当前位置:网站首页>Understanding and use of third-party library
Understanding and use of third-party library
2022-07-27 22:48:00 【Key knocker of shubihu】
Here's the catalog title
json The understanding of
1. When you want to realize network data transmission or persistent storage : It needs to be organized according to the specified data format , In this way, we can better analyze the data when using .
2.json The format of :json Is a data exchange format , Use text format completely independent of programming language to store and represent data .
The specific format and content are explained by the following example :
for example : This is the information of my classmate Xiao Ming as follows :
char* name = " Xiao Ming ";
int age = 18;
char* sex = " male ";
float score[] = {
60.5,99,68};
Then use json This data exchange format organizes these various data objects into a text string format , as follows :
[
{
" full name ":" Xiao Ming ",
" Age ":18,
" Gender ":" male ",
" achievement ":[60.5,99,68]
}
]
Organized in this format , For example, the above example , If there are many classmates , Then every student will put their information in {} In the form of key value pairs ( name : The number ) Display , And different students are [] Separated by commas .
among :
- json data type : object , Array , character string , Numbers .
- object : Use {} Enclosed represents an object .
- Array : Use [] Enclosed represents an array .
- character string : Use routine "" Enclosed is a string .
- Numbers : Including integer and floating point , It's all direct use .
jsoncpp The understanding of
1.jsoncpp Libraries are used to implement json Format serialization and deserialization , Complete the organization of multiple data objects into json Format string , And will be json The function of parsing format string to obtain multiple data objects .
2. This is josn Class , These class member functions can be found in jsoncpp Found in Library , as follows :
//json Data object class
class Json::Value
{
Value &operator=(const Value &other); //Value Reload the [] and =, Therefore, all assignment and data acquisition can be through
Value& operator[](const std::string& key);// Do it in a simple way val[" full name "] = " Xiao Ming ";
Value& operator[](const char* key);
Value removeMember(const char* key);// Remove elements
const Value& operator[](ArrayIndex index) const; //val[" achievement "][0]
Value& append(const Value& value);// Add array elements val[" achievement "].append(88), Because the array members are one by one , So want to use append To join in ;
ArrayIndex size() const;// Get the number of array elements val[" achievement "].size();
std::string asString() const;// turn string string name = val["name"].asString();
const char* asCString() const;// turn char* char *name = val["name"].asCString();
Int asInt() const;// turn int int age = val["age"].asInt();
float asFloat() const;// turn float
bool asBool() const;// turn bool
};
It's just a json Class , The main function of this class is to save data , But to serialize and deserialize data, you must use its corresponding class , as follows :
jsoncpp Implement serialization
1. about jsoncpp Implement serialization , The following classes should be used ( Different versions use different classes , Some lower versions do not support some content ):
//json Serialization class , It is easier to use this in the lower version
class JSON_API Writer
{
virtual std::string write(const Value& root) = 0;
}
class JSON_API FastWriter : public Writer
{
virtual std::string write(const Value& root);
}
class JSON_API StyledWriter : public Writer
{
virtual std::string write(const Value& root);
}
//json Serialization class , The higher version is recommended , If you use a lower version of the interface, there may be a warning
class JSON_API StreamWriter
{
virtual int write(Value const& root, std::ostream* sout) = 0;
}
class JSON_API StreamWriterBuilder : public StreamWriter::Factory {
virtual StreamWriter* newStreamWriter() const;
}
( Here we implement it with a higher version )
We can see that , The above library function code parameters are Value Object type , So when serializing , We will have saved the data Value Object is passed into this kind of function , Then this function serializes it .
Be careful :
①: We can see from the above code ,StreamWriter Class is a parent class , and StreamWriterBuilder Class is its subclass .
②: When you use it , We don't directly use the parent object and then call it write function ( because write Function is a virtual function , And this class is an abstract class , Objects cannot be instantiated directly ), When operating , Is to instantiate its subclasses first StreamWriterBuilder Class object , Then use the pointer of the parent object to point to the object of the subclass , Call the subclass's... Through the parent class pointer newStreamWriter function , Go is the object that implements the parent class .
③:write The parameters of the function :
- root: To serialize json object .
- sout: Where the serialized content is saved .( So let's check the content of this parameter directly , You can see what it looks like after serialization )
2. Simple implementation of the above example :
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<jsoncpp/json/json.h>
3 #include<string>
4 #include<sstream>
5 using namespace std;
6 int main()
7 {
8 // This is the data we want to serialize
9 const char* name = " Xiao Ming ";
10 int age = 18;
11 const char* sex = " male "; 12 float score[] = {
60.5,99,68};
13 //1. First save the data in json In the object
14 Json::Value val;
15 val[" full name "] = name;
16 val[" Age "] = age;
17 val[" Gender "] = sex;
18 val[" fraction "].append(score[0]);
19 val[" fraction "].append(score[1]);
20 val[" fraction "].append(score[2]);
21 //2. Use StreamWriter Object serialization ( Be careful : It must be used. StreamWriter Pointer to call StreamWriterBuilder Object's newStreamWriter After the function instantiates the object , To use write)
22 Json::StreamWriterBuilder swb;
23 Json::StreamWriter* sw = swb.newStreamWriter();
24 stringstream ss;
25 sw->write(val,&ss);
26 //3. Print out the serialized data
27 cout<<ss.str()<<endl;
28 delete sw;
29 return 0;
30 }
Then the running results are as follows :
Be careful : Because it is a third-party library , So you must link to the library later .
jsoncpp Implement deserialization
1. about jsoncpp Implement deserialization , Use the following classes :
//json Deserialize class , The lower version is simpler to use
class JSON_API Reader
{
bool parse(const std::string& document, Value& root, bool collectComments = true);
}
//json Deserialize class , Higher versions are more recommended
class JSON_API CharReader
{
virtual bool parse(char const* beginDoc, char const* endDoc,Value* root, std::string* errs) = 0;
}
class JSON_API CharReaderBuilder : public CharReader::Factory
{
virtual CharReader* newCharReader() const;
}
( It is implemented with a higher version )
Be careful : The implementation steps of deserialization and serialization are almost to instantiate subclass objects first , Then use the pointer of the parent object to point to the subclass object to call newCharReader The object returned by the , Then use the parent object to call parse function , To complete the operation .
among ,parse The parameters of the function are as follows :
- beginDoc: The starting position of the string to deserialize .
- endDoc: The end position of the string to deserialize .
- root: To deserialize josn object .
- errs: When there is an error in deserialization , Error retention information .
2. The simple implementation of the above example is as follows :
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<jsoncpp/json/json.h>
3 #include<string>
4 #include<sstream>
5 using namespace std;
6 int main()
7 {
8 // This is the data we want to serialize
9 const char* name = " Xiao Ming ";
10 int age = 18;
11 const char* sex = " male ";
12 float score[] = {
60.5,99,68};
13 //1. First save the data in json In the object
14 Json::Value val;
15 val[" full name "] = name;
16 val[" Age "] = age;
17 val[" Gender "] = sex;
18 val[" fraction "].append(score[0]);
19 val[" fraction "].append(score[1]);
20 val[" fraction "].append(score[2]);
21 //2. Use StreamWriter Object serialization ( Be careful : It must be used. StreamWriter Pointer to call StreamWriterBuilder Object's newStreamWriter After the function instantiates the object , To use write)
22 Json::StreamWriterBuilder swb;
23 Json::StreamWriter* sw = swb.newStreamWriter();
24 stringstream ss;
25 sw->write(val,&ss);
26 //3. Print out the serialized data
27 cout<<ss.str()<<endl;
28 //4. deserialize
29 Json::CharReaderBuilder crb;
30 Json::CharReader* cr = crb.newCharReader();
31 Json::Value Val;
32 string err;
33 string str = ss.str();
34 bool res = cr->parse(str.c_str(),str.c_str()+str.size(),&Val,&err);
35 if(res == false)
36 {
37 cout<<"error:"<<err<<endl;
38 delete cr;
39 return 0;
40 }
41 //5. View the contents after deserialization
42 cout<<Val[" full name "].asString()<<endl;
43 cout<<Val[" Age "].asInt()<<endl;
44 cout<<Val[" Gender "].asString()<<endl;
45 int sz = Val[" fraction "].size();
46 for(int i = 0;i < sz;++i)
47 {
48 cout<<Val[" fraction "][i].asFloat()<<endl;
49 }
50 delete sw;
51 delete cr;
52 return 0;
53 }
Then the execution results are as follows :
After deserialization , The data can still be printed .
bundle Understanding of file compression library
1.bundle library :bundle It's a Embedded compression library , Support 23 Compression algorithm and 2 Archive formats . When using, you only need to add two files bundle.h and bundle.cpp that will do .
among :
①:2 The three archive formats are as follows :
- Add all files to the compression class , Then compress together .( After compression, the file name suffix becomes .zip)
- Compress each file and then add the compression class , And then pack them together .( After compression, the suffix of the file name is .bun)
characteristic :
- Archive support :.zip and .bun Two compression storage methods .
- Stream support :DEFLATE, LZMA, LZIP, ZPAQ, LZ4, ZSTD, BROTLI, BSC, CSC, BCM, MCM, ZMOLLY, ZLING, TANGELO, SHRINKER, CRUSH, LZJB, BZIP2 and SHOCO( Streams are sequences of elements generated from sources that support data processing operations )
- Optimize compression
- Optimize compression speed
- The supporting configuration 、 encapsulation 、 The word contains 、 blend 、 Cross platform
- Optional infrastructure
- ZLIB/LibPNG Copyright agreement
②:23 The compression algorithm and efficiency are as follows :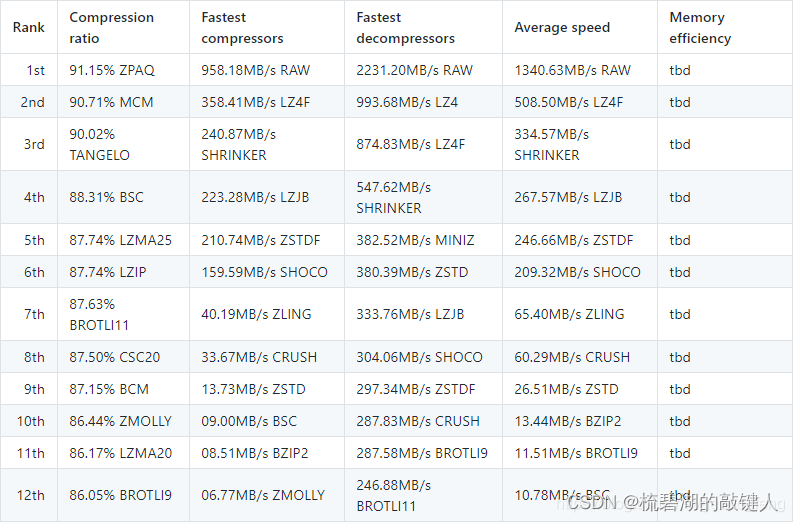

Compression rate and compression efficiency cannot be achieved at the same time , So when you use it, you can use it according to your needs .
2. Commonly used data compression program , as follows :
namespace bundle
{
// low level API (raw pointers)
bool is_packed( *ptr, len );
bool is_unpacked( *ptr, len );
unsigned type_of( *ptr, len );
size_t len( *ptr, len );
size_t zlen( *ptr, len );
const void *zptr( *ptr, len );
bool pack( unsigned Q, *in, len, *out, &zlen );
bool unpack( unsigned Q, *in, len, *out, &zlen );
// medium level API, templates (in-place)
bool is_packed( T );
bool is_unpacked( T );
unsigned type_of( T );
size_t len( T );
size_t zlen( T );
const void *zptr( T );
bool unpack( T &, T );
bool pack( unsigned Q, T &, T );
// high level API, templates (copy)
T pack( unsigned Q, T );
T unpack( T );
}
This is part of the library file , These are generally interfaces that use this library , If you want to see all the code , You can check in the Library .
Be careful : There are high-level, intermediate and low-level templates in the above code , We use a higher-level interface when implementing , These are the two functions in the last two lines above .
bundle Library to achieve file compression and decompression
1. First , We use bundle When I was in the library , Only bundle.h The function in this , however bundle.h The code used is bundle.cpp in , As a result, when linking it bundle.cpp Link together , But there is a lot of code in this , There are about 12 More than ten thousand lines , So it will be difficult to link , So let's generate a static library file first , Then the efficiency of linking is faster , as follows :
2. Achieve file compression , Please see the following procedure :
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<string>
3 #include<fstream>
4 #include"bundle.h"
5 using namespace std;
6 bool Read(const string &name,string *body)
7 {
8 ifstream ifs;// The file pointer
9 ifs.open(name,std::ios::binary);// The first parameter is the file name to open , The second parameter is how to open , The method used this time is to open in binary .
10 if(ifs.is_open() == false)// It is an interface used to check whether the file is successfully opened . 11 {
12 cout<<"read open false"<<endl;
13 return false;
14 }
15 ifs.seekg(0,std::ios::end);// Indicates the offset from the end position , The offset 0 A size
16 size_t fsize = ifs.tellg();// Get the offset of the current position from the starting position of the file .( This is why there is the last step > Why , Find the size of the file )
17 ifs.seekg(0,std::ios::beg);// Indicates the offset from the starting position , The offset 0 A size 18 body->resize(fsize);
19 ifs.read(&(*body)[0],fsize);// because string.c_str() The return value of const char* The type of , But first > The first parameter we need is the starting position of the file to be read , So we can get the address in one step .
20 if(ifs.good() == false)// Used to check whether the file reads data successfully .
21 {
22 cout<<"read read fasle"<<endl;
23 return false;
24 }
25 ifs.close();
26 return true;
27 }
28 bool Write(const string &name,const string &body)
29 {
30 ofstream ofs;// The file pointer .
31 ofs.open(name,std::ios::binary);
32 if(ofs.is_open() == false)
33 {
34 cout<<"write open false"<<endl;
35 return false;
36 }
37 ofs.write(body.c_str(),body.size());
38 if(ofs.good() == false)
39 {
40 cout<<"write write false"<<endl;
41 return false;
42 }
43 ofs.close();
44 return true;
45 }
46 void compress(const string &filename,const string &packname)
47 {
48 string body;
49 Read(filename,&body);// Put the contents of the file into body in .
50 string packed = bundle::pack(bundle::LZIP,body);// The first parameter of this function is the type to be compressed , The second one is Number is the file to be compressed .
51 Write(packname,packed);// Put the compressed content in packname in
52 }
53 void uncompress(const string &filename,const string &packname)
54 {
55 string packed;
56 Read(packname,&packed);// Read the data from the compressed package to packed in
57 string body = bundle::unpack(packed);// Decompress the data to be compressed , And put the decompressed data in body> in .
58 Write(filename,body);// from body Put the data in a new file .
59 }
60
61 int main()
62 {
63 compress("./hello.cpp","./hello.zip");
64 uncompress("./hi.txt","./hello.zip");
65 return 0;
66 }
Then run the program as follows :
The realization of will 100M The file of is compressed to 15k.
Be careful :dd if=/dev/zero of=./hello.txt bs=100M count=1: Is to create a file with a size of 100M The file of , And the file name is hello.txt.
3. Check whether there is an error in the compressed and decompressed file .
①: To verify whether the two files are the same , Then calculate the of two files MD5 value , If MD5 Same value , Then these two files are the same , If it's different , Something went wrong .
②:MD5: It's a hash algorithm , A lot of calculations will be carried out according to the data , Terminate to get a result , And the result is a string , But as long as the two files are a little different , Produced MD5 The value is completely different .
③: operation :md5sum file name
We will operate on the compressed and decompressed files above :
The two files correspond to md5 The value is as like as two peas , Prove that compression and decompression are perfect .
httplib Library's understanding
1.httplib library : One c++11 Single file cross platform HTTP/HTTPS library . It is very easy to install . Just include httplib.h Just introduce it into the code .
2. advantage : It is used to build a simple http Server or client library , And this third-party library , It can save us the time of setting up the server or client , Put more energy into specific business processing , Improve development efficiency .
3.httplib Knowledge of the code in the Library :
httplib There are two structures in the Library: request and response , as follows :
①: Request structure :
struct Request
{
std::string method;// Request method
std::string path;// The requested resource path
Headers headers;// Where the header fields are stored , Because header fields are generally stored in key value pairs , So this storage method is content map To carry out
std::string body;// Store text
// for server
std::string version;// Protocol version
Params params;// Deposit URL The query string in , It is also stored in the form of key value pairs
MultipartFormDataMap files;// It is used to store the data information of the body when uploading
Ranges ranges; // The data request range used to realize breakpoint continuation , It's also a key value pair .
bool has_header(const char *key) const;
std::string get_header_value(const char *key, size_t id = 0)const;
void set_header(const char *key, const char *val);
bool has_file(const char *key) const;
MultipartFormData get_file_value(const char *key) const;
};
②: Response structure :
struct Response
{
std::string version;// Protocol version
int status = -1; // Response status code
std::string reason;// State information
Headers headers;// Store header fields in a hash table
std::string body;// Response body information
std::string location; // source address
void set_header(const char *key, const char *val);// Set the header field
void set_content(const std::string &s, const char *content_type);// Set the text
};
Most of the data stored in the response structure and the request structure are http Form of agreement .( In use , We just need to upload the object of its structure , Specifically, the following client programs and server programs are used )
③: Server program
class Server
{
using Handler = std::function<void(const Request &, Response &)>;// Function pointer type , For different requests , We will use different functions to process the request
using Handlers = std::vector<std::pair<std::regex, Handler>>;// request - Processing function mapping table , One request corresponds to one mapping , Store in key value pairs
std::function<TaskQueue *(void)> new_task_queue;// Thread pool
Server &Get(const std::string &pattern, Handler handler);// This kind of function is to establish the relationship between request and mapping .
Server &Post(const std::string &pattern, Handler handler);
Server &Put(const std::string &pattern, Handler handler);
Server &Patch(const std::string &pattern, Handler handler);
Server &Delete(const std::string &pattern, Handler handler);
Server &Options(const std::string &pattern, Handler handler);
bool listen(const char *host, int port, int socket_flags = 0);// Start the server , Start listening .
};
④: Client program
class Client
{
Client(const std::string &host, int port); // Incoming server information ( Constructors )
Result Get(const char *path, const Headers &headers);// Send to server get request
Result Post(const char *path, const char *body, size_t content_length,const char *content_type);// Send to server post request ( Data submission )
Result Post(const char *path, const MultipartFormDataItems &items);// Send to server post request ( Upload files )
}
⑤:MultipartFormDataItems Structure , It mainly stores information with some data
struct MultipartFormData
{
std::string name; // name
std::string content; // Area body
std::string filename; // File name
std::string content_type; // annotation type
};
httplib Library setup simple server
1. Build a simple server , as follows :
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include"httplib.h"
3 using namespace std;
4 void Upload(const httplib::Request &req,const httplib::Response &rsp)
5 {
6 if(req.has_file("file"))// Judge whether there is name The fields are file Identification area of , The requested file name does not exist
7 {
8 httplib::MultipartFormData data = req.get_file_value("file");// Return some contents of this file , Yes d ata preservation
9 std::cout << data.name << std::endl; // Identification name of the area field
10 std::cout << data.filename << std::endl; // If it's file upload , Is the file name
11 std::cout << data.content << std::endl; // Area body data , If it's file upload , Is the content of the document
12 } 13 }
14 void Numbers(const httplib::Request &req,httplib::Response &rsp)
15 {
16 // This is the business processing function
17 rsp.body = req.path;
18 rsp.body += "-----------------";
19 rsp.body += req.matches[1];
20 rsp.status = 200;
21 rsp.set_header("Content-Type","text/plain");
22 }
23 int main()
24 {
25 //1. Instantiation Serve object
26 httplib::Server serve;
27 //2. Add yingguan , Tell the server , What request to the client , What function is used to handle , Two processing methods are added as follows , by Get and Post
28 serve.Get("/numbers/(\\d+)",Numbers);// The first parameter is the regular expression, that is, the requested resource path , The second parameter is Numbers, It's corresponding to Processing function of
29 serve.Post("/upload",Upload);
30 serve.listen("0.0.0.0",9090);
31 return 0;
32 }
After running the result , And then use netstat The command looks like this :
It shows that the server is already listening .
Then we will be the server ip Address and port number and request resource path ( Is the first parameter of the request ), Then the function will use the callback function to process , Then it will be displayed on the web page as follows :
httplib Simple client for library construction
1. Build a simple client as follows :
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include"httplib.h"
3 int main()
4 {
5 httplib::Client client("192.168.136.130",9090);// among , Here is the server ip Address and port number
6 // Namely Result Get(const char* path,const Headers& headers);
7 httplib::Headers headers = {
{
"connection","Close"}};
8 auto res = client.Get("/number/1234",headers);
9 if(res && res->status == 200)
10 {
11 std::cout<< res->body << std::endl;
12 }
13 ///
14 //Result post(const char* path,const MultipartFormDataItems &items);
15 httplib::MultipartFormDataItems items;
16 httplib::MultipartFormData item;
17 item.name = "file"; // File domain
18 item.filename = "zhang.txt";// file name
19 item.content = "hello"; // Body data
20 item.content_type = "application/octet-stream";// In binary stream
21 items.push_back(item);
22
23 res = client.Post("/upload",items);
24 return 0;
25 }
Cooperate with the server , Use as follows :
边栏推荐
- Are Transformers Effective for Time Series Forecasting?| Pit filling
- PX4模块设计之十三:WorkQueue设计
- 联合省选2022复习计划
- Uniswap集成sudoswap,能否拉开NFT流动性新序幕?
- PyQt5快速开发与实战 4.9 对话框类控件
- How to quickly pass the probation period for newly trained intermediate test engineers
- Time relay
- 格力口罩来了!KN95口罩只要5.5元一个!
- 2022/5/18 考试总结
- 10 years of technical career, those technical books that make me excited
猜你喜欢

【图解】三次握手,四次挥手 —— 用心看这一篇就够了

七大排序之希尔排序

Analysis on data collection and analysis of network security competition in national vocational college skill competition

Optocoupler relay

细胞CLE19多肽荧光成像牛血清白蛋白荧光猝灭量子点的制备

Buuctf brushes eleven questions (05)

Solid state relay

PyQt5快速开发与实战 4.9 对话框类控件

Time relay

Take you to master makefile analysis
随机推荐
SQL injection less26a (Boolean blind injection)
Nodejs NPM common instructions summary
Principle and application of CMOS transmission gate
Reed relay
Hc32f4a0 clock control
Leetcode15 -- sum of three numbers
MediaTek and Samsung launched the world's first 8K TV that supports Wi Fi 6
How to quickly pass the probation period for newly trained intermediate test engineers
CMOS开关(二)_参数提取
QT common operation collection
Starfish OS X metabell strategic cooperation, metauniverse business ecosystem further
It is said that Intel will adopt TSMC 6nm EUV process next year
Eight years of love between me and the message queue
初中三年回忆录
redis学习
If there is no reference ground at all, guess if you can control the impedance?
What is private traffic?
SQL注入 Less29(参数污染绕过WAF)
视频人体行为检测
Here comes Gree mask! Kn95 mask only costs 5.5 yuan!