当前位置:网站首页>Convolution neural network -- convolution of gray image
Convolution neural network -- convolution of gray image
2022-07-27 04:22:00 【Bubble Yi】
One 、 Premise introduction :
Convolution is often used for smoothing in image processing 、 Fuzzy 、 sharpening 、 Denoise 、 Edge extraction and other work . Convolution operation in image processing , It's actually using convolution kernel ( Templates ) Slide on the target image , Map the pixels on the image to the middle pixels of the convolution kernel in turn , After each pixel is aligned, multiply the pixel gray value on the image by the value on the corresponding position of the convolution kernel , Then add all the multiplied values , The result of the addition is the gray value of the current pixel , And finally slide all image pixels .
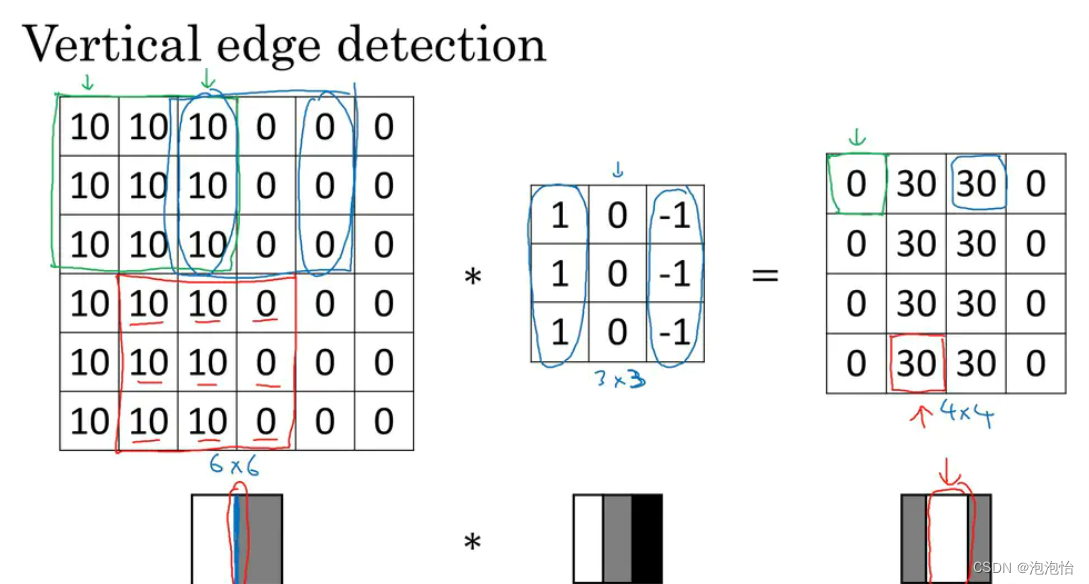
As shown in the figure above : The leftmost matrix is a grayscale image , In the middle is a 3*3 The small matrix of , be called “ Convolution kernel ” or “ filter ”.
1. Guide pack
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt2. The process :
# Convolution operation of image
# Input parameters
# image: Original image
# mfilter: filter
# Output parameters
# convImage: Convoluted image
3. Define the convolution function :
def ImageConvolution( image, mfilter ):
mI, nI = np.shape( image )
[mF, nF] = np.shape( mfilter )
halfHeight = int( mF / 2 )
halfWidht = int( nF / 2 )
convImage = np.zeros( (mI, nI) )# Convolution image
# Adjust and expand the range of the image according to the different parity of the filter length
if mF % 2 == 0:
imData = np.pad( image, (halfWidht, halfWidht-1), 'constant' )
else:
imData = np.pad( image, (halfWidht, halfHeight), 'constant' )
padmI, padnI = imData.shape
convHeight = padmI - mF + 1
convWidth = padnI - nF + 1
# Successively intercept image blocks with the same size as the filter for inner product operation
for i in range( convHeight ):
for j in range( convWidth ):
localImage = imData[ i:i+mF, j:j+nF ]
convImage[i][j] = np.sum( localImage * mfilter )
convImage1 = convImage.clip( 0, 255 )
return convImage1
4. Convolute the image according to the filter
filter1 = [ [-1, -2, -1], [0, 0, 0], [1, 2, 1] ]
imageConv = ImageConvolution( img, filter1 )
plt.figure( 'filter1' )
plt.imshow( imageConv, cmap = 'gray' )
plt.axis( 'off' )
filter2 = [ [1, -1], [1, -1] ]
imageConv = ImageConvolution( img, filter2 )
plt.figure( 'filter2' )
plt.imshow( imageConv, cmap = 'gray' )
plt.axis( 'off' )
filter3 = [ [-1, 1, 1, -1], [-1, 1, 1, -1], [-1, 1, 1, -1], [-1, 1, 1, -1] ]
imageConv = ImageConvolution( img, filter3 )
plt.figure( 'filter3' )
plt.imshow( imageConv, cmap = 'gray' )
plt.axis( 'off' )
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()result :




边栏推荐
- Okaleido生态核心权益OKA,尽在聚变Mining模式
- C get UUID
- A. Round Down the Price
- spicy之evt接口定义文件
- js修改对象数组的key值
- Elastic certification test: 30 day FastPass Study Guide
- 数据分析师岗位分析
- 标准C语言11
- 356 pages, 140000 words, weak current intelligent system of high-end commercial office complex, 2022 Edition
- C how to set different text watermarks for each page of word
猜你喜欢

spark练习案例(升级版)

Eureka-服务注册中心

2022 retraining question bank and answers for main principals of hazardous chemical business units

MySQL: understand the basic knowledge of MySQL and computer

ArrayList与LinkedList区别

Okaleido生态核心权益OKA,尽在聚变Mining模式

Plato Farm全新玩法,套利ePLATO稳获超高收益

一张图看懂KingbaseES V9

JVM原理简介

网工知识角|只需四个步骤,教会你使用SecureCRT连接到eNSP,常用工具操作指南必看
随机推荐
Maximum nesting depth of parentheses
xxx is not in the sudoers file. This incident will be reported
CloudCompare&PCL 匹配点距离抑制
标准C语言13
What is the principle difference between lateinit and lazy in kotlin
webpack打包vue项目添加混淆方式,解决缓存问题
Principle of bean validation --07
PX4模块设计之十二:High Resolution Timer设计
tcp协议知识详解
链表内指定区间反转
物联网智能家居项目---智能卧室
STM32基于HAL库的串口接受中断和空闲中断
[machine learning network] BP neural network and deep learning-6 deep neural networks (DNN)
People don't talk much, engineers don't talk much
How CentOS installs mysqldump
c# 获取uuid
spicy之evt接口定义文件
E-commerce system combined with commodity spike activities, VR panorama continues to bring benefits
What is animation effect? What is the transition effect?
Is VR panorama just needed now? After reading it, you will understand