当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode 2360. 图中的最长环 基环树找环+时间戳
LeetCode 2360. 图中的最长环 基环树找环+时间戳
2022-08-02 21:06:00 【超级码力奥】
给你一个 n 个节点的 有向图 ,节点编号为 0 到 n - 1 ,其中每个节点 至多 有一条出边。
图用一个大小为 n 下标从 0 开始的数组 edges 表示,节点 i 到节点 edges[i] 之间有一条有向边。如果节点 i 没有出边,那么 edges[i] == -1 。
请你返回图中的 最长 环,如果没有任何环,请返回 -1 。
一个环指的是起点和终点是 同一个 节点的路径。
示例 1:
输入:edges = [3,3,4,2,3]
输出去:3
解释:图中的最长环是:2 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 。
这个环的长度为 3 ,所以返回 3 。
示例 2:
输入:edges = [2,-1,3,1]
输出:-1
解释:图中没有任何环。
提示:
n == edges.length
2 <= n <= 105
-1 <= edges[i] < n
edges[i] != i
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-cycle-in-a-graph
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
对于内向基环树的概念和性质,我之前在 2127. 参加会议的最多员工数 的题解中作了详细介绍,本文不再赘述(把我那篇题解的代码拿来改一改就能过)。
除了使用那篇题解中的通用做法(拓扑排序)外,我们还可以利用时间戳来实现找环的逻辑。
具体来说,初始时间戳clock=1,首次访问一个点 x 时,记录访问这个点的时间time[x]=clock,然后将 clock 加一。
如果首次访问一个点,则记录当前时间 startTime=clock,并尝试从这个点出发,看能否找到环。如果找到了一个之前访问过的点 x,且之前访问 x 的时间不早于 startTime,则说明我们找到了一个新的环,此时的环长就是前后两次访问 x的时间差,即clock−time[x]。
取所有环长的最大值作为答案。若没有找到环,则返回 -1
作者:endlesscheng
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-cycle-in-a-graph/solution/nei-xiang-ji-huan-shu-zhao-huan-li-yong-pmqmr/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
当访问到一个已经被访问过的点的时候,有两种情况,有可能是找到了环,也有可能是之前被被人访问过了。需要分情况讨论。
class Solution:
def longestCycle(self, edges: List[int]) -> int:
# 时间戳,这个方法太帅了
n = len(edges)
time = [0] * len(edges)
clock, ans = 1, -1
for i in range(n):
# 访问过了
if time[i]: continue
# 否则
start_time = clock
x = i
# 开始找环
while x != -1:
if time[x]: # 如果召唤的过程中发现了访问过的
# 判断是找到了一个环呢,还是说访问了之前被访问过的
if time[x] >= start_time: # 找到了一个环
ans = max(ans, clock - time[x])
break
# 否则,继续往下走
time[x] = clock
clock += 1
x = edges[x]
return ans
class Solution {
public:
int longestCycle(vector<int>& p) {
int n = p.size();
int time[n]; // 草,这里忘了全部初始化为0了
memset(time, 0, sizeof(time));
int res = -1;
int clock = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
if(time[i]) continue;
// 开始找环
int start_time = clock;
int x = i;
while(x != -1)
{
if(time[x])
{
if(time[x] >= start_time)
{
res = max(res, clock - time[x]);
}
break;
}
// 否则,继续往下走
time[x] = clock;
clock ++;
x = p[x];
}
}
return res;
}
};
y总的写法:
开始:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV11S4y1x7iM?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0&vd_source=dc27dfeb3c137279f3aaf4ac12fd6796&t=2059.6
class Solution {
public:
// 这几个都是全局变量
vector<int> p;
vector<bool> st; // 表示是否被访问过
vector<int> in_stk; // 表示是否在栈中
int ans = -1;
void dfs(int u, int depth)
{
st[u] = true;
in_stk[u] = depth;
int j = p[u]; //下一个点
if(j != -1)
{
if(!st[j])
{
dfs(j, depth + 1);
}else if(in_stk[j])
{
ans = max(ans, depth + 1 - in_stk[j]);
}
}
// 恢复现场,因为u用完了
in_stk[u] = 0;
}
int longestCycle(vector<int>& p) {
// 如何让p变成全局变量?
this->p = p;
int n = p.size();
// 这两个初始化的时候默认为0
st = vector<bool>(n);
in_stk = vector<int>(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
if(!st[i])
// 从i开始,搜过的长度为1
dfs(i, 1);
return ans;
}
};
边栏推荐
- CS5213芯片|HDMI to VGA转换头芯片资料分享
- 【干货】分库分表最佳实践
- 微软SQL服务器被黑客入侵以窃取代理服务的带宽
- Electrical diagram of power supply system
- Li Mu hands-on learning deep learning V2-bert and code implementation
- js函数防抖和函数节流及其他使用场景
- 如何理解 swing 是非线程安全 (原创)
- Digital twins help visualize the construction of smart cities
- 命令行启动常见问题及解决方案
- YOLOv5+BiSeNet——同时进行目标检测和语义分割
猜你喜欢
Mysql用户管理
Common tools and test methods for interface testing (Introduction)

30天啃透这份Framework 源码手册直接面进大厂
博客主题美化第二弹

56.【全局变量和局部变量专题】
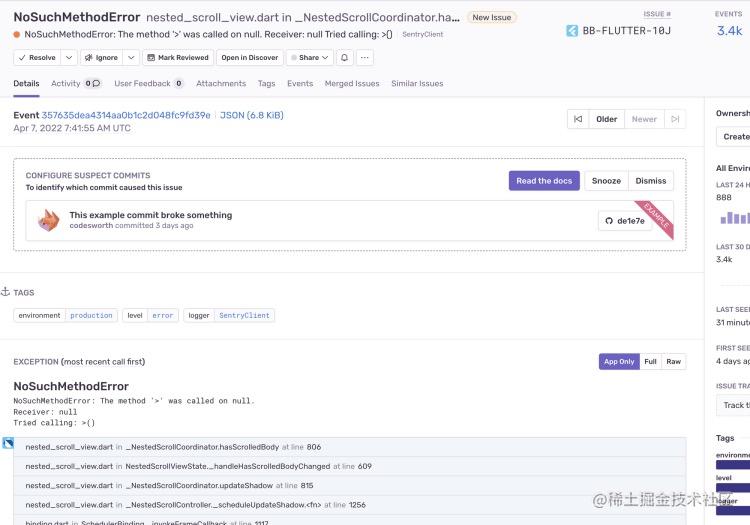
Flutter 常见异常分析
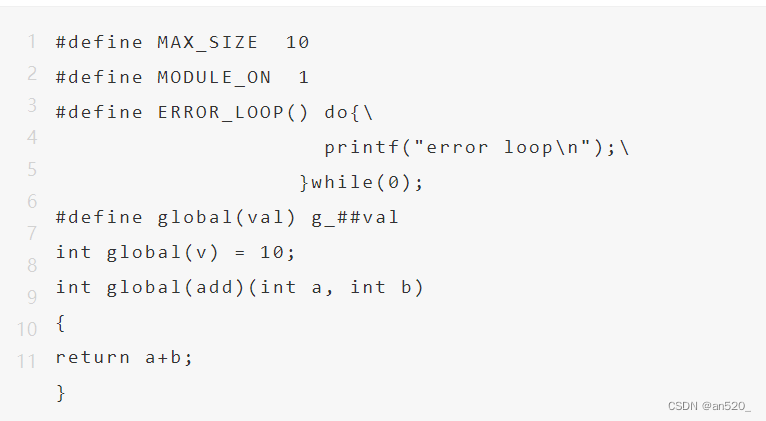
总结嵌入式C语言难点(2部分)

Intensive reading of the Swin Transformer paper and analysis of its model structure
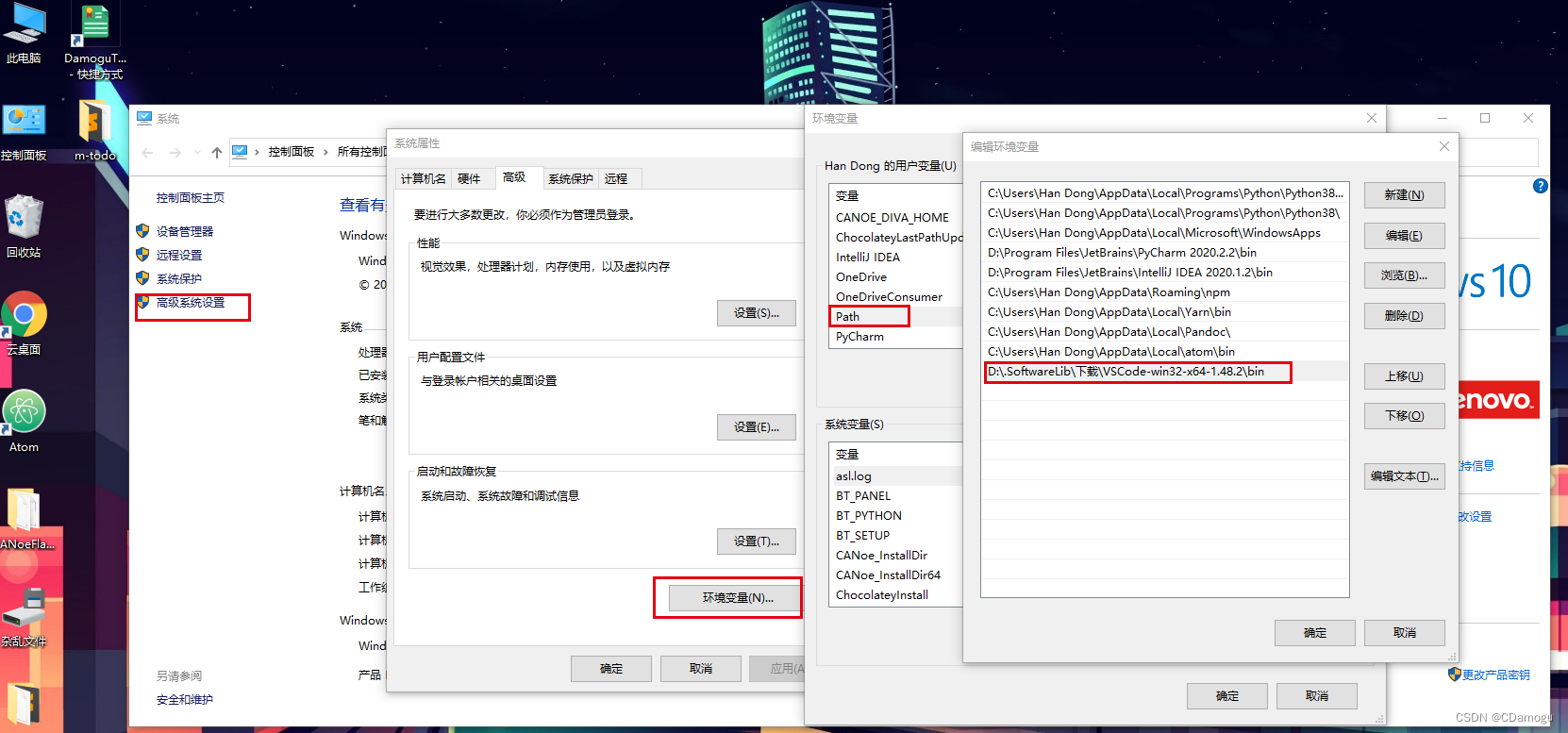
Vscode快速入门、 插件安装、插件位置、修改vscode默认引用插件的路径、在命令行总配置code、快捷键
命令行启动常见问题及解决方案
随机推荐
HCIP--BGP基础实验
PLC working principle animation
X 2 Earn必须依靠旁氏启动?GameFi的出路在哪?(下)
ACE JET NPOI
交 叉 数 组
用户之声 | 我与GBase的缘分
golang 刷leetcode:统计打字方案数
【目标检测】YOLOv5:640与1280分辨率效果对比
Packages and packages, access modifiers
面试了个985毕业的,回答“性能调优”题时表情令我毕生难忘
golang 刷leetcode:将字符串翻转到单调递增
面试官居然问我:删库后,除了跑路还能干什么?
VisualStudio 制作Dynamic Link Library动态链接库文件
How the sensor works
解道7-编程技术4
golang刷leetcode: 卖木头块
【3D视觉】realsense D435三维重建
golang刷leetcode:巫师的总力量和
YOLOv5+BiSeNet——同时进行目标检测和语义分割
Informatics Olympiad All-in-One (1260: [Example 9.4] Intercepting Missiles (Noip1999))