当前位置:网站首页>Which programming language is the most cumbersome to implement Hello world?
Which programming language is the most cumbersome to implement Hello world?
2022-06-25 04:42:00 【Dafang teacher talks about SCM】
Which programming language implements hello world Most cumbersome ?
explain :
· Because assembly is a language that directly faces the bottom layer , So the simplest program also involves many low-level details, which makes it obscure ( Unlike C Direct one printf Get it done );
· This article passes the simplest hello world Program , Understand registers 、 Memory 、 section 、 Instructions 、 system call , In the simple operation principle of the program ;
Talk is cheap, show me your code!
; Source file name :test.asm
; Execution file name :test
; Compiling method :
;nasm -f elf64 -g -F dwarf test.asm -l test.lst
;gcc -o test test.o -no-pie
section .data; stay .data Section writes data
msg: db "hello world",10;10 Corresponding ascii Is a newline
msgLen equ $-msg;equ It's a pseudo instruction , This line of code means msgLen Means msg The placeholder length of the string ( byte )
section .text; stay .text Write code
global main; The code entry label of the program is main( Enable the program to find the first instruction when executing )
main:; This label essentially refers to .text The memory address of the first instruction of section
; Screen printing
mov rax, 1;sys_write(x86-64)
mov rdi, 1;1 It's standard output
mov rsi, msg
mov rdx, msgLen; String length , barring 0
syscall;64 Bit int 0x80 Instructions
; Exit procedure
mov rax, 60;exit(x86-64)
mov rdi, 0; Parameters 0, Combined with the previous instruction is exit(0)
section sentence
To understand section The function of sentences , First of all, we should have a preliminary understanding of the execution principle of the program , as follows ,

· The compiler compiles the assembly code , According to Linux Of ELF(linux The executable file format of ) Compile ( For example, insert ELF header、program header、section header、got etc. );
· While the program is running , Load the code and some initialized data into the memory according to the format ( Distributed to all section);
·stack section , In the process of program running, data will be pushed or popped according to program logic (stack Section generally does not store code );
·heap section , An area for the most free data storage of a program ( For example, when C Of malloc This area is used when the function applies for memory );
·bss section , Used to store defined but uninitialized data ( for example C Of int i、char ch[10]), Commonly used in program data receiving buffer ;
·data section , Used to store data that has been defined and initialized ( Be similar to C The constant );
·text section , For storing code ( The code of the function is also stored in this area , It's not stored in stack Area );
in summary ,section Statement is used to distinguish regions of assembly code .
syscall And interrupt vector table
Introducing syscall Before the order , Need to introduce first linux Several key concepts of , as follows ,
· User space ( The essence of user space is the specified memory space . These spaces are used to run user programs , for example nginx、apache);
· Kernel space ( The essence of kernel space is also memory space , Kernel space is used to run the code of the operating system , In principle, user space applications cannot access kernel space , Or you can't directly access the kernel space , So the following concepts are introduced —— Interrupt vector table );
· Interrupt vector table ( The essence of interrupt vector table is an array , The elements of the array are memory addresses , These addresses point to kernel space )
syscall The relationship between the instruction and the interrupt vector table is as follows ,
 A user process wants to call a system service ( For example, output to screen 、 Open file ), It is necessary to uniformly pass the 128 Interrupt vectors , Send the system call service request according to the established data structure
A user process wants to call a system service ( For example, output to screen 、 Open file ), It is necessary to uniformly pass the 128 Interrupt vectors , Send the system call service request according to the established data structure
· Applications cannot access kernel space at will , Need to access through established rules , So the interrupt vector table is designed ( This design has safety significance );
· Because the interrupt vector table has “ indicator ” The direction meaning of , So it's called “ vector ” surface ;
in summary , At terminal ( It's usually the screen ) Print hello world, In essence, it is a process of calling system services .
linux system call (sys_write)
As mentioned above , Want to call system services , You need to follow the established data structure of this service , Then organize the data , Xiang di 128 The interrupt vector of No. sends a service call request , Here's the picture ,
 Organize what needs to be printed , adopt syscall Instruction to 128 No. interrupt sending “ standard output ” Service invocation request for
Organize what needs to be printed , adopt syscall Instruction to 128 No. interrupt sending “ standard output ” Service invocation request for
· register rax The content of should be set to 1. During a system call , This register is usually used to store the call number of the system service . The service number printed is “1”( To view the system call service number, view the file /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/asm/unistd_64.h)
· register rdi(destination index), File descriptor used to specify the printout ( The file descriptor of the screen is 1);
· register rsi(source index), Used to specify the address of the output content ( The storage address of the string );
· register rdx, Used to specify the length of the output content ( This can be customized , You decide how long you want to print ; The last article mentioned , Strings from an assembly point of view , Just continuous memory storage space )
in summary , Describe printing in a colloquial way hello world The process of ( System service call procedure ), as follows ,
·rax Registers tell the operating system , What system services need to be called (1 No. service is “ standard output ” service );
·rdi Registers tell the operating system , To print there ( Generally, it is printed on the terminal , That's the screen );
·rsi Registers tell the operating system , Where can I find what needs to be printed ;
·rdx Registers tell the operating system , How long does it take to print ( byte );
Last , After the print service is called , Need to end the program , amount to C Of exit(0) function , The principle is not repeated , See the code provided above for details .
边栏推荐
- Machine learning deep learning -- Vectorization
- Gbase 8s index b+ tree
- 2.0SpingMVC使用RESTful
- Sleep more, you can lose weight. According to the latest research from the University of Chicago, sleeping more than 1 hour a day is equivalent to eating less than one fried chicken leg
- 重磅直播 | 相移法+多频外差之数学原理推导+实现
- GBASE 8s的触发器
- PHP extracts and analyzes table contents, and collects bidding information
- 领导:谁再用 Redis 过期监听实现关闭订单,立马滚蛋!
- ThinkPHP is integrated with esaywechat. What's wrong with wechat payment callback without callback?
- 「 每日一练,快乐水题 」1108. IP 地址无效化
猜你喜欢

Unity Quad culls shaders with back faces and transparent parts
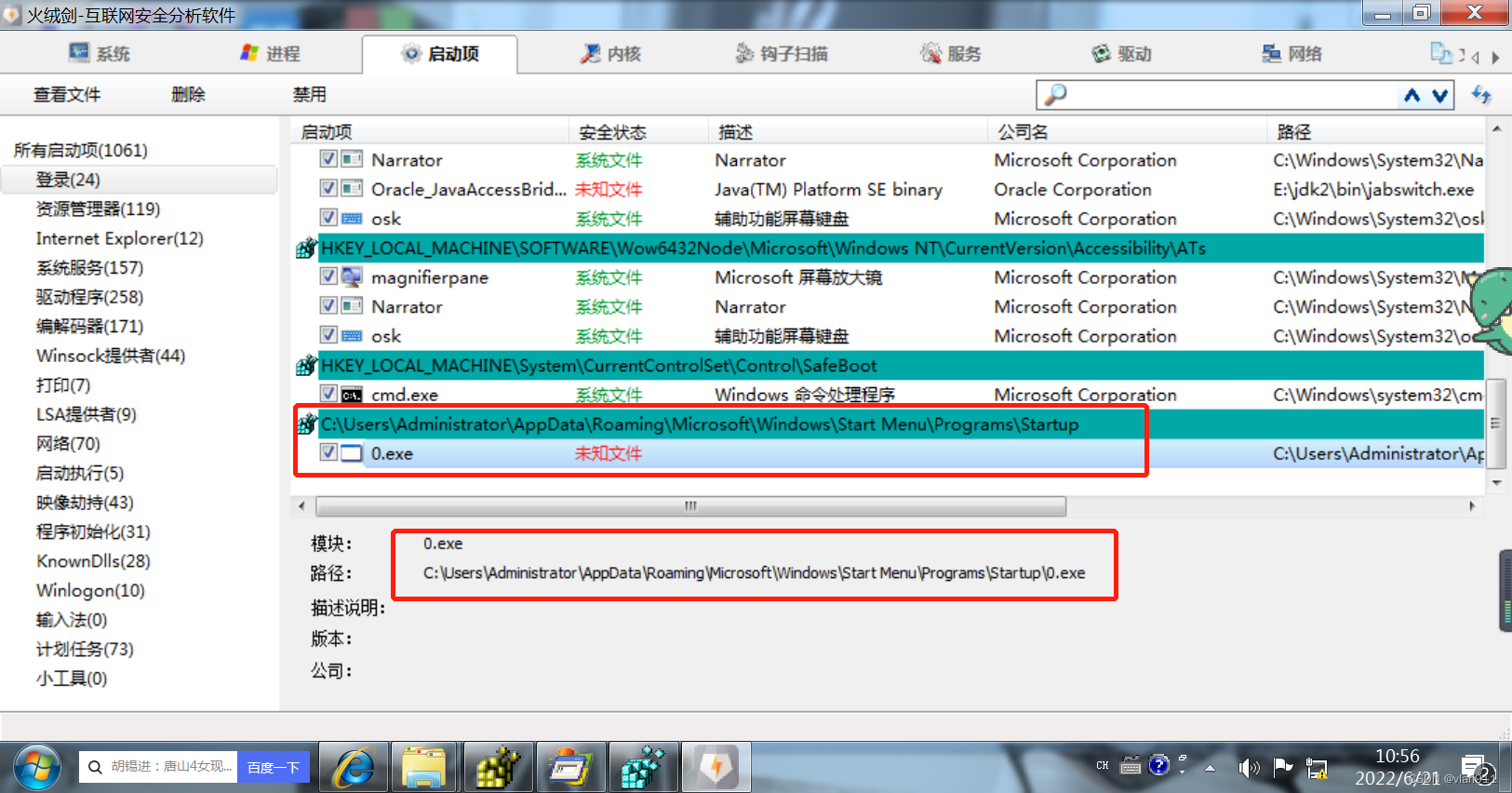
Simple text analysis of malicious samples - Introduction

i. Max development board learning record

我的IC之旅——资深芯片设计验证工程师成长——“胡”说IC工程师完美进阶
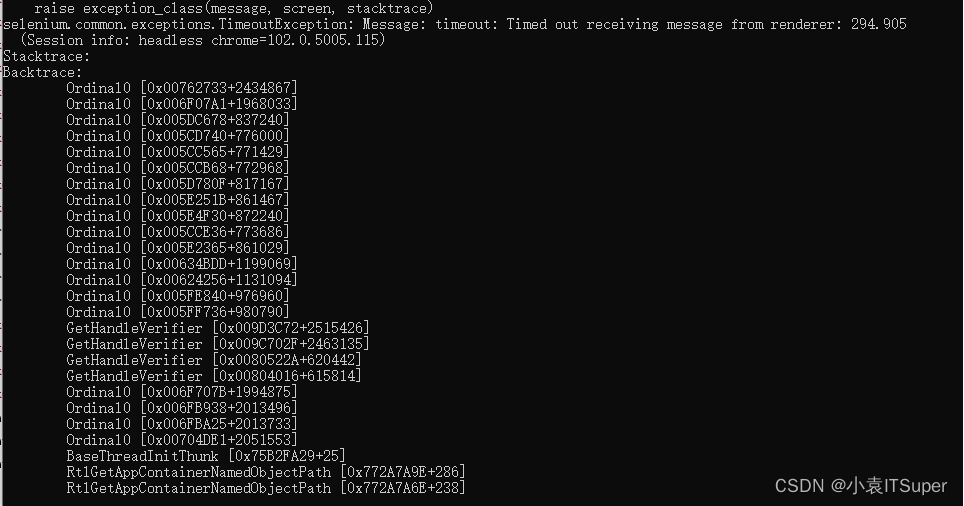
Successfully solved: selenium common. exceptions. TimeoutException: Message: timeout: Timed out receiving message from

Concat() in JS
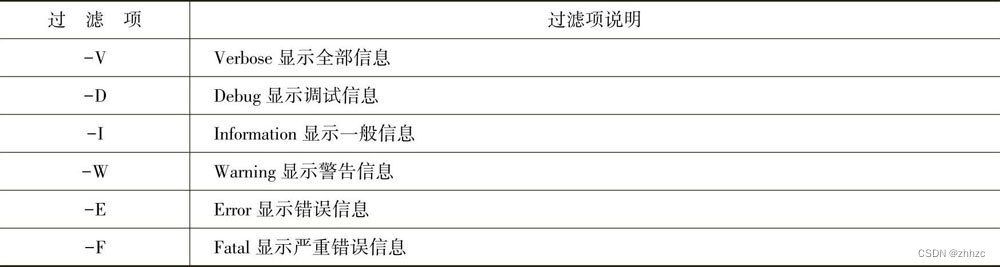
第九章 APP项目测试(2) 测试工具

Record small knowledge points

CTF_ Web: deserialization of learning notes (II) CTF classic test questions from shallow to deep

CTF_ Web: Changan cup-2021 old but a little new & asuka
随机推荐
What is the storage engine and the three common database storage engines for MySQL
js的call()和apply()
515. find the maximum value / Sword finger offer II 095 in each tree row Longest common subsequence
Xiaobai learns MySQL - Statistical 'opportunism'
GBASE 8s 索引R树
The consciousness of a programmer
Data import and export for gbase 8s
jsz中的join()
华为鸿蒙开发第四课
JS arguments
简单的恶意样本行文分析-入门篇
Gbase 8s stored procedure flow control
《牛客刷verilog》Part I Verilog快速入门
Retrofit source code analysis
OOP栈类模板(模板+DS)
小白学习MySQL - 统计的'投机取巧'
Cnpm: unable to load file c:\users\administrator\appdata\roaming\npm\cnpm PS1 because running scripts is prohibited on this system.
What is persistence? What are RDB and AOF in redis persistence?
Paper notes: multi label learning ESMC (I don't understand it, but I haven't written it yet, so I'll put it here for a place temporarily)
Gbase 8s parallel operation problem scenario description