当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode force deduction question
Leetcode force deduction question
2022-06-11 17:27:00 【Hua la la la la】
704. Two points search
Given a n The elements are ordered ( Ascending ) integer array nums And a target value target , Write a function search nums Medium target, If the target value has a return subscript , Otherwise return to -1.

class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
if (target < nums[0] || target > nums[nums.length - 1]){
return -1;
}
int left = 0,right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right){
// left + ((right - left) >> 1) Shift right operator >>, The result of the operation can correspond to exactly one-half of the value of an integer , This can just replace the mathematical division 2 operation , But than division 2 Fast calculation
int middle = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
// int middle = (left + right) / 2;
if (nums[middle] > target){
right = middle - 1;
} else if (nums[middle] < target){
left = middle + 1;
} else {
return middle;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
566. Reshaping the matrix (Java— Two dimensional array transformation )
Give a matrix represented by a two-dimensional array , And two positive integers r and c, Represent the number of rows and columns of the matrix to be reconstructed respectively .
The reconstructed matrix needs to fill all elements of the original matrix in the same row traversal order .
If the reshape The operation is feasible and reasonable , The new reshaping matrix is output ; otherwise , Output raw matrix .
Code implementation :
class Solution {
public int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] nums, int r, int c) {
boolean isReshape = true;
int[][] newArr = new int[r][c];
// If the size of the reconstructed matrix is not equal to that of the original matrix, it cannot be reconstructed
if(r * c != nums.length * nums[0].length)
isReshape = false;
else {
int tempR = 0;
int tempC = 0;
// Rows traverse the original matrix
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < nums[0].length; j++) {
// Fill in the reconstruction matrix
newArr[tempR][tempC++] = nums[i][j];
// When a line is filled in, a new line will appear
if(tempC == c) {
tempR++;
tempC = 0;
}
}
}
if(isReshape)
return newArr;
else
return nums;
}
}
118. Yang hui triangle
Given a nonnegative integer numRows, Generate 「 Yang hui triangle 」 Before numRows That's ok .
stay 「 Yang hui triangle 」 in , Each number is the sum of the numbers at the top left and right of it .

Code implementation :
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
// Initialize an array to store the results
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for(int i = 0;i < numRows;i++){
List<Integer> List = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int j = 0;j <= i;j++){
if(j==0||j==i){
List.add(1);
} else {
List.add(result.get(i-1).get(j-1) + result.get(i-1).get(j));
}
}
result.add(List);
}
return result;
}
}
73. Matrix zeroing
Given a m x n Matrix , If an element is 0 , Set all elements of the row and column to 0 . Please use In situ Algorithm .

Use the method of tag array to solve :
We can use two tag arrays to record whether there are zeros in each row and column .
In particular , We first traverse the array once , If an element is 0, Then set the position of the tag array corresponding to the row and column where the element is located to true. Finally, we iterate over the array again , Update the original array with the tag array .
class Solution {
public void setZeroes(int[][] matrix) {
//m,n They are the rows and columns of the matrix
int m = matrix.length,n = matrix[0].length;
// use Boolean Value to mark the elements in the matrix
boolean[] row = new boolean[m];
boolean[] col = new boolean[n];
// ergodic matrix
for(int i = 0;i < m; i++){
for(int j = 0;j < n; j++){
if(matrix[i][j] == 0){
row[i] = col[j] = true;
}
}
}
// // Traverse the array again , Update the original array with the tag array
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < n;j++){
//row[i] And col[j] by ture
if(row[i]||col[j]){
matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
}
36. Effective Sudoku
Please judge a 9 x 9 Is the Sudoku effective . It only needs According to the following rules , Verify that the numbers you have filled are valid .
Numbers 1-9 Only once in a row .
Numbers 1-9 It can only appear once in each column .
Numbers 1-9 Separated by thick solid lines in each 3x3 Only once in the palace .( Please refer to the example figure )
class Solution {
public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {
// Corresponding to lines respectively 、 Column 、 Sudoku
HashSet set1 = new HashSet();
HashSet set2 = new HashSet();
HashSet set3 = new HashSet();
// Judge each line , Each column
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] != '.') {
// If add return false It means that the repeating element appears
if (!set1.add(board[i][j])) {
return false;
}
}
if (board[j][i] != '.') {
if (!set2.add(board[j][i])) {
return false;
}
}
}
// Every line / A column of add Empty after completion set Convenient for next operation
set1.clear();
set2.clear();
}
// Judge 3X3 The submatrix of
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; ++j) {
// Double 0-3 The bad circulation represents 3*3 Sub Sudoku
for (int m = 3 * i; m < 3 * i + 3; ++m) {
for (int n = 3 * j; n < 3 * j + 3; ++n) {
// Of each Sudoku add
if (board[m][n] != '.') {
if (!set3.add(board[m][n])) {
return false;
}
}
}
}
set3.clear();
}
}
return true;
}
}
387. The first unique character in the string
Given a string s , find Its first non repeating character , And return its index . If it doesn't exist , Then return to -1 .
Ideas : Originally I saw the word "only" , The first reaction is to use a hash table to store , But the following conditions are all lowercase letters , I don't think it's necessary to use hash , Just use an array .
The general idea is that the letters are only 26 individual , So the number of times each letter appears is recorded in an array , And then traverse it in sequence , The first occurrence of an array is the first unique letter . It is really much simpler than the official solution . The code framework is as follows :
First new 26 An array of bits is used to store the number of occurrences of each letter (java The array is initialized to by default 0).
Then go through the string , Count the number of times each letter appears
Finally, go through the string again , If the letter appears only once , So just go back ; If traversing the entire string does not return , It means that all letters are repeated , Just go back to -1.
class Solution {
public int firstUniqChar(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0){
return -1;
}
int[] c = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
c[s.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
if(c[s.charAt(i) - 'a'] == 1){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
383. Ransom letter
Here are two strings :ransomNote and magazine , Judge ransomNote Can it be done by magazine The characters inside make up .
If possible , return true ; Otherwise return to false .
magazine Each character in can only be in ransomNote Used once in .
Ideas : Because the title has only lowercase letters , Then we can use the hash strategy of space for time , Use a length of 26 The array also records magazine The number of times the letters appear in .
And then use ransomNote To verify that the array contains ransomNote All the letters needed .
class Solution {
public boolean canConstruct(String ransomNote, String magazine) {
// Record the number of words in the magazine string
int[] arr = new int[26];
for(int i = 0;i<magazine.length();i++){
arr[magazine.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
for(int i = 0;i < ransomNote.length(); i++){
// For each character in the gold letter, look it up in the array
// Find the corresponding digit minus one , Otherwise, it cannot be found and returned fals
if (arr[ransomNote.charAt(i) - 'a'] > 0){
arr[ransomNote.charAt(i) - 'a']--;
} else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
242. Effective alphabetic words
Given two strings s and t , Write a function to determine t Whether it is s Letter heteronym of .
Be careful : if s and t Each character in the has the same number of occurrences , said s and t They are mutually alphabetic words
class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
int[] record = new int[26];
int temp;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
temp = s.charAt(i) - 'a';
record[temp]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < t.length();i++){
temp = t.charAt(i) - 'a';
record[temp]--;
}
// for (int i : record){
// if(i != 0){
// return false;
// }
// }
for (int i = 0; i < 26;i++){
if (record[i] != 0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
141. Circular list
Give you a list of the head node head , Judge whether there are links in the list .
If there is a node in the linked list , It can be done by continuously tracking next The pointer reaches again , Then there is a ring in the linked list . To represent a ring in a given list , The evaluation system uses an integer pos To indicate where the end of the list is connected to the list ( Index from 0 Start ). Be careful :pos Not passed as an argument . Just to identify the actual situation of the linked list .
If there are rings in the list , Then return to true . otherwise , return false .
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
/** * 1 Use the speed pointer ,1 individual 1 The first time 1 Step , another 1 individual 1 The first time 2 Step * 2 If the pointer comes null 了 , That means we have reached the end of the linked list , No ring , Out of the loop ,return false * 3 If there are rings , It's going to keep cycling , Until the two meet ,return true */
if (head == null || head.next == null){
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null){
// No ring will jump out of the loop
if (slow != fast){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;// Cycle all the time , Until the speed pointer meets
} else {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
142. Circular list II
Given the head node of a linked list head , Return to the first node of the link where the list begins to enter . If the list has no links , Then return to null.
If there is a node in the linked list , It can be done by continuously tracking next The pointer reaches again , Then there is a ring in the linked list . To represent a ring in a given list , The evaluation system uses an integer pos To indicate where the end of the list is connected to the list ( Index from 0 Start ). If pos yes -1, There are no links in the list . Be careful :pos Not passed as an argument , Just to identify the actual situation of the linked list .
No modification allowed Linked list .
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null){
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// And 141 There is something wrong with the question
if(slow == fast) {
ListNode index1 = fast;
ListNode index2 = head;
while (index1 != index2){
index1 = index1.next;
index2 = index2.next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return null;
}
}
21. Merge two ordered lists
Merge two ascending linked lists into a new Ascending Link list and return . The new linked list is made up of all the nodes of the given two linked lists .
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode result = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode index = result;
//index Is the tail pointer of the new linked list ,list1,list2 Is the header pointer of two lists
while (list1 != null && list2 != null){
if (list1.val <= list2.val) {
index.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
index.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
index = index.next;
}
// here list1 and list2 There is already a blank , Connect those that are not empty
index.next = list1 == null ? list2:list1;
return result.next;
}
}
203. Remove linked list elements
Give you a list of the head node head And an integer val , Please delete all the contents in the linked list Node.val == val The node of , And back to New head node .
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
/** How to add virtual nodes */
// Because the head node is involved , So set dymy node , Unified operation
ListNode dumy = new ListNode(-1,head);
ListNode pre = dumy;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
if (cur.val == val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return dumy.next;
}
}
206. Reverse a linked list
Here's the head node of the list head , Please reverse the list , And return the inverted linked list  1. Using double pointers
1. Using double pointers
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// Double pointer
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode temp = null;
while (cur != null){
temp = cur.next; // Save the next node first
cur.next = prev; // reverse
// to update prev,cur Location
prev = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return prev;
}
}
- Use recursion
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(null, head);
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode prev, ListNode cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return prev;
}
ListNode temp = null;
temp = cur.next;// Save the next node first
cur.next = prev;// reverse
// to update prev、cur Location
// prev = cur;
// cur = temp;
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
}
83. Delete duplicate elements from the sort list
Given the header of a sorted linked list head , Delete all duplicate elements , Make each element appear only once . return Sorted linked list .
Ideas :
- Appoint cur The pointer points to the head head
- cur and cur.next The existence of is the end of the loop condition , When one of the two does not exist, it means that there is no need to repeat the linked list .
- When cur.val and cur.next.val When equal , It means that the weight needs to be removed , Will cur The next pointer of points to the next , In this way, we can achieve the effect of de repetition .
- If it's not equal , be cur Move to the next position and continue the cycle .
The time complexity is O(n).
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null && cur.next != null){
if (cur.val == cur.next.val){
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
20. Valid parenthesis
Given one only includes ‘(’,‘)’,‘{’,‘}’,‘[’,‘]’ String s, Determines whether the string is valid .
Valid string needs to meet :
- Opening parentheses must be closed with closing parentheses of the same type .
- The left parenthesis must be closed in the correct order .

class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
// Stack solving
Deque<Character> deque = new LinkedList<>();
char ch;
for(int i = 0;i < s.length();i++){
ch = s.charAt(i);
// Touching the left bracket , Put the corresponding right parenthesis on the stack
if (ch == '('){
deque.push(')');
} else if(ch == '{'){
deque.push('}');
} else if(ch == '['){
deque.push(']');
} else if (deque.isEmpty() || deque.peek() != ch) {
return false;
} else {
// If it's right bracket , Then judge whether it matches the top element of the stack
deque.pop();
}
}
return deque.isEmpty();
}
}
232. Using stack to realize queue
Please use only two stacks to implement the FIFO queue . The queue should support all operations supported by the general queue (push、pop、peek、empty):
Realization MyQueue class :
- void push(int x) Put the element x Push to the end of the queue
- int pop() Remove from the beginning of the queue and return the element
- int peek() Returns the element at the beginning of the queue
- boolean empty() If the queue is empty , return true ; otherwise , return false
explain :
You can only use standard stack operations —— It's just push to top, peek/pop from top, size, and is empty Operation is legal .
The language you use may not support stacks . You can use list perhaps deque( deque ) To simulate a stack , As long as it's a standard stack operation .
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stackIn;
Stack<Integer> stackOut;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
stackIn = new Stack<>();
stackOut = new Stack<>();
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
stackIn.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
dumpstackIn();
return stackOut.pop();
}
public int peek() {
dumpstackIn();
return stackOut.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stackIn.isEmpty()&&stackOut.isEmpty();
}
// If stackOut It's empty , It will be stackIn Put all the elements in stackOut in
private void dumpstackIn(){
if (!stackOut.isEmpty()) return;
while(!stackIn.isEmpty()){
stackOut.push(stackIn.pop());
}
}
}
/** * Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such: * MyQueue obj = new MyQueue(); * obj.push(x); * int param_2 = obj.pop(); * int param_3 = obj.peek(); * boolean param_4 = obj.empty(); */
144. Preorder traversal of two tree
Give you the root node of the binary tree root , Of its node value Before the order Traverse .
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
// Recursive method : Preorder traversal is before and after the middle
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
preorder(root,result);
return result;
}
public void preorder(TreeNode root,List<Integer> result){
if (root == null){
return;
}
result.add(root.val);
preorder(root.left,result);
preorder(root.right,result);
}
}
94. Middle order traversal of binary trees
Given the root node of a binary tree root , return its Middle preface Traverse .
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
// In the sequence traversal : Front middle back
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Inoder(root,result);
return result;
}
public void Inoder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result){
if (root == null){
return;
}
Inoder(root.left,result);
result.add(root.val);
Inoder(root.right,result);
}
}
145. Postorder traversal of binary trees
Give you the root node of a binary tree root , Returns the After the sequence traversal .
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
OutOrder(root,result);
return result;
}
public void OutOrder(TreeNode root,List<Integer> result){
if (root == null){
return;
}
OutOrder(root.left,result);
OutOrder(root.right,result);
result.add(root.val);
}
}
102. Sequence traversal of binary tree
Give you the root node of the binary tree root , Returns the Sequence traversal . ( That is, layer by layer , Access all nodes from left to right ).
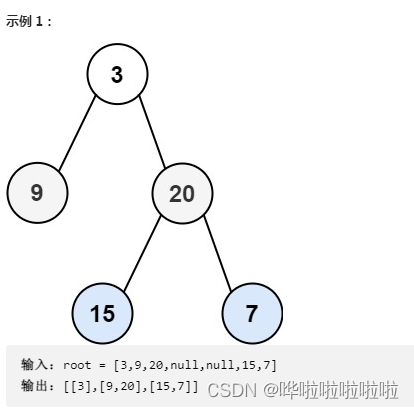
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
checkFun01(root,0);
return resList;
}
public void checkFun01(TreeNode node,Integer deep){
if (node == null) return;
deep++;
if(resList.size() < deep){
// As the hierarchy increases ,list Of Item Also increase , utilize List The index value of leads to the hierarchy definition
List<Integer> item = new ArrayList<Integer>();
resList.add(item);
}
resList.get(deep-1).add(node.val);
c/heckFun01(node.left,deep);
checkFun01(node.right,deep);
}
}
104. The maximum depth of a binary tree
Given a binary tree , Find out the maximum depth .
The depth of a binary tree is the number of nodes in the longest path from the root node to the farthest leaf node .
explain : A leaf node is a node that has no children .
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
} else {
int left = maxDepth(root.left);
int right = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}
}
}
Give you the root node of the binary tree root And an integer representing the sum of goals targetSum . Determine if there is Root node to leaf node The path of , The sum of the values of all nodes in this path is equal to the target and targetSum . If there is , return true ; otherwise , return false .
Leaf node A node without children .
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null){
return false;
}
targetSum -= root.val;
// leaf node
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
return targetSum == 0;
}
if (root.left != null){
boolean left = hasPathSum(root.left,targetSum);
if (left){
// eureka
return true;
}
}
if (root.left != null){
boolean right = hasPathSum(root.right,targetSum);
if (right){
// eureka
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
边栏推荐
- MATLAB中histogram函数的使用
- 《DAMA数据管理知识体系指南》:章节分值占比
- 自动化测试-Selenium
- Katalon Studio Enterprise
- 【Mysql】redo log,undo log 和binlog详解(四)
- [pytest learning] after the pytest case fails to execute, the others will not be executed
- Database backup (MySQL)
- 端口规划与APJ
- Authing 双周动态:应用市场上线(5 .10 —5 .22 )
- Go get downloaded package path
猜你喜欢

Recyclerview cache reuse analysis, source code interpretation

Intranet penetration based on UDP port guessing

vscode保存代碼時自動eslint格式化

Leetcode力扣刷题

04_特征工程—特征选择

Dynamic: capturing network dynamics using dynamic graph representation learning

Authing biweekly news: online application market (5.10-5.22)

04_ Feature engineering feature selection
Port planning and APJ

A set of ThinkPHP wechat applet mall source code with background management
随机推荐
CentOS7服务器配置(四)---安装redis
我的CのERROR们
Science popularization genius on the left, madman on the right
Vscode configures eslint to automatically format an error "auto fix is enabled by default. use the single string form“
ffmpeg硬编解码 Inter QSV
JSP page initial loading method
Is it safe for Xiaobai to open an account directly on the flush?
AXI协议基础知识
ShellBrowser . NET Crack
Use exe4j to convert The jar file is packaged as Exe file
为什么udp流设置1316字节
Create database instance
What subclasses inherit, polymorphism, and upward transformation
Computing philosophy behind authoring
JPA failed to save multiple entities circularly
Docker安装mysql5.7(开启binlog功能、修改字符)
Cs0006 C failed to find metadata file "c:\users\... Problem
用实际案例分析PMP与ACP应该考哪个?哪个更有用?
error:指针作为函数参数错误总结
vscode保存代碼時自動eslint格式化