当前位置:网站首页>DeepLearing4j's deep learning Yolo Tiny realizes target detection
DeepLearing4j's deep learning Yolo Tiny realizes target detection
2022-07-30 07:08:00 【victorkevin】
Yolo Tiny是 Yolo2的简化版,Although a bit outdated, it is still useful for many object detection application scenarios,本示例利用DeepLearing4j构建Yolo算法实现目标检测,The following figure is the network structure of this example:

// parameters matching the pretrained TinyYOLO model
int width = 416;
int height = 416;
int nChannels = 3;
int gridWidth = 13;
int gridHeight = 13;
// number classes (digits) for the SVHN datasets
int nClasses = 5;
// parameters for the Yolo2OutputLayer
double[][] priorBoxes = { { 1.5, 2.2 }, { 1.4, 1.95 }, { 1.8, 3.3 }, { 2.4, 2.9 }, { 1.7, 2.2 } };
double detectionThreshold = 0.8;
// parameters for the training phase
int batchSize = 10;
int nEpochs = 20;
int seed = 123;
Random rng = new Random(seed);
File imageDir = new File("D:\\train");
InputSplit[] data = new FileSplit(imageDir, NativeImageLoader.ALLOWED_FORMATS, rng).sample(null, 0.9, 0.1);
InputSplit trainData = data[0];
InputSplit testData = data[1];
ObjectDetectionRecordReader recordReaderTrain = new ObjectDetectionRecordReader(height, width, nChannels, gridHeight, gridWidth,
new YoloLabelProvider(imageDir.getAbsolutePath()));
recordReaderTrain.initialize(trainData);
ObjectDetectionRecordReader recordReaderTest = new ObjectDetectionRecordReader(height, width, nChannels, gridHeight, gridWidth,
new YoloLabelProvider(imageDir.getAbsolutePath()));
recordReaderTest.initialize(testData);
// ObjectDetectionRecordReader performs regression, so we need to specify it here
RecordReaderDataSetIterator train = new RecordReaderDataSetIterator(recordReaderTrain, batchSize, 1, 1, true);
train.setPreProcessor(new ImagePreProcessingScaler(0, 1));
RecordReaderDataSetIterator test = new RecordReaderDataSetIterator(recordReaderTest, 1, 1, 1, true);
test.setPreProcessor(new ImagePreProcessingScaler(0, 1));
ComputationGraph model;
String modelFilename = "D:\\model.zip";
if (new File(modelFilename).exists()) {
this.output("Load model...");
model = ComputationGraph.load(new File(modelFilename), true);
} else {
this.output("Build model...");
model = TinyYOLO.builder().numClasses(nClasses).priorBoxes(priorBoxes).build().init();
System.out.println(model.summary(InputType.convolutional(height, width, nChannels)));
this.output("Train model...");
model.setListeners(new ScoreIterationListener(1));
model.fit(train, nEpochs);
ModelSerializer.writeModel(model, modelFilename, true);
}
// visualize results on the test set
NativeImageLoader imageLoader = new NativeImageLoader();
CanvasFrame frame = new CanvasFrame("WatermelonDetection");
OpenCVFrameConverter.ToMat converter = new OpenCVFrameConverter.ToMat();
org.deeplearning4j.nn.layers.objdetect.Yolo2OutputLayer yout = (org.deeplearning4j.nn.layers.objdetect.Yolo2OutputLayer) model
.getOutputLayer(0);
List<String> labels = train.getLabels();
test.setCollectMetaData(true);
Scalar[] colormap = { RED, BLUE, GREEN, CYAN, YELLOW, MAGENTA, ORANGE, PINK, LIGHTBLUE, VIOLET };
while (test.hasNext() && frame.isVisible()) {
org.nd4j.linalg.dataset.DataSet ds = test.next();
RecordMetaDataImageURI metadata = (RecordMetaDataImageURI) ds.getExampleMetaData().get(0);
INDArray features = ds.getFeatures();
INDArray results = model.outputSingle(features);
List<DetectedObject> objs = yout.getPredictedObjects(results, detectionThreshold);
File file = new File(metadata.getURI());
Mat mat = imageLoader.asMat(features);
Mat convertedMat = new Mat();
mat.convertTo(convertedMat, CV_8U, 255, 0);
int w = metadata.getOrigW();
int h = metadata.getOrigH();
Mat image = new Mat();
resize(convertedMat, image, new Size(w, h));
for (DetectedObject obj : objs) {
double[] xy1 = obj.getTopLeftXY();
double[] xy2 = obj.getBottomRightXY();
String label = labels.get(obj.getPredictedClass());
int x1 = (int) Math.round(w * xy1[0] / gridWidth);
int y1 = (int) Math.round(h * xy1[1] / gridHeight);
int x2 = (int) Math.round(w * xy2[0] / gridWidth);
int y2 = (int) Math.round(h * xy2[1] / gridHeight);
rectangle(image, new Point(x1, y1), new Point(x2, y2), colormap[obj.getPredictedClass()]);
putText(image, label, new Point(x1 + 2, y2 - 2), FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 1, colormap[obj.getPredictedClass()]);
}
frame.setTitle(new File(metadata.getURI()).getName() + " - WatermelonDetection");
frame.setCanvasSize(w, h);
frame.showImage(converter.convert(image));
frame.waitKey();
}
frame.dispose();
参数讲解
图片的宽高 :int width = 416; int height = 416;是固定的
The number of channels in the image to color 是int nChannels = 3;The gray image isnChannels=1,默认为3
The number of feature extraction boxes of the algorithm,yolo tiny 默认个数为13 不能改变 int gridWidth = 13; int gridHeight = 13;
The number of categories to be detected,My example is5 个 int nClasses = 5
The aspect ratio of the feature extraction prior box double[][] priorBoxes = { { 1.5, 2.2 }, { 1.4, 1.95 }, { 1.8, 3.3 }, { 2.4, 2.9 }, { 1.7, 2.2 } };Yolo2The a priori box is extracted from the need to passKmeans函数,代码如下
YoloLabelProvider svhnLabelProvider = new YoloLabelProvider(trainDir.getAbsolutePath());
DistanceMeasure distanceMeasure = new YoloIOUDistanceMeasure();
KMeansPlusPlusClusterer<ImageObjectWrapper> clusterer = new KMeansPlusPlusClusterer<>(5, 15, distanceMeasure);
File[] pngFiles = trainDir.listFiles(new FilenameFilter() {
private final static String FILENAME_SUFFIX = ".png";
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
return name.endsWith(FILENAME_SUFFIX);
}
});
List<ImageObjectWrapper> clusterInput = Stream.of(pngFiles).flatMap(png -> svhnLabelProvider.getImageObjectsForPath(png.getName()).stream())
.map(imageObject -> new ImageObjectWrapper(imageObject)).filter(imageObjectWraper -> {
double[] point = imageObjectWraper.getPoint();
if (point[0] <= 32d && point[1] <= 32) {//Less than one cell does not count
return false;
}
return true;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
List<CentroidCluster<ImageObjectWrapper>> clusterResults = clusterer.cluster(clusterInput);
for (int i = 0; i < clusterResults.size(); i++) {
CentroidCluster<ImageObjectWrapper> centroidCluster = clusterResults.get(i);
double[] point = centroidCluster.getCenter().getPoint();
System.out.println(
"width:" + point[0] + " height:" + point[1] + " ratio:" + point[1] / point[0] + " size:" + centroidCluster.getPoints().size());
System.out.println("bbox amount:" + point[0] / 32 + "," + point[1] / 32);
ImageObjectWrapper maxWidthImage = centroidCluster.getPoints().stream()
.collect(Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparingDouble(ImageObjectWrapper::getWidth))).get();
ImageObjectWrapper maxHeightImage = centroidCluster.getPoints().stream()
.collect(Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparingDouble(ImageObjectWrapper::getHeight))).get();
System.out.println(" width:" + maxWidthImage.getWidth() + " height:" + maxHeightImage.getHeight());
System.out.println("-----------");
}
The above is mainly passedKmeasThe method obtains a representative aspect ratio in the training sample,需要重新Kmeasmethod of distance measurement,改成IOUFor details, please refer toYOLO v2Target detection detailed 2 计算iou - 灰信网(软件开发博客聚合)
detectionThreshold is the confidence threshold for object detection,The higher the value, the smaller the number of detected objects,准确率越高
My training set is passLabelImgproduced and formatted as Yolo,The training samples are as follows,Note that the size of the image depends on the parameters416x416的大小一致



The tag class file is classes.txt ,Includes five categoriesxi ,cake ,dan,ss,bi
The label explains the providing classYoloLabelProvider代码如下,主要作用是把LabelImg制作出来的txtThe data are transformed into algorithms that can be identified
public class YoloLabelProvider implements ImageObjectLabelProvider {
private String baseDirectory;
private List<String> labels;
public YoloLabelProvider(String baseDirectory) {
this.baseDirectory = baseDirectory;
Assert.notNull(baseDirectory, "The label directory cannot be empty");
if (!new File(baseDirectory).exists()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"baseDirectory directory does not exist. txt files should be " + "present at Expected location: " + baseDirectory);
}
String classTxtPath = FilenameUtils.concat(this.baseDirectory, "classes.txt");
File classFile = new File(classTxtPath);
Assert.isTrue(classFile.exists(), "classTxtPath does not exist");
try {
labels = Files.readAllLines(classFile.toPath());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public List<ImageObject> getImageObjectsForPath(String path) {
int idx = path.lastIndexOf('/');
idx = Math.max(idx, path.lastIndexOf('\\'));
String filename = path.substring(idx + 1, path.length() - 4); //-4: ".png"
String txtPath = FilenameUtils.concat(this.baseDirectory, filename + ".txt");
String pngPath = FilenameUtils.concat(this.baseDirectory, filename + ".png");
File txtFile = new File(txtPath);
if (!txtFile.exists()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not find TXT file for image " + path + "; expected at " + txtPath);
}
List<String> readAllLines = null;
BufferedImage image = null;
try {
image = ImageIO.read(Paths.get(pngPath).toFile());
readAllLines = Files.readAllLines(txtFile.toPath());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
int width = image.getWidth();
int height = image.getHeight();
List<ImageObject> imageObjects = readAllLines.stream().map(line -> {
String[] data = StringUtils.split(line, " ");
int centerX = Math.round(Float.valueOf(data[1]) * width);
int centerY = Math.round(Float.valueOf(data[2]) * height);
int bboxWidth = Math.round(Float.valueOf(data[3]) * width);
int bboxHeight = Math.round(Float.valueOf(data[4]) * height);
int xmin = centerX - (bboxWidth / 2);
int ymin = centerY - (bboxHeight / 2);
int xmax = centerX + (bboxWidth / 2);
int ymax = centerY + (bboxHeight / 2);
ImageObject imageObject = new ImageObject(xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, this.labels.get(Integer.valueOf(data[0])));
return imageObject;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
return imageObjects;
}
@Override
public List<ImageObject> getImageObjectsForPath(URI uri) {
return getImageObjectsForPath(uri.toString());
}
}First is training4个小时训练300多张图片,结果如下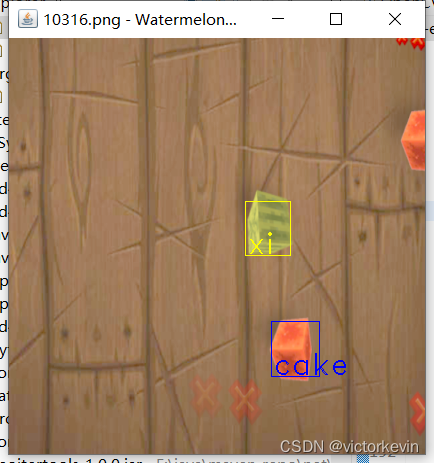
边栏推荐
- 二十一、Kotlin进阶学习:实现简单的网络访问封装
- 正则表达式语法详解及实用实例
- Self-augmented Unpaired Image Dehazing via Density and Depth Decomposition程序运行记录
- MySQL achievement method 】 【 5 words, single table SQL queries
- sql concat()函数
- TDengine cluster construction
- C语言实战小项目(传统卡牌游戏)
- Servlet basic principles and application of common API methods
- 遥感、GIS和GPS技术在水文、气象、灾害、生态、环境及卫生等应用
- Mysql client common exception analysis
猜你喜欢

常用损失函数(二):Dice Loss
Detailed introduction to the usage of Nacos configuration center

边境的悍匪—机器学习实战:第十章 Keras人工神经网络简介

基于全球模式比较计划CMIP6与区域气候-化学耦合模式 WRF-Chem 的未来大气污染变化模拟

Redis 发布/订阅

MySQL achievement method 】 【 5 words, single table SQL queries
MySQL - Multi-table query and case detailed explanation

十九、Kotlin进阶学习:1、管道数据的收和发;2、管道的关闭;3、生产者和消费者;4、管道的缓存区;

Use kotlin to extend plugins/dependencies to simplify code (after the latest version 4.0, this plugin has been deprecated, so please choose to learn, mainly to understand.)

标准化(Normalization)知识点总结
随机推荐
【总结】工业检测项目中如何选择合适的损失函数
mysql delete duplicate data in the table, (retain only one row)
The types of data structures and MySQL index
SQL Server database generation and execution of SQL scripts
基于PyTorch深度学习无人机遥感影像目标检测、地物分类及语义分割
生产力工具分享——简洁而不简单
Meta分析在生态环境领域里的应用
Knowledge distillation method of target detection
Pytorch(三):可视化工具(Tensorboard、Visdom)
Function functional interface and application
Arthas command parsing (jvm/thread/stack/heapdump)
线程的5种状态
Jdbc & Mysql timeout分析
ClickHouse查询语句详解
AAcell五号文档室——跨平台文件传输的小室一间一间的
十九、Kotlin进阶学习:1、管道数据的收和发;2、管道的关闭;3、生产者和消费者;4、管道的缓存区;
十四、Kotlin进阶学习:一、内联函数 inline;二、泛型;三、泛型约束;四、子类与子类型;
边境的悍匪—机器学习实战:第六章 决策树
Simulation of Future Air Pollution Changes Based on Global Model Comparison Program CMIP6 and Regional Climate-Chemistry Coupling Model WRF-Chem
边境的悍匪—机器学习实战:第十一章 训练深度神经网络