当前位置:网站首页>[fundamentals of machine learning 02] decision tree and random forest
[fundamentals of machine learning 02] decision tree and random forest
2022-06-22 06:54:00 【chad_ lee】
Decision tree

The figure above is the legend of a decision tree , Then the mathematical expression of the decision tree is :
G ( x ) = ∑ t = 1 T q t ( x ) ⋅ g t ( x ) G(\mathbf{x})=\sum_{t=1}^{T} q_{t}(\mathbf{x}) \cdot g_{t}(\mathbf{x}) G(x)=t=1∑Tqt(x)⋅gt(x)
among g t ( x ) g_{t}(\mathbf{x}) gt(x) It is also a decision tree , q ( x ) q(x) q(x) It means x x x Whether in G G G The path of t t t in . From the perspective of recursive tree :
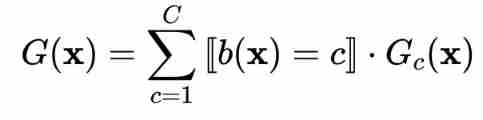
among :
- G ( x ) G(x) G(x) : full-tree hypothesis( The full tree model of the current root node )
- b ( x ) b(x) b(x) : branching criteria( Determine which branch )
- G c ( x ) G_{c}(x) Gc(x): sub-tree hypothesis at the c-th branch( The first c Subtree of branches )
Then the training process of decision tree is :

From the intuitive training process , We can see that there are four problems that need to be confirmed :
- number of branches( Number of branches ) C C C
- branching criteria( Branch condition ) b ( x ) b ( \mathbf { x } ) b(x)
- termination criteria( Termination conditions )
- base hypothesis( Base assumption function )$ g_t( \mathbf { x } )$
With so many options , There are many ways to implement the decision tree model , A common decision tree CART Trees (Classification and Regression Tree(C&RT))
C&RT
So how to solve the above four problems :
- Use a binary tree . The number of branches is 2( Binary tree ), Use decision stump( namely $ b( \mathbf { x })$ Implementation method ) Go into segments .
- Branch condition b ( x ) b( \mathbf { x }) b(x) That is, how to branch , Best branching function ( Model ) Selection of , Two parts of data used Yes No “ pure ” , First judge the purity of each segment of data, and then calculate the average value , As this decision stump Whether the evaluation criteria are selected .
b ( x ) = argmin decision stumps h ( x ) ∑ c = 1 2 ∣ D c with h ∣ ⋅ impurity ( D c with h ) b(\mathbf{x})=\underset{\text { decision stumps } h(\mathbf{x})}{\operatorname{argmin}} \sum_{c=1}^{2} \mid \mathcal{D}_{c} \text { with } h \mid \cdot \text { impurity }\left(\mathcal{D}_{c} \text { with } h\right) b(x)= decision stumps h(x)argminc=1∑2∣Dc with h∣⋅ impurity (Dc with h)
- Base assumption function g t g_t gt Is constant .
- The termination condition is that it cannot be in the branch ( All of the y n y_n yn or x n \mathbf{x}_n xn Are all the same , That is, stop when the impurity is zero or the decision can no longer be made ).
C&RT Training process :
function DecisionTree ( \left(\right. ( data D = { ( x n , y n ) } n = 1 N ) \left.\mathcal{D}=\left\{\left(\mathbf{x}_{n}, y_{n}\right)\right\}_{n=1}^{N}\right) D={ (xn,yn)}n=1N)
if cannot branch anymore
return g t ( x ) = E in g_{t}(\mathbf{x})=E_{\text {in }} gt(x)=Ein -optimal constant
else
1、 learn branch criteria:( This step is to traverse all the values of all the features )
b ( x ) = argmin decision stumps h ( x ) ∑ c = 1 2 ∣ D c with h ∣ ⋅ impurity ( D c with h ) b(\mathbf{x})=\underset{\text { decision stumps } h(\mathbf{x})}{\operatorname{argmin}} \sum_{c=1}^{2} \mid \mathcal{D}_{c} \text { with } h \mid \cdot \text { impurity }\left(\mathcal{D}_{c} \text { with } h\right) b(x)= decision stumps h(x)argminc=1∑2∣Dc with h∣⋅ impurity (Dc with h)
2、 split D \mathcal{D} D to 2 parts D c = { ( x n , y n ) : b ( x n ) = c } \mathcal{D}_{c}=\left\{\left(\mathbf{x}_{n}, y_{n}\right): b\left(\mathbf{x}_{n}\right)=c\right\} Dc={ (xn,yn):b(xn)=c}
3、 build sub-tree G C ← G_{C} \leftarrow GC← DecisionTree ( D C ) \left(\mathcal{D}_{C}\right) (DC)
4、 return G ( x ) = ∑ c = 1 2 【 b ( x ) = c 】 G c ( x ) G(\mathbf{x})=\sum_{c=1}^{2} 【 b(\mathbf{x})=c 】 G_{c}(\mathbf{x}) G(x)=∑c=12【b(x)=c】Gc(x)
Here is the impure function (Impurity Functions) Gini coefficient is commonly used in classification tasks (Gini index), Consider all classes , Calculated impurity :

Classification features (Categorical Features)
In a continuous feature , The branch conditions are implemented as follows :
b ( x ) = 【 x i ≤ θ 】 + 1 with θ ∈ R \begin{array}{l} b(\mathbf{x})=【 x_{i} \leq \theta 】+1 \\ \text { with } \theta \in R \end{array} b(x)=【xi≤θ】+1 with θ∈R
And in discrete features , Branching conditions are similar :
b ( x ) = 【 x i ∈ S 】 + 1 with S ⊂ { 1 , 2 , … , K } \begin{array}{r} b(\mathbf{x})=【 x_{i} \in S 】+1 \\ \text { with } S \subset\{1,2, \ldots, K\} \end{array} b(x)=【xi∈S】+1 with S⊂{ 1,2,…,K}
Pruning regularization
If all x n x_n xn Are different , that E i n ( G ) = 0 E_{in}(G) = 0 Ein(G)=0, That is to say, it is a fully grown tree , This can lead to over fitting , Because there is very little data to build in the lower subtree , So it is easy to cause over fitting . So here we think of using pruning to achieve regularization , Simply put, it is to control the number of leaves .
Use the number of leaves Ω ( G ) \Omega ( G ) Ω(G) Express :
Ω ( G ) = NumberOfLeaves ( G ) \Omega(G)=\text { NumberOfLeaves }(G) Ω(G)= NumberOfLeaves (G)
Then the optimization objective after regularization is :
argmin all possible G E in ( G ) + λ Ω ( G ) \underset{\text { all possible } G}{\operatorname{argmin}} E_{\text {in }}(G)+\lambda \Omega(G) all possible GargminEin (G)+λΩ(G)
Here is a difficult question , That's it all possible G G G, It is impossible to exhaust all , stay C&RT in , The following strategies are adopted :
G ( 0 ) = fully-grown tree G ( i ) = argmin G E in ( G ) such that G is one-leaf removed from G ( i − 1 ) G^{(0)}=\text { fully-grown tree } \\ G^{(i)}=\operatorname{argmin}_{G} E_{\text {in }}(G) \text { such that } G \text { is one-leaf removed from } G^{(i-1)} G(0)= fully-grown tree G(i)=argminGEin (G) such that G is one-leaf removed from G(i−1)
That is to say, it is removing $ i slice Trees leaf Of " Strategy Trees in look for Out sex can most optimal Of One star , The " Strategy Trees from pick fall Find the one with the best performance in the decision tree of a leaf , The decision tree is picked by slice Trees leaf Of " Strategy Trees in look for Out sex can most optimal Of One star , The " Strategy Trees from pick fall i−1 slice Trees leaf Of " Strategy Trees in most optimal Of One star Again pick fall One slice a have to . that Well false set up End whole Long become Of " Strategy Trees Of leaf Son Count The amount by The best one in the decision tree of a leaf is picked off to get . Then suppose that the number of leaves of a fully grown decision tree is slice Trees leaf Of " Strategy Trees in most optimal Of One star Again pick fall One slice a have to . that Well false set up End whole Long become Of " Strategy Trees Of leaf Son Count The amount by I$, So now you can get :
G ( 0 ) , G ( 1 ) , ⋯ , G ( I − ) where I − ≤ I G^{(0)}, G^{(1)}, \cdots, G^{\left(I^{-}\right)} \quad \text { where } I^{-} \leq I G(0),G(1),⋯,G(I−) where I−≤I
So from this pile G ( i ) G^{(i)} G(i) Use in Optimization objective of regularization Find the optimal decision tree .
Random forests (Random Forest)
Fully grown into a tree (fully-grown C&RT decision tree) The disadvantage of is the large variance , and bagging The function of is to reduce the variance , The essence of random forest is to combine the two .
random forest ( R F ) = bagging + fully-grown C&RT decision tree \text { random forest }(\mathrm{RF})=\text { bagging }+\text { fully-grown C\&RT decision tree } random forest (RF)= bagging + fully-grown C&RT decision tree
The random forest is made up of several trees CART form , The core is “ Two random ”.
Two random + No pruning
Random forest is random in two random :
Random sampling (bootstrap sampling)
If the training set size is N, For every tree , Randomly and put back from the training set N Training samples (bootstrap sample), As the training set of the tree ; From here we can know : The training set of each tree is different , And it contains repeated training samples .
Randomly selected features
If the characteristic dimension of each sample is M M M, Specify a constant m < < M m<<M m<<M, Randomly from M M M Selected from features m m m A subset of features , Every time a tree splits , From here m m m Choose the best of the features .
In other words, it is equivalent to making predictions in a subspace of sample features each time . for instance , Watermelon classification ,RF Each tree in the tree is based on a feature such as color 、 Pattern to do classification .
No pruning
Every tree is fully grown , No pruning . In this way, a single tree may be over fitted , But the diversity of each tree is good 、 Low tree to tree correlation , So the whole forest is not easy to be fitted .
Random forest classification effect ( Error rate ) It's related to two factors :
- The correlation of any two trees in the forest : The more relevant , The higher the error rate
- The ability to classify every tree in the forest : The stronger the ability of each tree to classify , The lower the error rate of the whole forest .
Reduce the number of feature selections m, Tree correlation and classification ability will also be reduced accordingly ; increase m, The two will increase as well . So the key question is how to choose the best m( Or the scope ), This is also the only parameter of random forest .
OOB Error
One advantage of random forest is that there is no need to reserve a validation data set , stay bootstrap sampling In the process of , The probability that a sample will not be sampled is about one third , So for every tree , Yes 1/3 Of the samples did not participate in the training , these OOB The sample is a natural validation set .OOB Error Estimation method of :
- Traversing all samples , For each sample , Calculate it as OOB Sample tree Classification of the sample .( about 1/3 The tree of )
- Then a simple majority vote is taken as the classification result of the sample ;
- Finally, the ratio of the number of misclassification to the total number of samples is used as the random forest oob Misclassification rate .
oob The error rate is an unbiased estimate of the generalization error of random forest , Its result is similar to that which needs a lot of calculation k Crossover verification .
边栏推荐
- [5g NR] ng setup of ngap protocol
- vue连接mysql数据库失败
- OpenGL - Draw Triangle
- Armadillo installation
- 【5G NR】UE注册管理状态
- [openairinterface5g] RRC NR resolution (I)
- Keil c's switch statement causes the chip to not run normally
- C语言——深入理解数组
- golang調用sdl2,播放pcm音頻,報錯signal arrived during external code execution。
- 高考是人生旅途的一处驿站
猜你喜欢

Cesium loading 3D tiles model

猿辅导最强暑假计划分享:暑假计划这样做,学习玩耍两不误

C skill tree evaluation - customer first, making excellent products

OpenGL - Draw Triangle

5G-GUTI详解

实训渗透靶场02|3星vh-lll靶机|vulnhub靶场Node1

Languo technology helps the ecological prosperity of openharmony
代理模式与装饰模式到底哪家强

Rebuild binary tree

Introduction to 51 single chip microcomputer - LED light
随机推荐
仙人掌之歌——进军To C直播(1)
Linux link sqlserver, offline installation
自然语言处理理论和应用
[openairinterface5g] RRC NR resolution (I)
JDBC query result set, which is converted into a table
[M32] SCM xxx Simple interpretation of map file
2021-05-12
The tidb community offline exchange meeting was seen by the partners from Tianjin and Shijiazhuang~
2022-06-21:golang选择题,以下golang代码输出什么?A:3;B:4;C:100;D:编译失败。 package main import ( “fmt“ ) func
5G终端标识SUPI,SUCI及IMSI解析
[5g NR] RRC connection reconstruction analysis
Xh_CMS渗透测试文档
Introduction to 51 Single Chip Microcomputer -- timer and external interrupt
Introduction to 51 Single Chip Microcomputer -- minimum system of single chip microcomputer
编程题:移除数组中的元素(JS实现)
[5g NR] mobile phone ID number IMEI and imeisv
首次用DBeaver连接mysql报错
Introduction to 51 single chip microcomputer - LED light
On the pit of delegatecall of solidity
Pytest data parameterization & data driven