当前位置:网站首页>Detailed explanation of activity life cycle and startup mode
Detailed explanation of activity life cycle and startup mode
2022-07-01 16:38:00 【Programmer Xiao He SS】
One 、Activity Life cycle
1. Normal condition :
(1) onCreate:
Express
ActivtyBeing created , This is aActivityThe first method of life cycle , Can do some initialization work , such as : Load layout , Binding controls , Initialization data, etc .
(2) onRestart:
Express Activity is again start-up , Usually by Activty Called when it changes from invisible to visible .
Triggering scenarios : Press Home Key to enter the desktop , Or start a new Activity, Now Activity Be suspended , And then back to the Activity , It's going to trigger onRestart.
(3) onStart:
At present Activity Is being activated , here Activity It's already visible , But it has not yet appeared in The front desk , Can't interact with users , Users can't see .
(4) onResume:
At present Activity Already visible , Appear at the front desk And start activities ,onStart and onResume All means Activity so ,onStart When Activity Still backstage ,onResume When Activity To the front desk .
(5) onPause:
At present Activity Stopping , It is still visible at this time , Under normal circumstances , Then it will call onStop Method .
Can do some data storage , Animation stop and other lightweight recycling work , Not too time consuming . Because it will affect the new Activity Display of , Only onPause After execution , new Activity Of onResume Method will be executed .
Be careful For example, pop up a non full screen Dialog Or start a transparent Activty, Then the current onStop Method does not call .
(6) onStop:
Express Activity About to stop , invisible , You can do some slightly heavyweight post meeting work , It can't be too time consuming .
(7) onDestroy:
Express Activity About to be destroyed , This is a Activity The last callback in the life cycle , You can do some recycling and finally release resources .
Life cycle flowchart

Expand the problem :
1.onStart and onResume,onPause and onStop What is the substantive difference ?
onStart and onStop It's from Activity Whether to callback from the visible angle , and onResume and onPause It's from Activity Whether the callback is in the foreground .
2.A start-up B, that B Of onResume and A Of onPause Which comes first ?
Conclusion :A Execute first
onPause()Method , Then B performonCreate() -> onSatar() -> onResume()Method , Then perform A OfonStop()
reason :
start-up Activity The request for
Instrumentationadopt Binder Interface to AMS Send a request ,AMS One is maintained internally ActivityStack And be responsible for the stack Activity State synchronization , nextAMSadoptIApplicationThread( In the current application process ) Of Binder Interface desynchronization Activity To complete the call to the lifecycle method .call ApplicationThread.scheduleLaunchActivity adopt handle.sendMessage notice ActivityThread Complete the new Activity Of onCreate,onStart,onResume Call procedure for .
ActivtyStack.resumeTopActivityInnerLocked();//
---TaskDisplayArea.pauseBackStacks();// Pause all stacks or only all activities in the post stack
----ActivtyStack.startPausingLocked();// Start pause is currently in resumed The activities of
------ActivityStackSupervisor.realStartActivityLocked();
.... app process
ActivtyThread.handleLaunchActivity(){
----ActivtyThread.performLaunchActivity();
----1.ContextImpl appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r);// Create the context Implementation class
----2.mInstrumentation.newActivity();// adopt appContext Class loader reflection creation Activity
----3.LoadedApk.makeApplication();// establish application
----4.appContext And activity Related to
----5. perform activity.attach() Method .
----6.mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate();// perform oncreate Method
2. Abnormal life cycle :
1. Changes in system configuration result in Activity Killed and recreated
Abnormal termination : I hit the back button , Lock screen , Click on Home key , There are others APP Enter the front desk ( Like answering the phone ) , We started a new Activity , The direction of the screen rotates ,APP Be killed .
All in all : System is only in Acitivity It will be triggered only when it is abnormally terminated
onSaveInstanceStateandonRestoreInstanceState
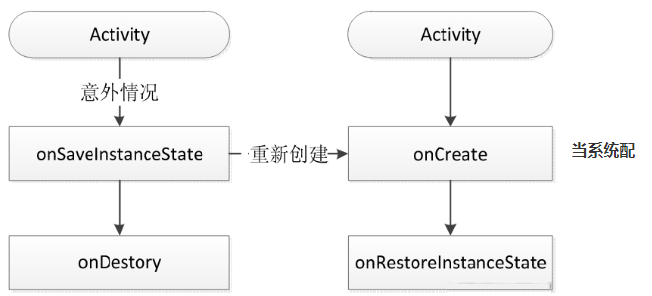
When the system configuration changes ,Activity The life cycle process after being destroyed and rebuilt :

Can be in
onSaveInstanceStateOfBundleSave data in , stayonRestoreInstanceStateRecovering data in . The system automatically does some recovery work for us . When Activity When rebuilding , The system will save the current... For us Activity The view structure of , And in Activity Recover data after restart .
View View data recovery :
Every
ViewThere areonSaveInstanceStateandonRestoreInstanceStateMethod .
ActivityWhen terminated maliciously ,Activity Would callonSaveInstanceStateTo save data , thenActivityWill commissionWindowTo save data , nextWindowThen delegate the top-level container above it to save data , Usually the top-level container is aViewGroup, Generally speaking, it is likely to beDecorVew. Finally, the bottom container notifies its children one by one View To save the data , That is to callViewGroupOfdispatchSaveInstanceState()Finally, call the specific View OfonSaveInstanceStateTo save data .Be careful :View Data recovery must be done at the current time xml Set... For it in ID, Otherwise, it cannot be recovered .
The specific saved data can be seen in View The concrete implementation of subclasses .
Activity State saving and recovery in
2. Insufficient resource memory resulted in Activty Be killed
Acitivty The priority of the :
1. The front desk Activity, Interacting with users , The highest priority .
2. Visible but not foreground , Like pop ups , transparent Activity start-up .
3. backstage Activity, Suspended Activity, The lowest priority .
Background work is not suitable for running independently of the four components , Such a process can easily be killed , Process priorities can be provided to reduce the risk of being killed .
3. How to avoid Activity The reconstruction
stay
AndroidManifestIn Chinese, it means Activity To configure configChanges Configuration to avoid... Due to configuration changes Acitivty Destroyed and rebuilt .This will only go Activity Of
onConfigurationChangedMethod .android:configChanges="screenSize|orientation|keyboardHidden|screenLayout"
2.Activity Start mode of
1.LaunchMode
standard: The standard model
The default mode of the system , One at a time
ActivityMetropolis Recreate a new instance , Whether this instance exists or not . A task stack can have multiple tasksActivityExample , Each instance can also be on a different task stack .In this mode , Who started the
Acitivty, At presentActivityIt's running on the one that started itActivityIn the task stack .Be careful : stay
standardIn mode , If you passApplicationContextStart upActivity, Abnormal transactions , becauseApplicationContextStarting upActivityThere is no task stack . The solution is for the to be startedActivityAppointFLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASKMarker bit , At startup, a new task stack will be created for it , It's time to startActivityIn fact, it is based onsingleTaskMode enabled .Application scenarios : majority Activity Applicable scenarios .
singleTop: Stack top reuse mode
If you want to create a new
ActivityAlready at the top of the task stack , So many timesActivityWill not be recreated , At the same time, itsonNewIntentMethod will be called , CorrespondingonCreateandonStartMethod will not be called .If the newly created
ActivityInstance already exists , But not at the top of the stack , So newActivityWill still be recreated .Application scenarios : Click on the received notification in the notification bar , Need to start a Activity, You can use it singleTop, Otherwise, each click will create a new Activity

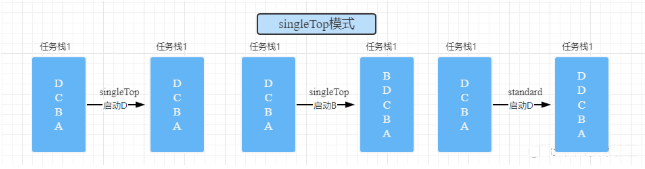
singleTask: In stack reuse mode
A singleton mode , as long as Activity Exists in a stack , that Start this more than once Activity Will not recreate the instance , The system calls it
onNewIntentMethod . When starting a mode issingleTaskOfAcitivityA When , The system first looks for A Desired task stack , If it doesn't exist , Then restart to create a task stack , take A Put it in . If the task stack exists , Check whether there is... In the task stack A Example , without , Create put . If there is A Example , Then the system will A Other aboveActivityremove , Give Way A Stack top , And callonNewIntentMethod .Application scenarios : majority App The home page of . For most applications , When we click the back button on the main interface, we exit the application. Then when we enter the main interface for the first time , The main interface is at the bottom of the stack , No matter how many we open later Activity, As long as we go back to the main interface again , You should use the main interface Activity On all the Activity Remove the way to make the main interface Activity At the top of the stack , Instead of adding a main interface to the top of the stack Activity Example , In this way, you can guarantee all of the Activity All can be reported for destruction .
Check... By command Activity Task stack :adb shell dumpsys activity
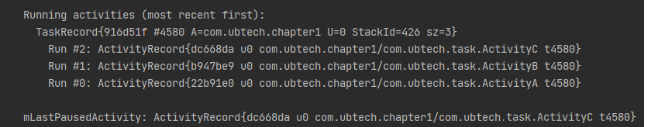
Scene one :A->B->C,B by singleTask Pattern , The current task stack is as follows :

stay 【A,B,C】 Start in B, The task stack is as follows :


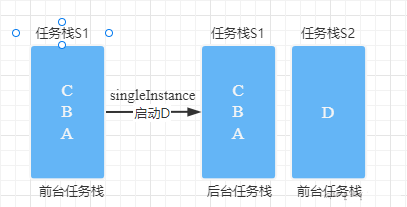
Scene two : The current task stack is :A->B->C, Then with singTask + taskAffinity = “com.ubtech.taskS2” start-up ActivityD

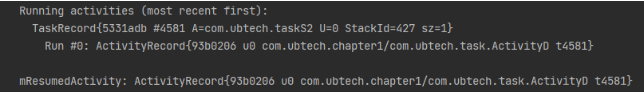
Directly by Back Key fallback :
D -> C -> B -> A -> desktop
Check the background task window of the mobile phone as follows :
1. At this point, if you open the task stack S2, The fallback stack becomes : D -> desktop
2. At this point, if you open the task stack S1, The fallback stack becomes :C->B->A-> desktop 
Uniapp There's a problem with development :
uniapp The Lord of Activity The task stack name of is actually the unique identification code of the packaged application 
singleInstance: Single instance mode
intensive
singleTask, With this patternActivityCan only be in a single task stack , There is only one instance of the whole system .** Application scenarios :** System interface , Such as incoming interface, etc .
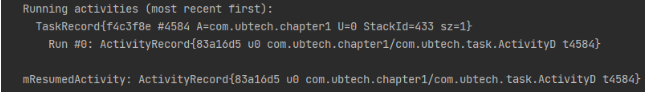
TaskAffinity
This parameter identifies a Activity The name of the required task stack , By default , be-all Activity The name of the task stack is the package name of the application .
The task stack is divided into foreground task stack , Background task stack , You can switch the background task stack to the foreground .
2.Activity in Flags meaning
FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK
- The purpose of this flag bit is to Activity Appoint “singleTask” Pattern , Effect and in xml This mode is the same as that specified in
FLAT_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP
- The purpose of this flag bit is to Activity Appoint “singleTop” Pattern , Effect and in xml This mode is the same as that specified in
FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP
- With this flag bit Activity, When it starts , In the same task stack, all the Activity They all have to go out , Need and
FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASKIn combination with , If the instance exists , Would callonNewIntentMethod .FLAG_ACTIVITY_EXCLUDE_FROM_RECENTS
- With this flag bit Activity Not in history Acitivity List of , If you don't want the user to go back to this... Through the history list Activity Use this marker position when , It's equivalent to being in xml It is specified in android:excludeFromRecents=“true”. Not the same as not having it in the fallback stack .
3. IntentFilter Matching rules
1. Show / Implicit call
1. Display call
//1. Display the calling method 1
Intent intent1 = new Intent(this,ActivityB.class);
startActivity(intent1);
//2. Display call mode 2
ComponentName component = new ComponentName(this,ActivityB.class);
Intent intent2 = new Intent();
intent2.setComponent(component);
startActivity(intent2);
//3. Display the calling method 3
Intent intent3 = new Intent();
intent3.setClass(this,ActivityB.class);
startActivity(intent3);
2. Implicit call
Be careful : You must add the default 

2. Matching rules
IntentFilter The filtering information in is action,category,data.
One IntentFilter There can be multiple action,category,data. The information of the same category restricts the matching process of the current category . only one Intent Simultaneous matching action Category ,category Category ,data Category is a perfect match .
One Activity There can be multiple IntentFilter, One Intent As long as you can match any group intent-filter that will do .
1. action Matching rules
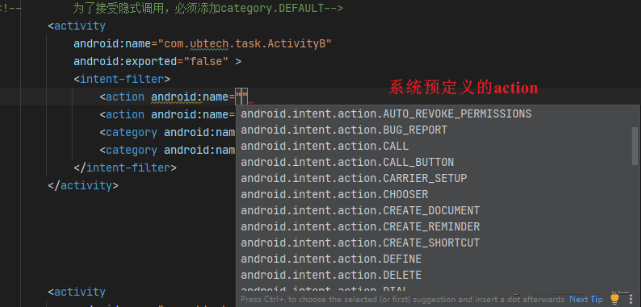
Intent Medium action Must be able to post and intent-filter Medium action matching , One intent-filter There are multiple action,Intent Medium action Just match one of them . If Intent Not specified in action, The match fails .action Case sensitive .
2.category Matching rules
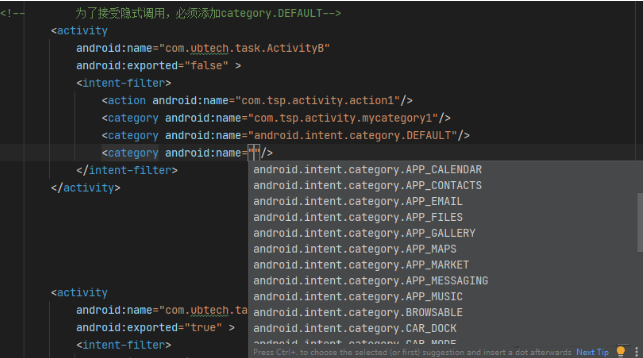
IntentIf anycategory, be-allcategoryAndintent-filterOne of the matches , IfIntentin The emergence ofcategoryMust beintent-filterAs defined in .Intentin There can be no category, Can still match successfully . The system is callingstartActivityThe default will beIntentadd to"android.intent.category.DEFAULT"Thiscategory.- in order to
activityCan accept implicit calls , Must be inintent-filterIt is specified in"android.intent.category.DEFAULT"Thiscategory.
3. data Matching rules
- If intent-filter It defines data, be Intent You must also define a matching data.
- data It consists of two parts : mimeType and URI
- mimeType Media type , such as imgage/jpeg,audo/* and video/* etc. , Can represent a picture , Text , Different media formats such as video .
- URI Each part of the is a separate attribute :
scheme、host、portandpath- ::
,eg:content://com.example.project:200/folder/subfolder/etc - Scheme: URI Pattern , such as http,file,content etc. , If URI Not specified , It doesn't work
- Host: URI The host name , If not specified, the whole URI It doesn't work .
- Port:URI Port number in , Only when the URI It is specified in scheme and host Parameters should be port It works .
- path: Path information
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-Ej9R78kJ-1656589436740)(https://p1-juejin.byteimg.com/tos-cn-i-k3u1fbpfcp/f1716c6edcb746569d91a6a419aa2f57~tplv-k3u1fbpfcp-zoom-in-crop-mark:1956:0:0:0.image?)]
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-mP7vMxsb-1656589436740)(https://p6-juejin.byteimg.com/tos-cn-i-k3u1fbpfcp/a3b60e7009a1497d8371eb26bf848802~tplv-k3u1fbpfcp-zoom-in-crop-mark:1956:0:0:0.image?)]
3. Implicit Activity Whether there is judgment
- adopt PackageManager.resolveActivity Judge
- adopt PackageManager.queryIntentActivities() Judge , This method returns a list of collections .
4. Expand the problem
1.Activity and Fragment The difference between
Activity Is one of the four components of the system , from
ActivityManagermanagement , The life cycle is controlled by the system .
FragmentIs in 3.0 Components introduced after , fromFragmentManagermanagement , Can beActivityFree control , Introduce or delete , More convenient .because
Fragmentyes Activity management , So when using , Pay special attention to , Before creating, you need togetFragmentByTagperhapsByIdCheck to see if there are already ,FragmentManagerAlso withActivityManagerThere is also a caching mechanism . The same TAG OffragmentIf added to more than once activity in , Then through thegetFragmentBytagobtain Fragment What is returned is the last added Fragment
fragmentIn the process of display to destruction, it will execute its own life cycle .onAttach->onCreate->onCreateView->onActivityCreate->onStart->onResume->onPause->onStop->onDestroyView->onDestroy->onDetachAt the same time activity The impact of the life cycle ,activity onPause Fragment The corresponding... Will also be executed onPause
2. Why setArgument The ginseng , Instead of using constructors with parameters ?
- You can use constructors and
setArgumentWay to pass parameters , Once you write a parameter constructor , It is necessary to build a parameterless constructor- Pass arguments through the constructor : When
FragmentBe recreated , The system will callFragmentThe default constructor in , As a result, the previously passed parameters are missing , The official recommendationsetArgument,fragmentAfter being destroyed and rebuilt , Finally, a new one will be instantiated through the reflection parameterless constructionFragment, And givemArgmentsInitialize to the original value , And the originalFragmentThe data of the instance is lost , And re initialize- Activity On re creation , Will rebuild what it manages Fragment, The original Fragment All field values will be lost , But by Fragment.setArguments(Bundle bundle) Method set bundle Will keep it , And restore it during reconstruction .
3.window、view and Activity The relationship between ?
Window yes Android Macro definition of window in , Mainly management View The creation of , As well as ViewRootImpl Interaction , take Activity And View decoupling .
Activity And PhoneWindow And DecorView What's the relationship between ?
One Activity Corresponding to one Window That is to say PhoneWindow, One PhoneWindow Hold one DecorView Example ,DecorView Itself is a FrameLayout.
4.finish How to get to onDestroy Of ?
stay Activity Call in finish() Method , What life cycle approaches will be taken ?
If
FirstActivtStart inSecondActivity, Will go firstFisrtActivityOfonPauseMethod , Then goSecondActivityOfonCreate->onStart->onResume-> Until thenFirstActivityOfonStop->onDestory
interviewer : Why? Activity.finish() after 10s only onDestroy ?
Activity Of
onStop/onDestroyIt's dependenceIdleHandlerCome back . Normally, when the main thread is idle, it will call . However, due to the problems in some special scenes , This causes the main thread to be idle for a long time ,onStop/onDestroy It will also be delayed in getting the call . But that doesn't mean Activity Never get recycled , The system provides a thorough mechanism , When onResume Callback 10s after , If still not called , It will trigger .
5.dialog Will it affect Activity Life cycle , Why? ?
Does not affect the ,Activity Lifecycle callbacks are all
AMSadoptBinderNotify the application process to call ; And pop upDialog、Toast、PopupWindowIt's all directly throughWindowManager.addViewAccording to the ( Not throughAMS), So it doesn't have any impact on the life cycle .Unless it starts Theme by Dialog Of Activity
Destroy It will also be delayed in getting the call . But that doesn't mean Activity Never get recycled , The system provides a thorough mechanism , When onResume Callback 10s after , If still not called , It will trigger .
5.dialog Will it affect Activity Life cycle , Why? ?
Does not affect the ,Activity Lifecycle callbacks are all
AMSadoptBinderNotify the application process to call ; And pop upDialog、Toast、PopupWindowIt's all directly throughWindowManager.addViewAccording to the ( Not throughAMS), So it doesn't have any impact on the life cycle .Unless it starts Theme by Dialog Of Activity
Last
If you have any good learning methods or suggestions, please leave a message in the comments , I hope you can learn together 、 Joint efforts 、 Common progress .
Xiaobian is here to wish you all the best in the future A promotion and pay increase , Be the general manager , As CEO, Marry Bai Fumei , Reach the peak of life !!
No matter what difficulties , Should not be the reason for us to give up !
A lot of people in the first contact with this industry or in the bottleneck period , There are always problems , For example, after learning for a period of time, I feel that I have no sense of direction , I don't know where to start to learn , I need a study material sorted out by Xiaobian Follow my homepage or click the QR code below to get it for free ~
This is about My own Android Study , Interview document , Video collection and collation , Interested partners can have a look at ~
If you see this , If you think the article is well written, give it a compliment ? If you think it's worth improving , Please leave me a message , I will check it carefully , Fix the problem , thank you .
边栏推荐
- 圈铁发音,动感与无噪强强出彩,魔浪HIFIair蓝牙耳机测评
- How does go use symmetric encryption?
- Basic use of MySQL
- How to optimize repeated if err in go language= Nil template code?
- 数据库系统原理与应用教程(001)—— MySQL 安装与配置:MySQL 软件的安装(windows 环境)
- Is the programmer's career really short?
- The supply of chips has turned to excess, and the daily output of Chinese chips has increased to 1billion, which will make it more difficult for foreign chips
- 【Hot100】20. 有效的括号
- MLPerf Training v2.0 榜单发布,在同等GPU配置下百度飞桨性能世界第一
- Rhcsa Road
猜你喜欢
![[observation] where is the consulting going in the digital age? Thoughts and actions of softcom consulting](/img/82/3bb382893682a30e8af130365ec4ef.jpg)
[observation] where is the consulting going in the digital age? Thoughts and actions of softcom consulting

Installation and use of sqoop
In the era of super video, what kind of technology will become the base?
PR basic clip operation / video export operation

VMware 虚拟机启动时出现故障:VMware Workstation 与 Hyper-v 不兼容...

Défaillance lors du démarrage de la machine virtuelle VMware: le poste de travail VMware n'est pas compatible avec hyper - V...
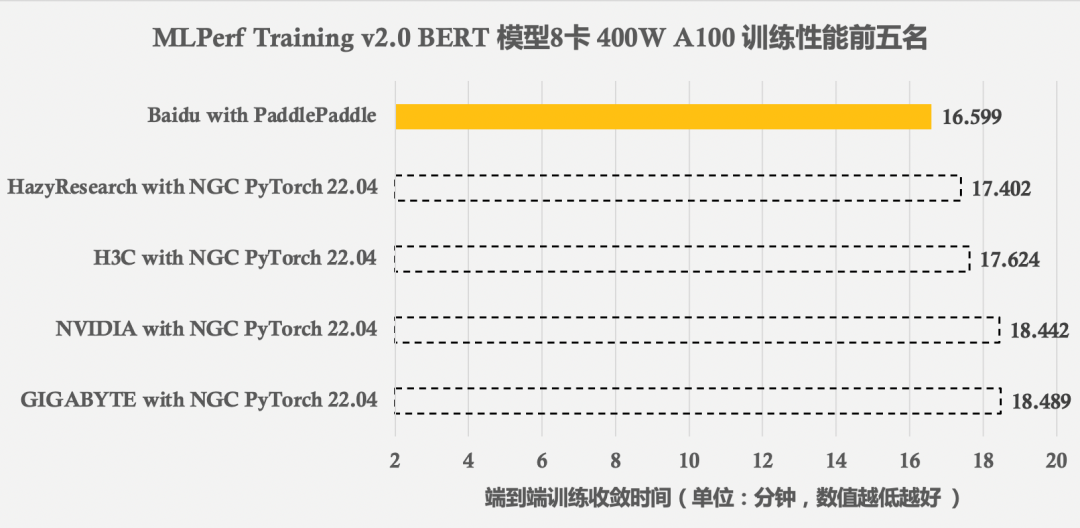
MLPerf Training v2.0 榜单发布,在同等GPU配置下百度飞桨性能世界第一
模板引擎Velocity 基础

Comprehensively view the value of enterprise digital transformation
毕业后5年,我成为了年薪30w+的测试开发工程师
随机推荐
In the past six months, it has been invested by five "giants", and this intelligent driving "dark horse" is sought after by capital
Go language source level debugger delve
數據庫系統原理與應用教程(006)—— 編譯安裝 MySQL5.7(Linux 環境)
投稿开奖丨轻量应用服务器征文活动(5月)奖励公布
Zabbix2.2 monitoring system and application log monitoring alarm
实现数字永生还有多久?元宇宙全息真人分身#8i
从大湾区“1小时生活圈”看我国智慧交通建设
Kali install Nessus
FPN网络详解
In the era of super video, what kind of technology will become the base?
vim用户自动命令示例
【Hot100】20. Valid parentheses
游戏行业安全选择游戏盾,效果怎么样?
Pico, do you want to save or bring consumer VR?
Mlperf training v2.0 list released, with the same GPU configuration, the performance of Baidu PaddlePaddle ranks first in the world
Idea start command line is too long problem handling
StoneDB 为国产数据库添砖加瓦,基于 MySQL 的一体化实时 HTAP 数据库正式开源!
Ring iron pronunciation, dynamic and noiseless, strong and brilliant, magic wave hifiair Bluetooth headset evaluation
芯片供应转向过剩,中国芯片日产增加至10亿,国外芯片将更难受
Apple's self-developed baseband chip failed again, which shows Huawei Hisilicon's technological leadership