当前位置:网站首页>100ask seven day IOT training camp learning notes - bare metal program framework design
100ask seven day IOT training camp learning notes - bare metal program framework design
2022-06-26 01:15:00 【_ kukukukiki__】
1. Preface
Signed up 100ask Organized a seven day IOT smart home training camp , Every day in the morning 2 An hour to talk about the basics , Afternoon 2 Hours of advanced lecture . After two days' study, I really feel more fulfilled . In the next few days, I will focus on the key points of each class 、 Record the difficulties and your understanding .
2. theory
2.1 Throw questions
In this lesson, Mr. Wei started the course with the program framework design as the starting point , Take embedded bare metal development as an example , Many beginners usually work in business layer code or even main Function , Directly call the interface used to describe or hardware ( Such as HAL library ):
void main(void)
{
GPIO_PinState key;
while (1)
{
key = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_6);
if (key == GPIO_PIN_RESET)
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
else
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_PIN_SET);
}
}
This will cause serious coupling between business layer code and board level code , Extend the following software functions 、 Hardware upgrade and code reuse will cause inconvenience , At the same time, it will also create obstacles for business layer developers who do not understand hardware .
To solve this problem , We layered the program structure , Separate business logic from hardware driver code :
// main.c
void main(void)
{
int key;
while (1)
{
key = read_key();
if (key == UP)
led_on();
else
led_off();
}
}
// key.c
int read_key(void)
{
GPIO_PinState key;
key = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_6);
if (key == GPIO_PIN_RESET)
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
// led.c
void led_on(void)
{
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
}
void led_off(void)
{
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_PIN_SET);
}
This solves the problem of coupling business logic code with hardware driver code , But there are still two unsolved problems :
One 、 Software compatibility problems caused by hardware version iteration
Two 、 Functional scalability issues
2.2 Introduce function pointer
Here we have to solve the first problem , Usually there are 3 Methods :
Macro switch
#define HARDWARE_VER 1 // key.c // Return value : 0 Indicates being pressed , 1 Indicates that it is loosened int read_key(void) { GPIO_PinState key; #if (HARDWARE_VER == 1) key = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_6); #else key = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_7); #endif if (key == GPIO_PIN_RESET) return 0; else return 1; }Macro switch if more than one , It will be a disaster to maintain .
stay EEPROM Save the hardware version number in , Call the hardware version difference interface according to the version number
// key.c // Return value : 0 Indicates being pressed , 1 Indicates that it is loosened int read_key(void) { GPIO_PinState key; int ver = read_hardware_ver(); if (ver == 1) key = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_6); else (ver == 2) key = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_7); if (key == GPIO_PIN_RESET) return 0; else return 1; }Similar to macro switches , More than one , It's hard to maintain .
A function pointer
// key.c int (*read_key)(void); // Return value : 0 Indicates being pressed , 1 Indicates that it is loosened int read_key_ver1(void) { GPIO_PinState key; key = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_6); if (key == GPIO_PIN_RESET) return 0; else return 1; } // Return value : 0 Indicates being pressed , 1 Indicates that it is loosened int read_key_ver2(void) { GPIO_PinState key; key = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_6); if (key == GPIO_PIN_RESET) return 0; else return 1; } void key_init() { int ver = read_hardware_ver(); if (ver == 1) read_key = read_key_ver1; else read_key = read_key_ver2; } // main.c void main(void) { int key; key_init(); while (1) { key = read_key(); if (key == UP) led_on(); else led_off(); } }
I think this method should belong to the 2 An upgraded version of the method , It is also necessary to write the hardware version number to EEPROM in , Make judgments in the software , But the difference lies in the introduction of function pointers , You only need to judge once according to the version number during power on initialization , Assign the interface corresponding to the version to the pointer , There is no need to make a lot of judgment calls in subsequent code .
So the first problem is solved , Let's look at the second question , How to solve the problem of software scalability ?
There is a design principle in the design pattern :OCP, Opening and closing principle , Good design needs to be open to extensions , Turn off for changes . In other words, only new code is added during function expansion , Do not modify the existing code .
Back to the question , If we need to increase the number of buttons , According to our previous thinking, it should be :
// key.c
// Return value : 0 Indicates being pressed , 1 Indicates that it is loosened
int read_key1(void)
{
GPIO_PinState key;
key = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_6);
if (key == GPIO_PIN_RESET)
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
// Return value : 0 Indicates being pressed , 1 Indicates that it is loosened
int read_key2(void)
{
GPIO_PinState key;
key = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_7);
if (key == GPIO_PIN_RESET)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
or
// key.c
// Return value : 0 Indicates being pressed , 1 Indicates that it is loosened
int read_key(int which)
{
GPIO_PinState key;
switch (which)
{
case 0:
key = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_6);
if (key == GPIO_PIN_RESET)
return 0;
else
return 1;
break;
case 1:
key = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_7);
if (key == GPIO_PIN_RESET)
return 1;
else
return 0;
break;
}
}
Both of these methods can alleviate the problem to some extent , But to cure the symptoms is not to cure the root . The former method will increase with the number of keys , More and more confusion at the call , Difficult to maintain . The latter method , As long as there is a button to add, it will modify our read_key function , In violation of the OCP principle .
2.3 Introduce structure
In order to solve problems with new ideas , Here new knowledge points are introduced : Structure .

Let's start by layering the program ,main Functions belong to the application layer or business logic layer ,key_manager It belongs to the middle layer , The bottom layer belongs to the hardware driver layer , The management of keys is realized through the middle layer , At the same time, the business logic layer and the driver layer are decoupled .
2.3.1 key_system
// key_manager.h
typedef struct key {
char *name;
void (*init)(struct key *k);
int (*read)(void);
}key, *p_key;
// Initialization of all keys
void key_init(void);
// According to the key name Get the key
key *get_key(char *name);
// key_manager.c
int key_cnt = 0;
key *keys[32];
void register_key(key *k)
{
keys[key_cnt] = k;
key_cnt++;
}
void key_init(void)
{
k1_init();
k2_init();
}
key *get_key(char *name)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < key_cnt; i++)
if (strcmp(name, keys[i]->name) == 0)
return keys[i];
return 0;
}
// key1.c
// Return value : 0 Indicates being pressed , 1 Indicates that it is loosened
static int read_key1(void)
{
GPIO_PinState key_status;
key_status = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_6);
if (key_status == GPIO_PIN_RESET)
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
static key k1 = {
"k1", 0, read_key1};
void k1_init(void)
{
register_key(&k1);
}
// key2.c
// Return value : 0 Indicates being pressed , 1 Indicates that it is loosened
static int read_key2(void)
{
GPIO_PinState key_status;
key_status = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_7);
if (key_status == GPIO_PIN_RESET)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
static key k2 = {
"k2", NULL, read_key2};
void k2_init(void)
{
register_key(&k2);
}
// main.c
void main(void)
{
key *k;
key_init();
/* Use a key */
k = get_key("k1");
if (k == NULL)
return;
while (1)
{
if (k->read(k) == 0)
led_on();
else
led_off();
}
}
2.3.2 key_system_read_multi_key
There are still some problems with the current code , There is no decoupling between the business layer and the driver layer , stay main There are also specific keys in the function read Function call and state judgment . meanwhile , As the business layer, the middle layer is expected to read the status of all keys at the same time .
Then optimize the implementation of the middle tier :
// key_manager.h
typedef struct key {
char *name;
unsigned char id;
void (*init)(struct key *k);
int (*read)(void);
}key, *p_key;
#define KEY_UP 0xA
#define KEY_DOWN 0xB
// Initialization of all keys
void key_init(void);
// Read the status of all keys
int read_key(void);
// key_manager.c
int key_cnt = 0;
key *keys[32];
void register_key(key *k)
{
keys[key_cnt] = k;
key_cnt++;
}
void key_init(void)
{
k1_init();
k2_init();
}
int read_key(void)
{
int val;
for (int i = 0; i < key_cnt; i++)
{
val = keys[i]->read();
if (val == -1)
continue;
else
return val;
}
return -1;
}
// key1.c
// Return value : 0 Indicates being pressed , 1 Indicates that it is loosened
#define KEY1_ID 1
static int read_key1(void)
{
static GPIO_PinState pre_key_status;
GPIO_PinState key_status;
key_status = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_6);
if (key_status == pre_key_status)
return -1;
pre_key_status = key_status;
if (key_status == GPIO_PIN_RESET)
return KEY_DOWN | (KEY1_ID << 8);
else
return KEY_UP | (KEY1_ID << 8);
}
static key k1 = {
"k1", KEY1_ID, NULL, read_key1};
void k1_init(void)
{
register_key(&k1);
}
// key2.c
// Return value : 0 Indicates being pressed , 1 Indicates that it is loosened
#define KEY2_ID 2
static int read_key1(void)
{
static GPIO_PinState pre_key_status;
GPIO_PinState key_status;
key_status = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_7);
if (key_status == pre_key_status)
return -1;
pre_key_status = key_status;
if (key_status == GPIO_PIN_RESET)
return KEY_UP | (KEY2_ID << 8);
else
return KEY_DOWN | (KEY2_ID << 8);
}
static key k2 = {
"k2", KEY2_ID, NULL, read_key2};
void k2_init(void)
{
register_key(&k2);
}
// main.c
void main(void)
{
int val;
key_init();
while (1)
{
val = read_key();
if (val == -1)
{
/* There are no buttons */
}
else
{
key_status = val & 0xFF;
key_id = (val>>8) & 0xFF:
switch (key_status)
{
case KEY_UP:
/* key_id Release */
break;
case KEY_DOWN:
/* key_id Press down */
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
2.3.3 key_system_read_usr_irq
however , There are still some problems with this code , For example, the key detection now belongs to polling , If you can change key detection to interrupt mode , In the use of RTOS There is no need to poll regularly , You can wait for an interrupt to trigger .
here , You can introduce a fifo, Interrupt events as producers of data , The application layer acts as a consumer of data , Further decoupling .
here fifo The realization is from github Casually found on the .
// key_manager.h
typedef struct key {
char *name;
unsigned char id;
void (*init)(struct key *k);
int (*read)(void);
}key, *p_key;
#define KEY_UP 0xA
#define KEY_DOWN 0xB
// Initialization of all keys
void key_init(void);
// Read key status
int read_key(void)
// towards fifo Write a key status
void put_buffer(int val);
// from fifo Read a key state
int read_buffer(void);
// key_manager.c
int key_cnt = 0;
key *keys[32];
// Define a Fifo Buffer
static RingBufferPointer fifo;
void put_buffer(int val)
{
ringBufferAdd(fifo, val);
}
int read_buffer()
{
int val = -1;
if (isRingBufferNotEmpty(fifo))
val = ringBufferGet(fifo);
return val;
}
void register_key(key *k)
{
keys[key_cnt] = k;
key_cnt++;
}
void key_init(void)
{
fifo = getRingBufferInstance(100);
k1_init();
k2_init();
}
int read_key(void)
{
return read_buffer();
}
// key0.c
#define KEY0_ID 0
static key k0 = {
"k0", KEY0_ID, NULL, NULL};
void k0_init(void)
{
register_key(&k0);
}
void key0_irq(void)
{
int val;
GPIO_PinState key_status;
key_status = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(KEY0_GPIO_Port, KEY0_Pin);
if (key_status == GPIO_PIN_RESET)
val = KEY_DOWN | (KEY0_ID << 8);
else
val = KEY_UP | (KEY0_ID << 8);
put_buffer(val);
}
// key1.c
#define KEY1_ID 1
static key k1 = {
"k1", KEY1_ID, NULL, read_key1};
void k1_init(void)
{
register_key(&k1);
}
void key1_irq(void)
{
int val;
GPIO_PinState key_status;
key_status = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_6);
if (key_status == GPIO_PIN_RESET)
val = KEY_DOWN | (KEY1_ID << 8);
else
val = KEY_UP | (KEY1_ID << 8);
put_buffer(val);
}
// key2.c
#define KEY2_ID 2
static key k2 = {
"k2", KEY2_ID, NULL, read_key2};
void k2_init(void)
{
register_key(&k2);
}
void key2_irq(void)
{
int val;
GPIO_PinState key_status;
key_status = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOF, GPIO_PIN_7);
if (key_status == GPIO_PIN_RESET)
val = KEY_DOWN | (KEY2_ID << 8);
else
val = KEY_UP | (KEY2_ID << 8);
put_buffer(val);
}
// stm32f7xx_it.c
void EXTI2_IRQHandler(void)
{
HAL_GPIO_EXTI_IRQHandler(KEY1_Pin);
}
void EXTI3_IRQHandler(void)
{
HAL_GPIO_EXTI_IRQHandler(KEY0_Pin);
}
void EXTI15_10_IRQHandler(void)
{
HAL_GPIO_EXTI_IRQHandler(KEY2_Pin);
}
// main.c
void main(void)
{
int val;
char key_status;
char key_id;
key_init();
// If it is rtos The polling method is not applicable
while (1)
{
val = read_key();
if (val != -1)
{
key_status = val & 0xFF;
key_id = (val >> 8) & 0xFF;
switch (key_status)
{
case KEY_DOWN:
if (key_id == 0)
{
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LED0_GPIO_Port, LED0_Pin, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
}
else if (key_id == 1)
{
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LED1_GPIO_Port, LED1_Pin, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
}
else if (key_id == 2)
{
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LED0_GPIO_Port, LED0_Pin, GPIO_PIN_SET);
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LED1_GPIO_Port, LED1_Pin, GPIO_PIN_SET);
}
break;
case KEY_UP:
break;
}
}
}
}
void HAL_GPIO_EXTI_Callback(uint16_t pin)
{
HAL_Delay(50);
switch (pin)
{
case KEY0_Pin:
key0_irq();
break;
case KEY1_Pin:
key1_irq();
break;
case KEY2_Pin:
key2_irq();
break;
default:
break;
}
}
3. Experimental process
According to the idea above , Practice on the development board .
3.1 establish cubemx engineering
After checking the schematic diagram of the development board, we know , The resources are distributed as follows :
- The development board has user buttons 3 individual , Namely KEY0(PH3)、KEY1(PH2)、KEY2(PC13)
- The development board has LED2 individual , Namely LED0(PB1)、LED1(PB0)

For this 5 individual GPIO To configure , And then generate the code .
3.2 Project structure

3.3 Experimental results
Press down KEY0,LED0 Light up , Press down KEY1,LED1 Light up , Press down KEY2,LED0、LED1 It goes out at the same time . The experiment is finished .
4. summary
Actually, according to Mr. Wei's course , take led A subsystem has also been established , Manage through the middle tier led, To reduce code coupling , Enhance code scalability 、 reusability . Because of ideas and key The subsystems are basically the same , There is no further implementation .
Through this lesson, I learned the idea of hierarchical design of software structure , Consider future functional extensions from the beginning of the design 、 The robustness of the code . By sacrificing a little bit of operational efficiency , To improve the maintainability of the whole project .
边栏推荐
- 经典面试题之老鼠试药与汉明码
- FreeRTOS+STM32L+ESP8266+MQTT协议传输温湿度数据到腾讯云物联网平台
- Idempotence of interfaces -- talk about idempotence of interfaces in detail, that is, solutions
- Spark log analysis
- Solve STM32 operation μ Solution to sudden failure of task scheduling in c/os-ii system
- Qt Cmake 纯C 代码调用系统控制台输入scanf 及 中文输出乱码
- 数据分析——切片器、数据透视表与数据透视图(职场必备)
- Case: drawing Matplotlib dynamic graph
- Balanced binary tree AVL
- 随便画画的
猜你喜欢

从查询数据库性能优化谈到redis缓存-谈一谈缓存的穿透、雪崩、击穿

About the use of hc-12 radio frequency module

Redis的安装及启动

.net使用Access 2010数据库
FreeRTOS+STM32L+ESP8266+MQTT协议传输温湿度数据到腾讯云物联网平台

FPGA notes -- implementation of FPGA floating point operation
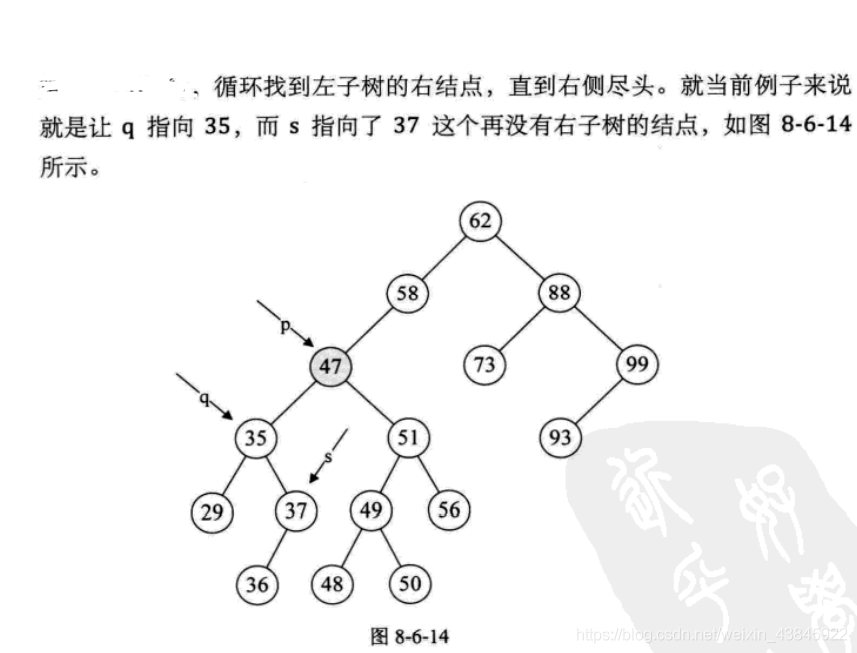
Binary sort tree

Msp430f5529lp official board (red) can not debug the problem

Duck feeding data instant collection solution resources

Case: drawing Matplotlib dynamic graph
随机推荐
Development and monitoring of fusion experiment pulse power supply by LabVIEW
Nacos registry
Spark log analysis
ETCD数据库源码分析——集群间网络层服务端接口
开窍之问答
Redis的安装及启动
. user. PHP website installation problems caused by INI files
FIFO code implemented in C language
containerd客户端比较
Final review [machine learning]
Post ordered clue binary tree
使用Gin框架运行Demo时报错“ listen tcp :8080: bind: An attempt was made to access a socket in a way forbidden”
返回值为Object型方法调用equals()
在线小工具分享(不定时更新,当前数量:2)
智慧家——全家具功能
Casually painted
Balanced binary tree AVL
RT-Thread 项目工程搭建和配置--(Env Kconfig)
认识map
下载安装Flume