当前位置:网站首页>Three elements of basic concepts and methods of machine learning
Three elements of basic concepts and methods of machine learning
2022-06-21 10:32:00 【I'm afraid I'm not retarded】
Purpose of the course
- Understand the principle
- Tools can be used to solve practical problems
- Use programming language to implement algorithms
- Improve the ability to optimize and improve algorithms
Learning goals
- Understand concepts related to machine learning
- Understand the essence of machine learning
- Learn about common loss functions
- Understand the empirical and structural risks
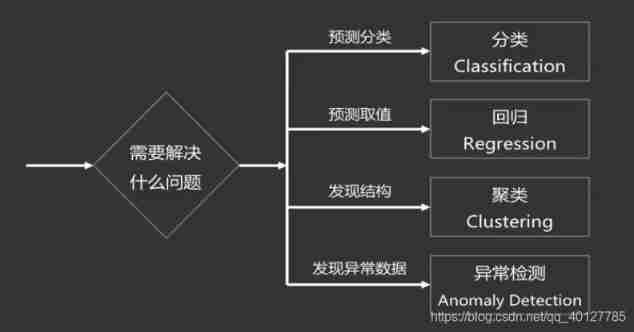
Some basic concepts of machine learning
Machine learning method flow
Take supervised learning as an example ,( Compare examples to do exercises )

input data ——》 Feature Engineering 《——》 model training ——》 Model deployment ——》 Model application
Model (Models): A process formed through extensive experience
Feature Engineering (Features): On the basis of input data , Arrangement 、 machining 、 Expand 、 Some new data features formed by merging, etc .
The modeling process is an iterative process , Loop optimization required .
After the model training reaches the expected effect, deploy it , Put it into practice .
notes : In the actual work process , Business 、 The data is changing dynamically , So the model has timeliness , Model lifecycle management is required in the process of use , Regular updates .
Input space and output space
- input space : The set of input values is called input space
- Output space : The set of all possible values of the output is called the output space
- The input space and output space can be a set of finite elements , It can also be the whole Euclidean space
- The input space and output space can be a continuous set of values , It can also be a set of discrete values
- Input space and output space can be the same space , It can also be different spaces
- Usually the output space is smaller than the input space
The feature space
features : The property . Each component of each input strength ( attribute ) Called original features , More derived features can be extended based on the original features .
Eigenvector : A collection composed of multiple features , It is called eigenvector
The feature space : The space where the eigenvector exists is called the eigenspace .
- Each dimension in the feature space corresponds to a feature ( attribute )
- The feature space can be the same as the input space , It can be different
- The instance needs to be mapped from the input space to the feature space
- The model is actually defined on the feature space
Hypothetical space
Hypothetical space : A set of mappings from input space to output space .
- Mr. Li Hang 《 Statistical learning method 》: The model belongs to an implicit set from input space to output space , This set is the hypothetical space . The determination of hypothesis space means the determination of learning range .
- zhou 《 machine learning 》: Hypothetical space refers to the space composed of all assumptions of the problem , We can think of the learning process as a process of searching in the hypothesis space , The search target is to find the training set “ matching ” Assumptions .
For every possible input , Can find a mapping , Corresponds to an output in the output space .
The essence of machine learning
Most machine learning is essentially an optimization problem , That is to find the model parameters ( Optimization variables ), Make the loss function ( Objective function ) Minimum , At the same time, in order to avoid over fitting , Add regular terms , That is, constrain the parameters to be optimized . Deep learning is a branch of machine learning , It is used for classification , It is also an optimization problem . The general optimization problem is not easy to solve , Because it is easy to fall into the local optimal solution , And can not get the global optimum . If this optimization problem happens to be a convex optimization problem , Then the optimal solution of the model can be solved efficiently , This is because , According to the properties of convex functions , The local optimum is the global optimum .
Three elements of machine learning methods
Machine learning methods are usually made up of models 、 Strategy and algorithm are composed of three parts : Method = Model + Strategy + Algorithm
- Model : Mapping from input space to output space . The learning process is to search the hypothesis space suitable for the current data .
- Strategy : Learning criteria or rules for selecting the optimal model from a large number of assumptions in the hypothesis space
- Algorithm : The specific calculation method of the learning model , The same is to solve the optimization problem
Model
Mapping from input space to output space . The learning process is to search the hypothesis space suitable for the current data .
Analyze current problems to be solved , Determine the model .
Strategy
Learning criteria or rules for selecting the optimal model from a large number of assumptions in the hypothesis space .
Choose the most appropriate model from the hypothetical space , The following problems need to be solved :
- Evaluate the effect of a model on a single training sample
- Evaluate the overall effect of a model on the training set
- Evaluate a model pair, including a training set 、 The overall effect of all data including the prediction set
Define several indicators to measure the above problems :
- Loss function :0-1 Loss function 、 Square loss function 、 Absolute loss function 、 Logarithmic loss function, etc ;
- Risk function : Empirical risk 、 Expected risk 、 Structural risk
Basic strategy :
- Experience risk is minimal (EMR:Empirical Risk Minimization)
- Minimum structural risk (SRM:Structural Risk Minimization)
Loss function
Loss function : Used to measure the gap between the predicted results and the real results , The less it's worth , It means that the more consistent the predicted results are with the real results . It's usually a non negative real valued function . The process of reducing the loss function in various ways is called optimization . The loss function is recorded as L(Y,f(x))
Common loss function types :
0-1 Loss function (0-1LF): If the predicted value is exactly equal to the actual value, then “ No loss ” by 0, Otherwise it means “ Total loss ”, by 1.
The predicted value and the actual value are exactly equal, which is a little too strict , You can use the method that the difference between the two is less than a certain threshold .
Absolute loss function : The absolute value of the difference between the predicted result and the real result . Simple and easy to understand , But the calculation is inconvenient ;
Square loss function : The square of the difference between the predicted result and the real result .
- The advantages of the square loss function are :
- The error of each sample is positive , The accumulation will not be offset ;
- The penalty of square for large error is greater than that of small error
- Simple mathematical calculation 、 friendly , The derivative is a first-order function
- The advantages of the square loss function are :
Logarithmic loss function ( Log likelihood loss function ): Logarithmic functions are monotonic , When solving optimization problems , The result is consistent with the original goal . You can convert multiplication into addition ( A simpler calculation ), simplified calculation :
L(Y,p(Y|X)) = -logP(Y|X)Exponential loss function : monotonicity 、 Excellent properties of nonnegativity , Make the closer to the correct result, the smaller the error ;
Folding loss function : Also known as hinge loss , The punishment for the points near the judgment boundary is high , Commonly used in SVM( Support vector machine ),
L(f(x)) = max(0,1 - f(x))The curves of different loss functions are also different

Different loss functions have different characteristics , For different scenarios :
- 0-1: Ideal state model
- log: Logical regression 、 Cross entropy
- Squared: Linear regression
- Exponential:AdaBoosting
- Hinge:SVM、soft margin
Empirical risk and structural risk
Empirical risk VS Risk function
Empirical risk : The loss function measures the prediction results of a single sample , To measure the difference between the predicted value and the real value of the whole training set , Make a prediction for all records of a real training set , Take the loss function , Add up all values , Experience risk . Empirical risk model f(x) The better the fitting degree of the training set .
Risk function : Also known as expected loss 、 Expected risk . All data sets ( Contains training set and prediction set , Follow joint distribution P(X,Y)) The expected value of the loss function .
Empirical risk vs Expected risk
- Expect the letter to be model to global ( All data sets ) The effect of ; Empirical risk is the impact of the model on the Bureau ( Training set ) The effect of ;
- The expected risk is often incalculable , Joint distribution P(X,Y) Usually unknown ; Empirical risk can be calculated ;
- When the training set is large enough , Empirical risk can replace expected risk , That is, the local optimum replaces the global optimum
The problem of experience risk :
When the sample is small , Focus only on experience risk , It can easily lead to over fitting
* namely : Using samples to calculate empirical risk , When forecasting a forecast set , The empirical risk is too close to the sample set , The prediction error rate of the prediction set is higher . The empirical risk obtained is only a local optimal solution .
resolvent :
Structural risk
Structural risk : On the basis of experience and risk , Add a regularization term or penalty term .
Structural risk vs Empirical risk
- The less experience risk , The more complex the model decision function , The more parameters it contains
- When the empirical risk function is small to a certain extent, there will be over fitting phenomenon
- Ways to prevent overfitting , It is necessary to reduce the complexity of the decision function , Let the punishment
J(f)To minimize the - It is necessary to minimize the complexity of both empirical risk function and model decision function
- The structural risk function is obtained by fusing the two formulas into one formula, and then the structural risk function is minimized .
Regularization term
Regularization term : Penalty function , This item penalizes the model vector , Thus the problem of over fitting is solved . The regularization method will automatically weaken the unimportant characteristic variables , Automatically from many characteristic variables “ extract ” Important characteristic variables , Reduce the order of magnitude of the characteristic variable .
summary
Some basic concepts of machine learning
The essence of machine learning ,
- A hypothesis is searched in the hypothesis space from input space to output space , Choose the best hypothesis for the current treatment .
Three elements of machine learning
- Model : Determine what kind of problems
- Strategy : How to evaluate the model
- Algorithm : How to optimize and improve within the scope required by the learning rules , Get the results you want
Empirical risk and structural risk
Use when dealing with the strategy of the three elements , In fact, the way to judge whether the model is good or bad , Structural risk is often used to assess
- The difference between structural risk and empirical risk
- Empirical risk only evaluates the performance of the model on the test set , The better on the test set , The less experience risk
- Structural risk should be considered in both aspects :1. The model performs well on the test set ;2. The complexity of the model is not high , The more complex the model , The worse the prediction effect on the follow-up , Easy to overfit
- The difference between structural risk and empirical risk
Optimize and improve within the scope required by the learning rules , Get the results you want
Empirical risk and structural risk
Use when dealing with the strategy of the three elements , In fact, the way to judge whether the model is good or bad , Structural risk is often used to assess
- The difference between structural risk and empirical risk
- Empirical risk only evaluates the performance of the model on the test set , The better on the test set , The less experience risk
- Structural risk should be considered in both aspects :1. The model performs well on the test set ;2. The complexity of the model is not high , The more complex the model , The worse the prediction effect on the follow-up , Easy to overfit
- The difference between structural risk and empirical risk
边栏推荐
- Optimisation des performances - compression, chargement et formatage des images
- Lodash real on demand approach
- 异常
- Electron checks the CPU and memory performance when the module is introduced
- Leader: who uses redis expired monitoring to close orders? Get out of here!
- Es composite query workload evaluation
- Unity中的地平面简介
- 领导:谁再用redis过期监听实现关闭订单,立马滚蛋!
- Appareils pris en charge par Arcore
- 音视频同步你一定要注意的知识点:
猜你喜欢

使用shapeit进行单倍型分析

Float floating layout clear floating

Matplotlib two methods of drawing torus!

中国国际电子商务中心与易观分析联合发布:2021年4季度全国网络零售发展指数同比增长0.6%

香农的信息论究竟牛在哪里?

Unity中的地平面简介

TC软件概要设计文档(手机群控)

Xidian AI ranked higher than Qingbei in terms of AI major, and Nantah ranked first in China in terms of Software Science in 2022
![触摸按键控制器TTP229-BSF使用心得[原创cnblogs.com/helesheng]](/img/2f/3594188c5e58d3501f76f4937a979c.png)
触摸按键控制器TTP229-BSF使用心得[原创cnblogs.com/helesheng]

New programmers optimize a line of code on Monday and are discouraged on Wednesday?
随机推荐
字符串
Tensorflow, danger! Google itself is the one who abandoned it
程序員新人周一優化一行代碼,周三被勸退?
The spingboot microservice is packaged into a docker image and connected to the database
ESP8266/ESP32 +1.3“ or 0.96“ IIC OLED指针式时钟
Odd number of characters exception
Original code, inverse code, complement calculation function applet; C code implementation;
获取配置文件properties中的数据
character string
Mqtt of NLog custom target
简易的安卓天气app(三)——城市管理、数据库操作
Xidian AI ranked higher than Qingbei in terms of AI major, and Nantah ranked first in China in terms of Software Science in 2022
How to be an interesting person
Inner class
DSP online upgrade (4) -- functions implemented by bootloader
110. JS event loop and setimmediate, process.nexttick
还在直接用localStorage么?全网最细:本地存储二次封装(含加密、解密、过期处理)
On the problem of class member variable pollution in the context of one-time concurrence
Application configuration management, basic principle analysis
DSP online upgrade (1) -- understand the startup process of DSP chip