当前位置:网站首页>【ROS进阶篇】第五讲 ROS中的TF坐标变换
【ROS进阶篇】第五讲 ROS中的TF坐标变换
2022-07-01 14:58:00 【生如昭诩】
【ROS进阶篇】第五讲 ROS中的TF坐标变换
文章目录
前言
在入门篇的ROS教程中,我们已经简单研究了有关TF坐标变换的内容,进阶篇的目的在于更加深入的从编程角度理解TF坐标变换的使用方法,并给出静态、动态以及多坐标变换等诸多情况下的调用,更加完善的掌握TF功能包。
一、TF功能包介绍
1. 概念
- TF:即TransForm Frame,指坐标变换;
- 坐标系:即物体的位置标定系统,以右手坐标系为标准;

- 作用:实现不同坐标系之间的点或者向量的转换
2. TF2与TF
- TF2:在现在的ROS系统中,TF2已经替换了TF使用,并且包含原有功能;
- 区别:
- TF2功能包对应tf2、tf2_ros;TF功能包对应tf包,TF2的功能包增强了内聚性,且内部的不同API完成了分包处理;
- TF2实现效率更高,这里以静态坐标变换演示;
- 静态坐标变换演示:由于信息固定,故TF2更加高效
- TF2:
变换指令:rosrun tf2_ros static_transform_publisher 0 0 0 0 0 0 /base_link /laser
查看话题消息(rostopic):rostopic echo /tf(循环输出)- TF:
变换指令:rosrun tf static_transform_publisher 0 0 0 0 0 0 /base_link /laser 100
TF启动参数更多,存在发布频率
查看话题消息(rostopic):rostopic echo /tf_static(单次输出)
- 常见功能包:
- tf2_geometry_msgs:可以将ROS消息转换成tf2消息。
- tf2: 封装了坐标变换的常用消息。
- tf2_ros:为tf2提供了roscpp和rospy绑定,封装了坐标变换常用的API。
- 参考网站地址:ROS WIki TF2
3. 坐标系查看方法
- 对应功能包:tf2_tools,安装指令如下
sudo apt install ros-noetic-tf2-tools
- 工具使用:生成对应pdf文件,图谱呈树形结构
- 启动广播坐标系程序
- 运行工具包指令:
rosrun tf2_tools view_frames.py- 生成日志如下:
[INFO] [1592920556.827549]: Listening to tf data during 5 seconds... [INFO] [1592920561.841536]: Generating graph in frames.pdf file...
- 打开目录下的pdf文件:
evince frames.pdf
4. 坐标信息
- 常用msg信息:
- geometry_msgs/TransformStamped:用于传输坐标系相关位置信息
std_msgs/Header header #头信息 uint32 seq #|-- 序列号 time stamp #|-- 时间戳 string frame_id #|-- 坐标 ID string child_frame_id #子坐标系的 id geometry_msgs/Transform transform #坐标信息 geometry_msgs/Vector3 translation #偏移量 float64 x #|-- X 方向的偏移量 float64 y #|-- Y 方向的偏移量 float64 z #|-- Z 方向上的偏移量 geometry_msgs/Quaternion rotation #四元数 float64 x float64 y float64 z float64 w
- geometry_msgs/PointStamped:用于传输某个坐标系中坐标点的信息
std_msgs/Header header #头 uint32 seq #|-- 序号 time stamp #|-- 时间戳 string frame_id #|-- 所属坐标系的 id geometry_msgs/Point point #点坐标 float64 x #|-- x y z 坐标 float64 y float64 z
- 查看msg信息指令:
rosmsg info
二、静态坐标变换
1. 情景假设
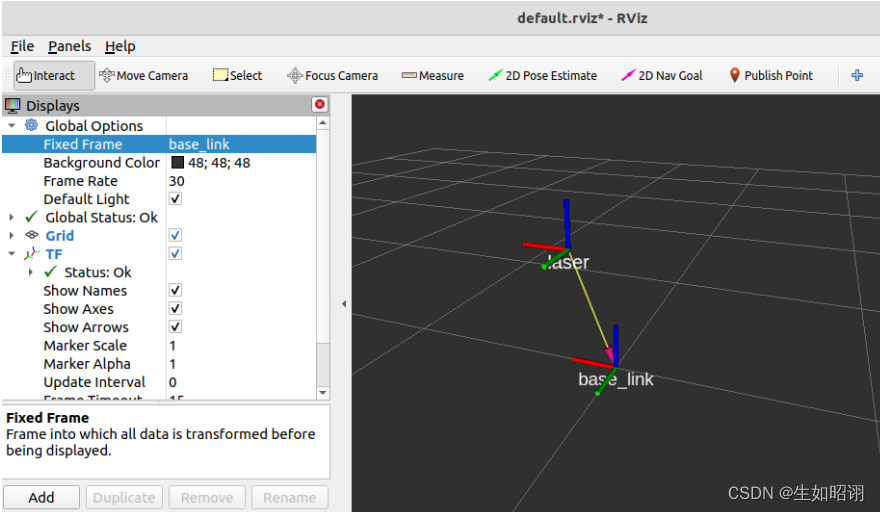
问题展示:假定一个机器人模型,躯干主体和雷达分别固接两个坐标系,二坐标系原点位于对应物理中心,雷达原点与躯干原点位移关系为:x:0.2 y:0.0 z:0.5,在雷达坐标系中有一物体坐标为(2.0 3.0 5.0),求此物体在躯干坐标系下的坐标?
3d下的演示:图中使用了rviz组件,具体使用方法见后续博客
2. 编程实现
- 基本思路:
- 创建功能包:需要包含tf2、tf2_ros、tf2_geometry_msgs、roscpp rospy std_msgs geometry_msgs等
- 创建发布者:发布躯干坐标系与雷达坐标之间的相对关系
- 创建订阅者:订阅已发布信息,根据物体信息,借助TF功能包实现坐标变换并输出;
注:ROS系统也提供了静态坐标转换的节点:
rosrun tf2_ros static_transform_publisher x偏移量 y偏移量 z偏移量 z偏航角度 y俯仰角度 x翻滚角度 父级坐标系 子级坐标系
- 发布者代码:
/* 静态坐标变换发布方: 发布关于 laser 坐标系的位置信息 实现流程: 1.包含头文件 2.初始化 ROS 节点 3.创建静态坐标转换广播器 4.创建坐标系信息 5.广播器发布坐标系信息 6.spin() */
// 1.包含头文件
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "tf2_ros/static_transform_broadcaster.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/TransformStamped.h"
#include "tf2/LinearMath/Quaternion.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
// 2.初始化 ROS 节点
ros::init(argc,argv,"static_brocast");
// 3.创建静态坐标转换广播器
tf2_ros::StaticTransformBroadcaster broadcaster;
// 4.创建坐标系信息
geometry_msgs::TransformStamped ts;
//----设置头信息
ts.header.seq = 100;
ts.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
ts.header.frame_id = "base_link";
//----设置子级坐标系
ts.child_frame_id = "laser";
//----设置子级相对于父级的偏移量
ts.transform.translation.x = 0.2;
ts.transform.translation.y = 0.0;
ts.transform.translation.z = 0.5;
//----设置四元数:将 欧拉角数据转换成四元数
tf2::Quaternion qtn;
qtn.setRPY(0,0,0);
ts.transform.rotation.x = qtn.getX();
ts.transform.rotation.y = qtn.getY();
ts.transform.rotation.z = qtn.getZ();
ts.transform.rotation.w = qtn.getW();
// 5.广播器发布坐标系信息
broadcaster.sendTransform(ts);
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
- 订阅者代码:
/* 订阅坐标系信息,生成一个相对于 子级坐标系的坐标点数据,转换成父级坐标系中的坐标点 实现流程: 1.包含头文件 2.初始化 ROS 节点 3.创建 TF 订阅节点 4.生成一个坐标点(相对于子级坐标系) 5.转换坐标点(相对于父级坐标系) 6.spin() */
//1.包含头文件
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "tf2_ros/transform_listener.h"
#include "tf2_ros/buffer.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/PointStamped.h"
#include "tf2_geometry_msgs/tf2_geometry_msgs.h" //注意: 调用 transform 必须包含该头文件
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
// 2.初始化 ROS 节点
ros::init(argc,argv,"tf_sub");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
// 3.创建 TF 订阅节点
tf2_ros::Buffer buffer;
tf2_ros::TransformListener listener(buffer);
ros::Rate r(1);
while (ros::ok())
{
// 4.生成一个坐标点(相对于子级坐标系)
geometry_msgs::PointStamped point_laser;
point_laser.header.frame_id = "laser";
point_laser.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
point_laser.point.x = 1;
point_laser.point.y = 2;
point_laser.point.z = 7.3;
// 5.转换坐标点(相对于父级坐标系)
//新建一个坐标点,用于接收转换结果
//--------------使用 try 语句或休眠,否则可能由于缓存接收延迟而导致坐标转换失败------------------------
try
{
geometry_msgs::PointStamped point_base;
point_base = buffer.transform(point_laser,"base_link");
ROS_INFO("转换后的数据:(%.2f,%.2f,%.2f),参考的坐标系是:",point_base.point.x,point_base.point.y,point_base.point.z,point_base.header.frame_id.c_str());
}
catch(const std::exception& e)
{
// std::cerr << e.what() << '\n';
ROS_INFO("程序异常.....");
}
r.sleep();
ros::spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}
三、动态坐标变换
1. 情景假设
问题展示:键盘控制海龟运动,动态发布海龟坐标系与世界坐标系之间的关系;
3d演示(rviz):

2. 编程实现
- 基本思路:
- 创建功能包:依赖项包含tf2、tf2_ros、tf2_geometry_msgs、roscpp rospy std_msgs geometry_msgs、turtlesim;
- 创建发布者:订阅turtle1/pose,获取乌龟在世界坐标系的 x坐标、y坐标、偏移量以及线速度和角速度,将 pose 信息转换成坐标系相对信息并发布
- 创建订阅者:订阅相对信息并输出;
- 发布者代码:
/* 动态的坐标系相对姿态发布(一个坐标系相对于另一个坐标系的相对姿态是不断变动的) 实现流程: 1.包含头文件 2.初始化 ROS 节点 3.创建 ROS 句柄 4.创建订阅对象 5.回调函数处理订阅到的数据(实现TF广播) 5-1.创建 TF 广播器 5-2.创建 广播的数据(通过 pose 设置) 5-3.广播器发布数据 6.spin */
// 1.包含头文件
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "turtlesim/Pose.h"
#include "tf2_ros/transform_broadcaster.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/TransformStamped.h"
#include "tf2/LinearMath/Quaternion.h"
void doPose(const turtlesim::Pose::ConstPtr& pose){
// 5-1.创建 TF 广播器
static tf2_ros::TransformBroadcaster broadcaster;
// 5-2.创建 广播的数据(通过 pose 设置)
geometry_msgs::TransformStamped tfs;
// |----头设置
tfs.header.frame_id = "world";
tfs.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
// |----坐标系 ID
tfs.child_frame_id = "turtle1";
// |----坐标系相对信息设置
tfs.transform.translation.x = pose->x;
tfs.transform.translation.y = pose->y;
tfs.transform.translation.z = 0.0; // 二维实现,pose 中没有z,z 是 0
// |--------- 四元数设置
tf2::Quaternion qtn;
qtn.setRPY(0,0,pose->theta);
tfs.transform.rotation.x = qtn.getX();
tfs.transform.rotation.y = qtn.getY();
tfs.transform.rotation.z = qtn.getZ();
tfs.transform.rotation.w = qtn.getW();
// 5-3.广播器发布数据
broadcaster.sendTransform(tfs);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
// 2.初始化 ROS 节点
ros::init(argc,argv,"dynamic_tf_pub");
// 3.创建 ROS 句柄
ros::NodeHandle nh;
// 4.创建订阅对象
ros::Subscriber sub = nh.subscribe<turtlesim::Pose>("/turtle1/pose",1000,doPose);
// 5.回调函数处理订阅到的数据(实现TF广播)
//
// 6.spin
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
- 订阅者代码:
//1.包含头文件
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "tf2_ros/transform_listener.h"
#include "tf2_ros/buffer.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/PointStamped.h"
#include "tf2_geometry_msgs/tf2_geometry_msgs.h" //注意: 调用 transform 必须包含该头文件
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
// 2.初始化 ROS 节点
ros::init(argc,argv,"dynamic_tf_sub");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
// 3.创建 TF 订阅节点
tf2_ros::Buffer buffer;
tf2_ros::TransformListener listener(buffer);
ros::Rate r(1);
while (ros::ok())
{
// 4.生成一个坐标点(相对于子级坐标系)
geometry_msgs::PointStamped point_laser;
point_laser.header.frame_id = "turtle1";
point_laser.header.stamp = ros::Time();
point_laser.point.x = 1;
point_laser.point.y = 1;
point_laser.point.z = 0;
// 5.转换坐标点(相对于父级坐标系)
//新建一个坐标点,用于接收转换结果
//--------------使用 try 语句或休眠,否则可能由于缓存接收延迟而导致坐标转换失败------------------------
try
{
geometry_msgs::PointStamped point_base;
point_base = buffer.transform(point_laser,"world");
ROS_INFO("坐标点相对于 world 的坐标为:(%.2f,%.2f,%.2f)",point_base.point.x,point_base.point.y,point_base.point.z);
}
catch(const std::exception& e)
{
// std::cerr << e.what() << '\n';
ROS_INFO("程序异常:%s",e.what());
}
r.sleep();
ros::spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}
注:关于动态坐标变换之间的进阶编程实际上在入门篇的介绍中就展示了海龟跟踪的编程实现即演示,请翻阅入门篇教程
四、多坐标变换
1. 情景假设
- 问题展示:假设存在三个坐标系,其中一个坐标系为父坐标系world,其余两个为子坐标系,父子相对关系已知,求两个子坐标系之间的关系;

2. 编程实现
- 基本思路:
- 创建功能包:依赖项包含tf2、tf2_ros、tf2_geometry_msgs、roscpp rospy std_msgs geometry_msgs、turtlesim
- 创建发布者:发布父子坐标系之间的坐标消息
- 创建订阅者:订阅相对关系,通过TF完成两坐标系转换
- 发布者代码:利用静态坐标变换发布
<launch>
<node pkg="tf2_ros" type="static_transform_publisher" name="son1" args="0.2 0.8 0.3 0 0 0 /world /son1" output="screen" />
<node pkg="tf2_ros" type="static_transform_publisher" name="son2" args="0.5 0 0 0 0 0 /world /son2" output="screen" />
</launch>
- 订阅者代码:
/* 实现流程: 1.包含头文件 2.初始化 ros 节点 3.创建 ros 句柄 4.创建 TF 订阅对象 5.解析订阅信息中获取 son1 坐标系原点在 son2 中的坐标 解析 son1 中的点相对于 son2 的坐标 6.spin */
//1.包含头文件
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "tf2_ros/transform_listener.h"
#include "tf2/LinearMath/Quaternion.h"
#include "tf2_geometry_msgs/tf2_geometry_msgs.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/TransformStamped.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/PointStamped.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
// 2.初始化 ros 节点
ros::init(argc,argv,"sub_frames");
// 3.创建 ros 句柄
ros::NodeHandle nh;
// 4.创建 TF 订阅对象
tf2_ros::Buffer buffer;
tf2_ros::TransformListener listener(buffer);
// 5.解析订阅信息中获取 son1 坐标系原点在 son2 中的坐标
ros::Rate r(1);
while (ros::ok())
{
try
{
// 解析 son1 中的点相对于 son2 的坐标
geometry_msgs::TransformStamped tfs = buffer.lookupTransform("son2","son1",ros::Time(0));
ROS_INFO("Son1 相对于 Son2 的坐标关系:父坐标系ID=%s",tfs.header.frame_id.c_str());
ROS_INFO("Son1 相对于 Son2 的坐标关系:子坐标系ID=%s",tfs.child_frame_id.c_str());
ROS_INFO("Son1 相对于 Son2 的坐标关系:x=%.2f,y=%.2f,z=%.2f",
tfs.transform.translation.x,
tfs.transform.translation.y,
tfs.transform.translation.z
);
// 坐标点解析
geometry_msgs::PointStamped ps;
ps.header.frame_id = "son1";
ps.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
ps.point.x = 1.0;
ps.point.y = 2.0;
ps.point.z = 3.0;
geometry_msgs::PointStamped psAtSon2;
psAtSon2 = buffer.transform(ps,"son2");
ROS_INFO("在 Son2 中的坐标:x=%.2f,y=%.2f,z=%.2f",
psAtSon2.point.x,
psAtSon2.point.y,
psAtSon2.point.z
);
}
catch(const std::exception& e)
{
// std::cerr << e.what() << '\n';
ROS_INFO("异常信息:%s",e.what());
}
r.sleep();
// 6.spin
ros::spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}
总结
- 声明:本节博客部分参考了CSDN用户赵虚左的ROS教程,从下篇博客起ROS进阶篇的教程将会步入ROSBAG的基础学习上,掌握这个强大的ROS记录工具的使用方法,敬请期待。
边栏推荐
- C#学习笔记(5)类和继承
- Junda technology - wechat cloud monitoring scheme for multiple precision air conditioners
- Solid smart contract development - easy to get started
- The first technology podcast month will be broadcast soon
- Markdown编辑器使用基本语法
- [leetcode 324] 摆动排序 II 思维+排序
- Task.Run(), Task.Factory.StartNew() 和 New Task() 的行为不一致分析
- 保证生产安全!广州要求危化品企业“不安全不生产、不变通”
- Solid basic basic grammar and definition function
- Hidden rules of the workplace that must be understood before 30
猜你喜欢

微服务追踪SQL(支持Isto管控下的gorm查询追踪)
![After twists and turns, I finally found the method of SRC vulnerability mining [recommended collection]](/img/ac/ab6053e6ea449beedf434d4cf07dbb.png)
After twists and turns, I finally found the method of SRC vulnerability mining [recommended collection]

Chapter 4 of getting started with MySQL: creation, modification and deletion of data tables

微信网页订阅消息实现

Build your own website (14)

leetcode:329. 矩阵中的最长递增路径

openssl客户端编程:一个不起眼的函数导致的SSL会话失败问题

Rearrangement of overloaded operators

JVM performance tuning and practical basic theory part II

The State Administration of Chia Tai market supervision, the national development and Reform Commission and the China Securities Regulatory Commission jointly reminded and warned some iron ores
随机推荐
[leetcode 324] 摆动排序 II 思维+排序
购物商城6.27待完成
Microservice development steps (Nacos)
Opencv Learning Notes 6 -- image feature [harris+sift]+ feature matching
Use the npoi package of net core 6 C to read excel Pictures in xlsx cells and stored to the specified server
After twists and turns, I finally found the method of SRC vulnerability mining [recommended collection]
[14. Interval sum (discretization)]
The data in the database table recursively forms a closed-loop data. How can we get these data
solidty-基础篇-基础语法和定义函数
数据产品经理需要掌握哪些数据能力?
tensorflow2-savedmodel convert to tflite
Task. Run(), Task. Factory. Analysis of behavior inconsistency between startnew() and new task()
竣达技术丨室内空气环境监测终端 pm2.5、温湿度TVOC等多参数监测
Ubuntu 14.04下搭建MySQL主从服务器
Some thoughts on software testing
音乐播放器开发实例(可毕设)
Problem note - Oracle 11g uninstall
MongoDB第二话 -- MongoDB高可用集群实现
openssl客户端编程:一个不起眼的函数导致的SSL会话失败问题
One of the first steps to redis
