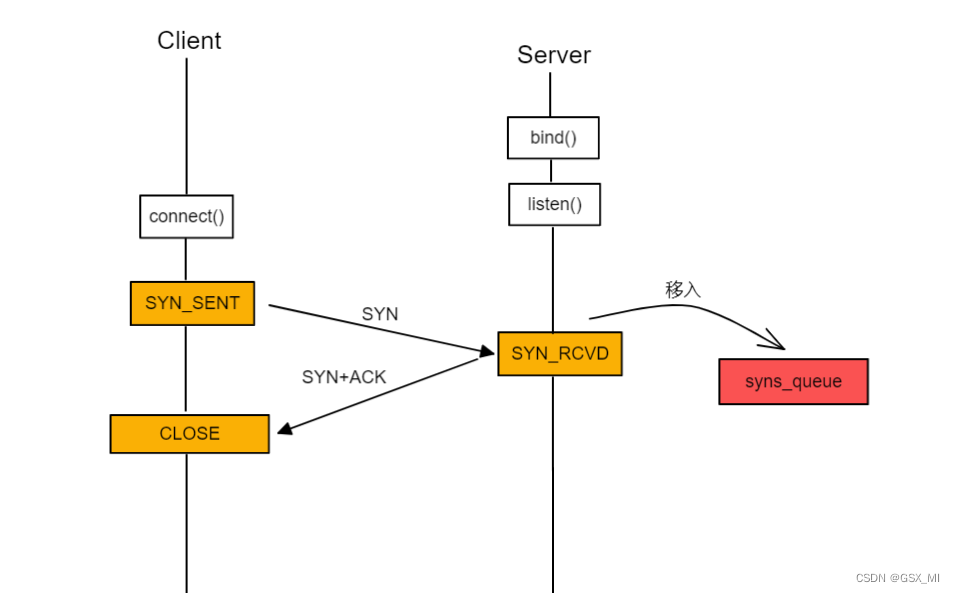
- At this time, the server needs to maintain these abnormal connections for a short time , But this situation is a minority after all , It won't have much impact on the server .
- But if a malicious user deliberately simulates this situation in large numbers : Send a large number of connection establishment requests to the server , But after receiving the message from the server SYN+ACK After that, it was deliberately not carried out ACK The reply .
- At this point, the server needs to maintain a very large semi connection queue , And these connections will not be established successfully in the end , It will not be moved to the full connection queue for the upper layer to obtain , Finally, the semi connection queue will become longer and longer .
- When the half connection queue is full , New connections will be rejected directly , Even if it is a normal connection establishment request , At this point, normal users will not be able to access the server .
- such Send a large number of messages to the server SYN request , But it does not affect the server SYN+ACK Conduct ACK Respond to , Eventually, the server may not be able to provide external services , This kind of attack is called SYN Flood attack (SYN Flood)
(3) How to solve SYN Flood attack
① First of all, it must be a comprehensive solution ,TCP As a transmission control protocol, it needs to be processed , The upper application layer should also try to avoid SYN Flood attack .
- For example, the application layer can record , The host information that initiates the connection establishment request to the server , If it is found that a host sends messages to the server multiple times SYN request , But never on the server SYN+ACK Conduct ACK Respond to , At this point, you can perform blacklist authentication on the host , From this host SYN Requests are not processed at all .
②TCP To guard against SYN Flood attack , Introduced syncookie Mechanism :
- The core problem now is that the semi connection queue is full , But you can't simply expand the semi connection queue , Even if the semi connection queue is large , Malicious users can also send more SYN Request to fill , And maintaining connections in the semi - connection queue is also costly .
- therefore TCP Introduced syncookie Mechanism , When the server receives a connection establishment request , According to this SYN The package calculates a cookie value , Make it the... To be returned SYN+ACK The initial sequence number of the package , Then put the connection into a temporary queue .
- When the server receives the ACK Response time , Will extract the cookie Value for comparison , A successful comparison indicates a normal connection , At this point, the connection will be moved from the staging queue to the full connection queue for the upper layer to read .

③ Introduced syncookie The benefits of the mechanism :
- introduce syncookie After the mechanism , These abnormal connections will not accumulate in the semi connection queue , The half connection queue will not be full .
- For normal connections , Generally, the server will be immediately SYN+ACK Conduct ACK The reply , Therefore, a normal connection will be established quickly .
- And the abnormal connection , Not to the server SYN+ACK Conduct ACK The reply , Therefore, abnormal connections will eventually accumulate in the staging queue .
边栏推荐
- Remember SQL optimization once
- What are the methods of array sorting in JS
- [noip2001 popularization group] packing problem
- 经典面试问题——OOP语言的三大特征
- STM32 - serial port learning notes (one byte, 16 bit data, string, array)
- hello world驱动(二)-初级版
- Istio三之VirtualService、Gateway、DestinationRule配置使用
- File operation (I) -- File introduction and file opening and closing methods
- Arthas' dynamic load class (retransform)
- Cloud native guide what is cloud native infrastructure
猜你喜欢

重装Win7系统如何进行?

Opencv报错:(parameter or structure field))Unrecognized or unsupported array type in functon ‘cvGetMat‘

Keyboardtraffic, a tool developed by myself to solve CTF USB keyboard traffic

LeetCode·

FPGA_Vivado软件初次使用流程_超详细

OxyCon 2022 网络抓取前沿大会即将开启!

Be highly vigilant! Weaponization of smartphone location data on the battlefield

Unknown-Aware Object Detection:Learning What You Don’t Know from Videos in the Wild(CVPR 2022)

Execution process behind shell commands

Quick check of OGC WebGIS common service standards (wms/wmts/tms/wfs)
随机推荐
Programming example of STM32 state machine -- fully automatic washing machine (Part 1)
els 修改光标、修改图标
els 初始化窗口类
ByteDance (Tiktok) software test monthly salary 23K post, technical two-sided interview questions are newly released
STM - exti external interrupt learning notes
Usage of '...' in golang
Qt 信号在多层次对象间传递 多层嵌套类对象之间信号传递
Win11麦克风权限的开启方法
Machine learning foundation plan 0-2: what is machine learning? What does it have to do with AI?
Matlab simulation of vertical handover between MTD SCDMA and TD LTE dual networks
Golang 中‘...‘的用法
在混合云中管理数据库:八个关键注意事项
事半功倍:学会WEB性能测试用例设计模型
How to close the case prompt icon of win11? Closing method of win11 case prompt Icon
经典面试问题——OOP语言的三大特征
YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement
[noip2001 popularization group] packing problem
[C language] deeply understand integer lifting and arithmetic conversion
Implement a method to find the sum of the number k and m in the array
[C Advanced] deeply explore the storage of data (in-depth analysis + interpretation of typical examples)