当前位置:网站首页>Memory alignment of structures
Memory alignment of structures
2022-06-24 22:45:00 【Ah Xing_】
We all knew before int The type size is 4 Bytes ,char The type is 1 Bytes ,double by 8 Bytes and so on .
But structures are made up of many types , So what's its size ? Is it the sum of all types, or is there another algorithm ?
We will discuss it in detail in the next two chapters .
Let's start with the conclusion : The structure size is not the sum of all types , Instead, there is a way to align memory , Make the types in the structure align in some way .
What kind of alignment is it ?
Let's look at the following code first :
struct S1
{
char c1;
int i;
char c2;
};
printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct S1));The size is not 1+4+1=6 Two bytes . Let's see the result first :

The result is 12. Isn't it very unreasonable .
The next two bullshit don't say much , Go straight up Memory alignment rules , Then I will analyze it one by one :
1. The first member is associated with the structure variable Offset by 0 The address of .
2. Other member variables should be aligned to Some number ( Align numbers ) An integral multiple of the address of .
Align numbers = Compiler default alignment number And The smaller value of the member size .
VS The default value in is 8
3. Structure Total size Is the maximum number of alignments ( Each member variable has an alignment number ) Of An integral multiple .
4. If nesting The situation of the structure , The nested structure is aligned to an integral multiple of its maximum alignment , The integrity of the structure
Body size is the maximum number of alignments ( The number of alignments with nested structures ) Integer multiple .
Let's analyze it sentence by sentence .
One . The first member is associated with the structure variable Offset by 0 The address of .
An offset can be abstractly understood as a location in memory . I will understand it later in the explanation . Very easy to
For example, the example above :
The first member is char c1;
Then the position offset is 0 The address of , It will be easier to understand if you draw like this .
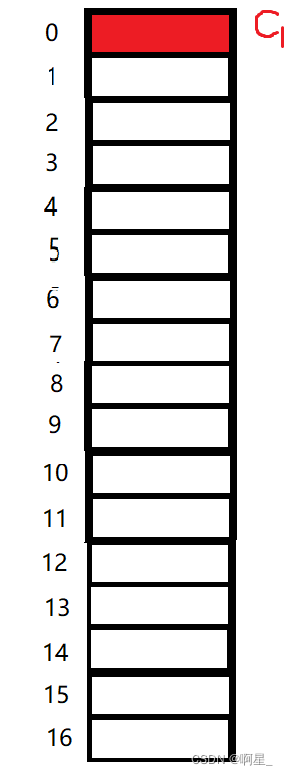
among 0 - 16 Numbers are all offsets , Numbers 2 The representative offset is 2,16 Then the offset is 16.
Then according to the first rule : The first member should be at offset 0 The location of , We put it in :
It becomes the picture above . Look at the next rule :
2. Other member variables should be aligned to Some number ( Align numbers ) At the address of the smallest integer multiple of .
Align numbers = Compiler default alignment number And The smaller value of the member size .
VS The default value in is 8
To align to an integer multiple of the alignment number . First, the alignment number is The compiler defaults to the smaller value of the structure member .
vs Compilation defaults to 8, Our next type, the second type, is int type , The size is 4 Bytes .
So we take a smaller value , namely 4, So the alignment number is 4.
It is necessary to 4 Integer multiple , We can only take 4 Of 1 The Times , If it is 0, be 4 Of 0 Times too 0, And the offset is 0 The place has been occupied , So we can only take 4 Of 1 times , That is, when the offset is 4 The place of , Start taking up a int Byte size , Empty space , If the offset is 1,2,3 The place is wasted , Don't bother . Here's the picture :

Next , The third member is char c2 :
The same way ,
vs Compilation defaults to 8, Our type is char type , The size is 1 Bytes .
So we take a smaller value , namely 1, So the alignment number is 1.
Then align to 1 The smallest multiple of , Since it is 1 Multiple , That must be as much ,1,2,3,4 All right , But our offset has now reached 7 The location of , So the next one can only occupy an offset of 8 The location of , namely 8 Multiple .
as follows :

At this point, all members have finished the , Then look at the third rule :
3. Structure Total size Is the maximum number of alignments ( Each member variable has an alignment number ) Of An integral multiple .
At this time, the maximum number of alignments is the largest of the structure members .
The structure member types are :char、int、char
The biggest type is int, namely 4 Bytes , That is, the maximum number of alignments is 4 Bytes ..
So the total size of the structure is 4 Integer multiple , Note that at this time, it has occupied 9 Bytes , No 8 Bytes !
Because the offset includes 0, So at this time, only the offset is 8, But it has taken up 9 Bytes .
So it can only be 4 Of 3 Multiple , namely 12 Bytes . if 4 Of 2 Multiple , It is 8, It is smaller than the bytes we have occupied , therefore 8 Definitely not .
So to sum up , The size of this structure is 12 Bytes .
So I understand , What should I do with the following code ?
struct S4
{
char c1;
struct S1 s1;
double d;
};
printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct S4));
notes :s1 The example above is s1
We are S4 There is a nested in the structure S1 Structural variable s1, So how do we calculate ?
First, follow the first rule , take c1 Put it at an offset of 0 The location of .

Here comes the point , The next member is a structural variable , At this point, it will no longer follow the 2 Bar rule , Look directly at the 4 Bar rule :
4. If nesting The situation of the structure , The nested structure is aligned to an integral multiple of its maximum alignment , The integrity of the structure
Body size is the maximum number of alignments ( The number of alignments with nested structures ) Integer multiple .
Normally , We compare the size of this member with the compiler default size to get the minimum value , Then find the smallest integral multiple of it . But if the member is a structure , It is no longer calculated according to its own size , But according to his own maximum alignment number . We already know S1 The maximum number of alignments is 4, So it is 4 Multiple , At this time, only from 4 The position begins , namely 4 Of 1 Multiple , as follows :

The next third member is double type , The size is 8 Bytes , Same as compiler default . Then take it 8, At this time, only 8 Of 2 times , The offset is 16 The location of . as follows :

Then the total size is all members ( The nested structure includes ) An integer multiple of the maximum alignment number of
Their alignment numbers are 1 4 8
So the maximum number of alignments is 8, Then integral multiples , Can only be 24, namely 8 Of 3 times .
That is, the size of this structure is 24. Let's see the result :

Results the correct .
Here are a few more questions , I hope I can consolidate my knowledge when I have time .
// seek S2 Size of structure
struct S2
{
char c1;
char c2;
int i;
};
// seek S3 Size of structure
struct S3
{
double d;
char c;
int i;
};As a result, you can run and try , See if it is consistent with your own calculation .
If there is any doubt , Welcome to contact us by private letter .
Digression :
Why is there memory alignment ?
Most of the references say that :
1. Platform reasons ( Reasons for transplantation ):
Not all hardware platforms can access any data on any address ; Some hardware platforms can only take some special data at some addresses
Certain types of data , Otherwise, a hardware exception will be thrown
2. Performance reasons :
data structure ( Especially stacks ) It should be aligned as far as possible on the natural boundary .
The reason lies in , To access unaligned memory , The processor needs to make two memory accesses ; Aligned memory access requires only one access
ask
Memory alignment of structures is a way of trading space for time .
--- From the teaching materials of bit employment course
Then the memory alignment of the structure is over , Still the same , If there is any doubt , Welcome to leave a message or a private letter .
边栏推荐
- AQS source code analysis
- ThreadLocal local thread
- Docker installs redis-5.0.12. Detailed steps
- Data communication and physical network
- 网上立案流程
- AttacKG: Constructing Technique Knowledge Graph from Cyber Threat Intelligence Reports代码复现
- STP spanning tree protocol Foundation
- Data center basic network platform
- Leetcode: calculate the number of elements less than the current element on the right (sortedlist+bisect\u left)
- Code farmers should also understand the IPv4 subnet division of point networks
猜你喜欢

Technology Review: what is the evolution route of container technology? What imagination space is there in the future?

The difference between interceptor and filter
CA Zhouji - the first lesson in 2022 rust

Basic principles of spanning tree protocol

Zero code can apply data visualization to enterprise management

AQS source code analysis

String exercise summary 2

Introduction, installation and use of postman tool

YGG recent game partners list

Fanuc robot_ Introduction to Karel programming (1)
随机推荐
AQS源码分析
Docker installs redis-5.0.12. Detailed steps
Web攻击之CSRF和SSRF
04A interrupt configuration
问题求解——嵌套列表
New features of go1.18: efficient replication, new clone API for strings and bytes standard library
Heavyweight! Fada is listed as a "specialized and new" enterprise
Data communication and physical network
How to solve the problem that the computer suddenly can't connect to WiFi
堆內存分配的並發問題
【软件工程】期末重点
CA Zhouji - the first lesson in 2022 rust
Online filing process
Interrupt, interrupted, isinterrupted differences
2022-06-16 work record --js- judge the number of digits in string type digits + judge the number of digits in numeric type digits + limit the text length (display n words at most, exceeding...)
Visitor tweets tell you which groups are consuming blind boxes
CDN principle
源码阅读 | OpenMesh读取文本格式stl的过程
Environment configuration | vs2017 configuring openmesh source code and environment
Introduction, installation and use of postman tool
