当前位置:网站首页>Promise basic summary
Promise basic summary
2022-07-24 09:03:00 【Invincible beautiful girl 2000】
1、promise What is it?
- “ Producer code (producing code)” Can do something , And it will take some time . for example , Code for loading data through the network .
- “ Consumer code (consuming code)” You want to get the results of the producer code as soon as it finishes its work . Many functions may need this result .
- Promise Yes, it will “ Producer code ” and “ Consumer code ” A special connected JavaScript object .
Promise The constructor of the object (constructor) The grammar is as follows :
let promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// executor( Producer code )
});
among , Pass to new Promise The function of is called executor. When new Promise Be created ,executor Automatically . It contains the producer code that should eventually produce the result .
Parameters resolve and reject By JavaScript Self provided Callback , Our own code is only in executor Inside .
When executor Get the results , One of the following callbacks should be called :
- resolve(value) - The task is successfully completed with results value
- reject(error) - If it does error,error That is to say error object
from new Promise The constructor returns promise Object has the following internal properties :
- state - Initially pending, And then in resolve When called, it becomes fulfilled, Or in reject When called, it becomes rejected.
- result - When the initial undefined, And then in resolve(value) When called, it becomes value, Or in reject(error) When called, it becomes error.
With the original "pedding" promise contrary , One resolved or rejected Of promise Will be called "settled".
promise In the object state and result Properties are internal . No direct access , But it can be used .then/.catch/.finally Method .
2、 consumer :then,catch
promise The object is executor and consumer Connection between , The latter will receive result or error, Can pass .then and .catch Method to register the consumption function .
2.1 then
The most basic and important thing is then
promise.then (
function(result) {
/* handle a successful result */},
function(error) {
/* handle an error */}
);
then Both parameters of are functions .
- The first parameter will be in promise resolved And execute after receiving the result ;
- The second parameter will be in promise rejected And receive error Execute after information .
let promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => resolve("done!"), 1000);
});
// resolve function .then First function of
promise.then(
result => alert(result), // 1s It shows done
error => alert(error) // Not running
);
If it is reject The situation of :
let promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => reject(new Error("oh no, it's an error!")), 1000);
});
If you are only interested in successful completion , You can just .then Provide a function parameter :
promise.then(alert);
2.2 catch
If only for error Interested in , Then you can set the first function parameter to null:
.then(null, errorHandlingFunction).
Or use .catch(errorHandlingFunction).
promise.catch(alert);
// catch(f) And .then(null, f) equally
3、 clear finally
It's like a routine try {...} catch {...} Medium finally Clause is the same ,promise There are also finally.
call .finally(f) Be similar to .then(f, f), Because when promise Status as settled when ,f Will execute : No matter what promise By resolve still reject.
finally The function of is to set a handler after the previous operation , Perform cleanup / End . for example , Stop loading indicator , Close connections that are no longer needed .
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// executor code... After that, the call may resolve, It may be reject
})
// stay promise by settled run ( Whether it's resolved still rejected)
.finally(() => stop loading indicator)
// So load the indicator loading indicator It will always stop before we continue
.then(result => show result, err => show error)
finally(f) and then(f, f) There are important differences in implementation :
- finally The handler has no parameters ,finally in , We don't know promise The success of .
- finally The handler will result or error Pass to the next appropriate handler .
For example, in the above example , Passed on to then.
in other words ,finally It doesn't deal with it promise Result , Whatever the outcome , Will be routinely cleaned . - finally The handler should also not return anything . If you return , The return value will also be ignored by default .
The only exception to this rule is when finally The handler throws error, This error( Not any previous result ) Will be transferred to the next handler .
4、Promise chain
Can pass .then Handler chain To pass result.
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 1000);
}).then(function(result) {
alert(result); // 1
return result * 2;
}).then(function(result) {
alert(result); // 2
return result * 2;
}).then(function(result) {
alert(result); // 4
return result * 2;
})
Each pair .then The call of will return a new promise, Therefore, you can use the next one .then.
Of course , Multiple .then Add to a promise On , But it's not promise chain chaining.
then In process , just so so Create and return one promise:
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 1000);
}).then(function(result) {
alert(result); // 1
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(result * 2), 1000);
})
}).then(function(result) {
alert(result); // 2
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(result * 2), 1000);
})
}).then(function(result) {
alert(result); // 4
})
The above procedure is performed every 1s Pop up a number ,then The handler returns a promise object , Will result Pass to next then The handler .
To be precise , The handler does not return exactly a promise, Instead, it returns a called “thenable” object —— One has .then Method , It will be treated as a promise To treat .
5、fetch
promise It is often used for network requests ,fetch Method is used to load user information from a remote server .
let promise = fetch(url);
Execute this statement , towards url Make a network request and return a promise. When the remote server returns header( Is in Before all corresponding loads are completed ) when , The promise Use one response Object to resolve.
In order to read the complete response , We should call response.text() Method : When all text content is downloaded from the remote server , Will return a promise, The promise Take the text just downloaded as result Conduct resolve.
fetch('url')
.then(function(response) {
// When url When loading is complete ,response.text() Will return a new promise object
return response.text();
}).then(function(text) {
alert(text);
})
from fetch Back to response Objects also include response.json() Method , This method reads the remote data and parses it into JSON.
fetch('url')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(user => alert(user.name));
6、then vs catch
promise.then(f1).catch(f2);
vspromise.then(f1, f2);
In the first example f1 If appear error, Will be catch Handle ; But the second example won't .
because error It passes along the chain , The second code f1 There is no chain below . let me put it another way ,.then take result/error Pass to next .then/.catch.
7、 Use promise Error handling
Promise Chains are very powerful in error handling , When one promise By reject when , Control will be transferred to the nearest rejection The handler .
.catch It doesn't have to be immediate , Can be in one or more .then After that . Capture all error The easiest way is , take .catch Attach to the end of the chain . Usually ,.catch Will not be triggered , But if any of the above promise By reject( Network problems or invalid json Or others ),.catch Will catch it .
Implicit try…catch
Promise The executor of the (executor) and promise Processing program (handler) There is an implicit try…catch, If something unusual happens , Will be captured , And is regarded as rejection To deal with .
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
throw new Error("oh no, it's an error!");
}).catch(alert);
The above code works exactly the same as the following code :
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(new Error("oh no, it's an error"));
}).catch(alert);
stay executor Implicit around try…catch Automatically captured error, And turn it into rejected promise.
This doesn't just happen executor Function , It also happens in its handler in . If in .then In process throw,promise The object will be rejected, Control is transferred to the nearest error The handler .
new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
throw new Error("Whoops!");
}, 1000);
}).catch(alert);
But the above .catch Will not be triggered , Because there are implicit try…catch, All synchronization errors will be handled . however ! In the above code , Mistakes are not in executor Generated at run time , It is generated later , therefore promise Can't process .
8、Promise API
8.1 Promise.all
Suppose we want to execute multiple... In parallel promise, And wait for all promise All ready . for example , Download several in parallel URL And wait until all the content has been downloaded before processing them .let promise = Promise.all(iterable);
Here we accept an iteratable object , Usually an array item is promise Array of , And return to a new promise. When all given promise all resolve when , new promise Will resolve, And take its result array as a new promise Result .
Promise.all([
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 3000)),
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(2), 2000)),
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(3), 1000))
]).then(alert); // 1,2,3
The order of the elements in the result array is the same as that in the source array promise In the same order . Even if the first one promise It took the longest time to resolve, But it is still the first in the result array .
A common technique is , Map a task array to a promise Array , Then package it into Promise.all:
let urls = [
'url1',
'url2',
'url3'
];
// Each one url Mapping to fetch To Promise in
let requests = urls.map(url => fetch(url));
// Promise.all Wait for all tasks to complete resolved
Promise.all(requests)
.then(responses => responses.forEach(
response => alert(`${
response.url}: ${
response.status}`)
));
stay Promise.all() in , If any one promise By reject, The return of the promise Will immediately reject, With corresponding quilt reject the promise Of error. in other words , If it does error, So the others promise Will be ignored .
Promise.all(iterable) Parameters are also allowed to be true or false promise General value of , This parameter will be passed to the result array as is .
Promise.all([
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 1000)
}),
2,
3
]).then(alert); // 1,2,3
8.2 Promise.allSettled
The API Wait for all promise All be settle( Whatever the outcome ) after , Returns an array of results :
- Response to success :{status: “fulfilled”, value: result}
- about error:{status: “rejected”, reason: error}
8.3 Promise.race
Just wait for the first settled Of promise And get it result /error.
8.4 Promise.any
Just wait for the first fulfilled Of promise, And return it . If given promise all rejected, Then return to rejected Of promise and AggregateError Wrong type error example —— A special error object , In its errors Property stores all promise error.
8.5 Promise.resolve/reject
Using the given value Create a resolved/rejected Of promise.
9、 Micro task Microtask
Promise Processing program .then, .catch, .finally It's all asynchronous .
Even one promise Was immediately resolve, The code under these handlers will also be executed before these handlers .
let promise = Promise.resolve();
promise.then(() => alert("promise done!"));
alert("code done!");
The above code will pop up first "code done!“, Then pop up "promise done!”. This is because of the micro task queue Microtask queue.
Asynchronous tasks need to be managed properly . So ,ECMA The standard specifies an internal queue PromiseJobs, Usually called “ Micro task queue ”.
queue queue It's first in, first out : The tasks that enter the queue first will be executed first .
Only in js There are no other task runtimes in the engine , To start executing tasks in the task queue .
Simply speaking , When one promise When ready ,.then/catch/finally The handler will be put in the queue , But it will not be implemented immediately .js After the engine executes the current code , Will get the task from the queue and execute .
If you need to ensure that a piece of code is executed after the handler , You can add it to the chain call .then in .
10、Async/await
10.1 Async function
Before function async Just express a simple thing : This function always returns a promise, Other values will be automatically wrapped in a resolved Of promise in .
async function f() {
return 1;
}
f().then(alert); // 1
You can also explicitly return a promise, Same as above :
async function f() {
return Promise.resolve(1);
}
f().then(alert);
10.2 Await
Only in async Work inside a function .
keyword await Give Way js The engine waits until promise complete settle And return the result .
async function f() {
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve("done!"), 1000)
});
let result = await promise; // wait for , until promise resolve
alert(result); // "done!"
}
f();
Function execution time , until promise settle, Get result Proceed as a result .await It actually pauses the execution of the function , until promise The status changes to settled, And then to promise Continue with the results of . This behavior will not cost any CPU resources , because js The engine can handle other tasks at the same time , such as : Execute other scripts , Dealing with events, etc .
Compared with promise.then, It's just getting promise The result of a more elegant Syntax .
边栏推荐
- C # briefly describe the application of Richter's replacement principle
- [FFH] openharmony gnawing paper growth plan -- Application of cjson in traditional c/s model
- redis学习一redis介绍及NIO原理介绍
- 链表——19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
- The solution of [an error occurred while trying to create a file in the destination directory: access denied] is prompted when installing the software
- xtrabackup 实现mysql的全量备份与增量备份
- 03_ UE4 advanced_ illumination
- Linked list - 24. Exchange nodes in the linked list in pairs
- Description of MATLAB functions
- Unity C tool class arrayhelper
猜你喜欢

Virtual machine terminator terminal terminator installation tutorial
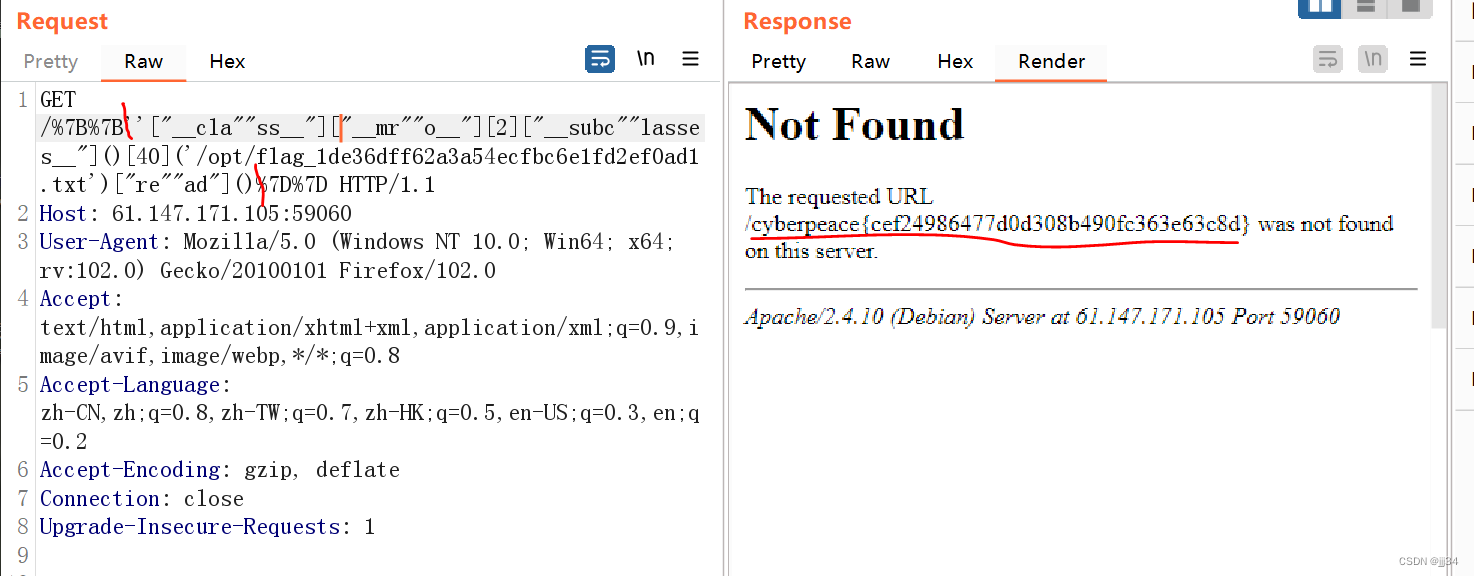
Attack and defense world ----- confusion1

Xiaobai learns Jenkins - installation and quick start

Detailed sequence traversal of leetcode102 binary tree

面试官:哥们Go语言的读写锁了解多少?

Configuration of uni app page.json title bar

Why does TCP shake hands three times instead of two times (positive version)

【翻译】使用gRPC和REST的微服务架构中的集成挑战

Discuz论坛搭建详细过程,一看就懂

dp最长公共子序列详细版本(LCS)
随机推荐
Xtrabackup realizes full backup and incremental backup of MySQL
[emotion] what is "excellent"
mysql URL
Rocky基础-Shell脚本基础知识
JUC强大的辅助类
Using OpenCV to do a simple face recognition
How to use redis' publish subscribe (MQ) in.Netcore 3.1 project
SQL problem summary
【FFH】实时聊天室之WebSocket实战
Opencv Chinese document 4.0.0 learning notes (updating...)
使用Go语言开发eBPF程序
Shell script backup mongodb database
Unity C#工具类 ArrayHelper
FreeRTOS - use of software timer
redis学习一redis介绍及NIO原理介绍
4、 Midway integrates swagger and supports JWT bearers
Notify consumers after provider information changes in RPC
【汇编语言实战】一元二次方程ax2+bx+c=0求解(含源码与过程截屏,可修改参数)
剑指 Offer II 024. 反转链表
After two days of tossing and turning, I finally wrote my first fluent app, which almost tortured me into a nervous breakdown