当前位置:网站首页>[STL source code analysis] summary notes (10): hashtable exploration
[STL source code analysis] summary notes (10): hashtable exploration
2022-06-11 07:17:00 【Janvis of the stark family】
00 Write it at the front
Balanced binary search tree RB-tree As a structure with balanced efficiency and complexity , Has been used for STL set and map Underlying support for .
【STL Source analysis 】 Summary notes (8): Red and black trees (RB-tree) To explore the
【STL Source analysis 】 Summary notes (9):set/multiset And map/multimap
And there is another structure , Hashtable ( Hereinafter referred to as hashtable), When the data has enough randomness , It is also able to maintain the function of inserting, deleting and other operations “ Constant average time ” performance . It's also unordered The foundation of the structure .
hashtable More is experience design
01 summary
hashtable Is a very common data structure , We also have contact in the data structure course .hash table It is a dictionary structure .
Suppose we have a lot of elements to store in an array , Then you can construct a simple array Can be realized .
But when the amount of data becomes larger , It may be unrealistic to apply for huge space , This is the time to consider another storage method .
Mapping function is a method , Map large numbers to decimals .
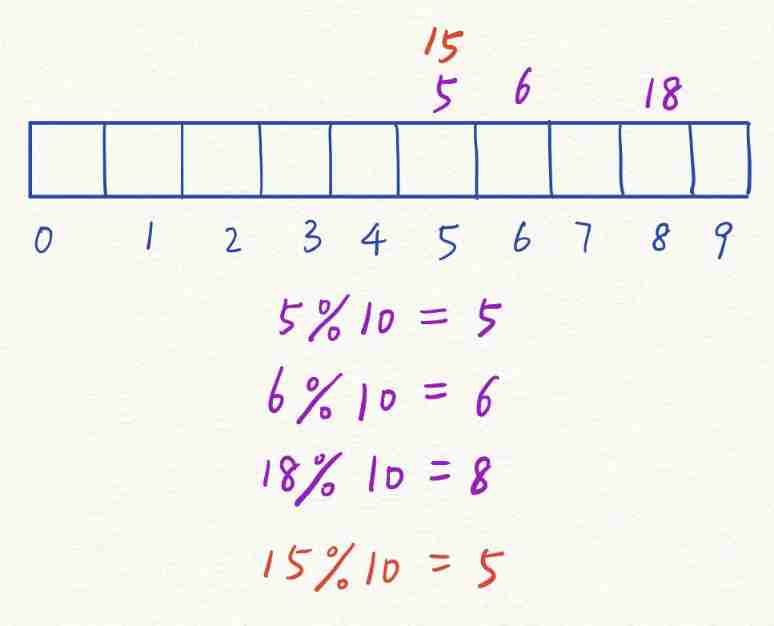
If the array length is tablesize, that x%tablesize The resulting number can be used as this number x The index of .
Solve the collision
such hash function There will be a problem , When the number of elements increases, it is inevitable that multiple elements are mapped to the same location . This situation is also called “ Collision ”. There are several common methods to solve collision :
Linear detection
When using hash function After calculating the position, it is found that the position has no space , We will continue to look down one by one for the positions where we can put the elements . If you reach the tail, start from the beginning .
This method is easy to understand , But there is also a very intuitive problem : After many vacant seats are occupied , There will be a phenomenon that new elements crash into the wall crazily and finally insert successfully , Increased average insertion cost .
Second detection
The second detection is about , Since one by one detection will cause problems , Then we will probe in the form of quadratic . Turned out to be h+1,h+2… Now it becomes h+(1 The square of ),h+(2 The square of )…
It is obvious that this method of detection is jumping , There will be no continuous impact on the wall , The effect will be much better . But it still happens when the calculated positions of two elements are the same , The efficiency waste caused by the same detection position .
Open chain
Open chain refers to maintaining a list, Let the elements with the same calculation position form a chain . This is also SGI STL in hash table Implementation method . We put forward separately that .
02 Open chain at hashtable The use of
hash table The form of is shown in the figure :

There are a lot of things in this form “ Wise remark of an experienced person ”( A design specification that everyone abides by, but the basis is unknown )
Like the whole buckets This vector The size of is usually a prime number .
And we can see that when there are more overlapping elements , This chain structure needs to maintain a long list . Then the search efficiency will be very low at this time .
So one rule is : When the number of elements is greater than buckets The number of spaces , It will buckets become 2 Double amplification , Then adjust it to prime number . In this way, the long chain can be shortened after recalculation .
In fact, it's not so easy STL These numbers are specified , We can have a look .
static const int _stl_num_primes=28;
static const unsigned long _stl_prime_list[_stl_num_primes]={
53,97,193,389,769,1543,3079,6151,12289,24593,1572869,3145739,6291469...
}
03 hashtable Structure
hash table The structure is as follows :
template <class Value,class Key,class HashFcn,class ExtractKey,class EqualKey,class Alloc=alloc>
class hashtable{
public:
typedef HashFcn hasher;
typedef EqualKey key_equal;
typedef size_t size_type;
private:
hasher hash;
key_equal equals;
ExtratKey get_key;
typedef _hashtable_node<Value>node;
vector<node*,Alloc>buckets;
size_type num_elements;
...
}
hashtable There are many template parameters , Take a look at .
- Value: The real value of the node
- Key: The key value of the node
- HashFcn:hash function, Used to get the element number ( That is, where to put it )
- ExtractKey: Take out key Methods , It is similar to the red and black tree getofvalue.
- EqualKey: Judge key Whether the same method
Below _hashtable_node yes hashtable The node structure of , contain next Pointers and value
template <class Value>
struct _hashtable_node{
_hashtable_node* next;
Value val;
}
Continue down to see buckets Is the use of vector Realized .
We can also calculate hashtable Size :
Three methods ( Function or functor ) Its size is 3.vector There are three pointers in the , Size is 12.size_type Size is 4. Total size is 19, For alignment, the system will be adjusted to 20.
04 hash function
hash function The important task of is to find the foothold of the element , That is, where to put it after calculation .
We all know that the calculation process is a modular process , But there will be some differences . For example, if you encounter characters and strings, you can't perform simple calculations .
stay STL Wrapped a function bkt_num(), Call in this function hash function.
size_type bkt_num_key(const key_type& key,size_t n)const
{
return hash(key)%n;
}
there hash The design method of partial specialization is used ( stay traits The design method I have seen )
Set different methods according to the passed in value .( Most don't need to be changed , Directly return the original value and then take the module )
// Generalized version
template <class Key> struct hash{};
// special version
_STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<char>{
size_t operator()(char x)const {return x;}
}
_STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<short>{
size_t operator()(short x)const {return x;}
}
_STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<unsigned short>{
size_t operator()(unsigned short x)const {return x;}
}
_STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<int>{
size_t operator()(int x)const {return x;}
}
...
None of the above needs to be changed , Return the original value directly .
Let's look at the practices that need to be changed ( For character strings ):
_STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<char*>{
size_t operator()(const char* s)const {return _stl_hash_string(s);}
}
_STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<const char*>{
size_t operator()(const char* s)const {return _stl_hash_string(s);}
}
And then jump to _stl_hash_string(s)
inline size_t _stl_hash_string(const char* s){
unsigned long h=0;
for(;*s;++s){
h=5*h+*s;
return size_t(h);
}
}
It is normal to fail to understand this practice , Because this itself is a very random piece of code .
for instance , We now have strings abc, Then the result will be calculated 5*(5*a+b)+c, there abc yes acsii code .
because hash function It is to ask for the code of an element to find the appropriate location , So this method is to calculate a value that is messy enough and not easy to repeat .
05 hashtable The iterator
Finally, let's talk about hashtable The iterator .
Because there are next The pointer , So you can easily jump to the next position .
node* cur;
hashtable* ht;
stay iterator There are two pointers in , The first is to point to the current list Pointer to the node in .
The second pointer is used in buckets Jump between , Because when we arrive list You need to jump to the next bucket. It's a bit like deque Control center .
Another digression , because hashtable You can only move forward ( Because only next), So it is easy for us to know its type .
typedef forward_iterator_tag iterator_category;
06 unordered
about unordered For containers , The underlying implementation is hashtable. The original non-standard name is hash set/multiset and hash map/multimap.
Let's take a look here hash set/multiset and hash map/multimap The implementation of the . And the one in front set/multiset,map/multimap similar , Can be seen as a container adapter .
hash set/multiset
hashset The bottom layer of depends on hashtable Realized , But unlike red and black trees hashtable No automatic sorting function , This is also unordered The origin of .
hashset How to use and set identical .
template <class Value,class HashFcn=hash<Value>,class EqualKey=equal_to<Value>,class Alloc=alloc>class hash_set{private: typedef hashtable<Value,Value,HashFcn.identity<Value>,EqualKey,Alloc>ht; ht rep; ...}
You can see hashset take key and value Set to the same value , Then call directly at the bottom hashtable Realization .
Empathy ,hash multiset And hashset The difference is that the insert function , The former uses insert_equal(), The latter uses insert_unique().
hash multiset And multiset The only difference is hash multiset The elements of are not automatically sorted .
hash map/multimap
map and set The difference is the key value , It is similar to the red black tree in terms of parameters .
template<class Key,class T,class HashFcn=hash<Key>,class EqualKey=equal_to<key>,class Alloc=alloc>class hash_map{private: typedef hashtable<pair<const Key,T>,Key,HashFcn,select1st<pair<const Key,T>>,EqualKey,Alloc>ht; ht rep;}
This is the same as what we said in the red and black tree const The usage is consistent , final map Save two parts , Part of it is key, The other part is key and data Composed of value.
hashmap How to use and map identical .
hash multimap And multimap The only difference is hash multiset The elements of are not automatically sorted .
边栏推荐
- Education expert wangzhongze shared his experience for many years: family education is not a vassal
- Modular notes
- [deploy private warehouse based on harbor] 2 machine preparation
- Set center alignment
- MySQL设置管理员密码无法生效的案例一则
- Duality-Gated Mutual Condition Network for RGBT Tracking
- MS office level II wrong question record [4]
- Senior openstacker - Bloomberg, vexxhost upgraded to the Gold member of openinfra Foundation
- Outer margin collapse
- WPF data binding (IV)
猜你喜欢

First day of database

软件测试周刊(第75期):唯有平视,才能看见真实的自己。

Biological sequence intelligent analysis platform blog (1)

Shutter restraint container assembly

2、 User login and registration
Gobang interface of mobile console (C language)

No response from win10 explorer when dragging files

Leetcode-104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree

Leetcode-141. Linked List Cycle
Crmeb/v4.4 Standard Version open version mall source code applet official account h5+app mall source code
随机推荐
JVM learning record (VII) -- class loading process and parental delegation model
big.js--使用/实例
337. house raiding III
1190. invert the substring between each pair of parentheses
Education expert Mr. wangzhongze: family education focuses on self growth
Detailed explanation of mutationobserver
【LeetCode】-- 17.电话号码的字母组合
2、 User login and registration
@JsonProperty注解
Adventure of small X
[并发进阶]——线程池总结
一、SQLServer2008安装(带密码)、创建数据库、C#窗体项目测试
Leetcode-104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
213. house raiding II
并发工具类
Atom, the top stream editor, will leave the historical stage on December 15
421. maximum XOR value of two numbers in the array
1442. number of triples forming two exclusive or equal arrays
Saltstack deployment LNMP
資深OpenStacker - 彭博、Vexxhost昇級為OpenInfra基金會黃金成員