当前位置:网站首页>Detailed explanation of this and static
Detailed explanation of this and static
2022-06-11 09:20:00 【lwj_ 07】
static:
1、static Translated into " static state "
2、 be-all static Keywords are class related , Class level
3、 all static Embellished , All use " Class name ." Mode of access
4、static Decorated variable : Static variables
5、static The method of decoration : Static methodsClassification of variables :
Variables are divided according to the declared location :
The variables declared in the method body are called : local variable
Variables declared outside the method are called : Member variablesMember variables can be divided into :
Instance variables
Static variables
class VarTest{
// For the following example , Are object related , Use when visiting " quote ." Mode of access , It needs to be done first new object
// Strength related , Must have object first , Ability to visit , A null pointer exception may occur
// Instance variables in member variables
int i;
// Example method
public void m1(){
}
// Static variables in member variables
static int k;
// Static methods
public static void m2(){
}
}When a variable is declared as an instance , When declared static ?
If a property value of all objects of this type is the same ,
It is not recommended to define as instance variable , Wasted memory space , The proposal is defined as
Class level features , It's defined as a static variable , Only one... Is left in the method area
Share , Save memory .An object is an instance variable
One copy of multiple objects is a static variable
public class staticTest02
{
public static void main(String[] args){
Chinese c1 =new Chinese("123456","junker"," China ");
Chinese c2 =new Chinese("00000","jun"," China ");
System.out.println(c1.id);
System.out.println(c1.name);
System.out.println(c1.country);
System.out.println(c2.id);
System.out.println(c2.name);
System.out.println(c2.country);
}
}
// Define a class : Chinese
class Chinese{
// ID number
// Everyone has a different ID number , So the ID number should be an instance variable , One object, one share
String id;
// full name
// Name is also a person a name , The name should also be an instance variable
String name;
// nationality
// about " Chinese " For this class , All nationalities " China ", It doesn't change with the change of the object
// Obviously nationality is not a characteristic of the object level
// Nationality is a characteristic of the whole class
String country;
// No parameter
public Chinese(){
}
// With parameters
public Chinese(String s1,String s2,String s3){
id =s1;
name =s2;
country =s3;
}
}When variables country Not for static The static memory diagram is as follows :

When variables country by static The code walkthrough and memory diagram for static variables are as follows :
Code walkthrough 2:( by static Static variables , You should use " Class name ." Mode of access )
public class staticTest02
{
public static void main(String[] args){
// Visiting Chinese nationality
// Nationality is static Static variables , You should use " Class name ." Mode of access
Chinese c1 =new Chinese("123456","junker");
System.out.println(Chinese.country);
// Report errors [id,name Is instance variable , Should first new An object adopt " quote ." Mode of access ]
//System,out.println(Chinese.id);
System.out.println(c1.id);
System.out.println(c1.name);
Chinese c2 =new Chinese("00000","jun");
System.out.println(c2.id);
System.out.println(c2.name);
System.out.println(Chinese.country);
}
}
// Define a class : Chinese
class Chinese{
// ID number
// Everyone has a different ID number , So the ID number should be an instance variable , One object, one share
String id;
// full name
// Name is also a person a name , The name should also be an instance variable
String name;
// nationality
// Focus on five stars : Plus static Variables are called static variables
// Static variables are initialized when the class is loaded , Unwanted new object , The space for static variables is opened up
// Static variables are stored in the method area
// Static variables usually give a value
static String country =" China ";
// No parameter
public Chinese(){
}
// With parameters
public Chinese(String s1,String s2){
id =s1;
name =s2;
}
}
Code walkthrough 3:
Example of : You have to use " quote ." To visit
Static : It is recommended to use " Class name ." To visit , But use " quote ." It's fine too , If you use " quote ." Visiting will make others confused : Programmers think it is an instance
public class staticTest02
{
public static void main(String[] args){
Chinese c1 =new Chinese("123456","junker");
// Report errors [id,name Is instance variable , Should first new An object adopt " quote ." Mode of access ]
//System,out.println(Chinese.id);
System.out.println(c1.id);
System.out.println(c1.name);
// Visiting Chinese nationality
// Nationality is static Static variables , You should use " Class name ." Mode of access
System.out.println(Chinese.country);
Chinese c2 =new Chinese("00000","jun");
System.out.println(c2.id);
System.out.println(c2.name);
// Use " quote ." Is still accessed through
System.out.println(c2.country); // China
}
}
// Define a class : Chinese
class Chinese{
String id;
String name;
static String country =" China ";
// No parameter
public Chinese(){
}
// With parameters
public Chinese(String s1,String s2){
id =s1;
name =s2;
}
}Null reference access static will not null pointer exception
public class staticTest02
{
public static void main(String[] args){
Chinese c1 =new Chinese("123456","junker");
System.out.println(c1.id);
System.out.println(c1.name);
System.out.println(Chinese.country);
Chinese c2 =new Chinese("00000","jun");
System.out.println(c2.id);
System.out.println(c2.name);
// c2 It's a null reference
c2 =null;
// There will be no null pointer exceptions
// Because static variables do not require the existence of objects
// In fact, the following code runs , still :System.out.println(Chinese.country);
System.out.println(c2.country);// Still pass
// A null pointer exception occurred because name Is instance variable
// System.out.println(c2.name);
}
}
// Define a class : Chinese
class Chinese{
String id;
String name;
static String country =" China ";
// No parameter
public Chinese(){
}
// With parameters
public Chinese(String s1,String s2){
id =s1;
name =s2;
}
}Add 【 master 】
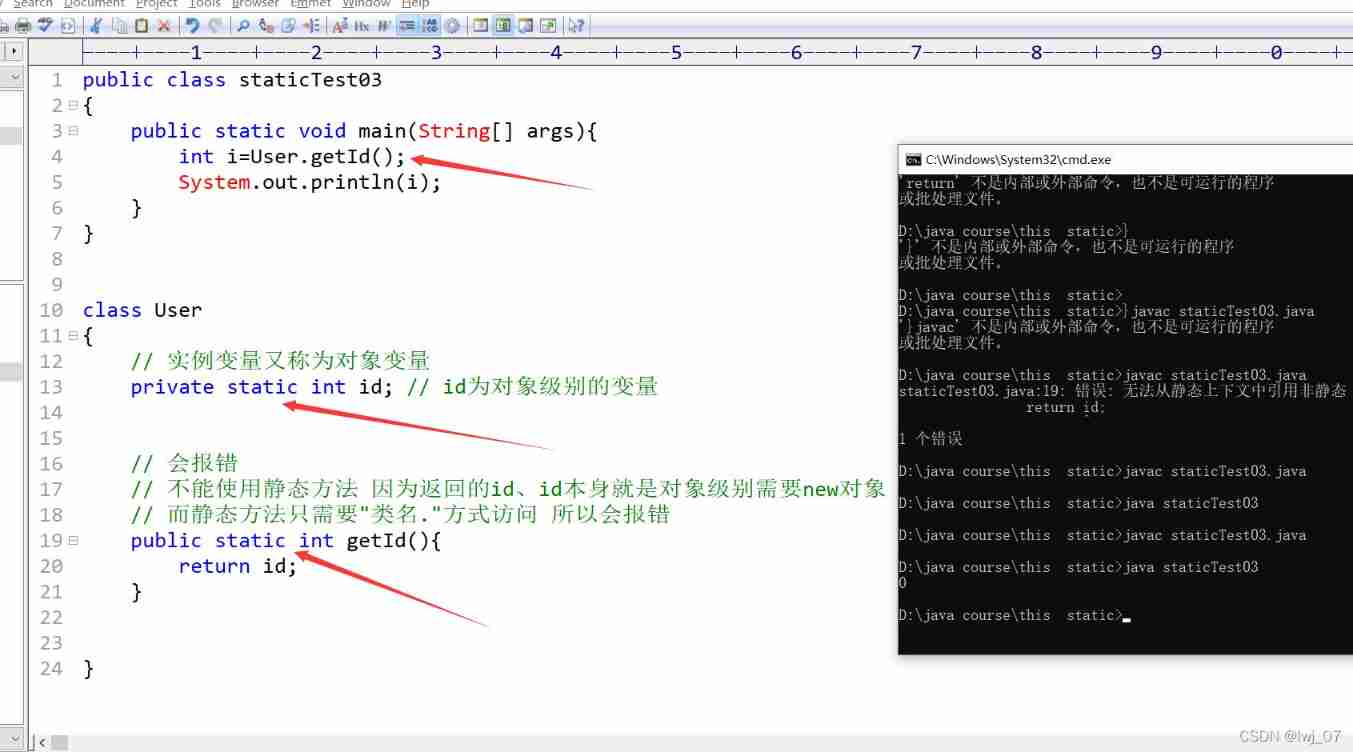
public class staticTest03
{
public static void main(String[] args){
User u =new User();
int i =u.getId();
System.out.println(i);
}
}
class User
{
// Instance variables are also called object variables
private int id; // id Object level variables
/*
// Will report a mistake
// Static methods cannot be used Because the returned id、id It is an object level requirement new object
// The static method only needs " Class name ." Access to So there's an error
public static int getId(){
return id;
}
*/
public int getId(){
return id;
}
}When a static method is used, the variables should also be static :
One 、 Static code block
1、 Use static Keywords can be defined : Static code block
2、 What is a static block of code , What is grammar ?
static{
java sentence ;
...
}3、static When do static code blocks execute ?
characteristic : When the class is loaded, execute , And only once
4、 Be careful : Static code blocks are executed when the class loads , And in main Method before execution5、 Static code blocks are generally executed in top-down order
6、 What do static code blocks do , What's the usage? ?
Specific business :
The project manager said : All the programs we write , As long as the class is loaded , Please record the log information of class loading
( In which year, month, day, hour and minute , Which class is loaded into JVM In the middle ) You need to use static code blocks
Code walkthrough :
public class staticTest04
{
// Static code block
static{
System.out.println("A");
}
// Multiple static code blocks can be written in a class
static{
System.out.println("B");
}
static{
System.out.println("C");
}
// Program entrance
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("come on~");
}
// Write a static code block
static{
System.out.println("D");
}
}Running results :( Conclusion : Static code blocks are executed when the class is loaded )

Two 、 Code execution order
( Conclusion : Static code block 1 and Static code block 2 In order 、 Static code blocks and static variables also have order )
Code demonstration :
public class staticTest05
{
// When static variables are initialized ? When the class loading
// Where are static variables stored ? Method area
static int i =100;
// When static code blocks are executed ? Class loading time
static{
System.out.println("i:"+i);
}
/*
Instance variables k Variables are instance variables , In the construction method ( Hidden object methods ) Execution time (new When ) Memory space will be opened up
error : Cannot reference non static from a static context Variable k
int k =6;
static{
// static The static code block executes when the class is loaded ,k Is instance variable So it will report a mistake
System.out.println(k);
System.out.println("name:"+name); // An error is also reported here : Illegal forward reference
}
// Report errors : Illegal forward reference
//static{System.out.println("name:"+name);}
//static String name ="junker";
*/
// Program entrance
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("main begin~");
}
}3、 ... and 、this Memory structure

1、this It's a keyword , All lowercase
2、this What is it? , In terms of memory ?
One object, one this.
this It's a variable , It's a reference ,this Save the memory address of the current object , Point to their own ,
therefore , Strictly speaking ,this It stands for " The current object "
this Inside objects stored in heap memory
3、this Can only be used in instance methods , Who calls this instance method ,this Who is the
therefore this It stands for : The current object
4、this In most cases, it can be omitted5、 Why? this Cannot be used in static methods ???
this Represents the current object , There is no object in the static method
Code walkthrough :[ master ]
public class ThisTest01
{
public static void main(String[] args){
// new An object
Customer c1 =new Customer("junker");
Customer c2 =new Customer("jun");
c1.shopping();
c2.shopping();
}
}
// Customers
class Customer
{
// attribute
// Instance variables ( You have to use " quote ." Mode of access )
String name;
// Construction method
public Customer(){
}
public Customer(String s){
name =s;
}
// How customers shop
// Example method
public void shopping(){
// there this Who is it ? this Is the current object
// c1 call shopping();,this Namely c1
// c2 call shopping();,this Namely c2
System.out.println(name+" Shopping ");
// doubt : String name Is instance variable ( You have to use " quote ." Mode of access )
// Why is there (name+" Shopping "); No ( quote .name+" Shopping ") Well
// Why not in this program (c1.name+" Shopping "); Well ?
// [ Be careful :new The citation that comes out c1 Is in ThisTest01 Method body This is Customer Class body ];
// answer : Actually (name+" Shopping "); The current object is hidden this ( See the memory diagram for details )
//System.out.println(this.name+" Shopping ");
}
}
Expand :
/*
analysis :i Variable in main Method ???
*/
public class ThisTest02{
int i =100; // Instance variables are object level Must first new Objects can only be used
static String k;
public static void main(String[] args){
// error : Cannot reference non static from a static context
//System.out.println(this.i);
//System.out.println(i); // The same mistake because i Is instance variable and main The method is static
// If you really want to main Method to access instance variables Then you need to manually new An object
ThisTest02 t =new ThisTest02();
System.out.println(t.i);
// Access static variables " Class name ." Mode of access
System.out.println(ThisTest02.k);
}
}this In which cases can not be omitted :
/*
1、this You can use in instance methods , Cannot be used in static methods .
2、this Keywords can be omitted in most cases , When can't we omit ?
*/
public class ThisTest06
{
public static void main(String[] args){
// No arguments
Student s1 =new Student();
s1.setName("jun");
s1.setNo(11111);
System.out.println(s1.getNo());
System.out.println(s1.getName());
// Ginseng
Student s2 =new Student(22222,"junker");
System.out.println(" Student number :"+s2.getNo());
System.out.println(" full name "+s2.getName());
}
}
// Analyze what is not well written in the following code ?
// The formal parameters are not clearly described
class Student
{
private int no;
private String name;
// Constructors
public Student(){}
public Student(int no,String name){
this.no =no;
this.name =name;
}
/*
// Report errors
public Student(int no,String name){ // Inside the formal parameters are local variables
no =no; // Sinister no Is instance variable Both virtual machines may think that the variables are the same , therefore
name =name;// Instance variables are object level variables need " quote ." Form visit this just : The current object
}
*/
// Construction method
public int getNo(){
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no){ // Shape parameter n The meaning of the expression is not obvious Some don't know no
this.no =no;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name =name;
}
}Running results :

this In addition to being used in instance methods , It can also be used in construction methods
New syntax : Call another constructor of this class through the current constructor , You can use the following syntax format :
this( List of actual parameters );
Through a construction method 1 To call the constructor 2, Code reuse can be achieved
Be careful :" Construction method 1" and " Construction method 2" They are all in the same category
demand :
1、 Define a date class , It can represent the year, month and day information .
2、 Requirements in requirements :
If you call a parameterless constructor , The default creation date is :1970 year 1 month 1 Japan .
Of course , In addition to calling the parameterless constructor , You can also call a parameter constructor to create a date object .
public class ThisTest07
{
public static void main(String[] args){
// No parameter
Date d1 =new Date();
d1.doSome();
// With parameters
Date d2 =new Date(1949,3,6);
d2.doSome();
}
}
class Date
{
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
/*
It is found that there are no parameter constructors and parameter constructors this.year this.month this.day repeat
Then you can call a parameterized constructor with a parameterless constructor grammar :this( List of actual parameters );
The actual parameter list corresponds to the parameters of the parameter construction method
*/
// Parameterless constructor
public Date(){
/*
this.year =1970;
this.month =1;
this.day =1;
*/
this(1970,1,1);
}
// There are parameter constructors
public Date(int year,int month,int day){
this.year =year;
this.month =month;
this.day =day;
}
// Set up checkpoints
// Reading data
public int getYear(){
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year){
this.year =year;
}
public int getMonth(){
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month){
this.month =month;
}
public int getDay(){
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day){
this.day =day;
}
public void doSome(){
//System.out.println(year); // Encapsulation in this class is invalid 1970( There is a default constructor to pass in 1970)
// When there is no constructor, the result is output int The type is 0 String-> null
System.out.println(year+" year "+month+" month "+day+" Japan ");
}
}Running results :

边栏推荐
- PD chip ga670-10 for OTG while charging
- 【软件】大企业ERP选型的方法
- 【ROS】noedic-moveit安装与UR5模型导入
- CUMT学习日记——ucosII理论解析—任哲版教材
- Résumé de la méthode d'examen des mathématiques
- Flutter development log - route management
- Output image is bigger (1228800b) than maximum frame size specified in properties (1048576b)
- Device = depthai Device(““, False) TypeError: _init_(): incompatible constructor arguments.
- 报错ModularNotFoundError: No module named ‘find_version’
- Day41 process pool and thread pool
猜你喜欢

Redis source code analysis hash object (z\u hash)

考研数学 【数列极限证明题】题型方法总结

Résumé de la méthode d'examen des mathématiques

openstack详解(二十二)——Neutron插件配置

报错RuntimeError: BlobReader error: The version of imported blob doesn‘t match graph_transformer

Kubelet error getting node help

实现边充边OTG的PD芯片GA670-10
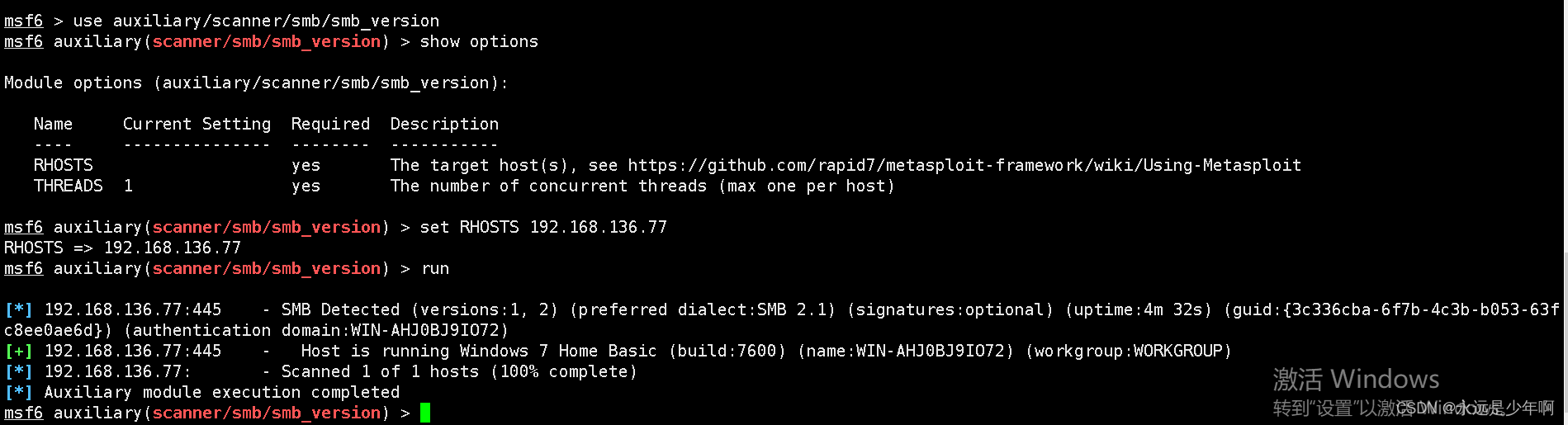
MSF基于SMB的信息收集

MSF给正常程序添加后门
![[C language - function stack frame] analyze the whole process of function call from the perspective of disassembly](/img/c5/40ea5571f187e525b2310812ff2af8.png)
[C language - function stack frame] analyze the whole process of function call from the perspective of disassembly
随机推荐
MSF adds back door to normal program
报错ModularNotFoundError: No module named ‘find_version’
Augmented reality experiment IV of Shandong University
机器学习笔记 - 卷积神经网络备忘清单
【芯片方案】红外人体测温仪方案设计
2161. 根据给定数字划分数组
openstack详解(二十四)——Neutron服务注册
Day41 process pool and thread pool
基于SIC32F911RET6设计的腕式血压计方案
Kubelet error getting node help
Fabric.js 动态设置字号大小
203. remove linked list elements
86. separate linked list
机器学习笔记 - Kaggle大师Janio Martinez Bachmann的故事
Day45 storage engine data type integer floating point character type date type enumeration and set type constraints table to table relationships
[scheme development] scheme of infrared thermometer
Openstack explanation (XXIII) -- other configurations, database initialization and service startup of neutron
【软件】大企业ERP选型的方法
2095. delete the intermediate node of the linked list
ERP体系能帮忙企业处理哪些难题?