当前位置:网站首页>Implementation of common function blocks for Beifu twincat3 servo control
Implementation of common function blocks for Beifu twincat3 servo control
2022-06-22 03:42:00 【Dusk and starry sky】
2、 servo PTP Function block definitions
2.1 Define axis variables
_axis1: AXIS_REF; // Axis variable
2.2 Add axis control command
Define function block variables :
MC_POWER_0: MC_POWER; // Shaft enable
MC_Reset_0: MC_Reset; // Axis reset
MC_Stop_0: MC_Stop; // The shaft stops
MC_Jog_0: MC_Jog;
MC_MoveAdditive_0: MC_MoveAdditive;
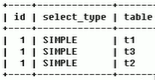
MC_MoveRelative_0: MC_MoveRelative;
MC_MoveAbsolute_0: MC_MoveAbsolute;
MC_MoveVelocity_0: MC_MoveVelocity;
MC_SetOverride_0: MC_SetOverride; // Set the axis speed scaling factor
MC_SetPosition_0: MC_SetPosition; // Set the current position
MC_ReadActualPosition_0: MC_ReadActualPosition;
MC_ReadActualVelocity_0: MC_ReadActualVelocity;
MC_ReadStatus_0: MC_ReadStatus;
2.3 Add global variable
Define global variables for control :
// Axis control command
bi_Power: BOOL; // Can make
bi_Reset: BOOL; // Reset
bi_Stop: BOOL; // stop it
bi_JogForward: BOOL; // Positive inching
bi_JogBackwards: BOOL; // Reverse inching
bi_MoveAdditive: BOOL; // Incremental position movement
bi_MoveRelative: BOOL; // Relative position motion
bi_MoveAbsolute: BOOL; // Absolute position motion
bi_MoveVelocity: BOOL; // Speed mode movement
bi_SetOverride: BOOL; // Axis speed scaling enabled
bi_SetPosition: BOOL; // Incremental servo , Set the current position value
bi_AxisRead: BOOL; // Read the state of the shaft
Define the input control parameter variables :
// Axis motion parameter setting
di_Stop_Deceleration: LREAL:=4000; // Stop speed (MC_Stop)
di_SetPosition: LREAL:=0; //
di_Jog_Velocity: LREAL;
di_Jog_Acceleration: LREAL:=3000;
di_Jog_Deceleration: LREAL:=3000;
di_Jog_Jerk: LREAL:=0; // Speed up .
di_MoveAdditive_Distance: LREAL:=0;
di_MoveAdditive_Velocity: LREAL:=100;
di_MoveAdditive_Acceleration: LREAL:=500;
di_MoveAdditive_Deceleration: LREAL:=500;
di_MoveAdditive_Jerk: LREAL:=0;
di_MoveRelative_Distance: LREAL:=0;
di_MoveRelative_Velocity: LREAL:=100;
di_MoveRelative_Acceleration: LREAL:=500;
di_MoveRelative_Deceleration: LREAL:=500;
di_MoveRelative_Jerk: LREAL:=0;
di_MoveAbsolute_Position: LREAL:=0;
di_MoveAbsolute_Velocity: LREAL:=100;
di_MoveAbsolute_Acceleration: LREAL:=500;
di_MoveAbsolute_Deceleration: LREAL:=500;
di_MoveAbsolute_Jerk: LREAL:=0;
di_MoveVelocity_Velocity: LREAL:=100;
di_MoveVelocity_Acceleration: LREAL:=500;
di_MoveVelocity_Deceleration: LREAL:=500;
di_MoveVelocity_Jerk: LREAL:=0;
di_MoveVelocity_Direction: MC_Direction:=1; //1:Positive 3:Negative
di_VelFactor: LREAL:=1.0; //1.0=100% Range :0.01-1.0
Define the axis state variables that store feedback
// Shaft status feedback
bo_AxisError: BOOL;
bo_ErrorStop: BOOL; // When the fault is not reset, rotate the motor again to output the fault stop signal
bo_Homing: BOOL; // Axis return to origin in progress
bo_Homed: BOOL; // The axis has returned to the original point
bo_Moving: BOOL; // Axis in motion
bo_Disabled: BOOL;
bo_Stopping: BOOL; // Stop signal output once
bo_StandStill: BOOL; // Standby
bo_DiscreteMotion: BOOL; // Discontinuous motion
bo_ContinuousMotion: BOOL; // Continuous motion
bo_SynchronizedMotion: BOOL; // Synchronous motion
bo_ConstantVelocity: BOOL; // In constant speed operation
bo_Accelerating: BOOL; // Accelerating
bo_Decelerating: BOOL; // Slowing down
//
do_ActualPosition: LREAL; // Axis current position
do_ActualVelocity: LREAL; // Current speed of axis
do_AxisErroID: DWORD; // Fault code
dg_ActualTorque AT%I*: INT; // Axises's Actual Torque
2.4 Axis control function block ST Language implementation
//* Shaft enable
MC_POWER_0(
Axis:= _axis1,
Enable:= bi_Power, //TRUE Can make ,FALSE To enable
Enable_Positive:= TRUE,
Enable_Negative:= TRUE,
Override:= ,
BufferMode:= ,
Options:= ,
Status=> ,
Busy=> ,
Active=> ,
Error=> ,
ErrorID=> );
//* Axis reset
MC_Reset_0(
Axis:= _axis1,
Execute:= bi_Reset, // The rising edge signal triggers
Done=> ,
Busy=> ,
Error=> ,
ErrorID=> );
//* Shaft shutdown
MC_Stop_0(
Axis:= _axis1,
Execute:= bi_Stop, // The rising edge signal triggers
Deceleration:= di_Stop_Deceleration,
Jerk:= ,
Options:= ,
Done=> ,
Busy=> ,
Active=> ,
CommandAborted=> ,
Error=> ,
ErrorID=> );
//Jog Inching
MC_Jog_0(
Axis:= _axis1,
JogForward:= bi_JogForward,
JogBackwards:= bi_JogBackwards,
Mode:= MC_JOGMODE_CONTINOUS, // Jog mode
Position:= ,
Velocity:= di_Jog_Velocity,
Acceleration:=di_Jog_Acceleration ,
Deceleration:= di_Jog_Deceleration,
Jerk:= di_Jog_Jerk,
Done=> ,
Busy=> ,
Active=> ,
CommandAborted=> ,
Error=> ,
ErrorID=> );
//* Relative positioning of the shaft -MoveAdd //
MC_MoveAdditive_0(
Axis:= _axis1,
Execute:= bi_MoveAdditive, // The rising edge signal triggers
Distance:= di_MoveAdditive_Distance,
Velocity:= di_MoveAdditive_Velocity,
Acceleration:= di_MoveAdditive_Acceleration,
Deceleration:= di_MoveAdditive_Deceleration,
Jerk:= di_MoveAdditive_Jerk,
BufferMode:= ,
Options:= ,
Done=> ,
Busy=> ,
Active=> ,
CommandAborted=> ,
Error=> ,
ErrorID=> );
//* Relative positioning of the shaft -MoveRela //
MC_MoveRelative_0(
Axis:= _axis1,
Execute:= bi_MoveRelative, // The rising edge signal triggers
Distance:= di_MoveRelative_Distance,
Velocity:= di_MoveRelative_Velocity,
Acceleration:= di_MoveRelative_Acceleration,
Deceleration:= di_MoveRelative_Deceleration,
Jerk:= di_MoveRelative_Jerk,
BufferMode:= ,
Options:= ,
Done=> ,
Busy=> ,
Active=> ,
CommandAborted=> ,
Error=> ,
ErrorID=> );
//** The shaft absolute positioning starts
MC_MoveAbsolute_0(
Axis:= _axis1,
Execute:= bi_MoveAbsolute, // The rising edge signal triggers
Position:= di_MoveAbsolute_Position,
Velocity:= di_MoveAbsolute_Velocity,
Acceleration:= di_MoveAbsolute_Acceleration,
Deceleration:= di_MoveAbsolute_Deceleration,
Jerk:= di_MoveAbsolute_Jerk,
BufferMode:= ,
Options:= ,
Done=> ,
Busy=> ,
Active=> ,
CommandAborted=> ,
Error=> ,
ErrorID=> );
//** Run at speed
MC_MoveVelocity_0(
Axis:= _axis1,
Execute:= bi_MoveVelocity, // The rising edge signal triggers
Velocity:=di_MoveVelocity_Velocity ,
Acceleration:= di_MoveVelocity_Acceleration,
Deceleration:= di_MoveVelocity_Deceleration,
Jerk:= di_MoveVelocity_Jerk,
Direction:= di_MoveVelocity_Direction, //MC_Negative_Direction -> reverse MC_Positive_Direction -> positive
BufferMode:= ,
Options:= ,
InVelocity=> ,
Busy=> ,
Active=> ,
CommandAborted=> ,
Error=> ,
ErrorID=> );
//** Axis speed scaling factor setting
MC_SetOverride_0(
Axis:= _axis1,
Enable:= bi_SetOverride, //TRUE take effect ,FALSE Invalid
VelFactor:= di_VelFactor, //1.0=100% 0.01-1.0
AccFactor:= ,
JerkFactor:= ,
Enabled=> ,
Busy=> ,
Error=> ,
ErrorID=> );
//* Current axis position setting ( Incremental encoder motor )
MC_SetPosition_0(
Axis:= _axis1,
Execute:= bi_SetPosition, //TRUE take effect ,FALSE Invalid
Position:= 0,
Mode:= ,
Options:= ,
Done=> ,
Busy=> ,
Error=> ,
ErrorID=> );
IF MC_SetPosition_0.Done THEN
bi_SetPosition:=FALSE;
END_IF
//* Read axis position
MC_ReadActualPosition_0(
Axis:= _axis1,
Enable:= bi_AxisRead, //TRUE take effect ,FALSE Invalid
Valid=> ,
Busy=> ,
Error=> ,
ErrorID=> ,
Position=> do_ActualPosition);
//* Shaft reading speed
MC_ReadActualVelocity_0(
Axis:= _axis1,
Enable:= bi_AxisRead, //TRUE take effect ,FALSE Invalid
Valid=> ,
Busy=> ,
Error=> ,
ErrorID=> ,
ActualVelocity=>do_ActualVelocity );
//* Axis reading status
MC_ReadStatus_0(
Axis:= _axis1,
Enable:= bi_AxisRead, //TRUE take effect ,FALSE Invalid
Valid=> ,
Busy=> ,
Error=> bo_AxisError,
ErrorID=>do_AxisErroID ,
ErrorStop=> bo_ErrorStop,
Disabled=> bo_Disabled,
Stopping=> bo_Stopping,
StandStill=> bo_StandStill,
DiscreteMotion=> bo_DiscreteMotion,
ContinuousMotion=> bo_ContinuousMotion,
SynchronizedMotion=> bo_SynchronizedMotion,
Homing=> bo_Homing,
ConstantVelocity=> bo_ConstantVelocity,
Accelerating=> bo_Accelerating,
Decelerating=> bo_Decelerating,
Status=> );
2.5 Ladder diagram of axis control function block (LD) Realization
1



2.6 Program online monitoring
ST Program online
advantage : The notes and procedures are clear at a glance 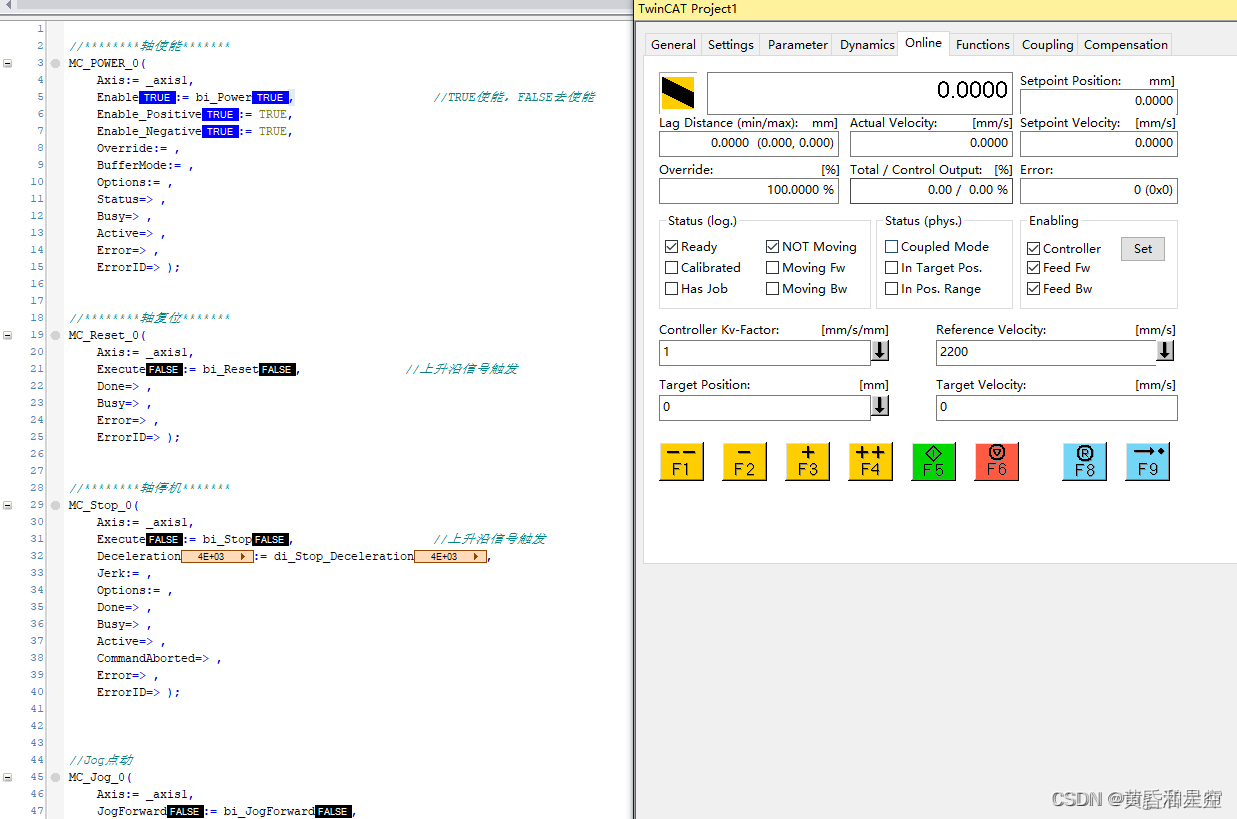
Ladder program online
advantage : The logic function is clear , The inputs and outputs of the function block are clear

3、 Other functions of third-party servo
3.1 Torque reading
Read the torque of the third-party servo , You need to associate PDO Maping The output of is read , Some manufacturers servo in IO Scan it out PDO Mapping in Torque, Some servo manufacturers did not scan it ,PDO Maping There is no Torque You need to add it manually . Delta A2 Hehuichuan IS620N Give examples :
First, in the PLC Add variables to the program :
hmi_ActualTorque AT%I*: INT; // Axises’s Actual Torque
After adding variables ,PLC Program engineering recompile .
Huichuan IS620N

3.2 Incremental servo return to zero
There are mainly two ways for the third-party incremental servo return to zero
The way 1:DS402 Inside the agreement PDO Mode returns to zero .
advantage : The servo operates by itself 、 High positioning accuracy
shortcoming : The program logic is complex 、 Different manufacturers have different data protocols
Please refer to :
TwinCAT3 Zhongtaida A2 Incremental encoder servo uses PDO Mode returns to zero _panjinliang066333 The blog of -CSDN Blog
The way 2: Use the servo function block MC_Jog and MC_SetPosition
advantage : It can be used by different manufacturers 、 The program logic is simple
shortcoming : Low positioning accuracy
usage : The zero return command starts , Servo to Jog The movement mode moves slowly to zero , When the zero point sensor detects the servo arrival signal Jog The movement stopped , And then use MC_SetPosition Set the current position to 0, That is, the servo return to zero is completed . If the servo is on the zero point sensor at the beginning , be Jog No movement , The servo position is directly set to zero .
Please refer to :
( Be careful : Because servo zeroing is moving in one direction , So no matter which way to return to zero , Make sure that the zero point sensor is at... When returning to zero for the first time Jog Within the direction of motion )
————————————————
Copyright notice : This paper is about CSDN Blogger 「Big_ Master pan 」 The original article of , follow CC 4.0 BY-SA Copyright agreement , For reprint, please attach the original source link and this statement .
Link to the original text :https://blog.csdn.net/panjinliang066333/article/details/123423911
边栏推荐
- 平衡二叉树——调整变换规则
- WPF 实现星空效果
- Cloud native architecture (02) - what is cloud native
- 系统漏洞利用与提权
- 基于51的超声波测距仪代码(截图版)
- [qnx hypervisor 2.2 user manual]5.5 starting and using guest
- R data analysis: significance and practice of calibration curve and DCA curve in clinical prediction model
- Flutter-状态管理
- Sword finger offer 68 - ii Nearest common ancestor of binary tree
- DM达梦数据的关键字与表的字段冲突的解决办法
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
MySQL 45 lecture learning notes (IV) index
Zombie process and orphan process
ES next 新特性
剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
DM达梦数据的关键字与表的字段冲突的解决办法
L'avenir est venu: l'âge du nuage
未来已来:云原生时代
MySQL 45 lecture learning notes (III) execution of SQL update statements
rabbmitMQ 简单模式<一>
WPF 实现星空效果
mysql 查询表的字段的属性、注释、字段信息
云原生架构(03)-架构
Float floating point number understanding
Mysql 45讲学习笔记(四)索引
1690. 石子游戏 VII-动态规划法
基于.NetCore开发博客项目 StarBlog - (12) Razor页面动态编译
How to break through the sales dilemma of clothing stores
1299. replace each element with the largest element on the right
Threejs realizes the fluctuation hot spot effect, fluctuation mark and fluctuation label display
C51的一些日记