当前位置:网站首页>Similarity calculation method
Similarity calculation method
2022-06-25 08:25:00 【Happy little yard farmer】
List of articles
Similarity calculation method
1. Text distance
1.1 Edit distance (Edit Distance)
Edit distance , English is called Edit Distance, also called Levenshtein distance , Between two strings , The minimum number of editing operations required to move from one to another .** If the edit distance between two strings is larger , The more different they are .** Permitted editing operations include adding a character Replace Into another character , Insert A character , Delete A character .
1.2 The longest public substring 、 Longest common subsequence (Long Common Subsequence,LCS)
Longest common subsequence problem : Given two strings , S S S( length n n n) and T T T( length m m m), Solve their longest common subsequence . Where common subsequence refers to : In left to right order S S S、 T T T A sequence of characters that appears in , The characters in the subsequence are S S S、 T T T in No continuous .
example : S S S = ABAZDC、 T T T = BACBAD, S S S and T T T The longest common subsequence of is :ABAD.
The longest public substring problem : Given two strings , S S S( length n n n) and T T T( length m m m), Solve their longest common substring . Where the common substring refers to : In left to right order S S S、 T T T String that appears in , The characters in the substring are S S S、 T T T in Need to be continuous .
example : S S S = ABAZDC、 T T T = BACBAD, S S S and T T T The longest common substring of is :BA.
1.3 Sentence vector representation (Word Averaging Model,WAM)
obtain Sentence Vector : We first segment the sentence , Then get the corresponding for each word Vector, And then all of the Vector Add and average , In this way, you can get Sentence Vector.

1.4 WMD
WMD(Word Mover’s Distance) It is called word shift distance in Chinese . The semantic similarity of two texts is measured by finding the pairing of the sum of the minimum distances between all words between two texts . yes EMD(Earth Mover’s Distance) stay NLP The extension of the field .
Each word in the two texts needs to be mapped one by one , Calculate the similarity , And the similarity is calculated with emphasis .
c ( i , j ) c(i,j) c(i,j) Means the word i , j i, j i,j Similarity calculation between , and T i j T_{ij} Tij Represents the weight of this similarity . Because the words between two texts have to be calculated for similarity , You know T It's a matrix . d i d_i di Is the normalized word frequency (normalized BOW), The importance of a word is related to its frequency of occurrence ( And normalize ). If a word i i i The number of occurrences in the text is c i c_i ci, Its normalized word frequency is : d i = c i ∑ j = 1 n c j d_i=\frac{c_i}{\sum_{j=1}^{n}c_j} di=∑j=1ncjci.
min T ≥ 0 ∑ i , j = 1 n T i j c ( i , j ) s . t : ∑ j = 1 n T i j = d i ∀ i ∈ 1 , … , n ∑ i = 1 n T i j = d j ′ ∀ j ∈ 1 , … , n \min_{T\ge0}\sum_{i,j=1}^{n}T_{ij}c(i,j)\\ s.t: \sum_{j=1}^{n}T_{ij}=d_i \quad \forall i\in{1,\dots,n}\\ \sum_{i=1}^{n}T_{ij}=d_j' \quad \forall j\in{1,\dots,n}\\ T≥0mini,j=1∑nTijc(i,j)s.t:j=1∑nTij=di∀i∈1,…,ni=1∑nTij=dj′∀j∈1,…,n
Calculate the... Between two documents WMD It is required to solve a large linear programming problem .
1.5 BM25
BM25 It is an algorithm used to evaluate the correlation between search terms and documents , It is an algorithm based on probability retrieval model : There is one q u e r y query query And a batch of documents Ds, Now we have to calculate q u e r y query query And every document D The correlation between , First pair q u e r y query query Segmentation , Get the word q i q_i qi, Then the score of the word is determined by 3 Part of it is made up of :
- Weight of each word W i W_i Wi, Can be IDF Express , I D F ( q i ) = l o g ( N − n ( q i ) + 0.5 n ( q i ) + 0.5 ) IDF(q_i)=log(\frac{N-n(q_i)+0.5}{n(q_i)+0.5}) IDF(qi)=log(n(qi)+0.5N−n(qi)+0.5)
- Correlation score R: Words and D The correlation between , Words and query The correlation between
S c o r e ( Q , d ) = ∑ i = 1 n W i ⋅ R ( q i , d ) R ( q i , d ) = f i ⋅ ( k 1 + 1 ) f i + K ⋅ q f i ⋅ ( k 2 + 1 ) q f i + k 2 K = k 1 ⋅ ( 1 − b + b ⋅ d l a v g d l ) Score(Q,d)=\sum_{i=1}^n W_i \cdot R(q_i, d)\\ R(q_i,d)=\frac{f_i\cdot (k_1+1)}{f_i+K}\cdot \frac{qf_i\cdot (k_2+1)}{qf_i+k_2}\\ K=k_1\cdot (1-b+b\cdot \frac{dl}{avgdl}) Score(Q,d)=i=1∑nWi⋅R(qi,d)R(qi,d)=fi+Kfi⋅(k1+1)⋅qfi+k2qfi⋅(k2+1)K=k1⋅(1−b+b⋅avgdldl)
- d l dl dl It's documentation d d d The length of , a v g d l avgdl avgdl Is the average length of documents in the entire document set ;
- f i f_i fi Is the word q i q_i qi In the document d d d The frequency of words in , q f i qf_i qfi Is the word q i q_i qi stay q u e r y query query The frequency of words in ;
- k 1 , b k_1, b k1,b Is the parameter ( Usually k 1 = 1.2 , b = 0.75 k_1=1.2, b=0.75 k1=1.2,b=0.75);
- In simplified cases , q u e r y query query It's shorter , Query word q i q_i qi stay q u e r y query query Only once will , namely q f i = 1 qf_i=1 qfi=1, Therefore, it can simplify R ( q i , d ) R(q_i,d) R(qi,d) in q f i ⋅ ( k 2 + 1 ) q f i + k 2 = 1 \frac{qf_i\cdot (k_2+1)}{qf_i+k_2}=1 qfi+k2qfi⋅(k2+1)=1.
Sum up ,BM25 The correlation score formula of the algorithm can be summarized as :
S c o r e ( Q , d ) = ∑ i = 1 n I D F ( q i ) ⋅ f i ⋅ ( k 1 + 1 ) f i + k 1 ⋅ ( 1 − b + b ⋅ d l a v g d l ) Score(Q,d)=\sum_{i=1}^n IDF(q_i) \cdot \frac{f_i\cdot (k_1+1)}{f_i+k_1\cdot (1-b+b\cdot \frac{dl}{avgdl})} Score(Q,d)=i=1∑nIDF(qi)⋅fi+k1⋅(1−b+b⋅avgdldl)fi⋅(k1+1)
TF/IDF and BM25 Also use Reverse document frequency Rate to distinguish common words ( Is not important ) And non ordinary words ( important ), It is also believed that the more frequently a word appears in the document , The more relevant the document is to the word . In fact, the function of a common word appearing in a large number in the same document will be due to the word in all Offset by a large number of occurrences in the document .
BM25 There is an upper limit , In the document 5 To 10 Words that appear only once or twice have a significant impact on the degree of correlation . But as shown here TF/IDF And BM25 Word frequency saturation See , Appears in the document 20 The words of times have almost the same influence as those that appear thousands of times .
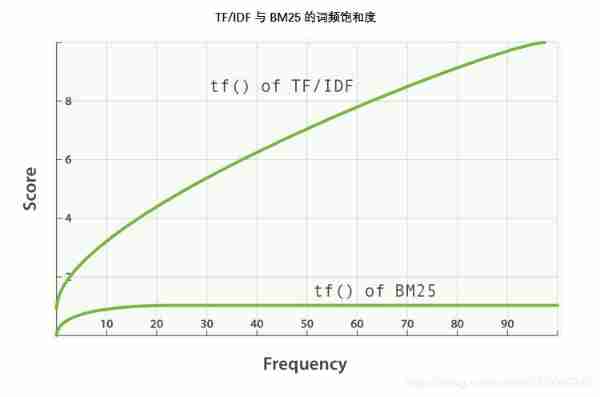
2. Statistical indicators
2.1 Cosine Similarity
Cosine distance , Also known as cosine similarity , The cosine of the angle between two vectors in vector space is used as a measure of the difference between two individuals .Cosine Similarity The greater the absolute value of , The more similar the two vectors are , The value is negative. , Two vectors are negatively correlated .
C o s i n e S i m i l a r i t y ( X , Y ) = ∑ i = 1 n x i y i ∑ i = 1 n x i 2 ∑ i = 1 n y i 2 CosineSimilarity(X,Y)=\frac{\sum_{i=1}^n x_iy_i}{\sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^n x_i^2}\sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^n y_i^2}} CosineSimilarity(X,Y)=∑i=1nxi2∑i=1nyi2∑i=1nxiyi
Cosine similarity is more about distinguishing differences in direction , It's not sensitive to absolute values , Therefore, it is impossible to measure the difference of values in each dimension , Will lead to such a situation :
Users rate content , Press 5 " ,X and Y Two users rated the two contents as (1,2) and (4,5), The result of cosine similarity is 0.98, The two are very similar . But in terms of the score X Don't seem to like 2 This Content , and Y I prefer , The insensitivity of cosine similarity to numerical value results in the error of results , The irrationality needs to be corrected to adjust cosine similarity , That is, all the values in all dimensions are subtracted from a mean value , such as X and Y The average score is 3, Then adjust it to (-2,-1) and (1,2), And then calculate the cosine similarity , obtain -0.8, The similarity is negative and the difference is not small , But it's obviously more realistic .
Adjust cosine similarity (Adjusted Cosine Similarity):
A d j u s t e d C o s i n e S i m i l a r i t y ( X , Y ) = ∑ i = 1 n ( x i − 1 n ∑ i = 1 n x i ) ( y i − 1 n ∑ i = 1 n y i ) ∑ i = 1 n ( x i − 1 n ∑ i = 1 n x i ) 2 ∑ i = 1 n ( y i − 1 n ∑ i = 1 n y i ) 2 AdjustedCosineSimilarity(X,Y)=\frac{\sum_{i=1}^n (x_i-\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^n x_i)(y_i-\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^n y_i)}{\sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^n (x_i-\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^n x_i)^2}\sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^n (y_i-\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^n y_i)^2}} AdjustedCosineSimilarity(X,Y)=∑i=1n(xi−n1∑i=1nxi)2∑i=1n(yi−n1∑i=1nyi)2∑i=1n(xi−n1∑i=1nxi)(yi−n1∑i=1nyi)
2.2 Jaccard Similarity
Jacquard coefficient , English is called Jaccard index, Also known as Jaccard similarity, It is used to compare the similarities and differences between finite sample sets .
Jaccard The larger the value of the coefficient , The higher the similarity of samples .
computing method : The intersection of two samples divided by the union , When two samples are exactly the same , The result is 1, When two samples are completely different , The result is 0.
Range of calculation results : [ 0 , 1 ] [0,1] [0,1].
J a c c a r d S i m i l a r i t y ( X , Y ) = X ∩ Y X ∪ Y JaccardSimilarity(X,Y)=\frac{X\cap Y}{X\cup Y} JaccardSimilarity(X,Y)=X∪YX∩Y
The opposite concept of the jacquard similarity coefficient is the jacquard distance (Jaccard Distance), It can be expressed by the following formula :
J a c c a r d D i s t a n c e ( X , Y ) = 1 − X ∩ Y X ∪ Y JaccardDistance(X,Y)=1-\frac{X\cap Y}{X\cup Y} JaccardDistance(X,Y)=1−X∪YX∩Y
Jacquard distance measures the differentiation of two sets by the proportion of different elements in all elements .
2.3 Pearson Correlation
Pearson correlation coefficient (Pearson Correlation) It is defined as the quotient of covariance and standard deviation between two variables . It's actually a cosine similarity , But first we've centered the vector , Subtract the mean from each of the two vectors , Then calculate the cosine similarity . When the mean of both vectors is 0 when , Pearson's relative coefficient equals cosine similarity .
Range of calculation results : [ − 1 , 1 ] [-1,1] [−1,1],-1 It means negative correlation ,1 Ratio means positive correlation .
computing method :
P e a r s o n C o r r e l a t i o n ( X , Y ) = c o v ( X , Y ) σ X σ Y = ∑ i = 1 n ( X i − X ˉ ) ( Y i − Y ˉ ) ∑ i = 1 n ( X i − X ˉ ) 2 ∑ i = 1 n ( Y i − Y ˉ ) 2 Pearson Correlation(X, Y)=\frac{cov(X,Y)}{\sigma_X\sigma_Y}=\frac{\sum_{i=1}^n(X_i-\bar{X})(Y_i-\bar{Y})}{\sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^n(X_i-\bar{X})^2}\sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^n(Y_i-\bar{Y})^2}} PearsonCorrelation(X,Y)=σXσYcov(X,Y)=∑i=1n(Xi−Xˉ)2∑i=1n(Yi−Yˉ)2∑i=1n(Xi−Xˉ)(Yi−Yˉ)
2.4 Euclidean Distance
Ming's distance (Minkowski Distance) Promotion of : p = 1 p=1 p=1 For Manhattan distance , p = 2 p=2 p=2 For Euclidean distance , Chebyshev distance is the form of the limit of Mings distance .
M i n k o w s k i D i s t a n c e = ( ∑ i = 1 n ∣ x i − y i ∣ p ) 1 / p M a n h a t t a n D i s t a n c e = ∑ i = 1 n ∣ x i − y i ∣ E u c l i d e a n D i s t a n c e = ∑ i = 1 n ( x i − y i ) 2 C h e b y s h e v D i s t a n c e = lim p → ∞ ( ∑ i = 1 n ∣ x i − y i ∣ p ) 1 / p = max ∣ x i − y i ∣ Minkowski Distance=(\sum_{i=1}^n |x_i-y_i|^p)^{1/p}\\ Manhattan Distance=\sum_{i=1}^n |x_i-y_i|\\ Euclidean Distance=\sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^n (x_i-y_i)^2}\\ Chebyshev Distance=\lim_{p \to \infty}(\sum_{i=1}^n |x_i-y_i|^p)^{1/p}=\max |x_i-y_i| MinkowskiDistance=(i=1∑n∣xi−yi∣p)1/pManhattanDistance=i=1∑n∣xi−yi∣EuclideanDistance=i=1∑n(xi−yi)2ChebyshevDistance=p→∞lim(i=1∑n∣xi−yi∣p)1/p=max∣xi−yi∣
If the eigenvalues of two points are not in the same order of magnitude , Large eigenvalues will overwrite small ones . Such as Y1(10000,1),Y2(20000,2).
Standard Euclidean distance The idea of : Standardize the data of each dimension : Standardized value = ( Value before standardization - Mean value of components ) / Standard deviation of component , Then calculate the Euclidean distance .
S t a n d a r d E u c l i d e a n D i s t a n c e = ∑ i = 1 n ( x i − y i s i ) 2 Standard Euclidean Distance=\sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^n (\frac{x_i-y_i}{s_i})^2} StandardEuclideanDistance=i=1∑n(sixi−yi)2
3. Depth match
Reference resources
Common distance algorithm and similarity ( The correlation coefficient ) computing method
Deep learning to solve NLP problem : Semantic similarity calculation
Pluggable similarity algorithm
Welcome to my official account. 【SOTA Technology interconnection 】, I will share more dry goods .

边栏推荐
- [Mobius inversion]
- How to analyze the coupling coordination index?
- Go language learning tutorial (13)
- VOCALOID notes
- 图像超分综述:超长文一网打尽图像超分的前世今生 (附核心代码)
- [supplementary question] 2021 Niuke summer multi school training camp 4-N
- How to calculate the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation index? How to calculate the four fuzzy operators?
- 物联网毕设(智能灌溉系统 -- Android端)
- Thread + thread problem record
- Use pytorch to build mobilenetv2 and learn and train based on migration
猜你喜欢

初体验完全托管型图数据库 Amazon Neptune

How to do factor analysis? Why should data be standardized?

Static web server

How to analyze the coupling coordination index?
![[thesis study] vqmivc](/img/38/a97ac763a7d6e71d4c7340c7abb6e7.png)
[thesis study] vqmivc

Apache CouchDB Code Execution Vulnerability (cve-2022-24706) batch POC

物联网毕设(智能灌溉系统 -- Android端)

Quickly build a real-time face mask detection system in five minutes (opencv+paddlehub with source code)
Sword finger offer (simple level)
Bluecmsv1.6- code audit
随机推荐
4个不可不知的采用“安全左移”的理由
Luogu p6822 [pa2012]tax (shortest circuit + edge change point)
Luogu p1073 [noip2009 improvement group] optimal trade (layered diagram + shortest path)
Not afraid of losing a hundred battles, but afraid of losing heart
RMQ interval maximum subscript query, interval maximum
Quickly build a real-time face mask detection system in five minutes (opencv+paddlehub with source code)
企业全面云化的时代——云数据库的未来
Measure the current temperature
是否可以给数据库表授予删除列对象的权限?为什么?
面试前准备好这些,Offer拿到手软,将军不打无准备的仗
[unexpected token o in JSON at position 1 causes and solutions]
Luogu p5994 [pa2014]kuglarz (XOR thinking +mst)
[Mobius inversion]
How to interpret the information weight index?
Is there no risk in the security of new bonds
Want to open an account, is it safe to open an online stock account?
Static web server
CVPR 2022 oral 2D images become realistic 3D objects in seconds
测一测现在的温度
Biweekly investment and financial report: capital ambush Web3 infrastructure