当前位置:网站首页>Dynamic programming problem (3)
Dynamic programming problem (3)
2022-07-29 00:21:00 【std i hurt o love】
One 、 The longest public substring
Solution 1 : enumeration
- We can traverse all strings of two strings as the starting
- Then start checking whether the characters are equal at the same time , Equality keeps moving back , Increase substring length , If the difference is not equal, it means that the substring starting from these two ends , There will be no more .
- Maintain the maximum value of the subsequent comparison length .
class Solution {
public:
string LCS(string str1, string str2) {
int length = 0;
string res = "";
// Traverse s1 Each starting point
for(int i = 0; i < str1.length(); i++){
// Traverse s2 Each starting point
for(int j = 0; j < str2.length(); j++){
int temp = 0;
string temps = "";
int x = i, y = j;
// Compare each substring starting from
while(x < str1.length() && y < str2.length() && str1[x] == str2[y]){
temps += str1[x];
x++;
y++;
temp++;
}
// Update larger length substrings
if(length < temp){
length = temp;
res = temps;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
Overtime , The test case cannot pass completely
Time complexity :O(m^2*n) among mmm yes str1 The length of ,n yes str2 The length of , Enumerate two strings, each character as the starting point , The worst way to check the length of the substring is to spend O(m)
Spatial complexity :O(n),res It belongs to returning the necessary space ,temps It belongs to temporary auxiliary space , In the worst case, the length is n
Solution 2 : Dynamic programming ( recommend )
- We can use dp[i][j] stay str1 In order to iii Characters ending in str2 In order to jjj The length of the common substring at the end of characters ,
- Iterate through two string fills dp Array , The transfer equation is : If the two characters of the bit traversed are equal , Then the length at this time is equal to the length of the previous two digits +1,dp[i][j]=dp[i−1][j−1]+1, If the two characters are not equal when traversing to this bit , Is set to 0, Because this is a substring , Must be continuously equal , Disconnect to restart .
- Each update dp[i][j] after , We maintain the maximum , And update the end position of the substring .
- Finally, the substring can be intercepted according to the end position of the maximum value .
class Solution {
public:
string LCS(string str1, string str2) {
//dp[i][j] To str1 The first i Everyone arrives at str2 The first j The length of the common substring up to
vector<vector<int> > dp(str1.length() + 1, vector<int>(str2.length() + 1, 0));
int max = 0;
int pos = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= str1.length(); i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= str2.length(); j++){
// If the two are the same
if(str1[i - 1] == str2[j - 1]){
// Then increase the length
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
}
else{
// The position is 0
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
// Update maximum length
if(dp[i][j] > max){
max = dp[i][j];
pos = i - 1;
}
}
}
return str1.substr(pos - max + 1, max);
}
};
Time complexity :O(mn), among m yes str1 The length of ,n yes str2 The length of , Traverse all characters of two strings
Spatial complexity :O(mn),dp The array size is m∗n
Two 、 Number of different paths ( One )
Solution 1 : recursive
First, when we are in the first grid in the upper left corner , There are two ways to walk : If you go right , It is equivalent to the following one (n−1)∗m To find the number of different paths from the upper left corner to the lower right corner ; And if you go down , It is equivalent to the following one n∗(m−1) To find the different number of paths from the upper left corner to the lower right corner . and (n−1)∗m The matrix of and n∗(m−1) The matrices of are n∗m Matrix subproblem , So you can use recursion .
- When the matrix gets longer n Reduced to 1 When , It is obvious that we can only go down , There's no other choice , Only 1 Paths ; Empathy m Reduced to 1 It's the same when . Therefore, the returned quantity is 1.
- For each level, the results returned from its two sub problems are added and returned to the upper level .
- Each level has two path choices: down or right , Enter the subproblem of the corresponding branch respectively .
class Solution {
public:
int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
// As long as one edge of the matrix is 1, There is only one path
if(m == 1 || n == 1)
return 1;
// Two branches
return uniquePaths(m - 1, n) + uniquePaths(m, n - 1);
}
};
Time complexity :O(m*n), among m、n Are the lengths of both sides of the matrix , Recursive procedure for each m At most, we have to go through every kind of n
Spatial complexity :O(m+n), The maximum depth of the recursive stack is from m、n All the 1
Solution 2 : Dynamic programming ( recommend )
- use dp[i][j] The size is i∗j The number of paths to the matrix , Subscript from 1 Start .
- When i perhaps j by 1 When , The representation matrix has only one row or one column , So there is only one path .
- The number of paths in each grid will only come from the number of grids on its left and the number of grids on its top , So the state transition is dp[i][j]=dp[i−1][j]+dp[i][j−1]

class Solution {
public:
int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
//dp[i][j] The size is i*j The number of paths to the matrix
vector<vector<int> > dp(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0));
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
// Only 1 when , There is only one path
if(i == 1){
dp[i][j] = 1;
continue;
}
// Only 1 At the time of listing , There is only one path
if(j == 1){
dp[i][j] = 1;
continue;
}
// The number of paths is equal to the number of paths in the left grid plus the number of paths in the upper grid
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1];
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
};
Time complexity :O(mn), among m、n Are the lengths of both sides of the matrix , Two layers of traversal fill the whole dp Array
Spatial complexity :O(mn), Auxiliary space dp The array is a two-dimensional array
Solution 3 : Combinatorial mathematics
Go from the upper left corner of the matrix to the lower right corner of the matrix , In total, we need to go down m−11 Step , Go to the right n−1 Step , The different path lies in the combination of down and right , That is, in a pile of down and right sequences , The situation of each arrangement , The sequence consists of m+n−2 A place , Choose one n−1 There are two positions to go down , That is, different walking methods are 
In this case
- Numerator and denominator from 1 Start
- Multiply and divide according to the formula
class Solution {
public:
int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
// Prevent overflow
long res = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
// According to the formula
res = res * (m + i - 1) / i;
return (int)res;
}
};
Time complexity :O(n), The calculation process needs to start from 1 Traversing n
Spatial complexity :O(1), Constant level variable , No additional auxiliary space
边栏推荐
- What is in word?:^ p
- vulnhub:BTRSys2
- 动态规划问题(六)
- "Method not allowed", 405 problem analysis and solution
- Event extraction and documentation (2018)
- Develop effective Tao spell
- Okaleido ecological core equity Oka, all in fusion mining mode
- Installation and use of pnpm
- Do like and in indexes in MySQL go
- Real time data warehouse: Netease strictly selects the practice of real-time data warehouse based on Flink
猜你喜欢

IDEA报错Error running ‘Application‘ Command line is too long解决方案
Web系统常见安全漏洞介绍及解决方案-CSRF攻击
centos7安装mysql8

ACM SIGIR 2022 | interpretation of selected papers of meituan technical team
curl (7) Failed connect to localhost8080; Connection refused

PHP语言基础知识(超详细)
IDEA2021.2安装与配置(持续更新)

Have passed hcip and joined the company of your choice, and share the learning experience and experience of Huawei certification

CV target detection model sketch (2)

The difference between {} and ${}
随机推荐
Advanced area of attack and defense world web masters ics-06
Idea connection database
Principle of meter skipping
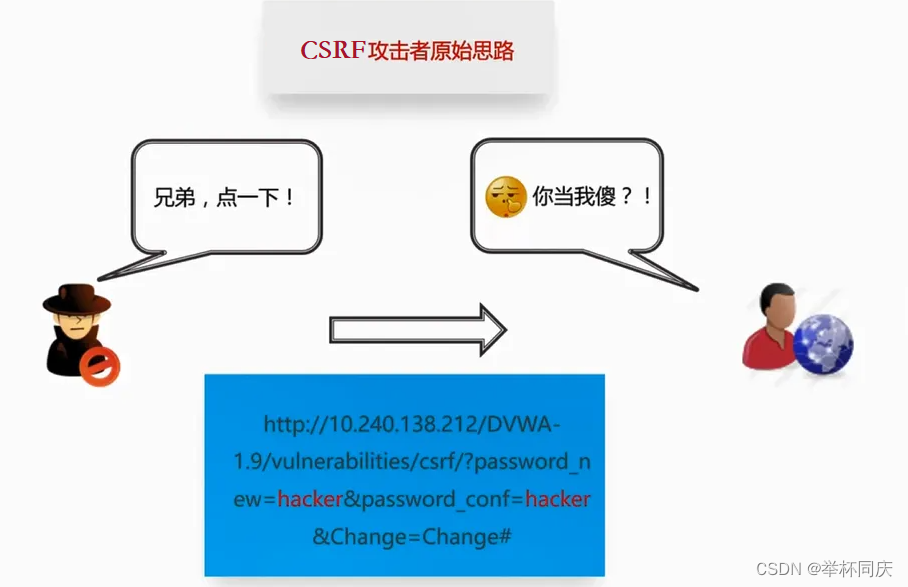
Introduction and solution of common security vulnerabilities in web system CSRF attack
JS four formulas for judging data types
vulnhub:BTRSys2
Applet waterfall flow, upload pictures, simple use of maps
Use hutool tool class to operate excel with more empty Sheet1
Advanced area of attack and defense world web masters training www robots
Network traffic monitoring tool iftop
Android studio connects to MySQL and completes simple login and registration functions
Advanced area of attack and defense world web masters -baby Web
熊市下PLATO如何通过Elephant Swap,获得溢价收益?
Leetcode 763. partition labels divide alphabetic intervals (medium)
Immutable x officially opens IMX token pledge detailed IMX pledge introduction optimistic about the development prospect of IMX
动态规划问题(五)
研发效能的道法术器
Oracle super full SQL, details crazy
@Detailed explanation of the use of transactional annotation
Event extraction and documentation (2008-2017)