当前位置:网站首页>Lambda and filter, index of list and numpy array, as well as various distance metrics, concatenated array and distinction between axis=0 and axis=1
Lambda and filter, index of list and numpy array, as well as various distance metrics, concatenated array and distinction between axis=0 and axis=1
2022-06-12 11:37:00 【king52113141314】
Lambda
lambda Function parameter : Function expression
# Function definition
def add(x,y):
return x+y
# The above function uses lambda rewrite
lambda x,y: x+y
filter
If the first argument is a function :
Set the second parameter ( You can iterate over the data ) Each element of the function is calculated as a parameter of the function , Will return true The value of is filtered out and returned as a list . Be careful : The return value of this function can only be True, Or False.
filter(lambda x: x, [-1, 0, 1]) #[-1, 1] filter(lambda x: not x, [-1, 0, 1]) #[0] def f(x): return True if x == 1 else False filter(lambda x: f(x), [-1, 0, 1]) #[1]
If the first parameter is None:
In the second parameter true Value filteredfilter(None, (True, 1, 0, -1, False)) #(True, 1, -1)
Want to use filter After the results of the , It's better to turn it into list:
list(filter_return)
Python in filter And lambda Combined use of _ Xiao Ge shelwin The blog of -CSDN Blog
List and numpy array The index of
Remove an item from a list in Python (clear, pop, remove, del)
l = list(range(10))
print(l)
# [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
l.clear()
print(l)
# []
print(l.pop(3))
# 4
print(l)
# [1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
print(l.pop())#If the argument is omitted, the last item is deleted.
# 9
print(l)
# [1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7]
del l[-1]
print(l)
# [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
del l[2:5]
print(l)
# [0, 1, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
###Removing items that satisfy the condition
#is equivalent to extracting items that do not satisfy the condition.
print([i for i in l if i % 2 != 0])
# [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
l = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'Bob', 'Dave']
print(l)
# ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'Bob', 'Dave']
l.remove('Alice')
print(l)
# ['Bob', 'Charlie', 'Bob', 'Dave']
aaa=np.arange(10)
iii=[0,5,2]
np.delete(aaa, iii, None)
#array([1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9])Check a nested list or numpy array Is it empty ?
How to check if a nested list or numpy array is essentially empty?
#1, recommend
#Use the any() function.
#This returns True if any list within the list is not empty.
alist = [[],[]]
if not any(alist):
print("Empty list!")
#2
l2 = []
if l2:
print("list is not empty")
elif not l2:
print("list is empty")
#3
if len(l2) == 0:
print("list is empty")
else:
print("list is not empty")
#4 Not recommended
alist = [[],[]]
if not np.any(alist):
print("Empty list!")
#1
arr1 = np.array([])
ran = not np.any(arr1)
if ran:
print('Array is empty')
else:
print('Array is not empty')
#2
arr = np.array([])
flag = np.size(arr)
if flag:
print('Array is not empty')
else:
print('Array is empty')
#3 recommend
a = np.array([])
if a.size == 0:
print("Empty")
#4 Not recommended such as arr = np.array([[0],[]])
arr = np.array([[],[]])
if not np.any(arr):
print("Empty!")
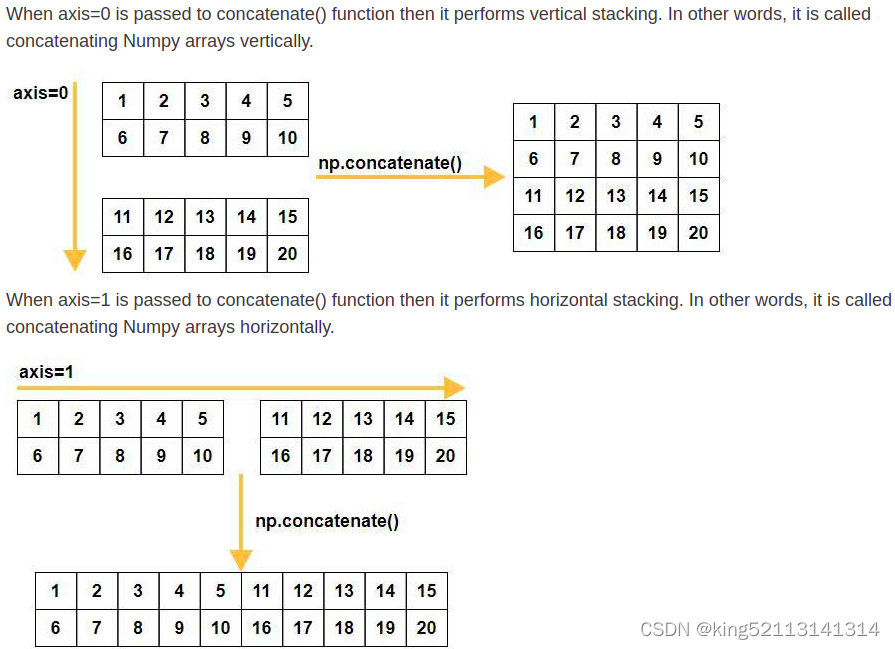
Concatenate arrays and axis=0 and axis=1 The distinction between
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
b = np.array([[11, 12, 13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18, 19, 20]])
print('Concatenate along axis=0:\n', np.concatenate((a,b), axis=0))
print('Concatenate along axis=0:\n', np.concatenate((a,b)))
print('Vertically stacked array:\n', np.vstack((a,b)))
##pass tuple or list of Numpy arrays is OK
print('Concatenate along axis=1:\n', np.concatenate([a,b], axis=1))
print('Horizontally stacked array:\n', np.hstack((a,b)))
Swap array columns or Rearrange columns of a given array
import numpy as np
array_nums = np.arange(20).reshape(4,5)
print("Original array:",array_nums)
### swapping the column with index of original array
array_nums[:,[0,3]] = array_nums[:,[3,0]]
print("\nAfter swapping column1 with column4:",array_nums)
############# Rearrange columns of a given array by indexes
array1 = np.array([[11, 22, 33, 44, 55],
[66, 77, 88, 99, 100]])
print("Original arrays:",array1)
i = [1,3,0,4,2]
result = array1[:,i]
print("New array:",result)


all distance-metrics
Recommended minkowski distance and the Mahalanobis distance.
Use scipy Function of
Distance computations (scipy.spatial.distance) — SciPy v1.8.1 Manual
scipy/distance.py at v1.8.1 · scipy/scipy · GitHub
GitHub - niranjanbsubramanian/distance-measures
Common in Data Science 9 A distance measure _ Visual algorithm blog -CSDN Blog
https://towardsdatascience.com/9-distance-measures-in-data-science-918109d069fa
4 Distance Measures for Machine Learning
Common distance measurement criteria - You know
Deep understanding of Euclidean distance and Mahalanobis distance - You know
Web of Science — Various distances - Hu Zheng's blog
import numpy as np
from math import sqrt
# Euclidean distance
def euclidean(x, y):
distance = 0
for a, b in zip(x, y):
distance += (sum([(pow((a-b),2))]))
return sqrt(distance)
print("Euclidean Distance:",euclidean([1,3,4,1],[3,2,1,1]))
#Calculate the Euclidean distance using linalg.norm()
# initializing points in
# numpy arrays
point1 = np.array((1, 2, 3))
point2 = np.array((1, 1, 1))
# calculating Euclidean distance
# using linalg.norm()
dist = np.linalg.norm(point1 - point2)
# using sum() and square()
sum_sq = np.sum(np.square(point1 - point2))# finding sum of squares
dist = np.sqrt(sum_sq)# Doing squareroot
# Manhattan distance
def manhattan(x, y):
distance=0
for a,b in zip(x,y):
distance += sum([abs(a-b)])
return distance
print("Manhattan Distance:",manhattan([1,3,4,1],[3,2,1,1]))
#chebyshev distance
def chebyshev(x,y):
distance = []
for a,b in zip(x,y):
distance.append(abs(a-b))
return max(distance)
print("Chebyshev Distance:",chebyshev([1,3,4,1],[3,2,1,1]))
#hamming distance
def hamming(x,y):
distance = 0
for a,b in zip(x,y):
if a != b:
distance += 1
return distance
print("Hamming Distance:",hamming("hello world","hallo warld"))
#cosine_similarity
def cosine_similarity(x,y):
numerator = 0
sum_x = 0
sum_y = 0
for a,b in zip(x,y):
numerator += sum([a * b])
sum_x += sum([a**2])
sum_y += sum([b**2])
denominator = round(sqrt(sum_x) * sqrt(sum_y))
return numerator / denominator
print("Cosine Similarity:", cosine_similarity([1,3,4,1],[3,2,1,1]))
#jaccard
def jaccard_similarity(x,y):
intersection = len(set(x).intersection(set(y)))
union = len(set(x).union(set(y)))
return (intersection / union)
print("Jaccard Similarity:",jaccard_similarity([0,1,2,5,6], [0,2,3,4,5,7,9]))
print("Jaccard Distance:", 1-jaccard_similarity([0,1,2,5,6],[0,2,3,4,5,7,9]))
#minkowski
# calculating minkowski distance between vectors
from math import sqrt
# calculate minkowski distance
def minkowski_distance(a, b, p):
'''
p=1, the distance measure is the Manhattan measure.
p=2, the distance measure is the Euclidean measure.
p = ∞, the distance measure is the Chebyshev measure.
'''
return sum(abs(e1-e2)**p for e1, e2 in zip(a,b))**(1/p)
# define data
row1 = [10, 20, 15, 10, 5]
row2 = [12, 24, 18, 8, 7]
# calculate distance (p=1)
dist = minkowski_distance(row1, row2, 1)
print(dist)
# calculate distance (p=2)
dist = minkowski_distance(row1, row2, 2)
print(dist)
#Mahalanobis
# Importing libraries
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import scipy as stats
# calculate Mahalanobis function to calculate
# the Mahalanobis distance
def calculateMahalanobis(y=None, data=None, cov=None):
y_mu = y - np.mean(data)
if not cov:
cov = np.cov(data.values.T)
inv_covmat = np.linalg.inv(cov)
left = np.dot(y_mu, inv_covmat)
mahal = np.dot(left, y_mu.T)
return mahal.diagonal()
# create new column in dataframe that contains
# Mahalanobis distance for each row
df['calculateMahalanobis'] = mahalanobis(x=df, data=df[['Price', 'Distance',
'Emission','Performance',
'Mileage']])GitHub - brando90/Normalized-Euclidean-Distance-and-Similarity-NED-NES-


边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

DS18B20数字温度计 (一) 电气特性, 寄生供电模式和远距离接线

十折交叉验证代码中的问题

Pytoch notes

K52. Chapter 1: installing kubernetes v1.22 based on kubeadm -- cluster deployment

6.6 RL:MDP及奖励函数

Byte order - how to judge the big end and the small end

多普勒效应的基本原理

正则表达式 | 浅解

Face recognition PIP failed to install Dlib Library

conda环境下pip install 无法安装到指定conda环境中(conda环境的默认pip安装位置)
随机推荐
K53. Chapter 2 installing kubernetes v1.22 based on binary packages -- cluster deployment
Unlimited growth, we will all go to the future | the 15th anniversary of the founding of InfoQ China
Construction and construction of meta Universe System
AcWing 1986. Mirror (simulation, ring diagram)
6.6 分离卷积
(37) How bee uses different data source instances at the same time
Windows10 install mysql-8.0.28-winx64
C# 37. textbox滚动条与多行
【藍橋杯單片機 國賽 第十一届】
人類想要擁有金錢、權力、美麗、永生、幸福……但海龜只想做一只海龜
6.6 分離卷積
Doris记录服务接口调用情况
Drqueueonrails integrated LDAP authentication
DS18B20 digital thermometer (I) electrical characteristics, power supply and wiring mode
selenium使用代理IP
systemctl里万恶的203
redis 總結
AcWing 1912. Odometer (enumeration)
Socket implements TCP communication flow
Epidemic home office experience | community essay solicitation