当前位置:网站首页>C. Array Elimination-- Codeforces Round #751 (Div. 2)
C. Array Elimination-- Codeforces Round #751 (Div. 2)
2022-08-03 21:03:00 【秦小咩】
C. Array Elimination
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
512 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
You are given array a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an, consisting of non-negative integers.
Let's define operation of "elimination" with integer parameter kk (1≤k≤n1≤k≤n) as follows:
- Choose kk distinct array indices 1≤i1<i2<…<ik≤n1≤i1<i2<…<ik≤n.
- Calculate x=ai1 & ai2 & … & aikx=ai1 & ai2 & … & aik, where && denotes the bitwise AND operation (notes section contains formal definition).
- Subtract xx from each of ai1,ai2,…,aikai1,ai2,…,aik; all other elements remain untouched.
Find all possible values of kk, such that it's possible to make all elements of array aa equal to 00 using a finite number of elimination operations with parameter kk. It can be proven that exists at least one possible kk for any array aa.
Note that you firstly choose kk and only after that perform elimination operations with value kk you've chosen initially.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases tt (1≤t≤1041≤t≤104). Description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains one integer nn (1≤n≤2000001≤n≤200000) — the length of array aa.
The second line of each test case contains nn integers a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an (0≤ai<2300≤ai<230) — array aa itself.
It's guaranteed that the sum of nn over all test cases doesn't exceed 200000200000.
Output
For each test case, print all values kk, such that it's possible to make all elements of aa equal to 00 in a finite number of elimination operations with the given parameter kk.
Print them in increasing order.
Example
input
Copy
5 4 4 4 4 4 4 13 7 25 19 6 3 5 3 1 7 1 1 1 5 0 0 0 0 0
output
Copy
1 2 4 1 2 1 1 1 2 3 4 5
Note
In the first test case:
- If k=1k=1, we can make four elimination operations with sets of indices {1}{1}, {2}{2}, {3}{3}, {4}{4}. Since && of one element is equal to the element itself, then for each operation x=aix=ai, so ai−x=ai−ai=0ai−x=ai−ai=0.
- If k=2k=2, we can make two elimination operations with, for example, sets of indices {1,3}{1,3} and {2,4}{2,4}: x=a1 & a3x=a1 & a3 == a2 & a4a2 & a4 == 4 & 4=44 & 4=4. For both operations x=4x=4, so after the first operation a1−x=0a1−x=0 and a3−x=0a3−x=0, and after the second operation — a2−x=0a2−x=0 and a4−x=0a4−x=0.
- If k=3k=3, it's impossible to make all aiai equal to 00. After performing the first operation, we'll get three elements equal to 00 and one equal to 44. After that, all elimination operations won't change anything, since at least one chosen element will always be equal to 00.
- If k=4k=4, we can make one operation with set {1,2,3,4}{1,2,3,4}, because x=a1 & a2 & a3 & a4x=a1 & a2 & a3 & a4 =4=4.
In the second test case, if k=2k=2 then we can make the following elimination operations:
- Operation with indices {1,3}{1,3}: x=a1 & a3x=a1 & a3 == 13 & 25=913 & 25=9. a1−x=13−9=4a1−x=13−9=4 and a3−x=25−9=16a3−x=25−9=16. Array aa will become equal to [4,7,16,19][4,7,16,19].
- Operation with indices {3,4}{3,4}: x=a3 & a4x=a3 & a4 == 16 & 19=1616 & 19=16. a3−x=16−16=0a3−x=16−16=0 and a4−x=19−16=3a4−x=19−16=3. Array aa will become equal to [4,7,0,3][4,7,0,3].
- Operation with indices {2,4}{2,4}: x=a2 & a4x=a2 & a4 == 7 & 3=37 & 3=3. a2−x=7−3=4a2−x=7−3=4 and a4−x=3−3=0a4−x=3−3=0. Array aa will become equal to [4,4,0,0][4,4,0,0].
- Operation with indices {1,2}{1,2}: x=a1 & a2x=a1 & a2 == 4 & 4=44 & 4=4. a1−x=4−4=0a1−x=4−4=0 and a2−x=4−4=0a2−x=4−4=0. Array aa will become equal to [0,0,0,0][0,0,0,0].
Formal definition of bitwise AND:
Let's define bitwise AND (&&) as follows. Suppose we have two non-negative integers xx and yy, let's look at their binary representations (possibly, with leading zeroes): xk…x2x1x0xk…x2x1x0 and yk…y2y1y0yk…y2y1y0. Here, xixi is the ii-th bit of number xx, and yiyi is the ii-th bit of number yy. Let r=x & yr=x & y is a result of operation && on number xx and yy. Then binary representation of rr will be rk…r2r1r0rk…r2r1r0, where:
ri={1, if xi=1 and yi=10, if xi=0 or yi=0ri={1, if xi=1 and yi=10, if xi=0 or yi=0
=========================================================================
首先二进制每一位都必须变成0才行,而且每一位的变化并不会影响其他位置,考虑单个位置来看,一旦我们选择的数里面这一位有0,那么我们无论如何也无法消去这一位,故必须选择有1的,加入有4个1,我们选1,2,4是可以的,选择3就不可以,5个1的时候,选1,5个是可以的,也就是必须选择因数,每个位置都必须是因数,那么就是全部位置gcd的因数
#include <iostream>
# include<algorithm>
# include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int ll;
ll cnt[50];
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
ll n;
cin>>n;
memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));
int flag=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
ll x;
cin>>x;
if(x)
flag=1;
int len=0;
while(x)
{
if(x%2)cnt[len]++;
x/=2;
len++;
}
}
ll ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<=30;i++)
{
if(cnt[i])
ans=__gcd(ans,cnt[i]);
}
if(!flag)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cout<<i<<" ";
}
continue;
}
for(int i=1;i<=ans;i++)
{
if(ans%i==0)
{
cout<<i<<" ";
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- glusterfs build and use
- 肝完 Alibaba 这份面试通关宝典,我成功拿下今年第 15 个 Offer
- 检测和控制影子IT的五个步骤
- LeetCode_位数统计_中等_400.第 N 位数字
- 华为设备配置VRRP与BFD联动实现快速切换
- Orcad Capture Cadence 新建原理图多部分smybol和Homogeneous、Heterogeneous类型介绍教程
- leetcode 16.01. Swap numbers (swap the values of 2 numbers without using temporary variables)
- 2022年1~7月语音合成(TTS)和语音识别(ASR)论文月报
- tkwebview2创作心得
- 在树莓派上搭建属于自己的网页(4)
猜你喜欢

ECCV 2022 | 清华&腾讯AI Lab提出REALY:重新思考3D人脸重建的评估方法
TweenMax.js向日葵表情变化
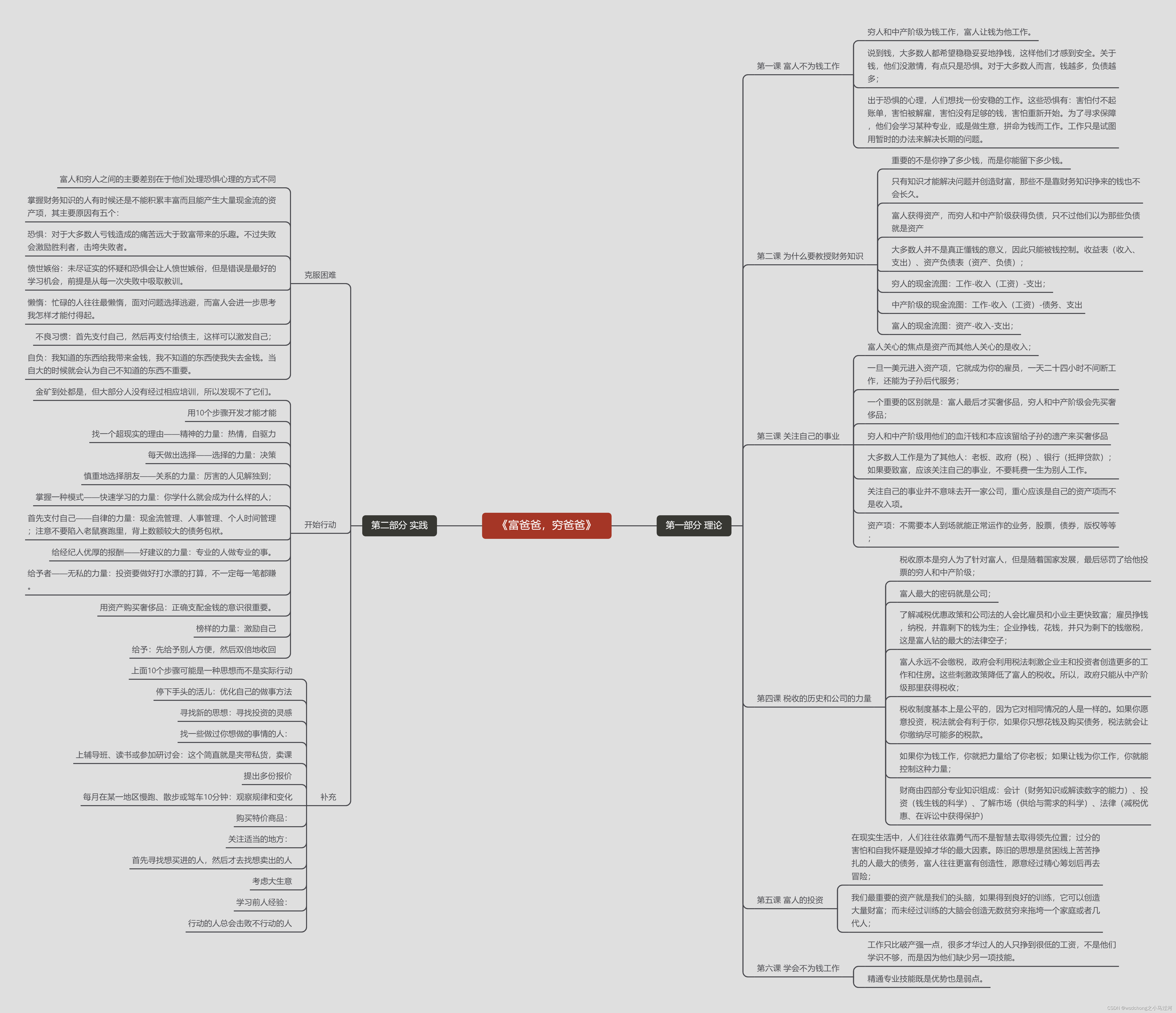
《富爸爸,穷爸爸》思维导图和学习笔记
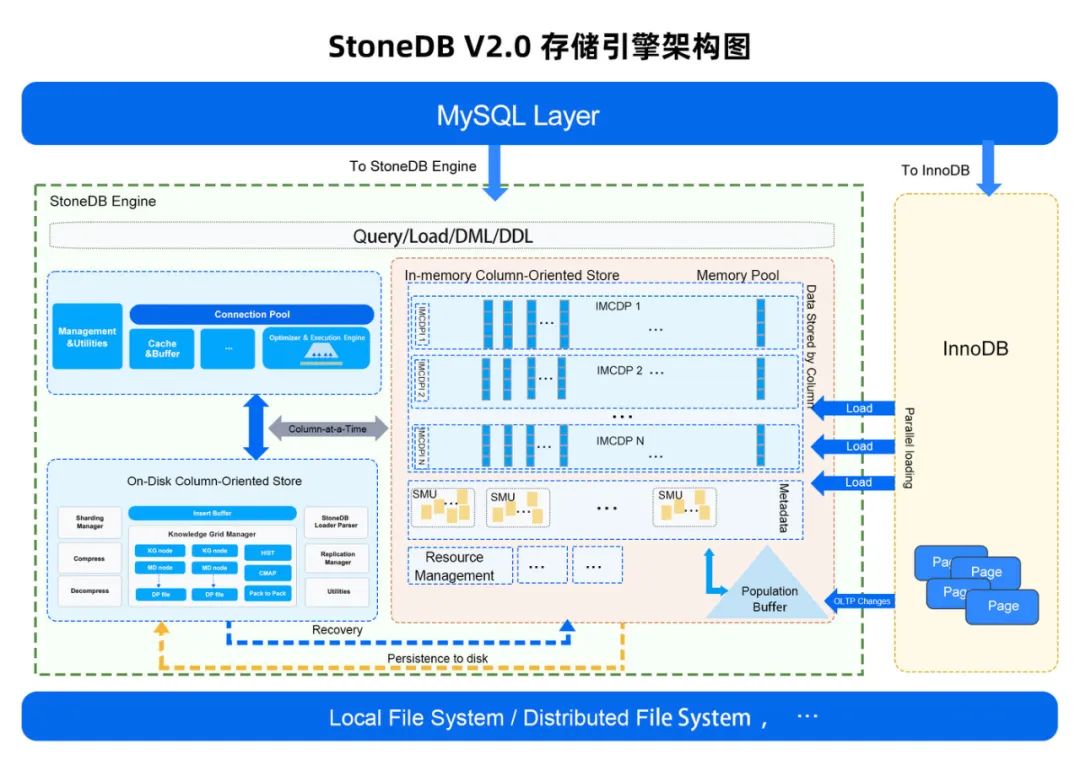
一体化HTAP数据库如此难,为什么他们还要做?
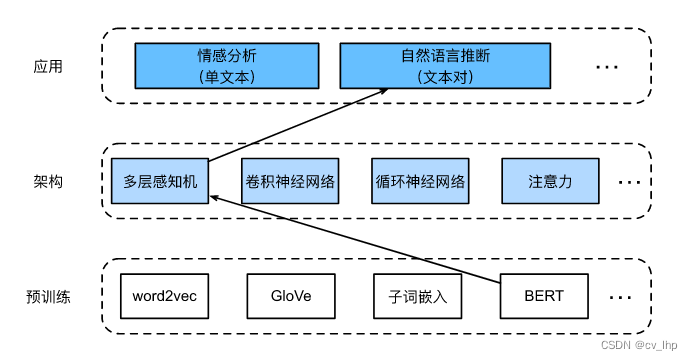
Li Mu hands-on learning deep learning V2-BERT fine-tuning and code implementation
通关剑指 Offer——剑指 Offer II 009. 乘积小于 K 的子数组
解决npm -v查看npm版本出现npm WARN config global `--global`, `--local` are deprecated. Use `--location报错

Cesium 修改鼠标样式
win10安装及配置Gradle
461. 汉明距离
随机推荐
leetcode 136. 只出现一次的数字(异或!!)
敏捷交付的工程效能治理
dataframe 多层索引 更换索引 df.swaplevel(axis=1)
Markdown语法
XSS线上靶场---haozi
idea2021.1.3配置Gradle步骤
【kali-漏洞扫描】(2.1)Nessus解除IP限制、扫描快无结果、插件plugins被删除(中)
简单又有效的基本折线图制作方法
tidyverse based on data.table?
李沐动手学深度学习V2-自然语言推断与数据集SNLI和代码实现
【使用 Pytorch 实现入门级的人工神经网络】
Likou 59 - Spiral Matrix II - Boundary Judgment
通关剑指 Offer——剑指 Offer II 009. 乘积小于 K 的子数组
ECCV 2022 | 清华&腾讯AI Lab提出REALY:重新思考3D人脸重建的评估方法
在树莓派上搭建属于自己的网页(3)
leetcode 268. 丢失的数字(异或!!)
PyCharm function automatically add comments without parameters
开源一夏 |如何优化线上服务器
【kali-漏洞扫描】(2.1)Nessus下载安装(上)
LitJson报错记录