当前位置:网站首页>Jetpack architecture component learning (3) -- activity results API usage
Jetpack architecture component learning (3) -- activity results API usage
2022-06-12 14:47:00 【Liziti】
High quality resource sharing
| Learning route guidance ( Click unlock ) | Knowledge orientation | Crowd positioning |
|---|---|---|
| 🧡 Python Actual wechat ordering applet 🧡 | Progressive class | This course is python flask+ Perfect combination of wechat applet , From the deployment of Tencent to the launch of the project , Create a full stack ordering system . |
| Python Quantitative trading practice | beginner | Take you hand in hand to create an easy to expand 、 More secure 、 More efficient quantitative trading system |
This article is original by the author , Reprint please indicate the source , Thank you for cooperating with the author :https://blog.csdn.net/stars-one/p/16364187.html
This article is about 4537 A word , Reading is expected to take 5.67 minute
Original address :Jetpack Architecture component learning (3)——Activity Results API Use - Stars-One My groceries nest
Technology keeps pace with the times , Page Jump value transfer has been using startActivityForResult Method , Now there is a new API Realization way , Learn and summarize
startActivityForResult review
MainActivity Code :

Main2Activity Code :

effect :
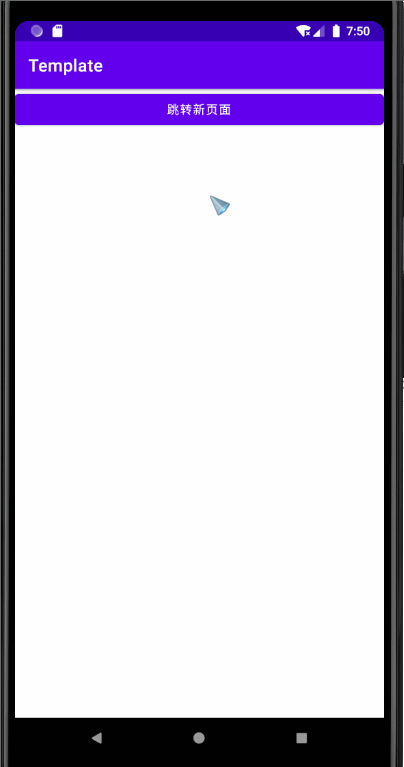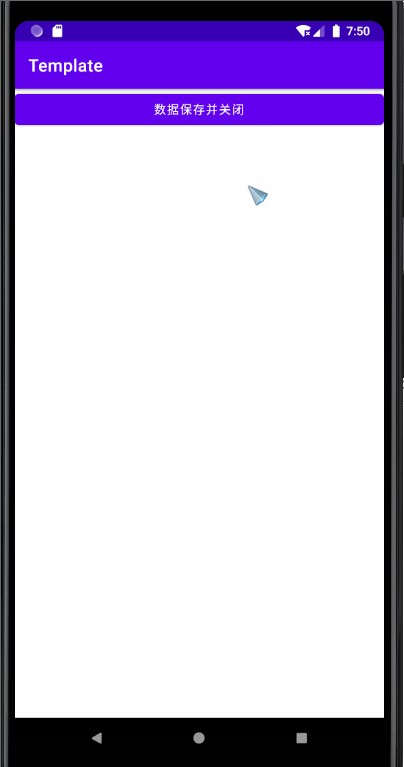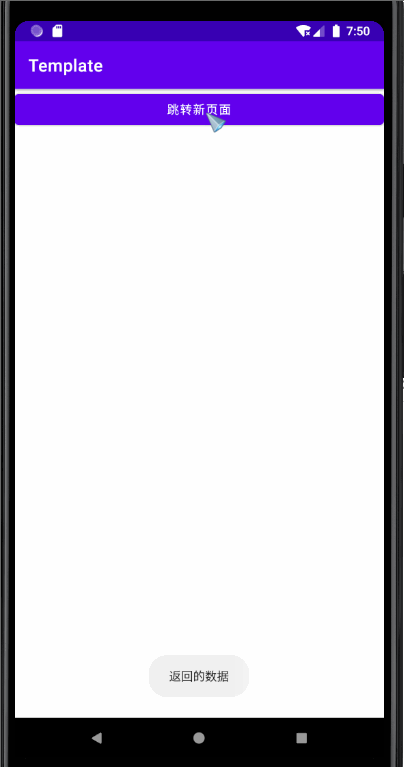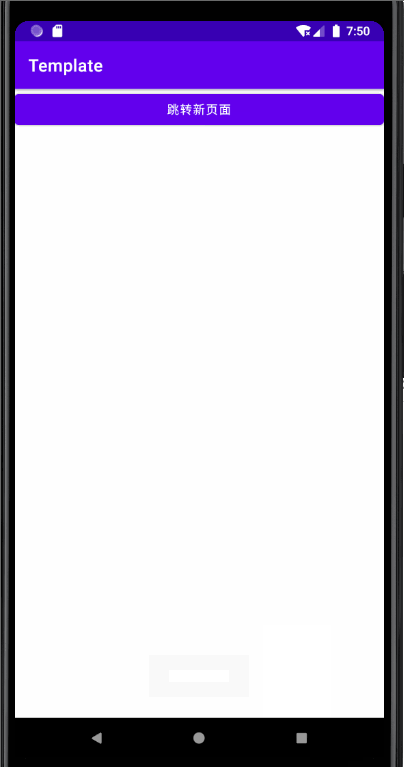
The above code should be the basic code , I won't go into details here
Mainly about some shortcomings
All logic is in onActivityResult() The method is used to judge , according to requestCode and resultCode Judge
If it's OK to say , But if there are more , You will see onActivityResult() In a pile if Logic , It is very tedious to read , And maintenance is difficult
Google officials also took this into account , So we launched a new version Activity Results API To replace the way described above , Here's how to use
Easy to use
1. Introduce dependencies
First , We need to introduce dependencies :
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.3.1'
PS: Please use 1.3.1 Above version , The lower version does not have this enumeration class
ActivityResultContracts
Let's start with the above example , Use Activity Results API
Main2Acitivity The code doesn't move , We just need to adjust MainActivity The code in the file , As shown below :
2. Create a contract
val contract = ActivityResultContracts.StartActivityForResult()
contract The object class name of the variable is ActivityResultContract
ActivityResultContracts Equivalent to an enumeration class , It's officially sealed by Google , There are some commonly used ActivityResultContract Class object for us to use
Like taking pictures , Apply for permission , You can see from the code prompt , As shown in the figure below :
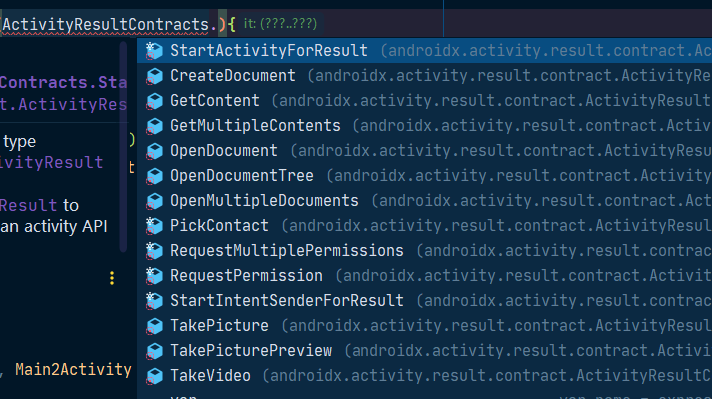
Here we choose StartActivityForResult(), The literal meaning should be easy to understand , It is applied in the scenario that the page jumps and returns data
PS: According to our choice ActivityResultContracts, Will affect the 4 The parameter type in the step
The corresponding selection instructions are supplemented below :
StartActivityForResult: General purpose Contract, No conversion ,Intent As input ,ActivityResult As the output , This is also the most commonly used protocol .CreateDocument: Prompt the user to select a document , Return to one (file:/http:/content:) At the beginning Uri.GetContent: Prompt to select a content , Return a pass through ContentResolver#openInputStream(Uri) Access to native data Uri Address (content:// form ) . By default , It increases the Intent#CATEGORY_OPENABLE, Return the content that can represent the stream .GetMultipleContents: Get multiple itemsOpenDocument: Prompt the user to select a file of the specified type ( Input parameter is mimeType), Returns the file selected by the user UriOpenDocumentTree: Prompt the user to select a directory , And return the user selected as a Uri return , The application can fully manage the documents returned to the directory .OpenMultipleDocuments: Prompt the user to select a document ( Multiple can be selected ), Return their... Respectively Uri, With List In the form of .PickContact: From address book APP Get contactsRequestMultiplePermissions: Used to request a set of permissionsRequestPermission: Used to request a single permissionTakePicturePreview: callMediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURETaking pictures , The return value is Bitmap pictureTakePicture: callMediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURETaking pictures , And save the picture to the given Uri Address , return true Indicates that the save was successful .TakeVideo: callMediaStore.ACTION_VIDEO_CAPTURETake a video , Save to given Uri Address , Return a thumbnail .
See the documentation when specific parameters and descriptions can be used ~
actually , If the above list does not meet our needs , Then we can also customize the contract operation , The following part of the article will be supplemented , I won't extend it here
3. Build a contract ( register Contact)
// register ActivityResultContract
val myLauncher = registerForActivityResult(contract){
if (it.resultCode==2) {
val data = it.data
if (data != null) {
val resultData = data.getStringExtra("mydata")
Toast.makeText(this, resultData, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
}
Use Activity Class registerForActivityResult() Method , Register the deed , In fact, it is equivalent to registering a listener , After from Main2Activity Page back MainActivity page , Will call back the methods in this
Be careful : this
registerForActivityResultThe method needs to be in Activity Life cycle ofonStart()Call before !!
4. Initiate page Jump
val intent = Intent(this, Main2Activity::class.java)
myLauncher.launch(intent)
call myLauncher Object's launch() Method , take intent Object transfer can realize the operation of page Jump
PS: This is still in the button click event , Easy to read omits
After from Main2Activity After the page returns , The operation in step 2 will be recalled , The effect is consistent with the above dynamic illustration , There is no need to re post a picture here
Customize ActivityResultContract
ActivityResultContract There are actually two generic types , Complete should be like this ActivityResultContract
Iby input It means , Meaning for Input parameter typeOby output It means , Meaning for Output parameter type
ActivityResultContract It's an abstract class , We want to implement customization , Then inherit it directly
class MyContract: ActivityResultContract<String, String>() {
override fun createIntent(context: Context, input: String?): Intent {
// here input The type of , Just as mentioned above I
}
override fun parseResult(resultCode: Int, intent: Intent?): String {
// Here, the result type returned by the method , Just as mentioned above O
}
}
Inheritance discovery , We need to implement two methods ,createIntent() and parseResult()
A glance at the past is actually easy to understand ,createIntent() To create a intent object , call launch() Method time ( The number used above 4 Step by step ), It will be based on this intent Jump to the page
and parseResult() Method , It is the step of establishing the contract , The data type of callback inside
Let's take the example above , It is found that we have to make a statement Intent Object delivery , And when you send it back, you have to pass intent Object to get data , A little fussy , Some of the code can be encapsulated into generic
According to this idea , We can achieve one Customize ActivityResultContract, Pass the page parameters to get Main2Activity Returned data , The code is as follows :
class MyContract: ActivityResultContract<KClass>, String>() {
override fun parseResult(resultCode: Int, intent: Intent?): String? {
if (resultCode == 2 && intent!=null) {
return intent.getStringExtra("mydata")
}
return null
}
override fun createIntent(context: Context, input: KClass<out Activity>?): Intent {
val intent = Intent(context,input?.java)
return intent
}
}
Use :
//1. Create a contract
val contract = MyContract()
//2. register ActivityResultContract
val myLauncher = registerForActivityResult(contract){
Toast.makeText(this, it, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
btnGo.setOnClickListener {
//2. Initiate page Jump
myLauncher.launch(Main2Activity::class)
}
Of course , You can also optimize , If we let MyContract Multiple constructors , This is the value key This can also be used to define
class MyContract(val key: String) : ActivityResultContractout Activity>, String>() {
override fun parseResult(resultCode: Int, intent: Intent?): String? {
if (resultCode == 2 && intent != null) {
return intent.getStringExtra(key)
}
return null
}
override fun createIntent(context: Context, input: KClass<out Activity>?): Intent {
val intent = Intent(context, input?.java)
return intent
}
}
Use :
// Create a contract and transfer parameters
val contract = MyContract("mydata")
Reference resources
边栏推荐
- PMP敏捷知识点
- [wechat applet] 5 Applet structure directory
- Appnium (II) installation and basic use of mitmproxy
- 如何给域名前加上 www
- Mysql之索引和视图
- Energy chain smart electronics landed on NASDAQ: Bain is the shareholder to become the first share of charging services in China
- Interview (XI) futu written test questions
- [wechat applet] 1 Introduction to wechat applet
- Recursive summary of learning function
- [system. Currenttimemillis()] current timestamp: the number of milliseconds that have elapsed since the current system time was 0:00:00 on January 1, 1970
猜你喜欢

Tu oses le croire? Il m'a fallu deux jours pour développer un système de gestion.

JUnit test suite method sorting (method 2 is not easy to use)

数据的收集

Software package for optimization scientific research field

Jetpack架构组件学习(3)——Activity Results API使用

Assertion of selenium webdriver

MAT的安装和使用

JS (III) convert ES6 syntax to Es5 syntax

函数相关事项
![JS (I) error [err\u module\u not\u found]: cannot find package 'UUID' imported](/img/a4/ef2d73576e027a2179ec9251167fa4.jpg)
JS (I) error [err\u module\u not\u found]: cannot find package 'UUID' imported
随机推荐
Selenium advanced
Simple code implementation of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division calculator
selenium进阶
数组相关内容
win10_ Home Edition cannot use remote desktop, and can be accessed by remote desktop.
C 字符串
jenkins相关
Jetpack架构组件学习(3)——Activity Results API使用
tc菜单分割
C 转义字符
左对齐,右对齐,随机数,goto,比较输出bool
【OCR】AspriseOCR C# 英文、数字识别(中文不行)
C secret arts script Chapter 5 (paragraph) (Section 3)
[wechat applet] 5 Applet structure directory
recursive learning
【Environment】1. Get the configuration in YML through the environment in the configuration class
三维重建系统 | L3双视角运动恢复结构(SFM双目SFM)
Recursive summary of learning function
【OCR】AspriseOCR C# 英文、數字識別(中文不行)
基于TensorRT的深度学习模型部署实战教程!