当前位置:网站首页>After unplugging the network cable, does the original TCP connection still exist?
After unplugging the network cable, does the original TCP connection still exist?
2022-06-25 06:27:00 【Xiaolin coding】
Hello everyone , I'm Xiao Lin .
today , Talk about an interesting question : Unplug the network cable for a few seconds , Plug it back in , The original TCP Does the connection still exist ?
Maybe some students will say , The network cables have been unplugged , That means the physical layer is disconnected , The transmission layer in the upper layer should also be disconnected , So the original TCP The connection won't exist . It's like , When we make a wired call , If a party's telephone line is unplugged , Then this call will be completely disconnected .
Is that really the case ?
There is a problem with the above logic . The problem lies in , Mistakenly believe that unplugging the network cable will affect the transport layer , In fact, it will not affect .
actually ,TCP Connected to the Linux In the kernel is a program called struct socket The structure of the body , The content of this structure includes TCP Connection status and other information . When unplugging the network cable , The operating system does not change anything of this structure , therefore TCP The state of the connection will not change .
I did a little experiment on my computer , I use ssh The terminal is connected to my ECs , Then I disconnect wifi To simulate the scene of unplugging the network cable , At this point to see TCP The state of the connection has not changed , Still in ESTABLISHED state .
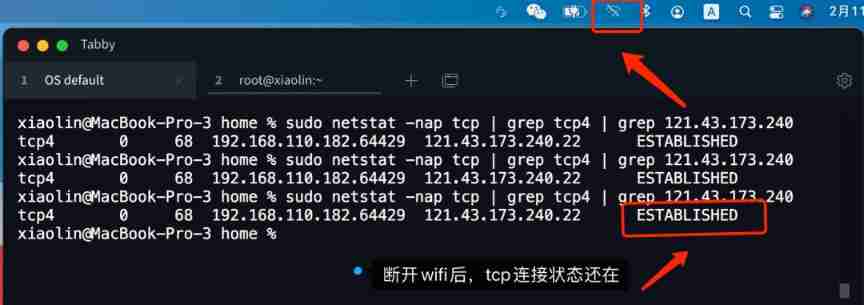
Through the above experimental results , We know , Unplugging the network cable will not affect TCP The state of the connection .
Next , It depends on unplugging the network cable , What did the two sides do .
therefore , In response to this question , We should discuss it in different scenes :
- After unplugging the network cable , There's data transmission ;
- After unplugging the network cable , No data transmission ;
After unplugging the network cable , There's data transmission
After the client unplugs the network cable , The data message sent by the server to the client will not get any response , After waiting for a certain length of time , The server will trigger Over time retransmission Mechanism , Retransmit unresponsive data message .
If in the process of retransmitting messages at the server , The client just plugged the network cable back in , Because unplugging the network cable will not change the client's TCP Connection status , And still in ESTABLISHED state , Therefore, at this time, the client can normally receive the data message sent by the server , Then the client will return ACK response message .
here , Client side and server side TCP The connection still exists , It feels like nothing has happened .
however , If in the process of retransmitting messages at the server , The client has not plugged the network cable back , When the number of times of retransmission message reaches a certain threshold , The kernel will determine that TCP There is a problem , And then through Socket The interface tells the application to TCP There's something wrong with the connection , So the server side TCP The connection will be broken .
And after the client plugs back into the network cable , If the client sends data to the server , Because the server has not the same four ancestors as the client TCP Connected to , Therefore, the server kernel will reply RST message , The client will release the... After receiving it TCP Connect .
here , Client side and server side TCP The connection has been disconnected .
that TCP How many times does the data message be retransmitted ?
stay Linux In the system , A name is provided tcp_retries2 Configuration item , The default value is 15, Here's the picture :

This kernel parameter is control , stay TCP When the connection is established , The maximum number of timeout retransmissions .
however tcp_retries2 Set up 15 Time , Doesn't mean TCP Retransmission over time 15 Will notify the application to terminate the TCP Connect , The kernel will also be based on 「 Maximum timeout 」 To determine .
The timeout time of each round increases in multiples , For example, the first time a timeout retransmission is triggered is in 2s after , The second time is in 4s after , The third time is 8s after , And so on .
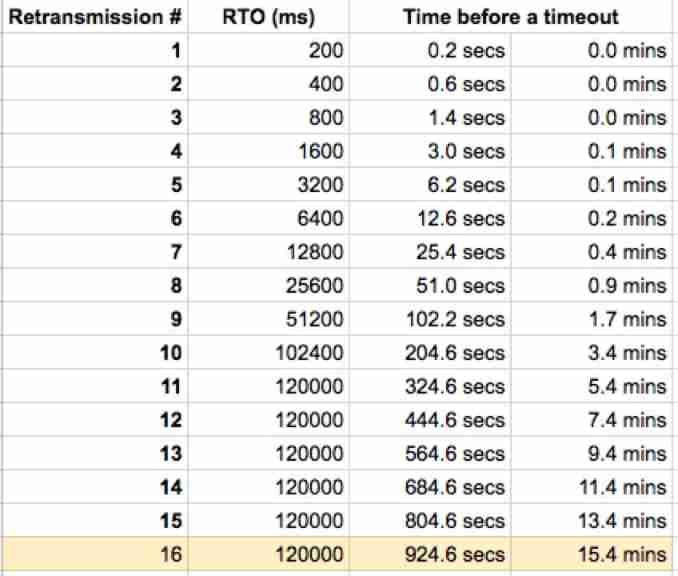
The kernel will be based on tcp_retries2 Set the value of the , Calculate a maximum timeout .
When the message is retransmitted and no response is received , Arrive first 「 Maximum number of retransmissions 」 perhaps 「 Maximum timeout 」 After one of these two conditions , Will stop retransmission , Then it will disconnect TCP Connect .
After unplugging the network cable , No data transmission
After unplugging the network cable , Scene without data transmission , It also depends on whether it is turned on TCP keepalive Mechanism (TCP The survival mechanism ).
If It's not turned on TCP keepalive Mechanism , After the client unplugs the network cable , And neither side has conducted data transmission , Then the client and server TCP The connection will always exist .
And if the Turn on 了 TCP keepalive Mechanism , After the client unplugs the network cable , Even if there is no data transmission on both sides , After a period of time ,TCP Will send a probe message :
- If The opposite end is working properly Of . When TCP The live detection message is sent to the opposite end , The opposite end will respond normally , such TCP The hold time will be reset , Wait for the next TCP The arrival of survival time .
- If Peer host crash , Or the message is unreachable due to other reasons . When TCP After the live detection message is sent to the opposite end , Under the , No response , Several times in a row , After reaching the number of live detection ,TCP It will be reported that TCP The connection is dead .
therefore ,TCP The livekeeping mechanism can be used when there is no data interaction between the two parties , By detecting messages , To determine the other person's TCP Is the connection alive .
TCP keepalive What is the specific mechanism ?
The principle of this mechanism is like this :
Define a time period , In this time period , If there is no connection related activity ,TCP The survival mechanism will start to work , Every other time interval , Send a probe message , The probe message contains very little data , If several consecutive probe messages are not responded to , The current TCP The connection is dead , The system kernel notifies the upper application of the error message .
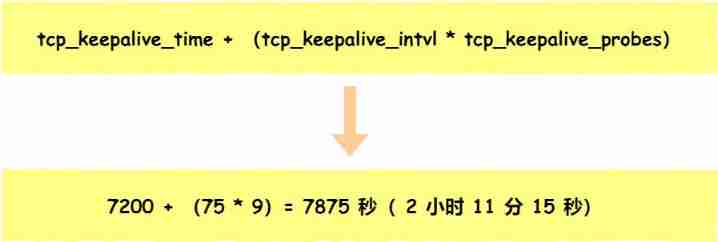
stay Linux The kernel can have corresponding parameters, and can set the live time 、 The number of live detections 、 Time interval for live detection , The following are the default values :
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time=7200
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl=75
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes=9
- tcp_keepalive_time=7200: The survival time is 7200 second (2 Hours ), It's just 2 If there is no connection related activity within hours , It will activate the survival mechanism
- tcp_keepalive_intvl=75: Represents the interval between each test 75 second ;
- tcp_keepalive_probes=9: Indicates detection 9 No response , Think the other person is not reachable , To break this connection .
That is to say Linux In the system , At least it needs to go through 2 Hours 11 branch 15 Seconds to find one 「 Death 」 Connect .
 picture
picture
Be careful , If the application wants to use TCP The survival mechanism needs to go through socket Interface setup SO_KEEPALIVE Options will work , If not set , Then you can't use TCP The survival mechanism .
TCP keepalive Mechanism detection takes too long ?
Right , It's a little long .
TCP keepalive yes TCP layer ( Kernel mode ) Realized , It is for all based on TCP Transmission protocol program, a thorough scheme .
actually , Our application layer can implement a set of detection mechanism , In a short time , Detect whether the other party is alive .
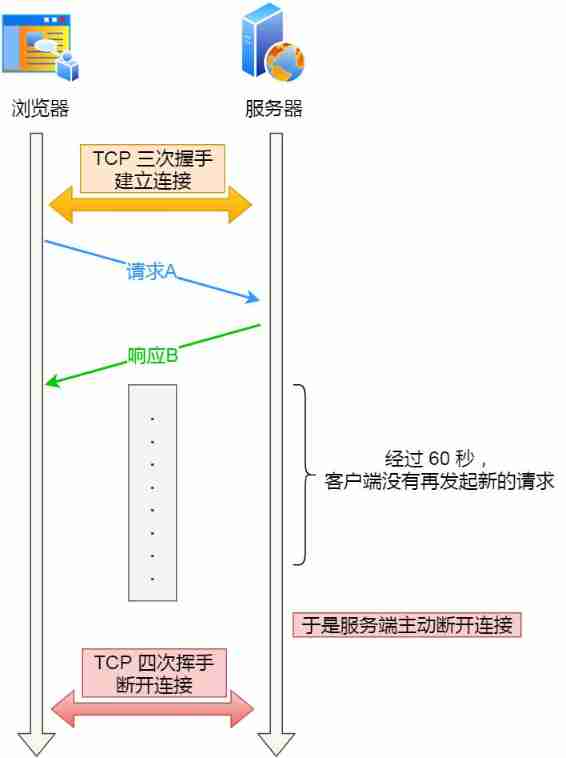
such as ,web Service software generally provides keepalive_timeout Parameters , Used to specify HTTP Long connection timeout . If set HTTP The timeout for long connections is 60 second ,web Service software will Start a timer , If the client is at the end of a HTTP After the request , stay 60 There's no new request in seconds , As soon as the timer is up , A callback function is triggered to release the connection .
summary
After the client unplugs the network cable , It doesn't directly affect TCP Connection status . therefore , After unplugging the network cable ,TCP Whether the connection will still exist , The key is to unplug the network cable , There is no data transmission .
There is data transmission :
- After the client unplugs the network cable , If the server sends a data message , Then, before the number of retransmissions on the server does not reach the maximum , The client is plugged back in , Then the original TCP The connection can still exist normally , It's like nothing happened .
- After the client unplugs the network cable , If the server sends a data message , Before the client plugs back into the network cable , The server has reached the maximum number of retransmissions , The server will be disconnected TCP Connect . Wait until the client plugs back into the network cable , Sent data to the server , Because the server has disconnected the same quadruple as the client TCP Connect , So I'll go back to RST message , The client will disconnect after receiving TCP Connect . thus , The two sides of the TCP The connection is broken .
Without data transmission :
- If neither side opens TCP keepalive Mechanism , After the client unplugs the network cable , If the client does not plug in the network cable all the time , Then the client and server TCP The connection state will always exist .
- If both sides open TCP keepalive Mechanism , After the client unplugs the network cable , If the client does not plug in the network cable all the time ,TCP keepalive The mechanism will detect each other's TCP The connection did not survive , Then it will be disconnected TCP Connect . And if TCP During detection , The client is plugged back into the network cable , Then the original TCP The connection can still exist normally .
Except for the scenario where the client unplugs the network cable , And the client 「 Downtime and killing processes 」 Two scenes of .
The first scene , The downtime of the client can't be perceived by the server just like unplugging the network cable , So if there is no data transmission , And it's not turned on TCP keepalive Mechanism ,, Server side TCP The connection will always be in ESTABLISHED Connection status , Until the server restarts the process .
therefore , We can get a point . Before use TCP The survival mechanism , And both sides do not transmit data , One side TCP The connection is in ESTABLISHED In the state of , Does not represent the other side of TCP The connection must still be normal .
The second scene , After killing the client's process , The kernel of the client will send... To the server FIN message , Four waves with the client .
therefore , Even if it's not turned on TCP keepalive, And there is no data interaction between the two sides , If one of the processes crashes , This process is perceptible to the operating system , So it's going to send FIN Message to the other party , And then with each other TCP Four waves .
End !
边栏推荐
- Digitalization, transformation?
- Arm register (cortex-a), coprocessor and pipeline
- 2022-02-19: fence installation. In a two-dimensional garden, there are some trees represented by (x, y) coordinates. As the installation cost is very expensive, your task is to enclose all the trees w
- Getting started with mongodb
- Socket, network model notes
- 3-7sql injection website instance step 3: attack type and attack strategy
- [speech discrimination] discrimination of speech signals based on MATLAB double threshold method [including Matlab source code 1720]
- Which of the top ten securities companies has the lowest Commission and is the most safe and reliable? Do you know anything
- delphi-UUID
- SAP QM executes the transaction code qp01, and the system reports an error -material type food is not defined for task list type Q-
猜你喜欢

Exercise: completion

How to deploy locally developed SAP ui5 applications to ABAP servers

Hands on deep learning (III)

ctfshow-misc
![[data visualization application] draw spatial map (with R language code)](/img/2d/04e5015573d10bdd6325ae497bfeb3.jpg)
[data visualization application] draw spatial map (with R language code)

Arm register (cortex-a), coprocessor and pipeline

Large funds support ecological construction, and Plato farm builds a real meta universe with Dao as its governance

Cannot activate inspection type when SAP retail uses transaction code mm41 to create commodity master data?

SAP QM executes the transaction code qp01, and the system reports an error -material type food is not defined for task list type Q-

JSON. toJSONString(object, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue); Second parameter action
随机推荐
[Suanli network] technological innovation of Suanli Network -- Key Technologies of green and security
MV command – move or rename files
Preliminary practice of niuke.com (summary)
Go uses channel to control concurrency
Distributed solar photovoltaic inverter monitoring
Sword finger offer II 095 Longest common subsequence
We cannot activate inspection type for article master in transaction code MM41?
Guess the size of the number
Vegetables sklearn - xgboost (2)
Large funds support ecological construction, and Plato farm builds a real meta universe with Dao as its governance
Understand what MTU is
Wechat applet simply realizes chat room function
[speech discrimination] discrimination of speech signals based on MATLAB double threshold method [including Matlab source code 1720]
Curl command – file transfer tool
What does cardinality mean in set
Methods for obtaining some information of equipment
IQ debugging of Hisilicon platform ISP and image (1)
Global and Chinese medical protective clothing market supply and demand research and investment value proposal report 2022-2028
北京网上开股票账户安全吗?
Monitoring access: how to grant minimum WMI access to the monitoring service account