当前位置:网站首页>SQL rewriting Series 6: predicate derivation
SQL rewriting Series 6: predicate derivation
2022-07-24 23:36:00 【Official blog of oceanbase database】
Introduction to the series of articles
OceanBase yes 100% Independent research and development , continuity 9 Annual stable support double 11, Innovative launch “ Three places five centers ” New urban disaster recovery standards , yes The only global stay TPC-C and TPC-H A domestic native distributed database that has set a new world record in the test , On 2021 year 6 The source code was officially opened in January . Query optimizer is the core module of relational database system , It is the key and difficult point of database kernel development , It is also a measure of the maturity of the whole database system “ Touchstone ”. To help you better understand OceanBase Query optimizer , We will write a series of articles about query rewriting , Take you to better grasp the essence of query rewriting , Familiar with complex SQL Equivalence of , Write effective SQL. This article is about OceanBase Rewrite the sixth part of the series , We will focus on predicate derivation , Welcome to explore ~
The columnist introduces
OceanBase Optimizer team , from OceanBase Senior technical expert Xifeng 、 Led by technical experts such as Shan Wen , We are committed to building a world leading distributed query optimizer .
Series content composition
This query rewriting series not only includes sub query optimization 、 Aggregate function optimization 、 Window function optimization 、 Four modules of complex expression optimization , This article will elaborate on the derivation of predicates , There are more modules , Coming soon .
Welcome to your attention OceanBase Open source users ( Nail No :33254054), Group entry and OceanBase Communicate with the query optimizer team .
One 、 Why predicate derivation is needed
Businesses usually only read part of the data when accessing the database , Therefore, some predicates will be specified to filter out unwanted data . When implementing a query semantics , We can use many different predicate combinations .
for example :Q1 and Q2 They are all read from the database with the number 1024 Remaining ticket information of film arrangement . These two queries use different predicate sets , The same query effect is achieved . In terms of query performance ,Q2 Filter predicates written better .Q2 Medium T.play_id = 1024 Is a base table filter predicate . It can filter out a batch of data in advance , Reduce the amount of data participating in the connection . further , When TICKETS Exists on the table (play_id, sale_date, seat) When indexing , On the one hand, the query optimizer can determine a very good data scanning range ; On the other hand, index order can also be used to eliminate ORDER BY The resulting sort operation . Final , The whole query only needs to read T Tabular 10 Row data .
Q1:
SELECT P.show_time, T.ticket_id, T.seat
FROM PLAY P, TICKETS T
WHERE P.play_id = T.play_id AND P.play_id = 1024 AND T.sale_date is NULL
ORDER BY T.seat LIMIT 10;
Q2:
SELECT P.show_time, T.ticket_id, T.seat
FROM PLAY P, TICKETS T
WHERE T.play_id = 1024 and P.play_id = 1024 AND T.sale_date is NULL
ORDER BY T.seat LIMIT 10;
To ensure good query performance , The database kernel needs to be capable of Q1 To query and deduce T.play_id = 1024 Such predicates . This ability we call “ Predicate derivation ”. stay OceanBase in , We aim at different predicate usage scenarios , Design and implement a variety of predicate derivation strategies . The following will mainly introduce these derivation strategies .
Two 、 Predicate derivation
Predicate derivation is based on multiple predicates , Some new predicates are derived . for example ,Q1 in P.play_id = T.play_id and P.play_id = 1024 Two predicates , A new predicate can be derived T.play_id = 1024. This is a T Single table filter predicate on table , It can be filtered out in advance T The data on the table , Reduce the amount of data involved in multi table connections . Deriving new predicates is meaningful in many optimization scenarios .
Size comparison derivation
Given multiple predicates for size comparison , We can arrange the size relationship between multiple expressions . for example , In the following query , There is T1.C1 > T2.C1 and T1.C1 < 10 Two predicates , Then we can arrange the size relationship between them as :T2.C1 <T1.C1 < 10 . obviously , For this scenario , We can derive a new predicate T2.C1 < 10 . This predicate can be filtered in advance T2 The data table , Reduce the amount of data participating in the connection .
SELECT * FROM T1, T2 WHERE T1.C1 > T2.C1 AND T1.C1 < 10;
SELECT * FROM T1, T2 WHERE T1.C1 > T2.C1 AND T1.C1 < 10 AND T2.C1 > 10;
Yes Q1 For inquiry , We can also use the size relationship given by the predicate (T.play_id = P.play_id = 1024), Derive a new predicate T.play_id = 1024. further , After deriving the new predicate , We can also eliminate a redundant join predicate P.play_id = T.play_id, Finally get the query Q2.
Complex predicate derivation
Except for size comparison 、 Besides the predicate of equivalence comparison , More complex predicates are often used in queries . for example , Use LIKE Prefix match the string . Given a complex predicate and some equivalent comparison Relations , We can also derive some new predicates . for example , The following query contains T1.C1 = T2.C1 and T1.C1 LIKE 'ABC%' Two predicates . because T1.C1 and T2.C1 There is an equivalence relationship , therefore ,T2.C1 LIKE 'ABC%' It must also be established . This predicate can also be filtered in advance T2 The data table , Reduce the amount of data participating in the connection .
SELECT *
FROM T1, T2 WHERE T1.C1 = T2.C1 AND T1.C1 LIKE 'ABC%';
SELECT *
FROM T1, T2 WHERE T1.C1 = T2.C1 AND T1.C1 LIKE 'ABC%' AND T2.C1 LIKE 'ABC%';
Given the equivalence relationship between two columns , And any predicate on one of the columns , We can almost derive predicates on another column . But that doesn't mean , We always have to derive new predicates . The computational cost of some complex predicates themselves may be relatively high , And the filterability of the predicate itself is not good , Derivation produces new complex predicates instead It will lead to query performance degradation . In fact, when making decisions , We should first judge whether the derived new predicate can filter out a large amount of data .
OR Predicate derivation
OR Predicates are also common in business queries . In the following query , There is a very interesting OR The predicate . First , This predicate refers to the data of multiple tables , therefore , This predicate can only filter the results after multi table connection . What's interesting is that : This OR In each branch of , It's all about T1 Predicate on table . We can construct T1 Filter predicates on the table :T1.C2 = 1 OR T1.C2 =2 . This is a single table filter predicate , It can be filtered in advance T1 The data of , Reduce the number of rows participating in the connection .
SELECT * FROM T1, T2
WHERE T1.C1 = T2.C1 AND
((T1.C2 = 1) OR (T1.C2 = 2 AND T2.C2 = 2))
SELECT * FROM T1 ,T2
WHERE T1.C1 = T2.C1 AND
(T1.C2 = 1 OR T1.C2 = 2) AND
((T1.C2 = 1) OR (T1.C2 = 2 AND T2.C2 = 2));
MIN/MAX Predicate derivation
The derivation of the above two scenarios is relatively intuitive . Now we introduce a more “ Obscurity ” Predicate derivation of .
In the following query , There is one. MAX(C2) > 10 Of HAVING The predicate . According to this predicate , We can derive a C2 > 10 Filter predicate of . The rationality here lies in : The original query is ultimately retained only MAX(C2) > 10 Group aggregation results , If a given row is not satisfied C2 > 10, There are two situations :
1、 This line is not in the same group C2 The maximum of ( It doesn't make sense for grouping aggregation , Can filter )
2、 This line is in the same group C2 The maximum of ( Will be HAVING Predicate filtering )
In both cases , dissatisfaction C2 > 10 All data can be filtered in advance . therefore , We can derive a new predicate C2 > 10.
SELECT C1, MAX(C2)
FROM T1
GROUP BY C1 HAVING MAX(C2) > 10;
=>
SELECT C1, MAX(C2)
FROM T1
WHERE C2 > 10
GROUP BY C1 HAVING MAX(C2) > 10;
Allied , Give the following band MIN Query of aggregate function , We can also derive a new predicate . These predicates can filter out some data in advance , Reduce the computation of grouping aggregation operations , Improve query performance .
SELECT C1, MIN(C2)
FROM T1
GROUP BY C1 HAVING MIN(C2) < 10;
=>
SELECT C1, MIN(C2)
FROM T1
WHERE C2 < 10
GROUP BY C1 HAVING MIN(C2) < 10;
This derivation method has many properties for the query form . Readers can consider , If there are other aggregate functions in the query , Whether the predicate derivation above can also be done ?
Derivation trap
There are also some pitfalls that are easy to make mistakes in deriving new predicates . for example : Consider the following query Q3, Can we according to T1.C_CI = ‘A’ and T1.C_CI = T2.C_BIN Derivation produces a new predicate T2.C_BIN = ‘A’ ?
This derivation is wrong .
This is because , When comparing predicates here , The way of comparison is different . stay T1.C_CI = ‘A’ in , String comparison is case insensitive , namely :‘a’, ‘A’ All meet the filtering conditions . but T1.C_CI = T2.C_BIN Is to compare strings in a case sensitive way . Combine these two predicates , It can only be inferred :T2.C_BIN The values for ‘a’ perhaps ‘A’. however T2.C_BIN = 'A’ Case sensitive comparison , It will directly filter out the value of ‘a’ The data of . therefore , It is incorrect to derive this new predicate .
CREATE TABLE T1 (C_CI VARCHAR(10) UTF8_GENERAL_CI);
CREATE TABLE T2 (C_BIN VARCHAR(10) UTF8_BIN);
Q3: SELECT * FROM T1, T2
WHERE T1.C_CI = 'ABC' AND T1.C_CI = T2.C_BIN;
=>
Q4: SELECT * FROM T1, T2
WHERE T1.C_CI = 'ABC' AND T1.C_CI = T2.C_BIN AND T2.C_BIN = 'ABC';
3、 ... and 、 summary
This paper mainly introduces the derivation of some predicates . Deriving new predicates is very important for query optimization . Based on the new predicate , The query optimizer can choose a better index , Generate better base table access paths . therefore , Predicate derivation is a very important optimization technique . There are many predicate related optimizations , In the next article , We will introduce the technology of predicate movement . It will adjust the position of predicates in the query , Move the predicate to a more reasonable position , Improve the performance of the whole query .
边栏推荐
- The specified data is grouped and the number of repetitions is obtained in Oracle
- 如何创建和管理自定义的配置信息
- 聊聊 Redis 是如何进行请求处理
- [zero basis] SQL injection for PHP code audit
- 解决JSP无法使用session.getAttribute()
- First engineering practice, or first engineering thought—— An undergraduate's perception from learning oi to learning development
- 常用在线测试工具集合
- Notes of Teacher Li Hongyi's 2020 in-depth learning series 4
- Coding builds an image, inherits the self built basic image, and reports an error unauthorized: invalid credential Please confirm that you have entered the correct user name and password.
- Remember the problem of using redisson to step on the pit once
猜你喜欢

Xiezhendong: Exploration and practice of digital transformation and upgrading of public transport industry

芯片的功耗
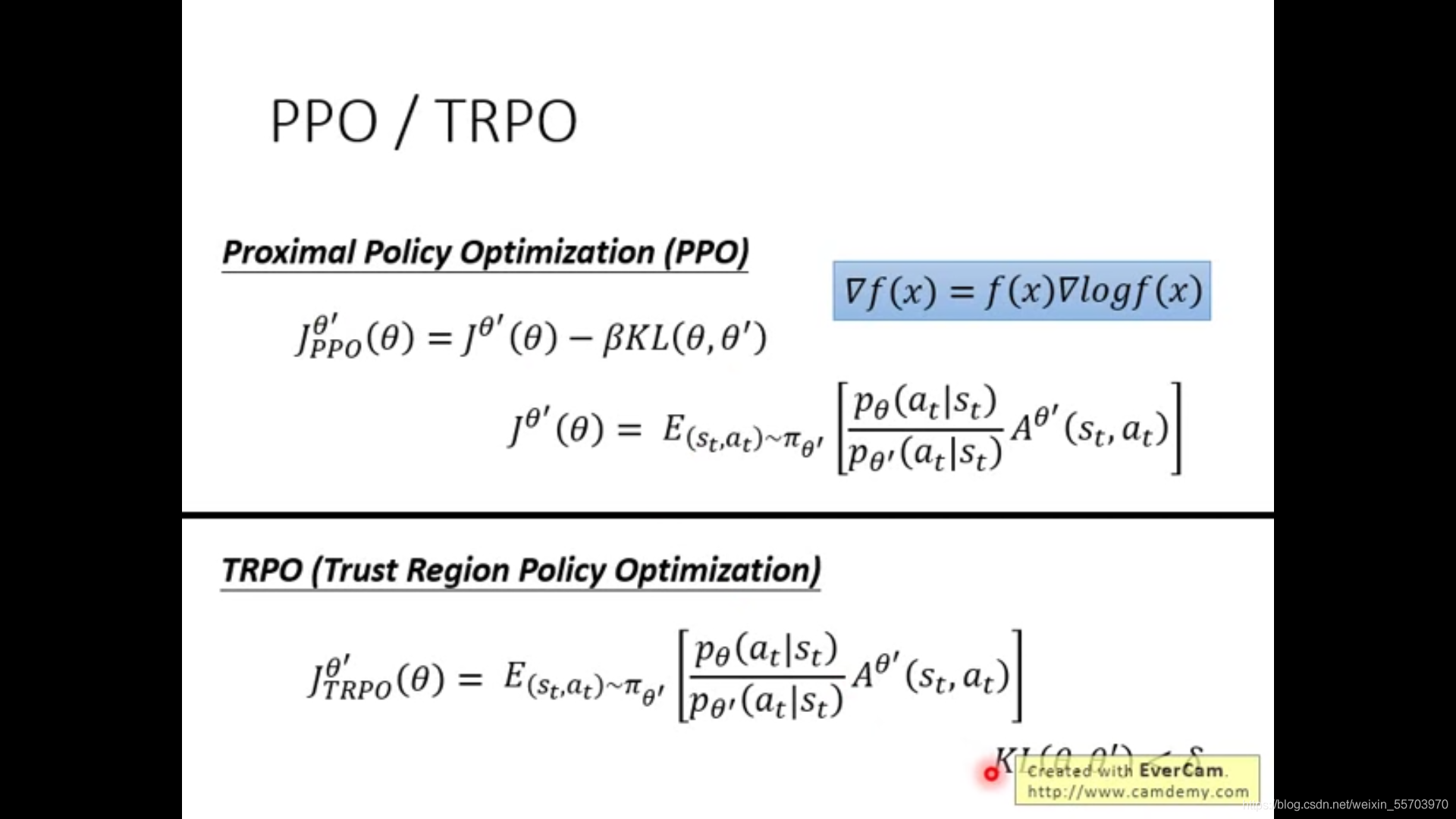
Notes of Teacher Li Hongyi's 2020 in-depth learning series 5

Paper notes: accurate causal influence on discrete data

云计算三类巨头:IaaS、PaaS、SaaS,分别是什么意思,应用场景是什么?

多线程&高并发(全网最新:面试题 + 导图 + 笔记)面试手稳心不慌

基于Verilog HDL的数字秒表

1、 MFC introduction

Go basic notes_ 4_ map

Understanding complexity and simple sorting operation
随机推荐
P3201 [hnoi2009] dream pudding heuristic merge
Qt | 事件系统 QEvent
ShardingSphere-数据库分库分表简介
Old Du servlet JSP
Nvida tensorrt deployment (I)
国信证券手机开户安全吗
Multithreading & high concurrency (the latest in the whole network: interview questions + map + Notes) the interviewer is calm
JS ------ Chapter 5 functions and events
Salesforce zero foundation learning (116) workflow - & gt; On flow
Notes of Teacher Li Hongyi's 2020 in-depth learning series 2
Browser cache
Notes of Teacher Li Hongyi's 2020 in-depth learning series lecture 1
SQLite database operation
Development direction and problems of optaplanner
Network Security Learning (IV) user and group management, NTFS
基于TensorFlow和Keras的卷积神经网络实现猫狗数据集分类实验
Let me introduce you to the partition automatic management of data warehouse
Background image and QR code synthesis
Js----- Chapter 4 array
Lidar obstacle detection and tracking: CUDA European clustering