当前位置:网站首页>Demand and business model innovation - demand 10- observation and document review
Demand and business model innovation - demand 10- observation and document review
2022-06-12 02:45:00 【SpriCoder】
Book10- Observation and document review
The model gives priority to objective information , Then place the part required by the customer .
1. Course extension
- Internet enterprise antitrust
- Google and Facebook face antitrust investigations by the federal and state governments
- The State Administration of market supervision is formulating 《 Antitrust guidelines in the field of platform economy 》, Public consultation has been completed
- Ali ( INtime )、 Reading passage ( Xinli )、 Fengchao ( China Post Zhidi ) Be punished separately 50 Thousands of yuan ( Less ? It's like nothing ?)
- The maximum fine is 50 Thousands of yuan
- Hui Wen Wang " retired " And the COVID-19 continues to worsen
- “ Workers ”-> “ The cook ”
- Z The deconstruction of generations of young people 、 Independence and optimism
- Look at the domestic demand for capital dialectically " Give preferential treatment "
2. Course review
- The first half of demand acquisition
- Determine the prospect and scope of the project : Problem analysis - Goal analysis - Business process analysis
- Stakeholder analysis : Stakeholder identification - Stakeholder description - Stakeholder assessment - Stakeholder representatives choose - Participation Strategy
- The second half of demand acquisition
- Based on use cases / Scenario expansion user requirements acquisition
- User access means
- Interview - Prototype - Observe
- Prototype : Abandonment and evolution , Control the cost , Deal with ambiguity and change
- Observe : Sampling observation and ethnography , Dealing with complex synergies
3. Observe
3.1. summary
- It is applied when the user cannot complete the active information notification
- Sampling observation (Sampling Observation): Traditional and simple , Observe a specific period of time or a specific event .
- Ethnography (Ethnography): Long term and immersion , The observer goes deep into the user for a long time
- Discourse Analysis (Discourse Analysis): Observe the user's conversation behavior , Observe and analyze interaction patterns or specific discourse analysis
- Protocol analysis (Protocol Analysis): Observation of user tasks , Perform tasks while observing objects
- Task analysis (Task Analysis): Observation of human-computer interaction behavior , Introduce relevant model methods to observe 、 Record and execute the user's interaction with the software system .
3.2. Application of observation methods
Situational : Some events can only be related to the specific circumstances in which they occur , To be understood
3.2.1. The situational nature of the event (situatedness)
- Emergence (Emergent): The event was caused by the collective , Emerge in the interaction , Don't limit yourself to your personal perspective
- Local (Local): Specific context , An accurate understanding may not be formed out of context
- temporary (Contingent): A moment in the evolution , Events and their interpretation depend on the current situation
- embodied (Embodied): We need to understand that the cognition and ability of participants are limited
- to open up (Open): Business is uncertain and open , Perfect later
- Fuzzy (Vague): The explanation of the event will not be particularly detailed , Based on potential knowledge , Not yet clearly expressed , Requirements engineers are hard to understand .
3.2.2. Problems solved by observation methods
- Observation focuses the findings on the context of the problem , Called social factors , Including the culture of the organization 、 The structure of the organization 、 User's working environment 、 User's work practice 、 Legal and policy constraints, etc .

- Understanding complex collaborative Events ( Emergence , More and more complex collaborative problems ): Ethnography
- Get exception handling at work ( Local , Abnormal flow is easy to be ignored ): Ethnography 、 Sampling observation
- Acquire practical knowledge that is inconsistent with user cognition ( temporary , There is a gap between cognition and practice , Validation explanation , Make corrections if necessary ): Ethnography 、 Sampling observation
- Understand the user's perception ( embodied , Be familiar with the habits of the group , Understand the tacit understanding of users ): Ethnography 、 Discourse Analysis ( Talk to understand the user's knowledge base at work )
- Get the default (tacit) knowledge ( Fuzzy , Part of the work is familiar and natural , The user will not describe ): Ethnography ( Discover default knowledge , High cost )、 Sampling observation ( Get default knowledge , Select a sample to observe , Record constraint information )、 Protocol analysis ( Speak out your thoughts , Make the default knowledge explicit )
3.3. Sampling observation
- Sampling observation is the simplest method of observation
- classification
- Time sampling : Observe users at different time intervals , such as 7 individual 8 Randomly assigned during the hour working day 5 individual 10 Observe at minute intervals .
- Event sampling : Select the whole event for observation , Such as " Board of directors " and " User training meeting ", Instead of randomly sampling time periods .

3.4. Ethnography
3.4.1. summary
- Ethnography was first proposed by anthropologists , To understand the social mechanism of primitive society .
- Ethnography requires anthropologists to spend a long time living in the society under study and carefully observe the actual activities in the society , Get first-hand observations .
- A typical example is a complex collaboration problem , These problems often have a certain sociality 、 Sudden situational .
- advantage
- Be able to understand information in depth , You can experience the difficulties personally 、 frustration 、 habit 、 Correlation and risk .
- Can make the social factors of the real world visible , Provide an opportunity to show that users are not aware of 、 Some required activities that cannot be described or are unwilling to be described , Especially the social factors in work .
- Break some wrong assumptions and misconceptions that people have
- shortcoming
- It takes a lot of time : Developers using ethnography will generally combine the current practical experience .
- It's hard to get the results across to the development process : The amount of data obtained from ethnography is relatively large , It is necessary to analyze and deal with the abstract description of the problem domain and the real world description of the problem generating part .
3.4.2. The implementation of
- The successful implementation of ethnography requires researchers to have no pre-existing ideas about the society being studied , There is no list of problems waiting to be solved , Nor will they apply their value judgments to the observed activities .
- Ethnography in the software will observe the key points and ignore the non key information .
3.4.2.1. Ethnography for complex collaborative problems
- Focus on three aspects :
- Distributed collaboration of work (Distributed Coordination)
- It refers to the method by which people cooperate with tasks in daily work
- A personal task is a single step in a complex series of tasks or other steps for others to complete a series of tasks , These steps together constitute a larger task .
- Think of the user's activities as part of an organized overall activity .
- Pay special attention to those who use notes 、 file 、 The collaboration of objects such as standard forms and the paperwork of creating these objects
- Observe the problem
- How can the division of work be reflected through individual work and work coordination ?
- How to define and distinguish people's responsibilities ?
- People's work for others 、 How about the evaluation of tasks and roles ?
- What is the work of personal altruism ?
- Work plans and procedures (Plans and Procedures)
- Data generated in a workplace 、 It is used to record the detailed steps and processes of various tasks , These tasks are integrated to meet the requirements of the whole work .
- Focus on how they are used in organizational activities
- Find deviations between actual work and documented procedures , because
- The document is not updated in time
- Different paths to work in the actual work environment
- Temporary situational events
- The way : Project plan 、 Project schedule 、 Procedure manual 、 Job description 、 Formal organization icons and workflow diagrams are common examples of plans and procedures .
- Observe the problem :
- How plans and procedures work in the workplace ?
- Do plans and procedures always work ?
- When will plans and procedures fail to apply , How to fail ?
- If the application of plans and procedures fails , What are the consequences ?
- Under what circumstances can plans and procedures be bypassed , How about bypassing ?
- The sense of work (Awareness of Work)
- Refers to a certain way of organizing activities , In this way , Activities can be visible or understandable to others who collaborate .
- Focus :
- How the workspace is arranged ? How does it affect the work ?
- How the personal space in the workplace is arranged ?
- What items are at hand to do your daily work better ?
- What documents do people at work usually refer to ?
- Where are the objects generated by the work located ? By whom ? How often is it used ?
- How individuals monitor the work of others ?
- How individuals make their work visible to others ?
- Distributed collaboration of work (Distributed Coordination)
3.4.2.2. Use the rules of ordinary ethnography
- Findings should be recorded regularly , Including observations 、 impression 、 Feeling 、 Premonitions and questions , Save your thoughts .
- Record as soon as possible the interviews that may occur during the observation , And sort it out in time .
- Review and update your ideas regularly
- Identify strategies for managing massive amounts of data , Summarize the information 、 Indexing and classification .
4. Application of document review method

- Document review is a traditional requirement acquisition method , It is dedicated to requirements acquisition activities for documents .
- The category includes related products ( Original products and competitive products ) Requirements specifications for 、 Hard data and customer requirements documentation ( Specification of commissioned development 、 Tender )
4.1. Requirements reuse
- When developing new products , You can often find the requirements specifications of related products , We can find similar or even identical problems to be solved , Analyze these parts as requirements acquisition sources
- Common reusable commonalities between products
- Problem domain information : No transfer due to system introduction , The problems solved are similar or the same
- User interface features :
- Specific user groups have specific human-computer interaction requirements , That is, specific user groups have specific user interface characteristics .
- The new product has the same user group as the original product 、 New products and competitive products also have great similarities in user groups .
- Business needs 、 Organizational strategies, policies and regulations, etc
- Business needs are similar
- Organizational strategies and policies and regulations are similar to some extent .
- The main points of : Once the requirements have been successfully established , And the product itself is successful , Then the requirements do not need to be redeveloped .
4.2. Document analysis
- Document analysis to examine collected hard data to determine potential requirements , It is to reverse engineer the documents generated or used in the work , Tap new needs .
- Analyze quantitative hard data , Get problem domain information 、 Organize business workflow 、 Problems in business information .
- Document analysis can ask questions ( Commonly used in data modeling activities )
- What is the purpose of this thing ?
- How do you use it? ? Why use ?
- The system uses it to do something ?
- Which business events use or reference this material ?
- Does this thing have a value ? for example , Does it have a number or code or quantity ?
- If so , It belongs to a collection of things ?
- What is the purpose of this thing ?
- Whether the document contains a set of repeated things ?
- If so , What is the collection of these things ?
- Can you find the connection between things ?
- What processes establish the connection between them ?
- What are the rules attached to everything ? In other words , Which part of the business strategy involves this thing ?
- What process ensures that these rules are followed ?
- What documents give users the most questions ?
- It is important to note that the documentation is not necessarily correct .
4.3. Demand stripping
- There are user requirements documents , Such as the specification of entrusted development 、 Bidding documents, etc , You can use the requirements stripping technology , Extract a single requirement from the requirements document and enter it into the new requirements document .
- It can be done by hand , But if there is an electronic format , Usually use a stripping tool , And complete requirements traceability and management tools .
- After all requirements are stripped , Persuade the customer to give up the original " description ", It's good for developers .
5. Summary of this chapter
- Among the many methods of requirements acquisition , The role of observation is becoming more and more important , It can help solve situational problems
- The application method of sampling observation is relatively fixed , But the application of ethnography is very complicated , It needs a lot of practice
- Document review method is a requirement acquisition method specially used to deal with various hard data
6. Thinking questions
- It is always difficult to observe users' work . It usually makes you and the user uncomfortable . To ensure that your access does not change the user's behavior , What should you do ? To make the observation look more natural , What should you do ?
- " I know you have a lot of material . What is in those materials ?"Betty Kant asked , She is MIS The head of the task force .MIS The task force is your system team liaison Sawder The bridge of furniture company . You dragged a lot of stuff , Just about to leave the building
- " Oh , Past 6 Some financial accounts for the last month 、 Production report , also Sharon Give me some performance reports , The performance report covers the past 6 Monthly goals and performance ." When you answer , Some paper fell to the ground ,“ Why do you ask this question ?”
- Betty Pick up the paper for you and put it on the nearest table , He replied :“ Because you don't need this garbage at all . You're here to do something , Just talk to us users . No useful information can be obtained from these materials .”
- Only tell Betty What you find in every document will convince her that every document is important . Explain in a paragraph what help the document provides to the requirements engineer ?
- Between you and Betty When talking , Realize that other quantitative documentation is actually required . List what you are missing .
边栏推荐
- Introduction to architecture - who moved my cake
- ACL 2022 - strong combination of pre training language model and graphic model
- One article to show you how to understand the harmonyos application on the shelves
- String number with special style
- GeForce GTX 2050/2080/3090/A6000自动安装nvidia显卡驱动
- Summary of force deduction solution 944- deletion of sequence
- 2022西式面点师(技师)复训题库及在线模拟考试
- 函数模板 Function Templates
- Min25 sieve
- min25筛
猜你喜欢
el-upload上传文件

How to prevent electrical fire in shopping malls?
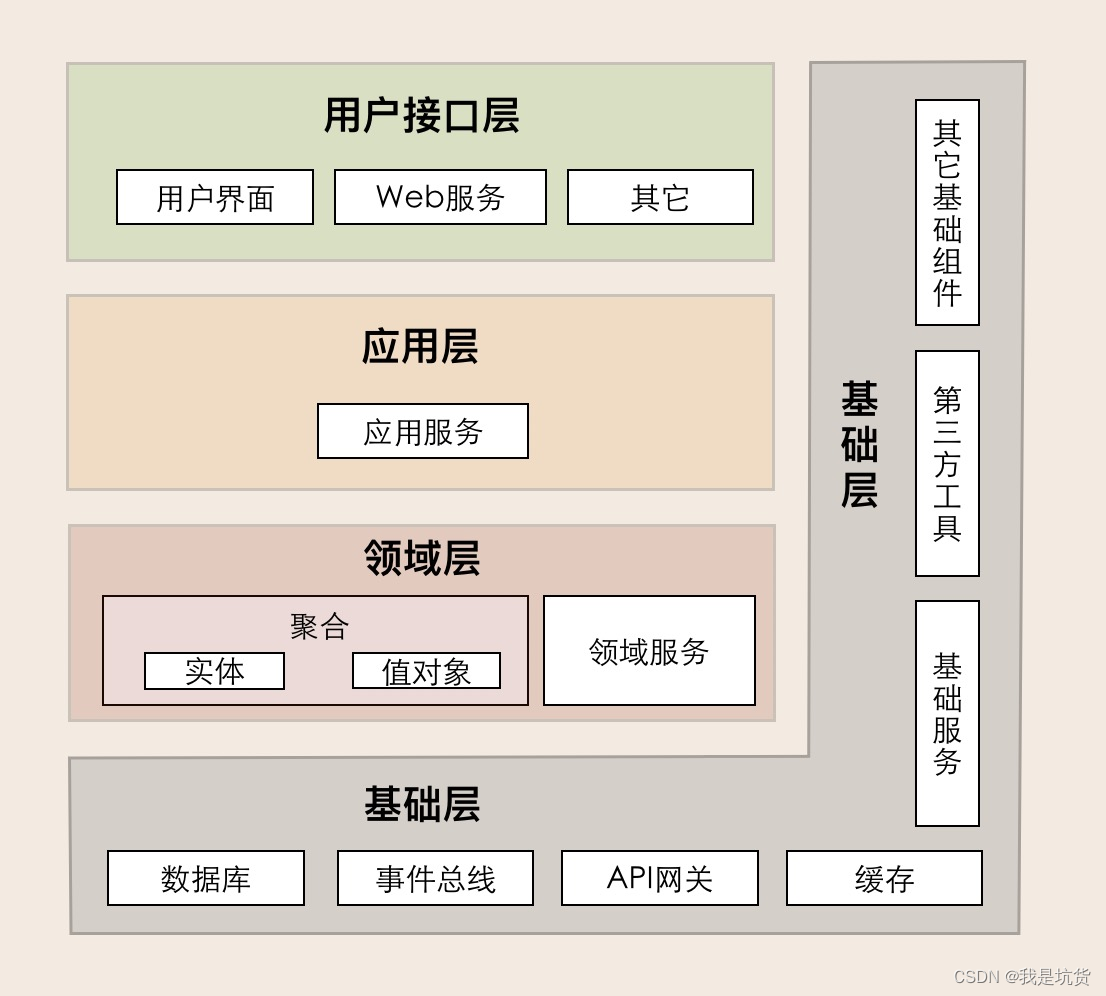
DDD的分层架构

Hypergraph tilted data is merged into root node and transferred to 3dfiles

Layered architecture of DDD

errno: -4091, syscall: ‘listen‘, address: ‘::‘, port: 8000

Proxy and reflection (II)

Acl2022 | DCSR: a sentence aware contrastive learning method for open domain paragraph retrieval

【高代码文件格式API】道宁为您提供文件格式API集——Aspose,只需几行代码即可创建转换和操作100多种文件格式

cupp字典生成工具(同类工具还有crunch)
随机推荐
Unscrambling 2021 of service grid: bid farewell to the "great leap forward" of architecture, and a hundred schools of thought contend for the technological ecology
What is SAP c/4hana Foundation
DbNull if statement - DbNull if statement
一起教育科技单季营收2.3亿:同比降51% 净亏大幅收窄
Force deduction solution summary 965- single valued binary tree
AcrelCloud-6000安全用电云平台在某商业广场的应用
架构入门讲解 - 谁动了我的蛋糕
errno: -4091, syscall: ‘listen‘, address: ‘::‘, port: 8000
中国银屑病药物市场评估与投资方向研究报告(2022版)
Force deduction solution summary interview question 01.05 Edit once
[digital signal processing] correlation function (power signal | cross correlation function of power signal | autocorrelation function of power signal)
Layered architecture of DDD
Query the duplicate values of multiple fields in the database, output the number, and add them.
Force deduction solution summary 675- cutting trees for golf competition
如何防止商场电气火灾的发生?
Oracle 11g graphic download installation tutorial (step by step)
ZABBIX notes: 6.0 lts source code installation
Ue4\ue5 touch screen touch event: single finger and double finger
【无标题】2022煤矿安全检查考题及在线模拟考试
The force deduction solution summarizes the shortest distance of 821 characters