当前位置:网站首页>PyTorch 单机多卡分布式训练
PyTorch 单机多卡分布式训练
2022-07-24 05:20:00 【滴滴滴'cv】
main.py train训练代码阅读心得
阅读代码官方的ImageNet例子
设备处理
args = parser.parse_args()
if args.seed is not None:
random.seed(args.seed)
torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
# 由于计算中有随机性,每次网络前馈结果有差异
# 为了避免这种结果波动,设置 cudnn.deterministic = True
cudnn.deterministic = True
warnings.warn('You have chosen to seed training. '
'This will turn on the CUDNN deterministic setting, '
'which can slow down your training considerably! '
'You may see unexpected behavior when restarting '
'from checkpoints.')
if args.gpu is not None:
warnings.warn('You have chosen a specific GPU. This will completely '
'disable data parallelism.')
# world_size 代表多少个计算节点
if args.dist_url == "env://" and args.world_size == -1:
args.world_size = int(os.environ["WORLD_SIZE"])
# 判断是否需要并行训练
args.distributed = args.world_size > 1 or args.multiprocessing_distributed
# 获取节点gpu设备数量
ngpus_per_node = torch.cuda.device_count()
if args.multiprocessing_distributed:
# Since we have ngpus_per_node processes per node, the total world_size
# needs to be adjusted accordingly
args.world_size = ngpus_per_node * args.world_size
# Use torch.multiprocessing.spawn to launch distributed processes: the
# main_worker process function
# 通过torch.multiprocessing.spawn来开启多进程
mp.spawn(main_worker, nprocs=ngpus_per_node, args=(ngpus_per_node, args))
else:
# Simply call main_worker function
main_worker(args.gpu, ngpus_per_node, args)
def main_worker(gpu, ngpus_per_node, args):
global best_acc1
args.gpu = gpu
if args.gpu is not None:
print("Use GPU: {} for training".format(args.gpu))
if args.distributed:
if args.dist_url == "env://" and args.rank == -1:
# rank 表示节点编号(n台节点即:0,1,2,..,n-1)
args.rank = int(os.environ["RANK"])
if args.multiprocessing_distributed:
# For multiprocessing distributed training, rank needs to be the
# global rank among all the processes
args.rank = args.rank * ngpus_per_node + gpu
# dist-backend gpu上一般设置为nccl,cpu上设置为gloo
# 根据官网的介绍, 如果是使用cpu的分布式计算, 建议使用gloo, 因为表中可以看到 gloo对cpu的支持是最好的,
# 然后如果使用gpu进行分布式计算, 建议使用nccl, 实际测试中我也感觉到, 当使用gpu的时候, nccl的效率是高于gloo的.
# 根据博客和官网的态度, 好像都不怎么推荐在多gpu的时候使用mpi
dist.init_process_group(backend=args.dist_backend, init_method=args.dist_url,
world_size=args.world_size, rank=args.rank)
# create model
if args.pretrained:
print("=> using pre-trained model '{}'".format(args.arch))
model = models.__dict__[args.arch](pretrained=True)
else:
print("=> creating model '{}'".format(args.arch))
model = models.__dict__[args.arch]()
if not torch.cuda.is_available():
print('using CPU, this will be slow')
elif args.distributed:
# For multiprocessing distributed, DistributedDataParallel constructor
# should always set the single device scope, otherwise,
# DistributedDataParallel will use all available devices.
if args.gpu is not None:
## 在生成网络对象之前:!!!
# CUDA使用指定显卡,类似export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
torch.cuda.set_device(args.gpu)
model.cuda(args.gpu)
# When using a single GPU per process and per
# DistributedDataParallel, we need to divide the batch size
# ourselves based on the total number of GPUs we have
args.batch_size = int(args.batch_size / ngpus_per_node)
args.workers = int((args.workers + ngpus_per_node - 1) / ngpus_per_node)
# pytorch的官网建议使用DistributedDataParallel来代替DataParallel,
# 据说是因为DistributedDataParallel比DataParallel运行的更快, 然后显存分屏的更加均衡.
# 而且DistributedDataParallel功能更加强悍, 例如分布式的模型(一个模型太大, 以至于无法放到一个GPU上运行,
# 需要分开到多个GPU上面执行). 只有DistributedDataParallel支持分布式的模型像单机模型那样可以进行多机多卡的运算.
# 注意要提前把模型加载到gpu, 然后才可以加载到DistributedDataParallel
model = torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model, device_ids=[args.gpu])
else:
model.cuda()
# DistributedDataParallel will divide and allocate batch_size to all
# available GPUs if device_ids are not set
model = torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model)
elif args.gpu is not None:
torch.cuda.set_device(args.gpu)
model = model.cuda(args.gpu)
else:
# DataParallel will divide and allocate batch_size to all available GPUs
if args.arch.startswith('alexnet') or args.arch.startswith('vgg'):
model.features = torch.nn.DataParallel(model.features)
model.cuda()
else:
model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model).cuda()
# ................
数据读取
# Data loading code
traindir = os.path.join(args.data, 'train')
valdir = os.path.join(args.data, 'val')
normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(
traindir,
transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
normalize,
]))
# 这步很重要,分布式训练的话需要将train_dataset进行分布式操作
# 将train_dataset送到了DistributedSampler中创造了一个train_sampler, 然后在构造train_loader的时候,
# 参数中传入了一个sampler=train_sampler. 使用这些的意图是, 让不同节点的机器加载自己本地的数据进行训练,
# 也就是说进行多机多卡训练的时候, 不再是从主节点分发数据到各个从节点, 而是各个从节点自己从自己的硬盘上读取数据.
# 使用DistributedSampler来创造一个sampler提供给DataLoader, sampler的作用自定义一个数据的编号,
# 然后让DataLoader按照这个编号来提取数据放入到模型中训练, 其中sampler参数和shuffle参数不能同时指定,
# 如果这个时候还想要可以随机的输入数据, 我们可以在DistributedSampler中指定shuffle参数,
if args.distributed:
train_sampler = torch.utils.data.distributed.DistributedSampler(train_dataset)
else:
train_sampler = None
# 加载训练数据集 pin_memory用于锁页内存,提升训练速度,若gpu显存不够,修改为False
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
train_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=(train_sampler is None),
num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True, sampler=train_sampler)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.ImageFolder(valdir, transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
normalize,
])),
batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=False,
num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True)
if args.evaluate:
validate(val_loader, model, criterion, args)
return
torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder函数解释
class ImageFolder(DatasetFolder):
"""A generic data loader where the images are arranged in this way: :: root/dog/xxx.png root/dog/xxy.png root/dog/xxz.png root/cat/123.png root/cat/nsdf3.png root/cat/asd932_.png Args: # 图片存储的根目录,即各类别文件夹所在目录的上一级目录。 root (string): Root directory path. # 对图片进行预处理的操作(函数),原始图片作为输入,返回一个转换后的图片。 transform (callable, optional): A function/transform that takes in an PIL image and returns a transformed version. E.g, ``transforms.RandomCrop`` # 对图片类别进行预处理的操作,输入为 target,输出对其的转换。如果不传该参数,即对 target # 不做任何转换,返回的顺序索引0,1, 2… target_transform (callable, optional): A function/transform that takes in the target and transforms it. # 表示数据集加载方式,通常默认加载方式即可。 loader (callable, optional): A function to load an image given its path. # 获取图像文件的路径并检查该文件是否为有效文件的函数(用于检查损坏文件) is_valid_file (callable, optional): A function that takes path of an Image file and check if the file is a valid_file (used to check of corrupt files) Attributes: # 用一个 list 保存类别名称 classes (list): List of the class names. # 类别对应的索引,与不做任何转换返回的 target 对应 class_to_idx (dict): Dict with items (class_name, class_index). # 保存(img-path, class) tuple的 list imgs (list): List of (image path, class_index) tuples """
def __init__(self, root, transform=None, target_transform=None,
loader=default_loader, is_valid_file=None):
super(ImageFolder, self).__init__(root, loader, IMG_EXTENSIONS if is_valid_file is None else None,
transform=transform,
target_transform=target_transform,
is_valid_file=is_valid_file)
self.imgs = self.samples
torch.utils.data.DataLoader()函数解释
class torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=False, sampler=None, num_workers=0, collate_fn=<function default_collate>, pin_memory=False, drop_last=False)
数据加载器。组合数据集和采样器,并在数据集上提供单进程或多进程迭代器。
参数:
- dataset (Dataset) – 加载数据的数据集。
- batch_size (int, optional) – 每个batch加载多少个样本(默认: 1)。
- shuffle (bool, optional) – 设置为
True时会在每个epoch重新打乱数据(默认: False). - sampler (Sampler, optional) – 定义从数据集中提取样本的策略。如果指定,则忽略
shuffle参数。 - num_workers (int, optional) – 用多少个子进程加载数据。0表示数据将在主进程中加载(默认: 0)
- collate_fn (callable, optional) –
- pin_memory (bool, optional) – 锁页内存,创建DataLoader时,设置pin_memory=True,则意味着生成的Tensor数据最开始是属于内存中的锁页内存,这样将内存的Tensor转义到GPU的显存就会更快一些。
- drop_last (bool, optional) – 如果数据集大小不能被batch size整除,则设置为True后可删除最后一个不完整的batch。如果设为False并且数据集的大小不能被batch size整除,则最后一个batch将更小。(默认: False)
模型选择
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.parallel
import torch.distributed as dist
import torch.optim
import torch.utils.data
import torch.utils.data.distributed
import torchvision.models as models
# 获取torch.models中已有的models并通过首字母排序
model_names = sorted(name for name in models.__dict__
if name.islower() and not name.startswith("__")
and callable(models.__dict__[name]))
#输出结果
# ['alexnet', 'densenet121', 'densenet161', 'densenet169', 'densenet201', 'googlenet', 'inception_v3', 'mnasnet0_5', 'mnasnet0_75', 'mnasnet1_0', 'mnasnet1_3', 'mobilenet_v2', 'resnet101', 'resnet152', 'resnet18', 'resnet34', 'resnet50', 'resnext101_32x8d', 'resnext50_32x4d', 'shufflenet_v2_x0_5', 'shufflenet_v2_x1_0', 'shufflenet_v2_x1_5', 'shufflenet_v2_x2_0', 'squeezenet1_0', 'squeezenet1_1', 'vgg11', 'vgg11_bn', 'vgg13', 'vgg13_bn', 'vgg16', 'vgg16_bn', 'vgg19', 'vgg19_bn', 'wide_resnet101_2', 'wide_resnet50_2']
# 选取模型
if args.pretrained:
print("=> using pre-trained model '{}'".format(args.arch))
model = models.__dict__[args.arch](pretrained=True)
else:
print("=> creating model '{}'".format(args.arch))
model = models.__dict__[args.arch]()
# define loss function (criterion) and optimizer
# 损失函数使用交叉熵,记得cuda
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda(args.gpu)
# 优化器使用SGD
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), args.lr,
momentum=args.momentum,
weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
分布式训练
# 通过mp.spawn来进行分布式训练。
# multiprocessing包用于在相同数据的不同进程中共享视图。
import torch.multiprocessing as mp
ngpus_per_node = torch.cuda.device_count()
if args.multiprocessing_distributed:
# Since we have ngpus_per_node processes per node, the total world_size
# needs to be adjusted accordingly
args.world_size = ngpus_per_node * args.world_size
# Use torch.multiprocessing.spawn to launch distributed processes: the
# main_worker process function
# 通过torch.multiprocessing.spawn来开启多进程
mp.spawn(main_worker, nprocs=ngpus_per_node, args=(ngpus_per_node, args))
else:
# Simply call main_worker function
main_worker(args.gpu, ngpus_per_node, args)
for epoch in range(args.start_epoch, args.epochs):
if args.distributed:
train_sampler.set_epoch(epoch)
adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, args)
# train for one epoch
train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch, args)
# evaluate on validation set
acc1 = validate(val_loader, model, criterion, args)
# remember best [email protected] and save checkpoint
# 记录最好的结果
is_best = acc1 > best_acc1
best_acc1 = max(acc1, best_acc1)
# rank:表示当前进程id,用于进程间通讯。0代表主机
# ngpus_per_node:表示每个节点的gpu数量。
# (args.multiprocessing_distributed and args.rank % ngpus_per_node == 0)代表只需要保存一次
# 不写的话会保存多次模型
if not args.multiprocessing_distributed or (args.multiprocessing_distributed
and args.rank % ngpus_per_node == 0):
save_checkpoint({
'epoch': epoch + 1,
'arch': args.arch,
'state_dict': model.state_dict(),
'best_acc1': best_acc1,
'optimizer' : optimizer.state_dict(),
}, is_best)
def save_checkpoint(state, is_best, filename='checkpoint.pth.tar'):
torch.save(state, filename)
if is_best:
shutil.copyfile(filename, 'model_best.pth.tar')
def train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch, args):
batch_time = AverageMeter('Time', ':6.3f')
data_time = AverageMeter('Data', ':6.3f')
losses = AverageMeter('Loss', ':.4e')
top1 = AverageMeter('[email protected]', ':6.2f')
top5 = AverageMeter('[email protected]', ':6.2f')
progress = ProgressMeter(
len(train_loader),
[batch_time, data_time, losses, top1, top5],
prefix="Epoch: [{}]".format(epoch))
# switch to train mode
# 启用 Batch Normalization 和 Dropout
model.train()
end = time.time()
for i, (images, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
# measure data loading time
data_time.update(time.time() - end)
if args.gpu is not None:
images = images.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
target = target.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
# compute output
output = model(images)
# loss += (label[k] - h) * (label[k] - h) / 2
loss = criterion(output, target)
# measure accuracy and record loss
acc1, acc5 = accuracy(output, target, topk=(1, 5))
losses.update(loss.item(), images.size(0))
top1.update(acc1[0], images.size(0))
top5.update(acc5[0], images.size(0))
# compute gradient and do SGD step
# 梯度置零,也就是把loss关于weight的导数变成0
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 反向传播求梯度
# d_weights = [d_weights[j] + (label[k] - h) * input[k][j] for j in range(n)]
loss.backward()
# 更新所有参数
# weights = [weights[k] + alpha * d_weights[k] for k in range(n)]
optimizer.step()
# measure elapsed time
batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
end = time.time()
if i % args.print_freq == 0:
progress.display(i)
模型加载
# optionally resume from a checkpoint
if args.resume:
if os.path.isfile(args.resume):
print("=> loading checkpoint '{}'".format(args.resume))
if args.gpu is None:
checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume)
else:
# Map model to be loaded to specified single gpu.
loc = 'cuda:{}'.format(args.gpu)
checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume, map_location=loc)
args.start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
best_acc1 = checkpoint['best_acc1']
if args.gpu is not None:
# best_acc1 may be from a checkpoint from a different GPU
best_acc1 = best_acc1.to(args.gpu)
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer'])
print("=> loaded checkpoint '{}' (epoch {})"
.format(args.resume, checkpoint['epoch']))
else:
print("=> no checkpoint found at '{}'".format(args.resume))
模型保存
is_best = acc1 > best_acc1
best_acc1 = max(acc1, best_acc1)
# rank:表示当前进程id,用于进程间通讯。0代表主机
# ngpus_per_node:表示每个节点的gpu数量。
# (args.multiprocessing_distributed and args.rank % ngpus_per_node == 0)代表只需要保存一次
# 不写的话会保存多次模型
if not args.multiprocessing_distributed or (args.multiprocessing_distributed
and args.rank % ngpus_per_node == 0):
save_checkpoint({
'epoch': epoch + 1,
'arch': args.arch,
'state_dict': model.state_dict(),
'best_acc1': best_acc1,
'optimizer' : optimizer.state_dict(),
}, is_best)
def save_checkpoint(state, is_best, filename='checkpoint.pth.tar'):
torch.save(state, filename)
if is_best:
shutil.copyfile(filename, 'model_best.pth.tar')
CUDNN加速
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
# 设置这个 flag 可以让内置的 cuDNN 的 auto-tuner 自动寻找最适合当前配置的高效算法,来达到优化运行效率的问题。
# 如果网络的输入数据维度或类型上变化不大,可以增加运行效率;
# 如果网络的输入数据在每次 iteration 都变化的话,会导致 cnDNN 每次都会去寻找一遍最优配置,这样反而会降低运行效率。
cudnn.benchmark = True
# 由于计算中有随机性,每次网络前馈结果有差异
# 为了避免这种结果波动,设置
cudnn.deterministic = True
验证函数
def validate(val_loader, model, criterion, args):
batch_time = AverageMeter('Time', ':6.3f')
losses = AverageMeter('Loss', ':.4e')
top1 = AverageMeter('[email protected]', ':6.2f')
top5 = AverageMeter('[email protected]', ':6.2f')
progress = ProgressMeter(
len(val_loader),
[batch_time, losses, top1, top5],
prefix='Test: ')
# switch to evaluate mode
# 不启用 Batch Normalization 和 Dropout。
model.eval()
# 不会track梯度
with torch.no_grad():
end = time.time()
for i, (images, target) in enumerate(val_loader):
if args.gpu is not None:
images = images.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
target = target.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
# compute output
output = model(images)
loss = criterion(output, target)
# measure accuracy and record loss
acc1, acc5 = accuracy(output, target, topk=(1, 5))
losses.update(loss.item(), images.size(0))
top1.update(acc1[0], images.size(0))
top5.update(acc5[0], images.size(0))
# measure elapsed time
batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
end = time.time()
if i % args.print_freq == 0:
progress.display(i)
# TODO: this should also be done with the ProgressMeter
print(' * [email protected] {top1.avg:.3f} [email protected] {top5.avg:.3f}'
.format(top1=top1, top5=top5))
return top1.avg
class AverageMeter(object):
"""Computes and stores the average and current value"""
def __init__(self, name, fmt=':f'):
self.name = name
self.fmt = fmt
self.reset()
def reset(self):
self.val = 0
self.avg = 0
self.sum = 0
self.count = 0
def update(self, val, n=1):
self.val = val
self.sum += val * n
self.count += n
self.avg = self.sum / self.count
def __str__(self):
fmtstr = '{name} {val' + self.fmt + '} ({avg' + self.fmt + '})'
return fmtstr.format(**self.__dict__)
class ProgressMeter(object):
def __init__(self, num_batches, meters, prefix=""):
self.batch_fmtstr = self._get_batch_fmtstr(num_batches)
self.meters = meters
self.prefix = prefix
def display(self, batch):
entries = [self.prefix + self.batch_fmtstr.format(batch)]
entries += [str(meter) for meter in self.meters]
print('\t'.join(entries))
def _get_batch_fmtstr(self, num_batches):
num_digits = len(str(num_batches // 1))
fmt = '{:' + str(num_digits) + 'd}'
return '[' + fmt + '/' + fmt.format(num_batches) + ']'
def accuracy(output, target, topk=(1,)):
"""Computes the accuracy over the k top predictions for the specified values of k"""
with torch.no_grad():
maxk = max(topk)
batch_size = target.size(0)
_, pred = output.topk(maxk, 1, True, True)
pred = pred.t()
correct = pred.eq(target.view(1, -1).expand_as(pred))
res = []
for k in topk:
correct_k = correct[:k].reshape(-1).float().sum(0, keepdim=True)
res.append(correct_k.mul_(100.0 / batch_size))
return res
lr动态更新
每30轮,学习率缩小10倍
def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, args):
"""Sets the learning rate to the initial LR decayed by 10 every 30 epochs"""
lr = args.lr * (0.1 ** (epoch // 30))
for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
param_group['lr'] = lr
边栏推荐
- 【activiti】组任务
- 数据库连接数过大
- Read "Enlightenment: a 20-year career experience of an IT executive"
- 达梦数据库_常用命令
- 多商户商城系统功能拆解06讲-平台端商家入驻协议
- 第三章 线性模型总结
- Introduction to PC mall module of e-commerce system
- Logical structure of Oracle Database
- Flink函数(2):CheckpointedFunction
- Detailed discussion on data synchronization tools ETL, ELT, reverse ETL
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Likeshop single merchant mall system is built, and the code is open source without encryption
达梦数据库_逻辑架构基础
Likeshop100%开源无加密-B2B2C多商户商城系统
Read "Enlightenment: a 20-year career experience of an IT executive"
Small operation of statistical signal processing -- detection of deterministic DC signal in Rayleigh distributed noise
‘Results do not correspond to current coco set‘
Multi merchant mall system function disassembly lecture 07 - platform side commodity management
Flink watermark mechanism
likeshop单商户SAAS商城系统无限多开
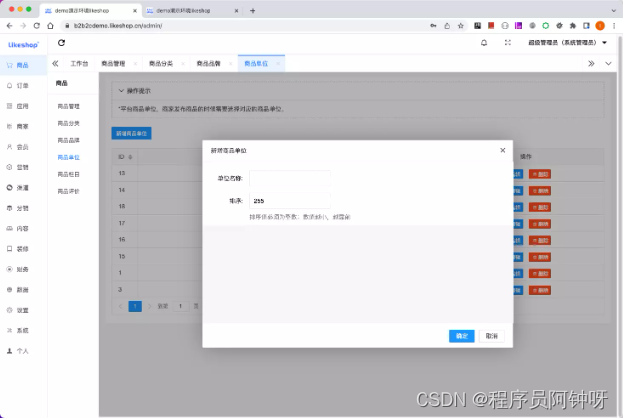
多商户商城系统功能拆解10讲-平台端商品单位
Could not load library cudnn_cnn_infer64_8.dll. Error code 126Please make sure cudnn_cnn_infer64_8.
Multi merchant mall system function disassembly lecture 05 - main business categories of platform merchants
What do programmers often mean by API? What are the API types?
How to quickly connect CRM system and ERP system to realize the automatic flow of business processes
数据集成的两种架构:ELT和ETL
传统的k-means实现
[data mining] zero foundation entry decision tree
likeshop单商户SAAS商城系统搭建,代码开源无加密。
ThreadLocal stores the current login user information
MySQL batch insert demo




![Use streaming media to transfer RSTP to the Web terminal for playback (II) [review]](/img/b9/2c0e6eb19acaa2356ff49f6e272826.png)