当前位置:网站首页>Embedded c learning notes
Embedded c learning notes
2022-06-26 01:35:00 【m0_ forty-six million three hundred and twenty-one thousand one】
Catalog
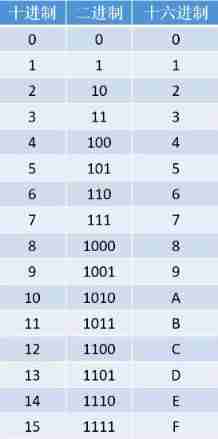
1. 2 Base number 、8 Base number 、16 The conversion of base systems
Binary representation :0B
Hexadecimal representation :0X
Hexadecimal said
2. Base conversion method
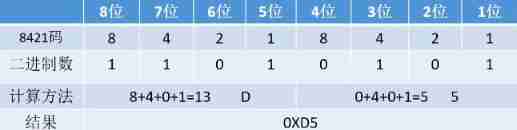
For binary to hexadecimal, a hexadecimal equals four bits of binary , adopt 8421 Code calculation
3. C Language structure
meaning
The ability to assemble multiple different data into one type ( It can contain multiple different data types )
Structure structure

Other uses of structs
Can pass typedef To define the structure , And define other parameters through this structure 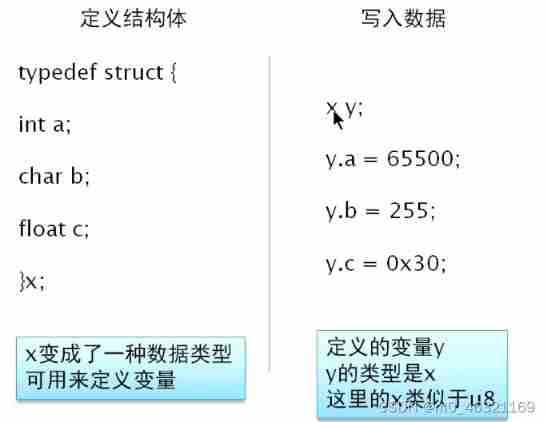
4. excent usage
extern yes C A key word in a language , Usually used before variable name or function name , The function is to explain “ This variable / Functions are defined elsewhere , To quote... Here ”,extern Most of this keyword should be in the storage type of variables
External variables ( Global variables )extern---- Global static storage
Standard definition format :extern Type name Variable name ;
effect
Use this variable in advance , Or reference variables in other files
Reference resources :extern( External variables )
5. const Usage method
effect
You can define an immutable variable , An error will be reported when there are other assignment operations ( Generally, this variable is capitalized to distinguish )
const int MaxNum = 100; // Maximum class size
const And a pointer
const int *p1;
int const *p2;
int * const p3;
In the last case , The pointer is read-only , That is to say p3 The value of itself cannot be modified ; In the first two cases , The data pointed to by the pointer is read-only , That is to say p1、p2 The value of itself can be modified ( Point to different data ), But the data they point to cannot be modified .
const And function parameters
stay C In language , Individually define const Variables have no obvious advantage , Totally usable #define Command instead of .const Usually used in function parameters , If the parameter is a pointer , To prevent modification of the data pointed to by the pointer inside the function , You can use it const To limit .
const He Fei const Type conversion
When a pointer variable str1 By const When the limit , And it's like const char *str1 This form , Indicates that the data pointed to by the pointer cannot be modified ; If you will str1 Assign a value to another one that is not const Decorated pointer variable str2, There's a risk . Because by str1 Can't modify data , And after assignment, it passes str2 Can modify the data , The meaning has changed , So the compiler doesn't advocate this behavior , Will give errors or warnings .
in other words ,const char * and char * It's a different type , Can't be const char * The data of type is assigned to char * Variable of type . But the reverse is possible , The compiler allows you to char * The data of type is assigned to const char * Variable of type .
This limitation is easy to understand ,char * The data pointed to has read and write permissions , and const char * The data pointed to has only read permission , Lowering data permissions will not cause any problems , However, increasing the authority of data may lead to danger .
C The parameters of many functions in the language standard library are const Limit , But we didn't pay attention to this problem in the previous coding process , Often non const Data of type is passed to const Type parameters , This has never caused any side effects , The reason is the above mentioned , Will not const Type conversion to const Type is allowed .
Reference resources C Language const A detailed explanation of the use of ,C Detailed definition of language constants
6. The pointer (* usage )
1. Defining a pointer requires *( as follows , Defines the pointer that should be , be called a)
2. When taking values, you need to use *( as follows , Need to use * To represent the address of the data )
3. For a defined pointer , no need * Represents the position of the pointer , Not the data 
Reference to pointer variable
printf("a=%d\n",a); // By name , Direct access to variables a Space ( Read )
printf("a=%d\n",*p); // Through the address , Indirect access to variables a Space ( Read )
*p=6;// Equivalent to a=6; Indirect access to a Corresponding space ( save )
printf("a=%d\n",*p);
Wild pointer ( Misquote )
int *pi,a; //pi uninitialized , No legal direction , by “ wild ” The pointer
*pi=3; // Runtime error ! Not right ” wild ” The space pointed to by the pointer is used for saving . This statement attempts to put 3 Deposit in “ wild ” The pointer pi In the random space referred to , Run time errors will occur .
a=*pi; // Runtime error ! Not right ” wild ” The space fetch operation pointed to by the pointer . This statement attempts to start from “ wild ” The pointer pi Fetch data from the indicated space , Then assign it to the variable a It will also generate runtime errors .
/* Quote... Correctly */
// & To get a The address of
pi=&a;// Give Way pi There is a legal point ,pi Point to a The space corresponding to the variable
*pi=3;// hold 3 Indirect deposit pi The variable pointed to a The corresponding space
The difference between pointer and multiplication
The following differences :a multiply b,1 multiply b,a Add the pointer b Value ,a Multiply by the pointer b Value 
7. Structure pointer
Just like ordinary variables , The structure pointer is the position of the represented structure , as follows :
# include <stdio.h>
# include <string.h>
struct AGE
{
int year;
int month;
int day;
};
struct STUDENT
{
char name[20]; // full name
int num; // Student number
struct AGE birthday; // Birthday
float score; // fraction
};
int main(void)
{
struct STUDENT student1; /* use struct STUDENT Structure type defines structure variables student1*/
struct STUDENT *p = NULL; /* Define a point struct STUDENT Pointer variables of struct type p*/
p = &student1; /*p Point to the structure variable student1 The first address , That is, the address of the first member */
strcpy((*p).name, " Xiao Ming "); //(*p).name Equivalent to student1.name
(*p).birthday.year = 1989;
(*p).birthday.month = 3;
(*p).birthday.day = 29;
(*p).num = 1207041;
(*p).score = 100;
printf("name : %s\n", (*p).name); //(*p).name Can not write p
printf("birthday : %d-%d-%d\n", (*p).birthday.year, (*p).birthday.month, (*p).birthday.day);
printf("num : %d\n", (*p).num);
printf("score : %.1f\n", (*p).score);
return 0;
}
It can also be useful -> To point to a special variable of a pointer , as follows :
# include <stdio.h>
# include <string.h>
struct AGE
{
int year;
int month;
int day;
};
struct STUDENT
{
char name[20]; // full name
int num; // Student number
struct AGE birthday; /* use struct AGE Structure type defines structure variables birthday, Birthday */
float score; // fraction
};
int main(void)
{
struct STUDENT student1; /* use struct STUDENT Structure type defines structure variables student1*/
struct STUDENT *p = NULL; /* Definition struct STUDENT Pointer variables of struct type p*/
p = &student1; /*p Point to the structure variable student1 The first address , That is, the address of the first item */
strcpy(p->name, " Xiao Ming ");
p->birthday.year = 1989;
p->birthday.month = 3;
p->birthday.day = 29;
p->num = 1207041;
p->score = 100;
printf("name : %s\n", p->name); //p->name Can not write p
printf("birthday : %d-%d-%d\n", p->birthday.year, p->birthday.month, p->birthday.day);
printf("num : %d\n", p->num);
printf("score : %.1f\n", p->score);
return 0;
}
Reference resources : Structure pointer description
8. Macro definition
Macro definition is a common preprocessing instruction , That is to use “ identifier ” To express “ Replace list ” The content in . The identifier is called the macro name , In the process of pretreatment , The preprocessor takes all the macro names in the source program , Replace with the contents of the replacement list in the macro definition .
There are parameter macro definitions
The format is :
#define identifier Replace list
The substitution list can be a numeric constant 、 character constants 、 String constants, etc , Therefore, a macro definition can be understood as using an identifier to represent a constant , Or symbolic constant .
Macro definition with parameters
The definition format of substitute meal macro is :
#define identifier ( Parameters 1, Parameters 2,..., Parameters n) Replace list
Reference resources Macro definition
9.Typedef
Define a new type name for the basic data type
All basic types by default can be used typedef Keyword to redefine the type nameFor custom data types ( Structure 、 Common body and enumeration type ) Define concise type names

Define concise type names for arrays
typedef int INT_ARRAY_100[100];
INT_ARRAY_100 arr;
- Define concise names for pointers
typedef char* PCHAR;
PCHAR pa;
Reference resources typedef
10. Conditional compilation
Conditional compilation means that the preprocessor compiles instructions according to conditions , Conditionally select part of the source code as the output , Send it to the compiler to compile . It's mainly for selective operation , Prevent macros from replacing content ( Such as documents, etc ) The repetition of contains . The common conditional compilation instructions are shown in the table .
| Conditional compilation instructions | explain |
|---|---|
| #if | If the condition is true , Then perform the corresponding operation |
| #elif | If the previous condition is false , And the condition is true , Then perform the corresponding operation |
| #else | If the previous conditions are all false , Then perform the corresponding operation |
| #endif | End the corresponding conditional compilation instructions |
| #ifdef | If the macro has been defined , Then perform the corresponding operation |
| #ifndef | If the macro is not defined , Then perform the corresponding operation |
11. Memory operations
One 、malloc/calloc
malloc and calloc Can allocate memory areas , but malloc Only one memory area can be requested at a time ,calloc You can apply for multiple memory areas at a time . in addition calloc The allocated memory area will be initially converted into 0,malloc No initialization .
Two 、 malloc/calloc
free Can be released by malloc or calloc Memory allocated by the memory allocation function . When the program is large , You may have to dynamically allocate memory multiple times during , If not released in time , The program will take up a lot of memory .
3、 ... and 、 memset
memset hold buffer Before the memory area referred to count Bytes set to a character ASCLL value . Generally used to give an array , String and other types of assignment .
Four 、 memcpy
memcpy Will be able to src The memory area referred to is copied count Byte to dest The memory area referred to . If count Than src The number of bytes is large ,strcpy Can copy ’/0’ After that . it is to be noted that dest and src Don't overlap .
memcpy Just copy memory space , Do not deal with spatial overlap .
边栏推荐
- Xinku online | cnopendata text data of IPO declaration and issuance of A-share listed companies
- shell正则表达式
- 如何有效地推广产品
- **MySQL例题一(根据不同问题,多条件查询)**
- C disk cleaning strategy of win10 system
- 经纬度 多点 获取中心点 已解决
- 使用Gin框架运行Demo时报错“ listen tcp :8080: bind: An attempt was made to access a socket in a way forbidden”
- Installing MySQL databases in FreeBSD
- mysql错误代码2003的解决办法
- 物联网?快来看 Arduino 上云啦
猜你喜欢

Shengxin weekly issue 33

Installing MySQL databases in FreeBSD

《产品思维30讲》精华及感想

多接口调用,使用Promise.all、Promise.race和Promise.any

The overall process of adding, deleting, modifying and querying function items realized by super detailed SSM framework

Endnote IEEE Transactions on industrial electronics/tie/tpel reference format template

Multiple interface calls, using promise all、Promise. Race and promise any

New library launched | cnopendata China new house information data

Xinku online | cnopendata text data of IPO declaration and issuance of A-share listed companies

CityJSON
随机推荐
Laravel basic course routing and MVC - routing
Inheritance -- holy grail mode
Is it safe to open a fund account? Are there any risks?
ETCD数据库源码分析——集群间网络层服务端接口
The overall process of adding, deleting, modifying and querying function items realized by super detailed SSM framework
2021-1-15 摸魚做的筆記Ctrl+c /v來的
JSON introduction
Simple making of master seal
远程增量同步神器rsync
100ask seven day IOT training camp learning notes - bare metal program framework design
Shell regular expression
2021-1-15 fishing notes ctrl+c /v
MySQL example - comprehensive case (multi condition combined query)
Region of Halcon: generation of multiple regions (4)
在FreeBSD中安装MySQL数据库
Is it safe for flush software to buy stocks for trading? How to open an account to buy shares
containerd客户端比较
RT-Thread 项目工程搭建和配置--(Env Kconfig)
智慧家——全家具功能
leetcode 300. Longest Increasing Subsequence 最长递增子序列 (中等)