当前位置:网站首页>4. Const and difine and the problem of initializing arrays with const and define
4. Const and difine and the problem of initializing arrays with const and define
2022-07-28 20:05:00 【A programmer who loves playing badminton】
1.const Constant
const Is a constant variable , Decorated variables cannot be changed .
const int num = 1;
// num = 2;
printf("num=%d", num);If you will num=2 Remove comments from , That is to modify const Value , You're going to report a mistake .
const int num = 1;
num = 2;
printf("num=%d\n", num);
At this time, we associate the definition of array ,int arr[] = ;
We know that variables cannot be placed in brackets when defining an array , but const The defined variable is an unchangeable variable , Can we put const Defined variables ?
The answer is C Not in the file , stay Cpp Medium can .
const int n = 10;
int arr[n] = {1, 2, 3};
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
printf("%d", arr[i]);
}
return 0;This code is written in C In file
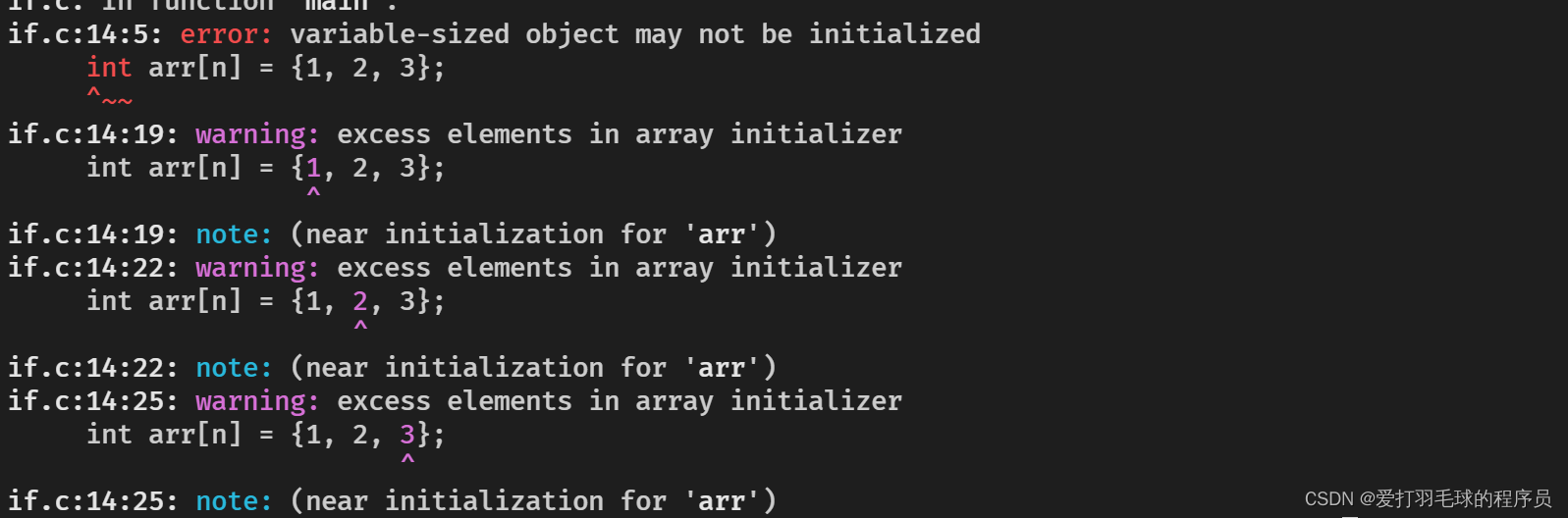
Written in Cpp In file
Why does it appear in this problem ?
First, we need to understand what constants are , What is a read-only variable ?
- Constant It must be read-only , For example, digital 6, character string “abc” etc. , It must be read-only , because There is no place in the program to store its value , Of course, we can't modify it .
- A read-only variable It is in Open a place in memory to store its value , Only this value is limited by the compiler Not allowed to be modified .
- C Language Subscripts must be constants when defining arrays , Read only variables are not allowed .
therefore
stay C In language ,const It is a modifier used to limit that a variable is not allowed to be changed , Read only variable , Because it occupies storage space , So the compiler doesn't know the value at run time , So I don't know how big the array should be defined .
stay C++ in , const The modified can be regarded as a constant at compile time
For basic data types : The compiler will put it in the symbol table , Without allocating storage space .
about ADT(Abstract Data Type Abstract data types )/ UDT( User defined type ) Of const Objects need to allocate storage space ( Big object ).
And in some cases, it is also necessary to allocate storage space , For example, the mandatory declaration is extern Or get the address of the Symbolic Constant .
So how to C As in the C++ Then you can define the array ? Let's see define
2.define
define Used to define identifier constants , It's also called hongdefination , The program will use define Defined content Replace
for example define N 100, Will be 100 To replace all N, In other words , differ const Constant ,define In fact, it is essentially the replacement of text content .
So in C You can use define To initialize an array
#define MAX 10
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int arr[MAX] = {0};
printf("%d", MAX);
return 0;
}It won't make a mistake .
Sum up , Let's see const and define The difference between
1.define Is a macro definition , The program will use define Replace the defined content . So when the program is running , There's no use in the constant table define Defined constant , The system does not allocate memory for it . and const Defined constant , When the program is running , Exists in the constant table , And The system allocates memory for it .
2.define Defined constant , The preprocessing is just a direct replacement , Therefore, data type verification cannot be performed at compile time .
and const Defined constant , stay Strict type checking at compile time , You can avoid mistakes .
tips:
We are choosing define still const When initializing the array , If it says C Language , Then use define, And in the c++ It is more recommended to use const, because define In the pretreatment stage Lack of type detection mechanism , Therefore, the type cannot be specified correctly , It will lead to some mistakes . and define Preprocessing macros are global . So in C++ So much emphasis on namespaces 、 In the language of such things , The best thing for the overall situation is to have as few things as possible .
边栏推荐
- XOR operation and its usage
- English translation Portuguese - batch English conversion Portuguese - free translation and conversion of various languages
- MySQL command statement (personal summary)
- How to write the SQL statement of time to date?
- 利用STM32的HAL库驱动1.54寸 TFT屏(240*240 ST7789V)
- Machine learning -- model evaluation, selection and verification
- Prometheus deployment
- Leetcode day3 find duplicate email addresses
- [C language] simulation implementation of pow function (recursion)
- leetcode day3 超过经理收入的员工
猜你喜欢

2022年下半年系统集成项目管理工程师认证8月20日开班

Question bank and answers of the latest national fire-fighting facility operators (intermediate fire-fighting facility operators) in 2022

Design of air combat game based on qtgui image interface
![[C language] string reverse order implementation (recursion and iteration)](/img/c3/02d0a72f6026df8a67669293e55ef2.png)
[C language] string reverse order implementation (recursion and iteration)

Cloud computing notes part.2 - Application Management
![[NPP installation plug-in]](/img/6f/97e53116ec4ebc6a6338d125ddad8b.png)
[NPP installation plug-in]

河北邯郸:拓展基层就业空间 助力高校毕业生就业

【微信小程序开发】页面导航与传参

Oracle insert数据时字符串中有‘单引号问题

Idea properties file display \u solution of not displaying Chinese
随机推荐
Oracle insert数据时字符串中有‘单引号问题
Getting started with enterprise distributed crawler framework
Cell review: single cell methods in human microbiome research
Saltstack advanced
Know small and medium LAN WLAN
How navicate modifies the database name
MySQL8 tmp_ table_ Size and Max_ heap_ table_ size
冲刺金九银十丨熬夜半个月汇集大厂Android岗1600道面试真题
C+ + core programming
Application skills of programming rising and falling edge instructions of botu 1200/1500plc (bool array)
Source code analysis of scripy spider
[C language] function
Advanced notes (Part 2)
mmo及时战斗游戏中的场景线程分配
[C language] Hanoi Tower problem [recursion]
河北:稳粮扩豆助力粮油生产提质增效
[C language] random number generation and `include < time. H > 'learning
Const pointer of C language and parameter passing of main function
Crawl IP
Cloud computing notes part.2 - Application Management