当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode probability interview shock series 11~15
Leetcode probability interview shock series 11~15
2022-06-24 07:14:00 【Slow ploughing of stupid cattle】
Catalog
14. The first 2 The strong player takes the second place
11. Perfect hand
Problem description
From a deck of washed cards (52 Zhang ) To draw 13 Zhang , Get the perfect hand ( To get the 13 Zhang is of the same design and color ) What's the probability of .
Ideas and algorithms
from 52 Zhang renqu 13 Zhang's general ( Because it has nothing to do with order ) The number of combinations is  .
.
among 13 The only ones with the same color are 4 In this case .
So the probability is 
Monte Carlo simulation
import numpy as np
# Be careful , If you don't specify 'float32' The data type of will overflow and cause calculation error
nomi = np.prod(range(52,39,-1),dtype='float32')
denom = np.prod(range(1,14),dtype='float32')
combinations_52_13 = nomi/ denom
p = 4/combinations_52_13
print(nomi, denom, combinations_52_13,p) from math import factorial as fac
p = 4.0 * fac(13) * fac(39) / fac(52)
print("{:.6e}".format(p))
12. Double dice
Problem description
Dice is a popular game in America , The following rules :
Roll two dice at a time and only look at the points and . The sum of the points on the first throw is recorded as x. if x yes 7 or 11, Players win , Game over ; if x yes 2、3 or 12, You lose , In other cases, you need to continue throwing . From the second throw , If you throw the first count and x, Then win ; If you throw 7, You lose . Repeat the toss until the winner is decided .
ask : What is the probability of winning ?
Ideas and algorithms
Use a state machine to represent the progress state of the game .

The possible value of points per throw is {2,3,4,...,12}, The probabilities are {1/36, 2/36, 3/36, 4/36, 5/36, 6/36, 5/36, 4/36, 3/36, 2/36, 1/36}.
As can be seen from the above state machine , The probability of winning the first throw is 2/9, The probability of failure is 1/9.
Enter after the first throw CONTINUE The probability of the state is 2/3, Among them is {4,5,6,8,9,10} this 6 It's possible  value . Get into CONTINUE Post state , Yes 1/6 The probability of hitting 7 Lose the game , Need to hit the same... As the first time
value . Get into CONTINUE Post state , Yes 1/6 The probability of hitting 7 Lose the game , Need to hit the same... As the first time  Worth winning , The probability is
Worth winning , The probability is  , This probability depends on the value of the first throw
, This probability depends on the value of the first throw  ; In addition, there are
; In addition, there are  The probability remains at CONTINUE Status to continue the game , So for every possible
The probability remains at CONTINUE Status to continue the game , So for every possible  value ( The following calculates the probability of failure , This is easier than calculating the probability of winning ):
value ( The following calculates the probability of failure , This is easier than calculating the probability of winning ):
The probability of failure after the second throw is 1/6
The probability of failure after the third throw is  , Because it needs to be kept at... After the second throw CONTINUE state
, Because it needs to be kept at... After the second throw CONTINUE state
Similarly ...
In the k The probability of failure after a throw is  ...
...
From this we can get First throw value  Of Under the condition of , from ( Enter after the first throw )CONTINUE The total probability of failure at the beginning of the state is
Of Under the condition of , from ( Enter after the first throw )CONTINUE The total probability of failure at the beginning of the state is  .
.
Thus, the total winning probability is the sum of the winning probability after the first throw and the winning probability in the subsequent throws , The first 2 Part of it is 6 It's possible  The sum of conditional probabilities under the condition of , As shown below :
The sum of conditional probabilities under the condition of , As shown below :
![P(loss) = \frac{1}{9} + \sum\limits_{x\in [4,5,6,8,9,10]}P(loss|x)\cdot P(x) = \sum\limits_{x\in [4,5,6,8,9,10]}\frac{P(x)}{1+6P(x)}](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/24/202206240051274264_8.gif)
By calculation, we can get  ,
,
therefore ,
Monte Carlo simulation
from multiprocessing import Pool
import numpy as np
def throw2(x0):
# After the second throw
x1 = np.random.randint(1, 7)
x2 = np.random.randint(1, 7)
x = x1 + x2
if x == 7:
return 0
elif x == x0:
return 1
else:
return throw2(x0)
def throw1():
# The first throw
x1 = np.random.randint(1, 7)
x2 = np.random.randint(1, 7)
x = x1 + x2
if x == 7 or x == 11:
return 1
elif x == 2 or x == 3 or x == 12:
return 0
else:
return throw2(x)
def test(T):
np.random.seed()
n = 0
for _ in range(T):
n += throw1()
return n / T
T = int(1e7)
args = [T] * 8
pool = Pool(8)
probs = pool.map(test, args)
for prob in probs:
print("Probability of win: {:.6f}".format(prob))
author :FennelDumplings
link :https://leetcode.cn/leetbook/read/probability-problems/no5h33/
source : Power button (LeetCode)
The copyright belongs to the author . Commercial reprint please contact the author for authorization , Non-commercial reprint please indicate the source .13. Collect coupons
Problem description
There is a coupon in each box , The coupons are 5 Kind of , The number is 1 To 5. All must be collected 5 Coupons to get prizes .
ask : How many boxes do you need to open to collect a complete set of coupons ?
Ideas and algorithms
Collect the first , Just open a box . Because every box must have a coupon .
Collect the second , It is required that the coupons contained in the opened box are different from those already collected . Yes 1/5 The probability is the same ,4/5 The probability is different ...
The following state transition diagram can be obtained :

among , state k Indicates that... Has been collected k Different coupons . The number on the edge represents the transition probability .
remember  Represents slave state
Represents slave state  Set out to collect full 5 Zhang coupons ( I.e. reaching the state 5) Mathematical expectation of the number of boxes to be opened , Then the equation shown in the above figure can be listed , Finally, we can get
Set out to collect full 5 Zhang coupons ( I.e. reaching the state 5) Mathematical expectation of the number of boxes to be opened , Then the equation shown in the above figure can be listed , Finally, we can get  That is, the collection is full 5 The mathematical expectation of the total number of open boxes required for a coupon .
That is, the collection is full 5 The mathematical expectation of the total number of open boxes required for a coupon .
The official solution gives another idea , Excerpts are as follows for reference :

And so on ...
Monte Carlo simulation
import numpy as np
import operator
from multiprocessing import Pool
from functools import reduce
def run():
setting = set()
n = 0
while True:
n += 1
x = np.random.randint(1, 6)
if x in setting:
continue
setting.add(x)
if len(setting) == 5:
break
return n
def test(T):
np.random.seed()
y = (run() for _ in range(T))
n = reduce(operator.add, y)
return n / T
T = int(1e7)
args = [T] * 8
pool = Pool(8)
ts = pool.map(test, args)
for t in ts:
print("{:.6f} coupons on average are required".format(t))
author :FennelDumplings
link :https://leetcode.cn/leetbook/read/probability-problems/no5h33/
source : Power button (LeetCode)
The copyright belongs to the author . Commercial reprint please contact the author for authorization , Non-commercial reprint please indicate the source .14. The first 2 The strong player takes the second place
Problem description

One by 8 Individual elimination tournament , The match chart is shown in the figure above .8 Individuals are randomly assigned to 1~8 The location .
The second best people always lose to the strongest people , At the same time, it will always win the rest of the people . The loser in the final gets the runner up in the competition .
ask : What is the probability that the second best person will win the second place ?
Ideas and algorithms
The implicit premise of this question is that the winning and losing relationship is determined by the strength ranking .
therefore , Ranking the first 2 In fact, the probability that a contestant will win the second place is that he and the No 1 The probability that the contestants will score in different half zones .8 Individuals are randomly assigned to 1~8 The total number of allocations at position is the number of permutations  , How many of these permutations are the two in different half zones ?
, How many of these permutations are the two in different half zones ?
Make  Express 1 Contestant No. 1 is in the upper half ;
Express 1 Contestant No. 1 is in the upper half ; Express 1 Contestant No. 1 is in the second half ;
Express 1 Contestant No. 1 is in the second half ; Express 2 Contestant No. 1 is in the upper half ;
Express 2 Contestant No. 1 is in the upper half ; Express 2 Contestant No. 1 is in the second half . Then the probability of the two points in different half regions is obtained by the following full probability formula :
Express 2 Contestant No. 1 is in the second half . Then the probability of the two points in different half regions is obtained by the following full probability formula :

consider 1 Contestant No. 1 is divided into the lower half of the area 2 The conditional probability that contestant No. 1 will score in the upper half of the zone .1 Contestant No. 1 has occupied a position in the lower half of the area , Next, assign 2 Contestant No , Yes 7 Two locations are optional , Among them, the probability of selecting the upper half area is naturally  . The same can be ( Or from symmetry )1 Contestant No. 1 is divided into the first half of the zone 2 The conditional probability for contestant No. 1 to score in the lower half of the zone is also
. The same can be ( Or from symmetry )1 Contestant No. 1 is divided into the first half of the zone 2 The conditional probability for contestant No. 1 to score in the lower half of the zone is also  . By substituting the above full probability formula, we can get that the probability of the two distributions in different half regions is :
. By substituting the above full probability formula, we can get that the probability of the two distributions in different half regions is :
Monte Carlo simulation
import numpy as np
import operator
from multiprocessing import Pool
from functools import reduce
ladder = range(8)
def run():
l = np.random.permutation(ladder)
x = int(np.where(l == 0)[0][0])
y = int(np.where(l == 1)[0][0])
return (x <= 3 and y >= 4) or (x >= 4 and y <= 3)
def test(T):
np.random.seed()
y = (run() for _ in range(T))
n = reduce(operator.add, y)
return n / T
T = int(1e7)
args = [T] * 8
pool = Pool(8)
ts = pool.map(test, args)
for t in ts:
print("P(the second-best player wins the runner-up cup): {:.6f}".format(t))
author :FennelDumplings
link :https://leetcode.cn/leetbook/read/probability-problems/no5b8m/
source : Power button (LeetCode)
The copyright belongs to the author . Commercial reprint please contact the author for authorization , Non-commercial reprint please indicate the source .
Source of topic ( The explanation and code also refer to ):
See also :
Leetcode Probability interview assault series 1~5
Leetcode Probability interview assault series 6~10
Leetcode General catalogue of daily questions ( Dynamic update ...)
边栏推荐
- 【愚公系列】2022年6月 ASP.NET Core下CellReport报表工具基本介绍和使用
- High energy ahead: Figure 18 shows you how to use the waterfall chart to visually reflect data changes
- One year since joining Tencent
- Huawei cloud database advanced learning
- 0 foundation a literature club low code development member management applet (I)
- Web messaging and woker classification: talking about the cross thread and cross page communication of PostMessage
- JVM調試工具-Arthas
- 【均衡器】LS均衡器,DEF均衡器以及LMMSE均衡器的误码率性能对比仿真
- What is domain name resolution? What if the domain name cannot be resolved?
- What is the OSI seven layer model? What is the role of each layer?
猜你喜欢

Decryption of the original divine square stone mechanism

MAUI使用Masa blazor组件库
【帧率倍频】基于FPGA的视频帧率倍频系统verilog开发实现
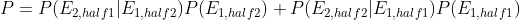
Leetcode概率题面试突击系列11~15

You have a chance, here is a stage
File system notes

In JS, the regular expression verifies the hour and minute, and converts the input string to the corresponding hour and minute
【小技巧】使用matlab的深度学习工具箱deepNetworkDesigner快速设计

Unexpected token u in JSON at position 0
Canal安装配置
随机推荐
Huawei cloud database advanced learning
c#:互斥锁的使用
大厂不是衡量能力的唯一出路,上财学姐毕业三年的经验分享
The data synchronization tool dataX has officially supported reading and writing tdengine
How do I turn off win10 automatic update? What are the good ways?
Outils de débogage JVM - Arthas
Tencent host security captures Yapi remote code execution 0day vulnerability for wild exploitation. The attack is spreading and can be intercepted by firewall
Win11怎么设置让CPU性能全开?Win11CPU怎么设置高性能模式?
JVM調試工具-Arthas
【云驻共创】华为云HCIA-IoT V2.5培训系列内容之物联网概览
MFC使用控制台时 项目路径中不能有空格和中文,否则会报错误 LNK1342 未能保存要编辑的二进制文件的备份副本等
Unexpected token u in JSON at position 0
Interpreting top-level design of AI robot industry development
多传感器融合track fusion
【问题解决】虚拟机配置静态ip
Become TD hero, a superhero who changes the world with Technology | invitation from tdengine community
RealNetworks vs. Microsoft: the battle in the early streaming media industry
MFC多线程 信号量CSemaphore 临界区与互斥 事件
Record the problem location experience when an application is suddenly killed
Decryption of the original divine square stone mechanism