当前位置:网站首页>05_ Feature Engineering - dimension reduction
05_ Feature Engineering - dimension reduction
2022-06-11 17:21:00 【IT-cute】
List of articles
One 、 Dimension reduction
Feature dimensionality reduction can only be carried out after feature selection .
When feature selection is complete , You can train the model directly , But it may be due to too large characteristic matrix , Resulting in a large amount of calculation , The problem of long training time , Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the dimension of feature matrix .
Common dimensionality reduction methods include be based on L1 The penalty model Outside , also Principal component analysis (PCA) and Linear discriminant analysis (LDA), The essence of both methods is Map the original data to the sample space with lower dimension ;
But in a different way ,PCA To make the mapped sample have Greater divergence ,LDA To make the mapped sample have Best classification performance .
Besides using PCA and LDA Dimension reduction outside , You can also use Theme model To achieve the effect of dimension reduction .
1.1 Necessity of dimension reduction
In actual machine learning projects , feature selection / Dimensionality reduction is Must be carried out Of , Because there are several problems in the data :
- Data Multicollinearity : There is a correlation between feature attributes . Multicollinearity will lead to the spatial instability of the solution , Thus, the generalization ability of the model is weak ;
- High latitude spatial samples have sparsity , This makes it difficult for the model to find data features ;
- Too many variables will prevent the model from finding rules ;
- Only considering the influence of a single variable on the target attribute may ignore the potential relationship between variables .
1.2 Dimensionality reduction purpose
The purpose of dimensionality reduction is :
- Reduce the number of feature attributes .
- Make sure that there is... Between feature attributes Are independent of each other Of .( Features are independent of each other )
Two 、 Dimension reduction —PCA( Unsupervised )
Principal component analysis (PCA): Merge the feature vectors of high latitude into the feature attributes of low latitude , It's a kind of Unsupervised Dimension reduction method of .
- n_components: The number of new features .

2.1 PCA principle
- PCA(Principal Component Analysis) It is a commonly used linear dimensionality reduction method , It's an unsupervised dimension reduction algorithm . The goal of the algorithm is through some kind of Linear projection , Mapping high dimensional data to low dimensional space to represent , also It is expected that the variance of the data on the projected dimension is the largest ( Maximum variance theory ), In order to use fewer data dimensions , At the same time, the characteristics of more original data points are retained .
- Generally speaking , If you map all the points together , Then the dimension must be reduced , But at the same time, almost all the information ( Including the distance between dots ) It's all lost , and ** If the mapped data has a large variance , Then it can be considered that the data points will be scattered , In this case , You can keep more information .** So we can see PCA It is an unsupervised linear dimensionality reduction method with the least loss of original data information .
- stay PCA In dimension reduction , The data is converted from the original coordinate system to the new coordinate system , The choice of the new coordinate system is determined by the characteristics of the data itself . The first axis is selected from the original data The direction with the largest variance , Statistically speaking , This is the most important direction ; Second axis selection and first axis vertical perhaps orthogonal The direction of ; The third axis selection and the first 、 The second axis is vertical perhaps orthogonal The direction of ; The process is repeated , The calculation ends when the number of dimensions in the new coordinate system is consistent with that in the original coordinate system . The data characteristics represented by these directions are called **“ The principal components ”**.

2.2 PCA Calculation
hypothesis X Is already centralized (z-score) Passed data matrix , One sample per column ( One feature per line ); Sample points xi The projection on the hyperplane in the new space is :WTxi; If the projections of all sample points can be separated as far as possible , It means that the variance of each dimension of the point after projection should be maximized , that The sum of variances of each dimension of projected sample points It can be expressed as :

2.3 PCA Implementation process of
Input : Sample set X={x1,x2,…,xn}; Each sample has m Whitman's sign ,X It's a m That's ok n Columns of the matrix .
step :
1、 Data centric : Yes X Each line in ( A characteristic attribute ) Let's do zero averaging , Minus the mean of this row .( Standardization )
2、 Find out the matrix after data centralization X The covariance matrix of ( That is, the matrix formed by the covariance between features )
3、 Solve the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the covariance matrix
4、 The arrangement of eigenvectors in columns from large to small according to eigenvalues is called a matrix , Get the top k Column data forms a matrix W.
5、 Using the matrix W And sample set X The multiplication of the matrix is reduced to k The final data matrix of dimension .
2.4 PCA Case study

2.5 PCA Reduced dimensional SVD The solution

3、 ... and 、 Dimension reduction —LDA( Supervised )
Linear judgment analysis (LDA): LDA It is an operation of merging feature attributes based on classification model , It's a kind of Supervised Dimension reduction method of .
3.1 LDA principle
- LDA The full name is Linear Discriminant Analysis( Linear discriminant analysis ), Is a supervised learning algorithm .
- LDA The principle is , The tagged data ( spot ), By means of projection , Projected into a lower dimensional space , Make the projected point , Will form a classification , Cluster by cluster , Points of the same category , Will be closer to... In the projected space . In a word, it is :“ Minimum intra class variance after projection , Maximum variance between classes ”

3.2 LDA problem solving
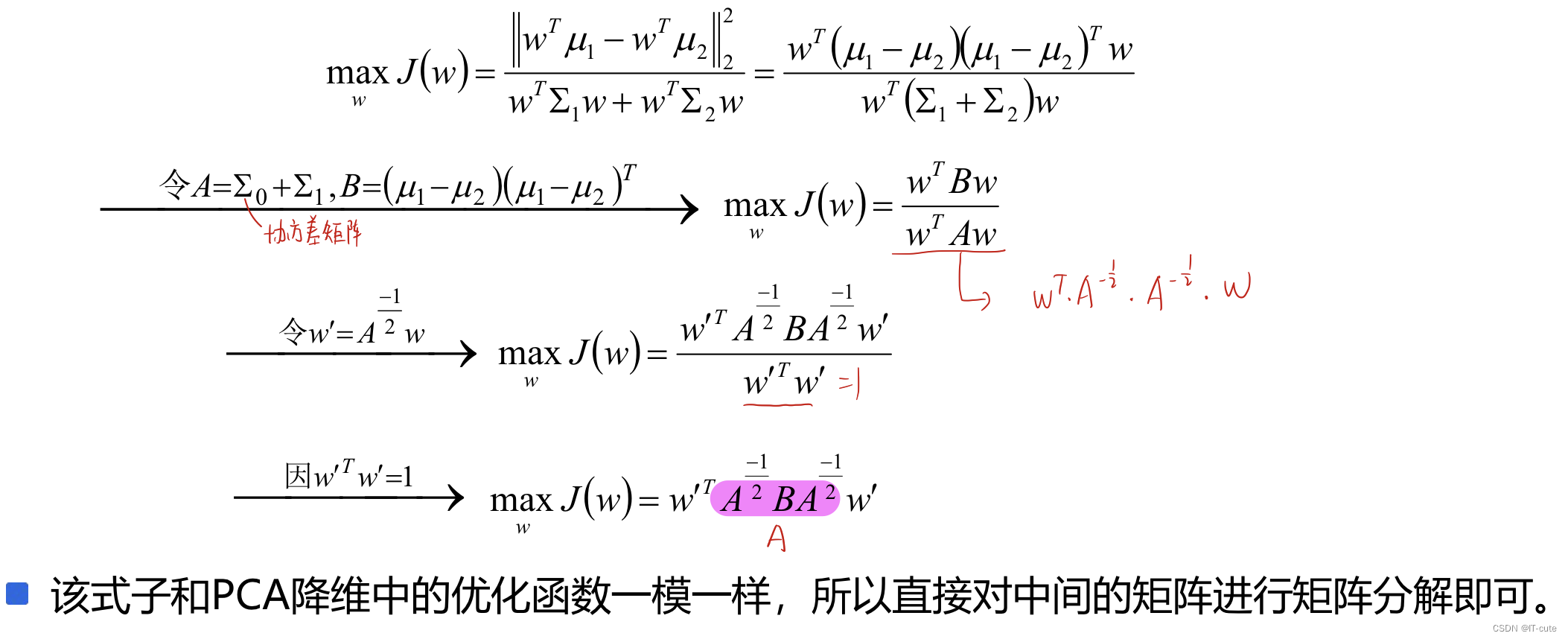
- Assume conversion to w, Then the linear transformation function is x’= wTx; And the converted data is one-dimensional .
- Consider the case of binary classification , Consider the converted value Greater than a certain threshold , Belong to a certain category , Less than or equal to a certain threshold , Belong to another category , Using the class sample Center point To represent category information , At this time, the distance between the two centers is the farthest :

- At the same time, it is required that the sample data in the same category should be as close as possible , That is, the covariance of projection points of the same category should be as small as possible .

- Combine the two , So our final objective function is :

- Transform the objective function (A、B For the square ,A Is a positive definite matrix ):
Four 、PCA and LDA similarities and differences
The same thing :
- Both of them can reduce the dimension of data .
- Both of them use the idea of matrix decomposition to reduce the dimension .
- Both assume that the data is Gaussian .
Difference :
- LDA It is a supervised dimensionality reduction algorithm ,PCA It is an unsupervised dimensionality reduction algorithm .
- LDA Dimensionality reduction can be reduced to the number of categories at most k-1 Dimension of , and PCA There is no limit to .
- LDA In addition to dimension reduction , It can also be applied to classification .
- LDA Choose the projection with the best classification performance , and PCA Select the direction where the sample point projection has the maximum variance .

边栏推荐
- Typescript learning notes (II)
- Guide to Dama data management knowledge system: percentage of chapter scores
- Analysis report on sales status and supply and demand prospects of phosphoric acid fuel cell industry in the world and China 2022-2028 Edition
- 通过Xshell连接有跳板机/堡垒机的服务器
- error:指针作为函数参数错误总结
- GemBox.Bundle 43.0 Crack
- Dynamic: capturing network dynamics using dynamic graph representation learning
- GUI guess number game, directly open play
- Authing biweekly news: online application market (5.10-5.22)
- Classic reading of multi task learning: MMOE model
猜你喜欢

Sohu tout le personnel a été escroqué, quels problèmes ont été exposés?

二级造价工程师值得考吗?发展前景如何?

How to become an optimist organization?

用实际案例分析PMP与ACP应该考哪个?哪个更有用?

vscode保存代码时自动eslint格式化

GemBox. Bundle 43.0 Crack

What problems are exposed when all Sohu employees are cheated?

Format eslint automatique lorsque vscode enregistre le Code

Pycharm使用小技巧 - 如何设置背景图片

The use of histogram function in MATLAB
随机推荐
SQL injection attack under seed emulator (including SQL environment configuration)
Authing CEO 谢扬入选福布斯 2021 年 30 Under 30 亚洲榜单
小白在同花顺上直接办理账户是安全的吗?
满k叉树编号为 i 的节点的孩子编号公式推导
String to numeric value
Talk about the interview questions of the collection
Global and Chinese molten carbonate fuel cell industry outlook and market panoramic Research Report 2022-2028
mysql 大表的拆分方式
Oracle analysis function over and MySQL achieve similar effects
^31 prototype interview questions
LeetCode-384. 打乱数组
Web security - shooting range notes
JPA循环保存多个实体失败
Report on the operation situation and future prospects of China's gear oil industry (2022-2028)
[pytest learning] after the pytest case fails to execute, the others will not be executed
Derivation of child numbering formula for nodes numbered I in full k-ary tree
Analyze which should be tested in PMP and ACP with actual cases? Which is more useful?
Splitting method of MySQL large tables
GUI guess number game, directly open play
Xie Yang, CEO of authing, was selected into Forbes' 30 under 30 Asia list in 2021