当前位置:网站首页>Explain in detail the three types of local variables, global variables and static variables
Explain in detail the three types of local variables, global variables and static variables
2022-06-26 00:03:00 【Little fish like to eat vegetables】
It's better to do than not , Better finish than delay
Today I want to talk about the knowledge of local variables , Because I just turned to this topic today , I happened to collect some information , So I wanted to talk about .
List of articles
1. local variable
First , Here's what I'm going to say , Local variables are defined in a function , It is only valid in this function , For example, let's take a look at such an example
public class jichu {
void a(){
String b=" Liu San ";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
jichu b1=new jichu();
b1.a();
System.out.println(b);
}
}
In this , Let me show you the screenshot again 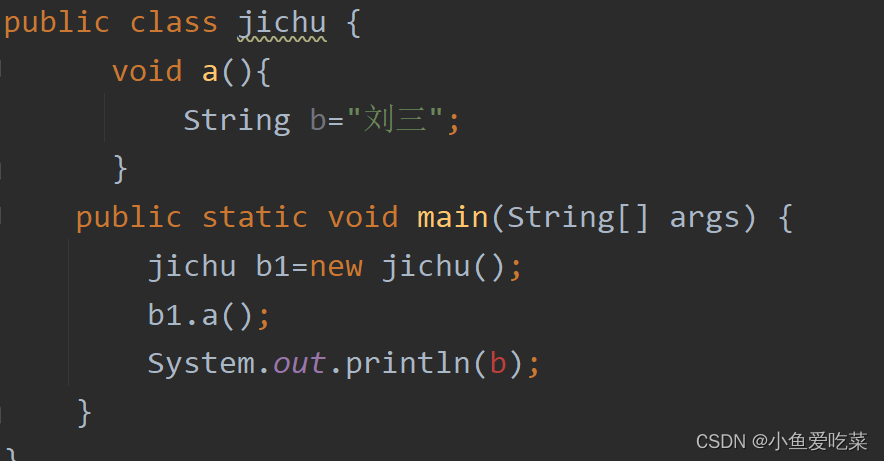
What is the cause of this , Because I define local variables in the method body , So you can't use it in the global context at this time , Now you should be able to understand local variables ?
2. Global and static variables
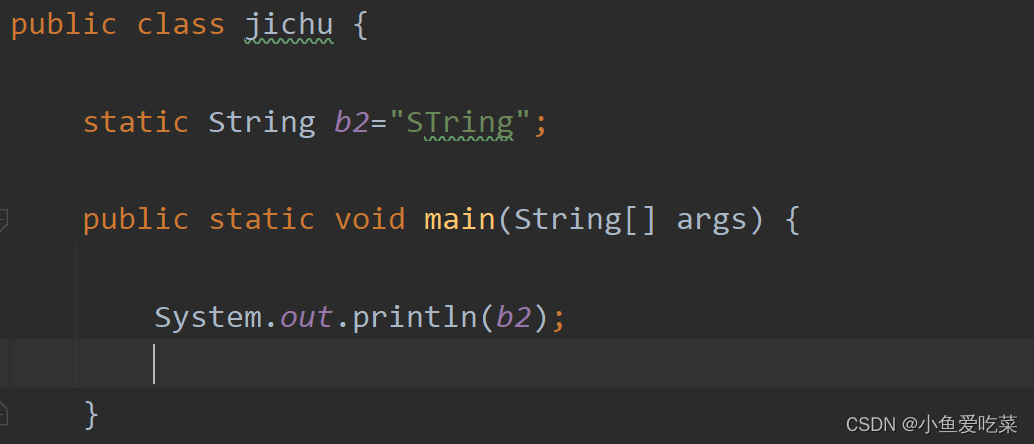
This refers to the static variable symbol static To set , So here you may think , I remember that global variables also operate outside the method body , Can you tell us the difference between the two ?
Global variables ( External variables ) Before the description of static It's a static global variable . Global variables themselves are static storage ,
Static global variables are also static storage . There is no difference between the two in the way of storage . The difference between the two is that the scope of non static global variables is the whole source program , When a source program consists of multiple source files , Non static global variables are valid in all source files . Static global variables limit their scope ,
That is, it is only valid in the source file where the variable is defined ,
It cannot be used in other source files of the same source program . Because the scope of static global variables is limited to one source file , Can only be used for functions within the source file , So you can avoid causing errors in other source files . As can be seen from the above analysis ,
Changing a local variable to a static variable changes its storage mode, that is, its lifetime . Changing a global variable to a static variable changes its scope , It limits its use .
In the middle of it , In fact, static variables refer to two settings in the method body , Another is that it can be used in the whole class .
1. The scope of a static variable depends on its position , If in a function , Is a static local variable , The scope is this function ;
2. Static global variables , Only in this document can , Although the whole program contains multiple files , But static global variables can only be used in the file that defines them , But it can't be used in other files in the program . It is an external variable that defines the storage factor as static , Its scope is from the definition point to the end of the program , The difference is that the storage type determines the storage location , Static variables are stored in the data area of memory ,
They allocate fixed bytes before the program starts running , The size of the bytes allocated during program operation does not change , Only when the program is finished , To release the occupied memory .
3. summary
- Both global variables and static variables allocate space in the static storage area , Local variables are stored on the stack , Because the method area is in the stack .
- Global variables 、 The lifetime of a static variable is the same as that of a program , After the program ends, the operating system reclaims space .
Okay , This is the end of this issue , Minghuai, I'm going to have dinner , I'll see you next time .
边栏推荐
- js实现输入开始时间和结束时间,输出其中包含多少个季,并且把对应年月打印出来
- Using Google protobuf protocol environment configuration in PHP
- 两种块级元素居中的方式
- 关于scrapy爬虫时,由spider文件将item传递到管道的方法注意事项
- 6.常用指令(上)v-cloak,v-once,v-pre
- 详解synchronize关键字
- How postman tests interfaces that require login
- Object类常用方法
- 别再吃各种维生素C片了,这6种维生素C含量最高的水果
- Talk about singleton mode!
猜你喜欢
Unsigned and signed vernacular

STEP7主站与远程I/O组网_过路老熊_新浪博客

手工制作 pl-2303hx 的USB转TTL电平串口的电路_过路老熊_新浪博客

Analyse des cinq causes profondes de l'échec du développement de produits

懒人教你用猕猴桃一月饱减16斤_过路老熊_新浪博客

文献调研(三):数据驱动的建筑能耗预测模型综述

6. common instructions (upper) v-cloak, v-once, v-pre

Literature research (IV): Hourly building power consumption prediction based on case-based reasoning, Ann and PCA
Common problems encountered when creating and publishing packages using NPM
![[wechat official account H5] generates a QR code with parameters to enter the official account attention page to listen to user-defined menu bar for official account events (server)](/img/d9/935bad29005e5846dc514c966e3b0e.png)
[wechat official account H5] generates a QR code with parameters to enter the official account attention page to listen to user-defined menu bar for official account events (server)
随机推荐
Talk about singleton mode!
Hand made pl-2303hx USB to TTL level serial port circuit_ Old bear passing by_ Sina blog
Shredding Company poj 1416
Implement const in Es5
推荐系统设计
PHP interprocess pass file descriptor
DHCP review
Stop eating vitamin C tablets. These six fruits have the highest vitamin C content
Some common operation methods of array
Use Baidu map API to set an overlay (infowindow) in the map to customize the window content
Common knowledge points in JS
Establishment of multiple background blocks in botu software_ Old bear passing by_ Sina blog
Prototype chain test questions in JS --foo and getname
Read CSV file data in tensorflow
《网络是怎么样连接的》读书笔记 - 集线器、路由器和路由器(三)
Literature research (IV): Hourly building power consumption prediction based on case-based reasoning, Ann and PCA
今天说说String相关知识点
Line height for small use
Sword finger offer 48 Longest substring without duplicate characters
关于scrapy爬虫时,由spider文件将item传递到管道的方法注意事项