当前位置:网站首页>[high concurrency] 28000 words' summary of callable and future interview knowledge points. After reading it, I went directly to ByteDance. Forgive me for being a little drifting (Part 1)
[high concurrency] 28000 words' summary of callable and future interview knowledge points. After reading it, I went directly to ByteDance. Forgive me for being a little drifting (Part 1)
2022-06-29 13:57:00 【Hua Weiyun】
Hello everyone , I'm glacier ~~**
stay Java In multithreading programming , except Thread Classes and Runnable Outside the interface , It has to be said that Callable Interface Future The interface . Using inheritance Thread Class or implementation Runnable Thread of interface , Unable to return final execution result data , Can only wait for thread execution to complete . here , If you want to get the return result of thread execution , that ,Callable and Future That comes in handy .
notes : The whole process of the article is high energy , Recommended collection , If the article helps you a little , Guys, one button three times , Thank you very much! ~~
Callable Interface
1.Callable The interface is introduced
Callable Interface is JDK1.5 New generic interface , stay JDK1.8 in , Declared as a functional interface , As shown below .
@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface Callable<V> { V call() throws Exception;}stay JDK 1.8 Only one method's interface is declared as a functional interface in , Functional interfaces can be used @FunctionalInterface To modify , You can also not use @FunctionalInterface To modify . As long as an interface contains only one method , that , This interface is a functional interface .
stay JDK in , Realization Callable The subclass of the interface is shown in the figure below .

The default subclass hierarchy diagram is not clear , here , Can pass IDEA Right click Callable Interface , choice “Layout” To specify the Callable Interface implementation, different structure of class diagram , As shown below .
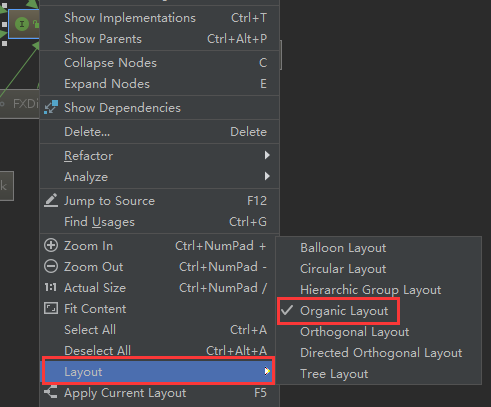
here , You can choose “Organic Layout” Options , After selection Callable The structure of subclasses of interfaces is shown in the figure below .
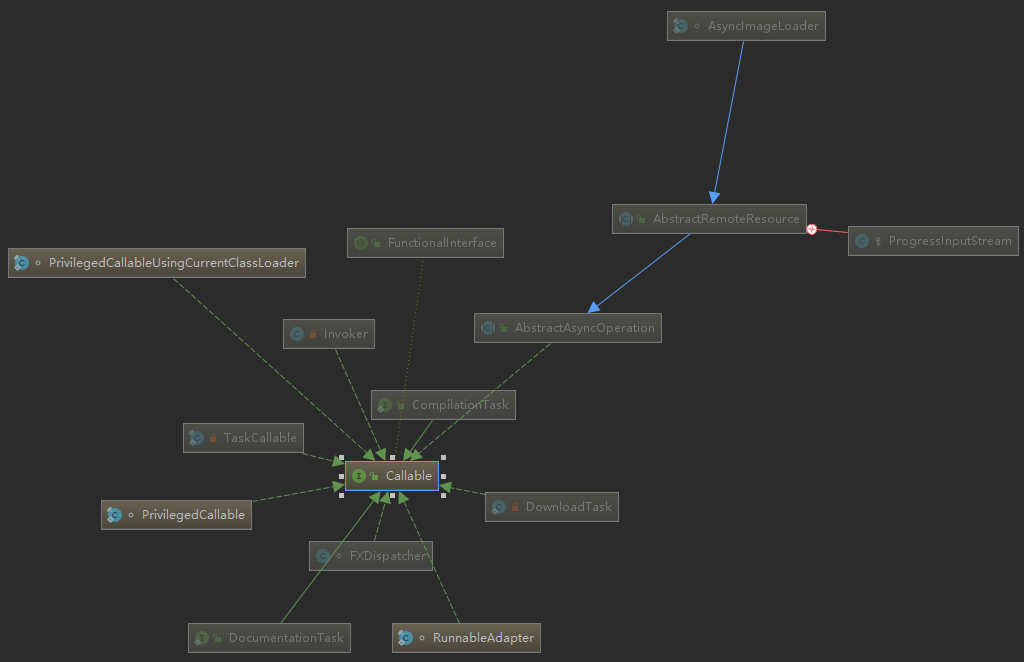
In the realization of Callable In subclasses of interfaces , There are several important classes , As shown in the figure below .
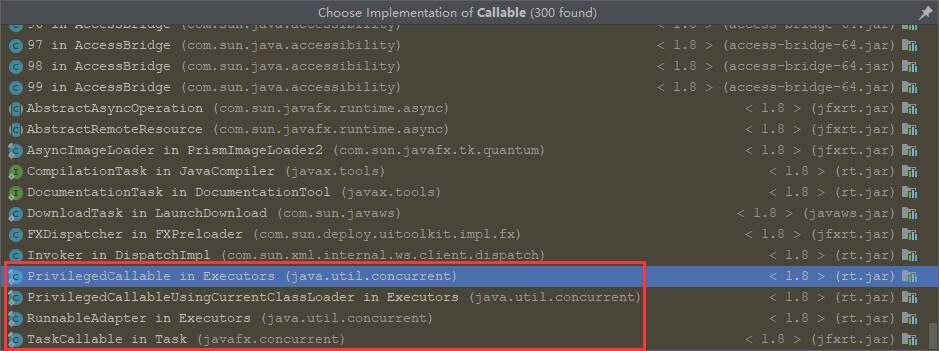
Namely :Executors Static inner class in class :PrivilegedCallable、PrivilegedCallableUsingCurrentClassLoader、RunnableAdapter and Task Under class TaskCallable.
2. Realization Callable Analysis of important classes of interfaces
Next , The main classes analyzed are :PrivilegedCallable、PrivilegedCallableUsingCurrentClassLoader、RunnableAdapter and Task Under class TaskCallable. Although these classes are rarely used directly in practical work , But as a qualified Development Engineer , The setting is for baldness senior experts , Understanding and mastering the implementation of these classes will help you further understand Callable Interface , And improve professional skills ( Another batch of hair loss , Whoahaha ...).
- PrivilegedCallable
PrivilegedCallable Class is Callable A special implementation class for interfaces , It shows that Callable Objects have certain privileges to access certain resources of the system ,PrivilegedCallable The source code for the class is as follows .
/** * A callable that runs under established access control settings */static final class PrivilegedCallable<T> implements Callable<T> { private final Callable<T> task; private final AccessControlContext acc; PrivilegedCallable(Callable<T> task) { this.task = task; this.acc = AccessController.getContext(); } public T call() throws Exception { try { return AccessController.doPrivileged( new PrivilegedExceptionAction<T>() { public T run() throws Exception { return task.call(); } }, acc); } catch (PrivilegedActionException e) { throw e.getException(); } }}from PrivilegedCallable Class source code , Can be PrivilegedCallable See it as right Callable Interface encapsulation , And this class also inherits Callable Interface .
stay PrivilegedCallable Class has two member variables , Namely Callable The instance object of the interface and AccessControlContext class , As shown below .
private final Callable<T> task;private final AccessControlContext acc;among ,AccessControlContext Class can be understood as a context class with system resource access decision , Through this class, you can access specific resources of the system . Through the class construction method, we can see that , In instantiation AccessControlContext Class , Just pass it on Callable Object of interface subclass , As shown below .
PrivilegedCallable(Callable<T> task) { this.task = task; this.acc = AccessController.getContext();}AccessControlContext Class objects are created through AccessController Class getContext() Method acquired , here , see AccessController Class getContext() Method , As shown below .
public static AccessControlContext getContext(){ AccessControlContext acc = getStackAccessControlContext(); if (acc == null) { return new AccessControlContext(null, true); } else { return acc.optimize(); }}adopt AccessController Of getContext() The method shows that , First, through getStackAccessControlContext() Method to get AccessControlContext Object instances . If you get AccessControlContext Object instance is empty , By calling AccessControlContext Class constructor instantiation , otherwise , call AccessControlContext Object instance optimize() Method returns AccessControlContext Object instances .
here , Let's take a look first getStackAccessControlContext() What the hell is the method .
private static native AccessControlContext getStackAccessControlContext();It turned out to be a local method , Method literally means to get the decision context object that can access the system stack .
Next , We go back to PrivilegedCallable Class call() Method , As shown below .
public T call() throws Exception { try { return AccessController.doPrivileged( new PrivilegedExceptionAction<T>() { public T run() throws Exception { return task.call(); } }, acc); } catch (PrivilegedActionException e) { throw e.getException(); }}By calling AccessController.doPrivileged() Method , Pass on PrivilegedExceptionAction. Interface objects and AccessControlContext object , And finally returns the generic instance object .
First , look down AccessController.doPrivileged() Method , As shown below .
@CallerSensitivepublic static native <T> T doPrivileged(PrivilegedExceptionAction<T> action, AccessControlContext context) throws PrivilegedActionException;You can see , Another local approach . in other words , The final implementation will be PrivilegedExceptionAction Interface objects and AccessControlContext Object instance is passed to the local method execution . And in PrivilegedExceptionAction Of the interface object run() Call in method Callable Interface call() Method to execute the final business logic , And return the generic object .
- PrivilegedCallableUsingCurrentClassLoader
This class is represented as running under the specific access control that has been established and the current class loader Callable class , The source code is as follows .
/** * A callable that runs under established access control settings and * current ClassLoader */static final class PrivilegedCallableUsingCurrentClassLoader<T> implements Callable<T> { private final Callable<T> task; private final AccessControlContext acc; private final ClassLoader ccl; PrivilegedCallableUsingCurrentClassLoader(Callable<T> task) { SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); if (sm != null) { sm.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.GET_CLASSLOADER_PERMISSION); sm.checkPermission(new RuntimePermission("setContextClassLoader")); } this.task = task; this.acc = AccessController.getContext(); this.ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); } public T call() throws Exception { try { return AccessController.doPrivileged( new PrivilegedExceptionAction<T>() { public T run() throws Exception { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ClassLoader cl = t.getContextClassLoader(); if (ccl == cl) { return task.call(); } else { t.setContextClassLoader(ccl); try { return task.call(); } finally { t.setContextClassLoader(cl); } } } }, acc); } catch (PrivilegedActionException e) { throw e.getException(); } }}This class is easy to understand , First , Three member variables are defined in the class , As shown below .
private final Callable<T> task;private final AccessControlContext acc;private final ClassLoader ccl;Next , Injected by constructor Callable object , In the constructor , First, get the instance of the system security manager object , Check whether there is access through the system security manager object instance ClassLoader And set up ContextClassLoader Authority . And assign values to three member variables in the construction method , As shown below .
PrivilegedCallableUsingCurrentClassLoader(Callable<T> task) { SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); if (sm != null) { sm.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.GET_CLASSLOADER_PERMISSION); sm.checkPermission(new RuntimePermission("setContextClassLoader")); } this.task = task; this.acc = AccessController.getContext(); this.ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();}Next , By calling call() Methods to perform specific business logic , As shown below .
public T call() throws Exception { try { return AccessController.doPrivileged( new PrivilegedExceptionAction<T>() { public T run() throws Exception { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ClassLoader cl = t.getContextClassLoader(); if (ccl == cl) { return task.call(); } else { t.setContextClassLoader(ccl); try { return task.call(); } finally { t.setContextClassLoader(cl); } } } }, acc); } catch (PrivilegedActionException e) { throw e.getException(); }}stay call() Method is also called AccessController Class doPrivileged, Pass on PrivilegedExceptionAction The instance object of the interface and AccessControlContext Object instance of class .
The specific execution logic is : stay PrivilegedExceptionAction Object's run() Method ContextClassLoader object , If you get in the constructor ClassLoader Object is the same as ContextClassLoader Objects are the same object ( Not just object instances , And the memory address is the same ), Call directly Callable Object's call() Method returns the result . otherwise , take PrivilegedExceptionAction Object's run() Method of the current thread ContextClassLoader Set to the class loader object obtained in the constructor , Next , Call again Callable Object's call() Method returns the result . Finally, the current thread's ContextClassLoader Reset to the previous ContextClassLoader.
- RunnableAdapter
RunnableAdapter Class is simpler , Given the tasks and results to run , Run the given task and return the given result , The source code is as follows .
/** * A callable that runs given task and returns given result */static final class RunnableAdapter<T> implements Callable<T> { final Runnable task; final T result; RunnableAdapter(Runnable task, T result) { this.task = task; this.result = result; } public T call() { task.run(); return result; }}- TaskCallable
TaskCallable Class is javafx.concurrent.Task Static inner class of class ,TaskCallable Class mainly implements Callable Interface and is defined as FutureTask Class , And in this class we are allowed to intercept call() Method to update task The status of the task . The source code is as follows .
private static final class TaskCallable<V> implements Callable<V> { private Task<V> task; private TaskCallable() { } @Override public V call() throws Exception { task.started = true; task.runLater(() -> { task.setState(State.SCHEDULED); task.setState(State.RUNNING); }); try { final V result = task.call(); if (!task.isCancelled()) { task.runLater(() -> { task.updateValue(result); task.setState(State.SUCCEEDED); }); return result; } else { return null; } } catch (final Throwable th) { task.runLater(() -> { task._setException(th); task.setState(State.FAILED); }); if (th instanceof Exception) { throw (Exception) th; } else { throw new Exception(th); } } }}from TaskCallable The source code of the class shows that , Only one... Is defined Task A member variable of type . The main analysis is as follows TaskCallable Class call() Method .
When the execution of the program enters call() When the method is used , First of all, will task Object's started Property is set to true, The task has begun , And set the state of the task to State.SCHEDULED and State.RUNNING, Trigger the scheduling event and the running event of the task in turn . As shown below .
task.started = true;task.runLater(() -> { task.setState(State.SCHEDULED); task.setState(State.RUNNING);});Next , stay try Code block Task Object's call() Method , Returns a generic object . If the mission is not cancelled , Then update the task's cache , Will call call() Method returns a generic object bound to Task Object ObjectProperty<V> In the object , among ,ObjectProperty<V> stay Task The definitions in the class are as follows .
private final ObjectProperty<V> value = new SimpleObjectProperty<>(this, "value");Next , Set the status of the task to success . As shown below .
try { final V result = task.call(); if (!task.isCancelled()) { task.runLater(() -> { task.updateValue(result); task.setState(State.SUCCEEDED); }); return result; } else { return null; }}If the program throws an exception or error , Will enter catch() Code block , Set up Task Object's Exception And set the status to State.FAILED, That is to mark the task as failed . Next , Determine the type of exception or error , If it is Exception Exception of type , Then it will be changed into Exception Type and throw . otherwise , Encapsulate an exception or error as Exception Object and throw , As shown below .
catch (final Throwable th) { task.runLater(() -> { task._setException(th); task.setState(State.FAILED); }); if (th instanceof Exception) { throw (Exception) th; } else { throw new Exception(th); }}边栏推荐
- Win32 Tetris (essential for learning MFC)
- 二叉树习题总结
- OpenSSL certificate tool user manual
- Horizon development board configuration network segment
- 在线文本过滤小于指定长度工具
- Technology sharing | broadcast function design in integrated dispatching
- Appkey when applying for offline packaging of uniapp
- Return value‘s Lifetime
- STM32 watchdog study
- 手把手教你在windows上安装mysql8.0最新版本数据库,保姆级教学
猜你喜欢

Cisco simulator simple campus network design, final assignment difficulty
【毕业季】这四年一路走来都很值得——老学长の忠告

思科模拟器简单校园网设计,期末作业难度

别再重复造轮子了,推荐使用 Google Guava 开源工具类库,真心强大!

Exploring the way of automated testing - Preparation

Weserver Publishing Map Service

Use Gerrit + Zadig to realize trunk development and trunk publishing (including byte flying Book Practice)

如何优雅的写 Controller 层代码?

自主可控再下一城!首套国产ARTIQ架构量子计算测控系统发布
![[system design] proximity service](/img/3b/b0dbd25945f9c914b097140890d8f9.png)
[system design] proximity service
随机推荐
iMile 利用 Zadig 多云环境周部署千次,跨云跨地域持续交付全球业务
ANSVC无功补偿装置在河北某购物广场中的应用
[cloud resident co creation] break through the performance bottleneck of image recognition through rust language computing acceleration technology
LeCun用62页论文公布未来十年研究计划:AI自主智能
Appkey when applying for offline packaging of uniapp
Uncover the practice of Baidu intelligent test in the field of automatic test execution
C language__ VA_ ARGS__ Usage of
丢弃 Tkinter!简单配置快速生成超酷炫 GUI!
Create an API rapid development platform, awesome!
Valueerror: only TF native optimizers are supported in Eagle mode
Koa2+better-sqlite3 to add, delete, change and query
【毕业季·进击的技术er】1076万毕业生,史上最难就业季?卷又卷不过,躺又躺不平,敢问路在何方?
Exploring the way of automated testing - Preparation
Solution to inconsistency between RTC time and world time on the server
Getting started with SQLite3
golang7_TCP编程
在线文本过滤小于指定长度工具
手把手教你在windows上安装mysql8.0最新版本数据库,保姆级教学
HTAP X 云原生: TiDB 加速释放数据价值,实现数据敏捷
Aurora · Huffman tree generation (segment tree structure non pointer) (imitating adjacency table)