当前位置:网站首页>Some introduction and precautions about XML
Some introduction and precautions about XML
2022-07-03 00:32:00 【Champion_ me】
Catalog
1、 What is? XML
Study XML First of all, of course, you should know XML What is it? , What is? XML?
- XML Extensible markup language (Extensible Markup Language)
- XML It's a kind of Markup language , Is very similar HTML
- XML The purpose of the design is To transmit data , Instead of displaying data (XML Transmit information , have Cross platform features )
- XML The label is not predefined . You need to Define your own label .
- XML Designed to have self-description .
- XML yes W3C The recommended standard of .
2、XMl And HTML Major differences
- XML No HTML An alternative .
- XML and HTML Designed for different purposes
- XML Designed to transmit and store data , The focus is on the content of the data .
- HTML Designed to display data , The focus is on the appearance of the data .
- HTML To show information , and XML Designed to transmit data
3、 Transmission data can also be used JSON,XML and JSON The difference between :
JSON and XML The difference between :
1、JSON yes JavaScript Object Notation;XML Is an extensible markup language .
2、JSON Is based on JavaScript Language ;XML Derived from SGML.
3、JSON Is a way of representing objects ;XML It's a markup language , Use tag structures to represent data items .
4、JSON There is no support for namespaces ;XML Namespace support .
5、JSON Support array ;XML Arrays are not supported .
6、XML The document is relatively difficult to read and interpret ; And XML comparison ,JSON The file is very easy to read .
7、JSON Do not use end tags ;XML There are start and end labels .
8、JSON It's less secure ;XML Than JSON More secure .
9、JSON Comments are not supported ;XML Support comments .
10、JSON Support only UTF-8 code ;XML Supports all kinds of coding .
4、XML Tree structure
XML Documents form a tree structure , He from “ root ” Start , And then expand to “ Leaf ”.
One XML Document instance
XMl Documents use simple, self descriptive Syntax :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<note>
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body>
</note>
The first line is XML Statement . It defines XML Version of (1.0) And the code used (UTF-8: unicode , Various languages can be displayed ). The next line describes the root element of the document ( It's like saying :“ A text file is a note ”)
<note>
Next 4 Line describes the root of 4 Sub elements (to, from, heading as well as body):
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body>
The last line defines the end of the root element :
</note>
You can assume , From this example ,XML The document contains a Jani written Tove My note .
XML With excellent self description , Do you agree ?
XML Documents form a tree structure
XML The document must contain the root element . This element is the parent of all other elements .
XML The elements in the document form a document tree . This tree starts at the root , And extend to the bottom of the tree .
All elements can have child elements :
<root>
<child>
<subchild>.....</subchild>
</child>
</root>
Father 、 Terms such as children and siblings are used to describe the relationships between elements . The parent element has children . Child elements at the same level become siblings ( Brother or sister ).
All elements can have text content and attributes ( similar HTML in ).
example :
The figure above shows the following XML A book in English :
<bookstore>
<book category="COOKING">
<title lang="en">Everyday Italian</title>
<author>Giada De Laurentiis</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>30.00</price>
</book>
<book category="CHILDREN">
<title lang="en">Harry Potter</title>
<author>J K. Rowling</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>29.99</price>
</book>
<book category="WEB">
<title lang="en">Learning XML</title>
<author>Erik T. Ray</author>
<year>2003</year>
<price>39.95</price>
</book>
</bookstore>
The root element in the instance is . All of the The elements are contained in in .
Elements have 4 Sub elements :
5、XML Rule of grammar
XML The rules of grammar are very simple , And it's very logical . These rules are easy to learn , It's also easy to use .
XML The document must have a root element
XML Must contain the root element , It's the parent of all the other elements , For example, in the following example root It's the root element :
<root>
<child>
<subchild>.....</subchild>
</child>
</root>
In the following example note Is the root element :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<note>
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body>
</note>
XML Statement
XML Optional parts of the declaration file , If it exists, you need to put it on the first line of the document , As shown below :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
The above examples include XML edition (
UTF-8 It's also HTML5, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, and SQL The default encoding for .
be-all XML Element must have a close tag
stay HTML in , Some elements don't have to have a close tag :
<p>This is a paragraph.
<br>
stay XML in , It's illegal to omit the closing tag . All elements must have a close tag :
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<br />
** notes :** From the example above , You may have noticed XML The statement does not close the label . It's not a mistake . The statement is not XML Part of the document itself , It has no close tab .
XML Tags are case sensitive
XML Tags are case sensitive . label And labels Is different .
Open and close tags must be written in the same case :
<Message> This is wrong </message>
<message> That's right </message>
** notes :** Opening and closing tags are often referred to as start tags and end tags . Whatever term you like , They all have the same concept .
XML Must nest... Correctly
stay HTML in , You will often see elements that are not nested correctly :
<b><i>This text is bold and italic</b></i>
stay XML in , All elements must be nested correctly within each other :
<b><i>This text is bold and italic</i></b>
In the example above , Correct nesting means : because The elements are in Open in the element , Then it must be in Close inside the element .
XML Attribute values must be quoted
And HTML similar ,XML Elements can also have attributes ( name / Pairs of values ).
stay XML in ,XML Property values of must be quoted .
Please study the following two XML file . The first one is wrong , The second is correct :
<note date=12/11/2007>
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
</note>
<note date="12/11/2007">
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
</note>
The error in the first document is ,note In the element date Attribute is not quoted .
Entity reference
stay XML in , Some characters have a special meaning .
If you put the character “<” Put it in XML In the elements , There will be mistakes , This is because the parser takes it as the beginning of a new element .
This will produce XML error :
<message>if salary < 1000 then</message>
To avoid this mistake , Please use entity references instead of “<” character :
<message>if salary < 1000 then</message>
stay XML in , Yes 5 Predefined entity references :
| < ; | < | less than |
|---|---|---|
| > ; | > | greater than |
| & ; | & | ampersand |
| &apos ; | ’ | apostrophe |
| " ; | " | quotation mark |
notes : stay XML in , Only characters “<” and “&” It's illegal . The greater than sign is legal , But it's a good habit to replace it with entity references .
XML The comments in
stay XML The syntax and syntax of writing comments in HTML The grammar of English is very similar .
<!-- This is a comment -->
stay XML in , Spaces will be reserved
HTML Will cut multiple consecutive space characters ( Merge ) For one :
stay XML in , Spaces in the document will not be deleted .
XML With LF Store newlines
stay Windows In the application , Newlines are usually stored as a pair of characters : A carriage return (CR) And line breaks (LF).
stay Unix and Mac OSX in , Use LF To store new lines .
In the old Mac In the system , Use CR To store new lines .
XML With LF Store newlines .
6、XML Elements
XML Document contains XML Elements .
What is? XML Elements ?
XML Element means from ( And includes ) Start tagging until ( And includes ) End the part of the tag .
An element can contain :
- Other elements
- Text
- attribute
- Or mix all of the above …
<bookstore>
<book category="CHILDREN">
<title>Harry Potter</title>
<author>J K. Rowling</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>29.99</price>
</book>
<book category="WEB">
<title>Learning XML</title>
<author>Erik T. Ray</author>
<year>2003</year>
<price>39.95</price>
</book>
</bookstore>
In the example above , and There are Element content , Because they contain other elements . Elements also have attributes (category=“CHILDREN”).
XML Naming rules
XML Elements must follow the following naming rules :
- Names can contain letters 、 Numbers and other characters
- Names cannot begin with numbers or punctuation
- The name cannot be in letters xml( perhaps XML、Xml wait ) Start
- The name cannot contain spaces
- You can use any name , There are no reserved words .
Best naming habits
Make the name descriptive . It's also nice to use underlined names :<first_name>、<last_name>.
The name should be short and simple , such as :<book_title>, instead of :<the_title_of_the_book>.
avoid “-” character . If you name it this way :“first-name”, Some software will think you want to go from first Subtract... From it name.
avoid “.” character . If you name it this way :“first.name”, Some software will think “name” It's the object “first” Properties of .
avoid “:” character . Colons are converted to namespaces to use ( Later on ).
XML Documents often have a corresponding database , The fields will correspond to XML Elements in the document . Have a practical experience , That is, use the database naming rules to name XML Elements in the document .
stay XML in ,éòá It's perfectly legal to wait for non English letters , But we need to pay attention to , Problems that may arise when your software vendor does not support these characters .
XML Elements are extensible
XML Elements are extensible , To carry more information .
Please look at the following XML example :
Tove Jani Don't forget me this weekend! Let's imagine , We created an application , Can be 、 as well as Elements from XML Extracted from the document , And produce the following output :MESSAGE
To: Tove
From: JaniDon’t forget me this weekend!
Imagine ,XML Some additional information added by the author of the document :
<note>
<date>2008-01-10</date>
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body>
</note>
So will the application break or crash ?
Can't . This application can still find XML In document 、 as well as Elements , And produce the same output .
XML One of the advantages of , It can be extended without interrupting the application .
7、XML attribute
XML Elements have attributes , similar HTML.
attribute (Attribute) Provide additional information about the element .
XML attribute
stay HTML in , Property provides additional information about the element :
<img src="computer.gif">
<a href="demo.html">
Attributes usually provide information that is not part of the data . In the following example , File types have nothing to do with data , But it's important for the software that needs to deal with this element :
<file type="gif">computer.gif</file>
XML Attribute must be quoted
Property values must be enclosed in quotation marks , However, single and double quotation marks can be used . For example, a person's gender ,person Elements can be written like this :
<person sex="female">
Or it could be :
<person sex='female'>
If the property value itself contains double quotes , You can use single quotes , Like this example :
<gangster name='George "Shotgun" Ziegler'>
Or you can use character entities :
<gangster name="George "Shotgun" Ziegler">
XML Elements vs. attribute
Look at these examples :
<person sex="female">
<firstname>Anna</firstname>
<lastname>Smith</lastname>
</person>
<person>
<sex>female</sex>
<firstname>Anna</firstname>
<lastname>Smith</lastname>
</person>
In the first example ,sex Is an attribute . In the second example ,sex Is an element . Both instances provide the same information .
There are no rules to tell us when to use properties , And when to use elements . My experience is that HTML in , Attributes are easy to use , But in XML in , You should try to avoid using properties . If information feels like data , So use elements .
My favorite way
The next three XML The document contains exactly the same information :
The first example uses date attribute :
<note date="10/01/2008">
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body>
</note>
In the second example date Elements :
<note>
<date>10/01/2008</date>
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body>
</note>
The third example uses the extended date Elements ( This is my favorite ):
<note>
<date>
<day>10</day>
<month>01</month>
<year>2008</year>
</date>
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body>
</note>
avoid XML attribute ?
Some problems caused by using attributes :
Property cannot contain more than one value ( Elements can )
Property cannot contain tree structure ( Elements can )
Properties are not easy to extend ( For future changes )
Properties are hard to read and maintain . Try to use elements to describe the data . Only attributes are used to provide data independent information .
Don't do such a stupid thing ( This is not XML The way it should be used ):
<note day="10" month="01" year="2008" to="Tove" from="Jani" heading="Reminder" body="Don't forget me this weekend!">
</note>
For metadata XML attribute
Sometimes elements are assigned ID quote . these ID An index can be used to identify XML Elements , The way it works and HTML in id The attributes are the same . This example shows us this situation :
<messages>
<note id="501">
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body>
</note>
<note id="502">
<to>Jani</to>
<from>Tove</from>
<heading>Re: Reminder</heading>
<body>I will not</body>
</note>
</messages>
above id An attribute is just an identifier , Used to identify different notes . It's not part of the memo data .
The idea we are trying to convey to you here is : Metadata ( Data about data ) Should be stored as an attribute , And the data itself should be stored as elements .
8、XML verification
Having the right grammar XML go by the name of " In good form " Of XML.
adopt DTD Verified XML yes " legal " Of XML.
In good form XML file
" In good form " Of XML The document has the right syntax .
The grammar rules described in the previous chapter :
- XML The document must have a root element
- XML Element must have a close tag
- XML Tags are case sensitive
- XML Elements must be nested correctly
- XML Attribute values must be quoted
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<note>
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body>
</note>
verification XML file
legal XML The document is " In good form " Of XML file , This also fits the document type definition (DTD) The rules of :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> Tove Jani Reminder Don't forget me this weekend! In the example above ,DOCTYPE The declaration is external DTD References to documents . The following paragraphs show the contents of this file .XML DTD
DTD The purpose of this is to define XML Document structure . It uses a series of legal elements to define the document structure :
<!DOCTYPE note [ <!ELEMENT note (to,from,heading,body)> <!ELEMENT to (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT from (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT heading (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT body (#PCDATA)> ]>
If you want to learn DTD, Please find it on our homepage DTD course .
XML Schema
W3C Support a method based on XML Of DTD Substitute , It's called XML Schema:
<xs:element name="note">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="to" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="from" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="heading" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="body" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
If you want to learn XML Schema, Please find it on our homepage Schema course .
A generic XML Validator
To help you check XML The syntax of the document , We created XML Validator , So that you can understand any XML File syntax check .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Bigder: how to deal with the bugs found in the 32/100 test if they are not bugs
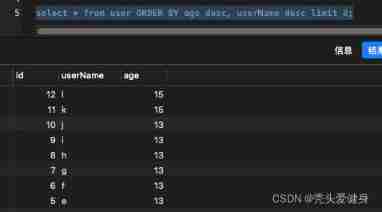
Talk with the interviewer about the pit of MySQL sorting (including: duplicate data problem in order by limit page)
![Luogu_ P1149 [noip2008 improvement group] matchstick equation_ Enumeration and tabulation](/img/4a/ab732c41ea8a939fa0983fec475622.png)
Luogu_ P1149 [noip2008 improvement group] matchstick equation_ Enumeration and tabulation
![洛谷_P2010 [NOIP2016 普及组] 回文日期_折半枚举](/img/a3/55bb71d39801ceeee421a0c8ded333.png)
洛谷_P2010 [NOIP2016 普及组] 回文日期_折半枚举

What are the recommended thesis translation software?

ftrace工具的介绍及使用

Should you study kubernetes?
MySQL 23 classic interview hanging interviewer
redis21道经典面试题,极限拉扯面试官
How do educators find foreign language references?
随机推荐
Form form instantiation
Question e: merged fruit -noip2004tgt2
TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading ***)
TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading ***)
NC24840 [USACO 2009 Mar S]Look Up
Redis21 classic interview questions, extreme pull interviewer
【雅思阅读】王希伟阅读P1(阅读判断题)
使用jenkins之二Job
How to specify const array in the global scope of rust- How to specify const array in global scope in Rust?
One of the reasons why setinterval timer does not take effect in ie: the callback is the arrow function
node_ Modules cannot be deleted
洛谷_P2010 [NOIP2016 普及组] 回文日期_折半枚举
Luogu_ P2010 [noip2016 popularization group] reply date_ Half enumeration
collections. What is the purpose of chainmap- What is the purpose of collections. ChainMap?
Missing number
Free we media essential tools sharing
[shutter] image component (image component introduction | image constructor | image.network constructor | image.asset constructor)
[shutter] Introduction to the official example of shutter Gallery (project introduction | engineering construction)
Bypass AV with golang
Sysdig analysis container system call