当前位置:网站首页>Mongodb basic knowledge summary
Mongodb basic knowledge summary
2022-07-06 04:58:00 【Dream demon】
One 、 install
Linux:
Command to install
sudo apt install -y mongodb-org
Source code installation
Download the source code —— decompression —— Move to /usr/local/ Under the table of contents —— stay shell Initialization script for .bashrc Add mongodb Executable to environment variable path in .( stay .bashrc The last addition of the file export PATH=/usr/local/mongodb/bin:$PATH)
Two 、 Easy to use
Default port :27017
The location of the default configuration file :/etc/mongodb.conf
Default log location :/var/log/mongodb/mongodb.log
Starting mode :
Local test mode startup , It only has the function of adding, deleting, modifying and querying local data , It mainly verifies whether the database can run normally
The production environment starts , It has complete functions , Server deployment started
Local test mode startup :
start-up sudo service mongodb start
stop it sudo service mongodb stop
restart sudo service mongodb restart
The formal start-up mode of the production environment :
sudo mongod Optional parameters
Only in sudo mongod Command startup , By default, the data is stored in /data/db Under the table of contents , Manual creation required
Optional parameters :
--dbpath= Database storage path ( Absolute path )
--logpath= The storage path of the log file , After restart, the log will overwrite the original log , Not append write
Add after –append perhaps –logappend You can set the log writing mode to append mode
--fork perhaps -fork Start a new child process to run under the current process mongodb service , Once opened successfully , The parent process will exit
--auth Start with authority authentication
-f Profile name You can write the above configuration information to the file , Then load and start through the parameters in the file
For example, the configuration file is written as follows :
dbpath= Database storage path
logpath= The storage path of the log file
logappend=true( Be careful not to write append)
fork=true
auth=true
start-up mongodb The client of :
Start local client mongo
sign out exit perhaps ctrl+c
view help mongo --help
Operation of database
View the current database db ( If the database is not switched, it is used by default test database )
View all databases show dbs perhaps show databases ( Out of sight test Database is because the database is not on disk , It's in memory , You can only view the databases that exist on the disk )
Switch database use Database name , If the database doesn't exist , Then create the database , Otherwise switch to the specified database . After creating show dbs It doesn't show , You need to insert data into it (db. Collection name .insert({key:value}) If the collection does not exist, it will be created automatically ) Or create a collection to display it
Delete the current database dp.dropDatabase()
Operations on collections
Sets are similar to mysql In the table
See all sets show collections When there is no data, the set cannot be seen , You need to insert data first
Show the creation set of db.createCollection( name , Optional parameters )
db.createCollection(“sub”,{capped:true,size:10})
capped The default is false, Means no upper limit is set ;size Represents the number of bytes occupied by the collection , When capped by true This parameter needs to be set when , When the document reaches the upper limit , Writing data overwrites the previous data , First overwrite the first inserted (size Is less than or equal to 256 when , In fact, they are all 256)
Set data with upper limit cannot be modified , And the query speed will be relatively fast
Check whether the collection has an upper limit db. Collection name .isCapped() false There is no upper limit ,true Upper limit
View a collection of data db. Collection name .find()
Delete the collection db. Collection name .drop()
3、 ... and 、 Common data types
Object ID: file / Data ID, Is the primary key of the data , The index is created by default
String: character string , The most commonly used , Must be effective UTF-8
Boolean: Boolean value ,true perhaps false, It must be in lowercase
Integer: Integers ,32 perhaps 64 position , Depends on the server
Double:( Double precision ) Floating point numbers
Arrays: Array 、 list
Object:mongodb One of the data in ( file ), That is, documents are nested
Null: Null value
Timestamp: Time stamp , From 1970-1-1 The number of seconds to now
Date: Store the current date or time UNIX Time format
Be careful : Each document has an attribute of _id, Ensure the uniqueness of each document ,mongodb It is used as the primary key by default , Its value can be set manually , If not set ,MongoDB A unique value is provided for each document , The type is ObjectID
ObjectID It's a 12 Hexadecimal number of bytes , Each byte occupies two bits , Is the total 24 position ( Hexadecimal numeric string )
The first four bytes ( Top eight ): Current timestamp
The next three bytes ( Six ): Mechanical ID
The next two bytes ( Four place ):MongoDB The service process of ID
The last three bytes ( Six ): Simple incremental values
Four 、 Additions and deletions
insert data
Mode one
db. Collection name .insert({key:value}) key You can do it without quotes , The terminal will automatically add ,value Is a number without quotation marks , The string must be quoted
db. Collection name .insert([{},{},{}…]) Batch insert
If you want to modify _id Value , Insert data as key, Value as value, Put it into a piece of data to be inserted ( The document ) Just in front
Such as :db. Collection name .insert({_id:“ value ”,key:value})
Mode two
db. Collection name .save(_id: value ,key:value) If id If the value already exists and other data are different, modify ( All the original data will be deleted , Update to new data ), If id If the value does not exist, add new data
db. Collection name .save(key:value) MongoDB Will specify id
Query data
db. Collection name .find() Will query all data
db. Collection name .find({ Condition document })
db. Collection name .findOne() Just return the first one
db. Collection name .findOne({ Condition document })
db. Collection name .pretty() Format the results , Unable to join findOne() Use it together
db. Collection name .find({ Condition document }).pretty()
Condition document :
Comparison operator
be equal to : Default is equal to judgment , There are no operators
Less than :$lt That is to say less than
Less than or equal to :$lte That is to say less than euqal
Greater than :$gt That is to say greater than
Greater than or equal to :$gte That is to say greater than equal
It's not equal to :$ne That is to say no equal
db.stu.find({age:{$gte:18}}) Query age is greater than or equal to 18 All students of
Logical operators
and:$and
Or directly in a {} Write multiple conditions in
or:$or Value is an array ( list ), Each element in the array is json, Represents a condition
db.stu.find({age:{$lt:18},gender:‘male’}) The query age is less than 18, The gender is male All students of
db.stu.find({ KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: or:[{age:{ ne:18}},{gende:‘female’}]}) Inquiry age is not equal to 18 Or the gender is female All students of
db.stu.find({ KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: or:[{age:{ gt:18}},{age:12}],gender:“male”}) Query age is greater than 18 Or age equals 12 And the gender is male All of the Student
Range operator
$in The data searched is in the array
$nin The data searched is not in the array
db.stu.find({age:{$in:[12,23,34]}}) Query age is 12、23、34 All students of
Regular expressions
$regex Generally, the stored value is a string
db.stu.find({name:{$regex:’^ yellow ’}}) Inquire about name With “ yellow ” All students at the beginning
Custom query
mongo shell It's a js Execution environment , Use $where Write a js function , Return data that meets the criteria
db.stu.find({$where:function(){return this.age>30;}}) Return age is greater than 30 All students of ,this Be similar to MySQL The cursor of
Operate the query results
skip and limit
limit( Numbers ) Read a specified number of documents
skip( Numbers ) Skip the specified number of documents
skip Has a higher priority than limit
db.stu.find().limit(5).skip(5) Skip the first five data , Display the following first five data , change skip and limit The result is the same
Projection
Only the selected fields are displayed in the query results
db. Collection name .find({},{ Field name :1, Field name :1…})
Fill in the blank brackets in front of the query criteria , If it is not written, the query condition is null and the value is 1 Presentation display , The value is 0 Means not to show
_id Columns are displayed by default , If not shown, it needs to be set to 0
Other fields cannot be set to 0 Field of , Also set to 1 Field of
PS: except _id outside , Want to see which field is set to 1 Just do it
Sort
sort()
db. Collection name .find().sort({ Field name :1,…}) 1 Stands for ascending order ,-1 In descending order Sort
db.stu.find().sort({gender:-1,age:1}) Sort by sex in descending order , When the gender is the same, they are sorted in ascending order according to age
Number of Statistics
count() Count the number of documents in the query result set
db. Collection name .find({ Conditions }).count() be equal to db. Collection name .count({ Conditions })
duplicate removal
db. Collection name .distinct(“ Field name ”) Only all values of this field name after de duplication will be displayed , It's a list
db. Collection name .distinct(“ Field name ”,{ Query criteria }) Display all the values of this field name after de duplication according to the query criteria
Display details of the operation
db. Collection name .find().explain(“executionStats”) You can view various information such as the execution time of the operation
Update data
db. Collection name .update({ Query criteria },{ update operation },{multi:true/false})
multi Is an optional parameter , The default is false, Indicates that only the first data found is updated ,true Indicates that all data meeting the conditions are updated
db.stu.update({name:“hr”},{name:“mc”}) Will find name by hr The first data of name Change it to mc, And will put other words Segment value deletion
db.stu.update({name:“hr”},{$set:{name:“mc”}}) Will find name by hr The first data of name Change it to mc, Other values remain unchanged
db.stu.update({},{$set:{gender:“female”}},{multi:true}) Change the gender of all students to female
PS:multi:true It has to be with $set Use it together !
upsert Parameters
db.stu.update({name:“liu”},{$set:{age:1000}},{upsert:true}) Inquire about name by liu The first data of , If it age The value is already 1000 Then do nothing , If not, update age The value of is 1000, If it does not exist age Field, add this field , If the search fails, insert this piece of data
Use at the same time multi and upsert Words , Write them in curly braces , commas
Delete data
db. Collection name .remove({ Query criteria },{justOne:true/false})
justOne Optional , The default is false, Delete all , by true or 1 Indicates that only the first found data is deleted
db. Collection name .remove({}) Delete all data in this collection , Even if the query condition is empty , Of the first query condition {} You can't omit
5、 ... and 、 Aggregation operation
polymerization (aggregate) It's an aggregation pipeline based on data processing , Each document passes through multiple stages (stage) The pipes that make up , The pipes of each stage can be grouped 、 Filtration, etc. , Then it is processed , Output the corresponding result
db. Collection name .aggregate({ Pipeline command :{ expression }})
One {} It's a pipe
The output of the previous pipe is used as the input of the next pipe
Common pipeline commands
stay mongodb in , After processing the document , Next treatment by pipeline
$group: Group documents in a collection , Can be used for statistical results
$match: Filtering data , Output only documents that meet the criteria
$project: Modify the structure of the input document , Such as rename 、 increase 、 Delete field 、 Create calculation results
$sort: Sort the input documents and output
$limit: Limit the number of documents returned by the aggregation pipeline
$skip: Skip the specified number of documents , And return the remaining documents
$unwind: Split the specified field , Reptiles are not used much
Common expression
Expressions are used to process input documents and output
grammar : expression :’$ Name ’
s u m : meter count total and , sum: Calculate the sum , sum: meter count total and ,sum:1 It means counting the number by one time
$avg: Calculate average
$min: Get the minimum
$max: Get the maximum
$push: Insert the specified value of the result into an array
$group
db.stu.aggregate({ KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: group:{_id:'gender’,sum_age:{ s u m : ‘ sum:‘ sum:‘age’},name_list:{ p u s h : ′ push:' push:′name’}}}) _id Indicates which fields are grouped , Other field names can be Write it yourself , The result is that the students will install gender grouping , And calculate the total age of each group , Save the names of each group under the name name_list List of
Or you can divide the whole document into a group for statistics , The query shows all the document data
db.stu.aggregate({ KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …:null,counter:{ sum:1}}}) amount to db.stu.find().count()
Pivoting
db.stu.aggregate({ KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …_id:null,name:{ push:’$name’}}}) Put all the name Put it on a list
db.stu.aggregate({ KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …null,data_stu:{ push:’$$ROOT’}}}) Put the entire document in the array
$match
and find The difference is that $match The filtered result can be used as the input of the next pipeline
$match The value of can be the five query methods mentioned above
db.stu.aggregate({ KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: match:{age:{ gt:20}}}) Query age is greater than 20 Of the students
db.stu.aggregate({ KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: match:{age:{ gt:20}}},{ KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: group:{_id:"gender",counter:{$sum:1}}}) Query age is greater than 20 The number of boys and girls
$project
Similar to projection operation , The output result is that each piece of data is in a {} in
db.stu.aggregate({$project:{_id:0,name:1,age:1}}) Output only the student's age and name
db.stu.aggregate({ KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …nder",counter:{ sum:1}}},{$project:{_id:0,counter:1}}) Query the number of boys and girls , Output only the number of people
$sort
db.stu.aggregate({$sort:{age:1}}) Search for student information , Output in ascending order of age
db.stu.aggregate({ KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …nder",counter:{ sum:1}}},{$sort:{counter:-1}}) Check the number of boys and girls , Output in descending order according to the number of people
l i m i t and limit and limit and skip
Attention and in find() Differences when used in
db.stu.aggregate({ KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '}' at position 8: limit:2}̲,{ skip:1}) Only the second data will be displayed
db.stu.aggregate({ KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '}' at position 7: skip:1}̲,{ limit:2}) Only the second and third data will be displayed
$unwind
Split , Understanding can
db. Collection name .aggregate({ KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: unwind:{path:" The field name you want to split ",preserveNullAndEmptyArrays:true})
6、 ... and 、 Indexes
Indexes : Speed up query ; De duplication of data
The original data structure will be adjusted after the index is created , The adjusted structure is similar to a binary sort tree , The query efficiency is O(logn)
Create index
db. Collection name .ensureIndex({ attribute :1or-1}) 1 Expressing ascending order ,-1 Representation of descending order
Look at the index
By default _id Is the index of the collection
db. Collection name .getIndexes()
Delete index
db. Collection name .dropIndex({“ The index name ”:1})
Create unique index
When inserting data, you will check whether the data already exists , If it exists, the insertion fails
It will reduce the insertion speed
db. Collection name .ensureIndex({“ Field name ”:1},{“unique”:true})
Build composite index
db.collection_name.ensureIndex({ Field 1:1, Field 2:1}) The principle of left ( With fields 1 Query using index , With fields 1 And field 2 Use the index together , But with fields 2 Queries do not use indexes )
Be careful :
Select if you want to create a unique index
Whether index fields are in ascending or descending order does not affect query efficiency in the case of a single index , But with a composite index there is an impact
An index needs to be created only when there is a large amount of data and the database is read out very frequently , If write operations are frequent , Creating an index affects write speed
PS: When querying, if the field 1 You need to sort the output in ascending order , Field 2 You need to sort the output in descending order , At this time, the establishment of the composite index needs to put the fields 1 Set to 1, Field 2 Set to -1
Generally, when the read-write operations are very frequent and the data volume is huge, the read-write separation strategy is adopted
7、 ... and 、 Rights management
Just installed MongoDB By default, permission authentication is not used to start , And you don't have permission to install it , When the public network is running, permissions need to be set to ensure data security .
MongoDB There is no default administrator account , So add the administrator account first , also MongoDB The server needs to turn on authentication mode when running .
Users can only log in to the database where they are ( Create the user's database ), Including administrator account .
Administrators can manage all databases , But you can't directly manage other databases , Certification is required before .
Create a superuser
Kill first mongod process
And then start in the way of authority authentication mongodb Server side
sudo mongod --auth Or will auth=true Write to configuration file ,sudo mongod -f Profile name , This starts
Open client ,mongo, At this time, executing various database statements will report permission errors , Authentication is required to perform the operation
use admin Switch database ( The name must be admin)
db.createUser({“user”:“ user name ”,“pwd”:“ password ”,“roles”:[“root”]}) Add Super Administrator
Login Administrator
use admin Because it is in admin Users created on the database , So you must switch to this database ( Users can switch to the database on which they are created )
db.auth(“ user name ”,“ password ”) Is shown as 1 Login succeeded , by 0 Login failed
After successful login, the statement can be executed normally
Create a normal user
Create a normal user on the database you are using
If you add a super administrator , And log in with authority authentication , You must authenticate before you can create
use test1
db.createUser({“user”:“user1”,“pwd”:“user1”,“roles”:[“read”]}) If it is readWrite, Is read / write permission
show users View the user status in the current database
stay admin Create normal users on the database
Because it is tedious to create a user on each database , Therefore, in most cases, users are created in admin On the database
use admin
First, verify the administrator permissions db.auth(“python”:“python”)
Add regular users
db.createUser({user:“user2”,pwd:“user2”,roles:[{db:“test2”,role:“read”},{db:“test3”,role:“readWrite”}]})
here user2 The user is in test2 The permissions on the database are read , stay test3 Permission on is read / write
PS: Sign in user2 The user should be in admin Log in to the database , Because this user is created on this database !
Delete user
You can delete other users only when you log in as a super administrator
First enter the database where the account data is located
db.dropUser(“ user name ”) Delete user
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
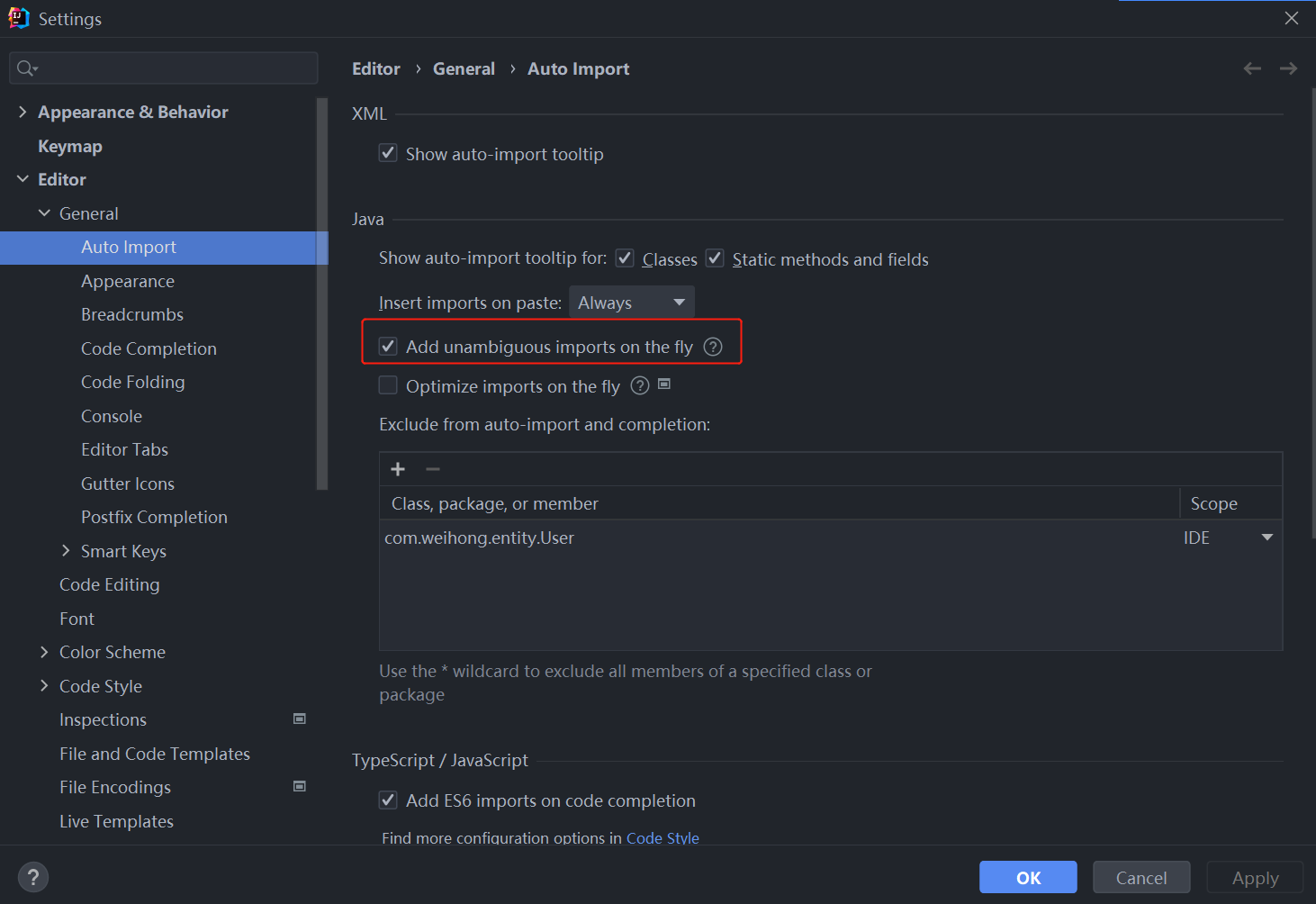
Idea one key guide package
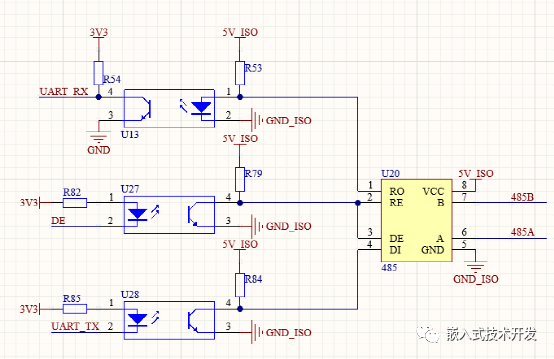
Introduction of several RS485 isolated communication schemes
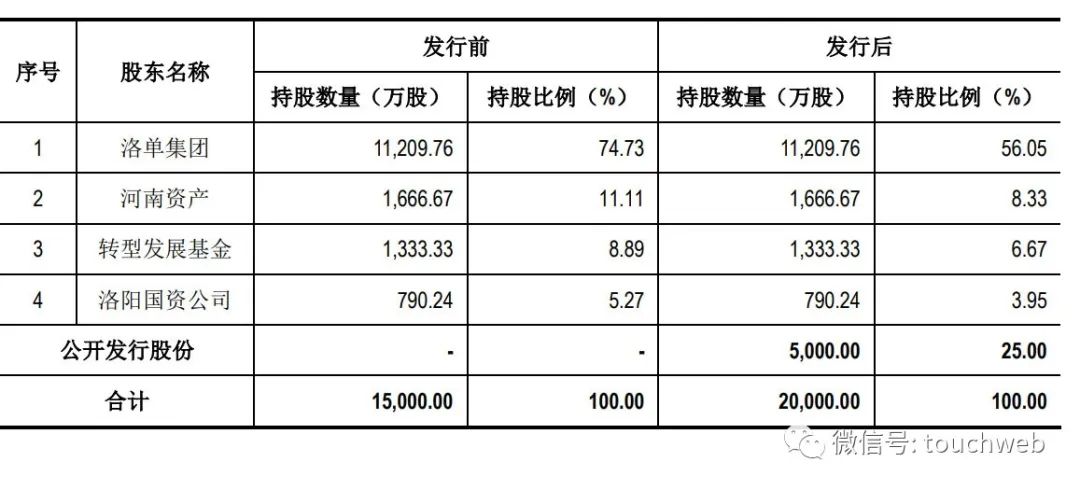
麥斯克電子IPO被終止:曾擬募資8億 河南資產是股東

比尔·盖茨晒18岁个人简历,48年前期望年薪1.2万美元
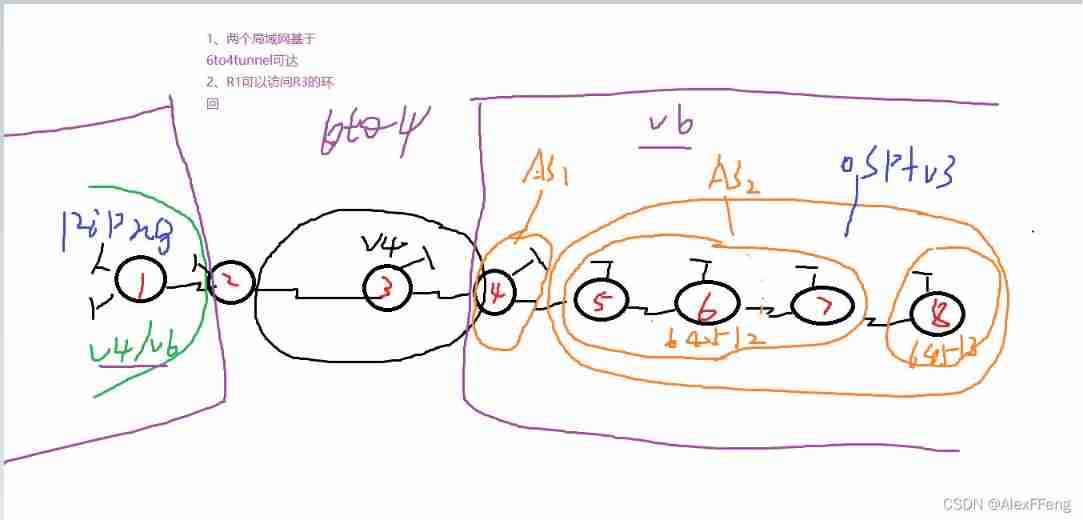
IPv6 comprehensive experiment
GAMES202-WebGL中shader的編譯和連接(了解向)
Yolov5 tensorrt acceleration

Selection of slow motion function
![[FreeRTOS interrupt experiment]](/img/8f/54422d346bb54d23fab824be2f17a3.jpg)
[FreeRTOS interrupt experiment]
Golang -- TCP implements concurrency (server and client)
随机推荐
[noip2009 popularization group] score line delimitation
Summary of redis AOF and RDB knowledge points
The kernel determines whether peripherals are attached to the I2C address
DMA use of stm32
集合详解之 Map + 面试题
Supreme Court, judgment standard of divorce cases
Distributed transaction solution
[NOIP2008 提高组] 笨小猴
Orm-f & Q object
Bubble sort
Programmers' position in the Internet industry | daily anecdotes
饼干(考试版)
Sorting out the knowledge points of multicast and broadcasting
也算是學習中的小總結
Vite configures the development environment and production environment
内核判断i2c地址上是否挂载外设
关于es8316的音频爆破音的解决
Finance online homework
Selection of slow motion function
The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower