当前位置:网站首页>April 13, 2021 interview with beaver family
April 13, 2021 interview with beaver family
2022-06-26 10:47:00 【Pig man blogs】
The interview process
Introduce yourself first
Let's talk about the project first
Talk about the modules you are responsible for in your project
Start to follow the project module and ask in detail
When it comes to multithreading updating cached data , I was asked if there would be concurrent problems , How to solve ( Mainly redis The update operation is not atomic , There may be concurrent operations )
Add synchronized On the way , Or if it's just coverage setnx The order guarantees atomicity
Start asking about your resume
Design patterns
Observer mode
I talked about the listener mode , I didn't make it clear
( You can talk about proxy mode )
Linux
How to check the log tail -f -n Number Query the log of the latest rows
Look up the key words Add | grep
Ignore case when querying keywords ( Can't ) grep -i file name
Number of query log lines ( Can't )nl file name
Have you checked the system parameters ( Can't )
df -h View disk space
cloud
Tell me about your understanding of the registry ( Service registration process , Discovery process , Self-protection mechanism )
sql The experience of optimization
Said explain Use type keys Explanation of the field ,
Said The function found in the work slows down the query speed , Index addition , The leftmost matching principle and the associated field reference
Talk about how you learn
My brain went out of my head and said that I had been watching jvm The book of , Isn't this digging ,
Then the five steps of the class loading mechanism are put aside
When it comes to verification , Asked only class Is the file format verified ?
The class loading mechanism complements
I was asked how I learned when I was working , What has been learned ?
Just learn from yourself gitlab Version of ci ,docker To write dockerfile Said , But the interviewer didn't go on
The interviewer said, is there anything you want to ask ?
- What kind of business
- Those used in the technology stack
summary :
Generally speaking, the interview was a failure , Be asked a little more by the interviewer , It won't be , It seems that the depth of learning is not enough , We should strengthen our study .
Knowledge supplement
linux The order added
grep Use
Regexp selection and interpretation: -E, --extended-regexp PATTERN is an extended regular expression (ERE) -F, --fixed-strings PATTERN is a set of newline-separated fixed strings -G, --basic-regexp PATTERN is a basic regular expression (BRE) -P, --perl-regexp PATTERN is a Perl regular expression -e, --regexp=PATTERN use PATTERN for matching -f, --file=FILE obtain PATTERN from FILE -i, --ignore-case ignore case distinctions -w, --word-regexp force PATTERN to match only whole words -x, --line-regexp force PATTERN to match only whole lines -z, --null-data a data line ends in 0 byte, not newline Miscellaneous: -s, --no-messages suppress error messages -v, --invert-match select non-matching lines -V, --version display version information and exit --help display this help text and exit Output control: -m, --max-count=NUM stop after NUM matches -b, --byte-offset print the byte offset with output lines -n, --line-number print line number with output lines --line-buffered flush output on every line -H, --with-filename print the file name for each match -h, --no-filename suppress the file name prefix on output --label=LABEL use LABEL as the standard input file name prefix -o, --only-matching show only the part of a line matching PATTERN -q, --quiet, --silent suppress all normal output --binary-files=TYPE assume that binary files are TYPE; TYPE is 'binary', 'text', or 'without-match' -a, --text equivalent to --binary-files=text -I equivalent to --binary-files=without-match -d, --directories=ACTION how to handle directories; ACTION is 'read', 'recurse', or 'skip' -D, --devices=ACTION how to handle devices, FIFOs and sockets; ACTION is 'read' or 'skip' -r, --recursive like --directories=recurse -R, --dereference-recursive likewise, but follow all symlinks --include=FILE_PATTERN search only files that match FILE_PATTERN --exclude=FILE_PATTERN skip files and directories matching FILE_PATTERN --exclude-from=FILE skip files matching any file pattern from FILE --exclude-dir=PATTERN directories that match PATTERN will be skipped. -L, --files-without-match print only names of FILEs containing no match -l, --files-with-matches print only names of FILEs containing matches -c, --count print only a count of matching lines per FILE -T, --initial-tab make tabs line up (if needed) -Z, --null print 0 byte after FILE name Context control: -B, --before-context=NUM print NUM lines of leading context -A, --after-context=NUM print NUM lines of trailing context -C, --context=NUM print NUM lines of output context -NUM same as --context=NUM --group-separator=SEP use SEP as a group separator --no-group-separator use empty string as a group separator --color[=WHEN], --colour[=WHEN] use markers to highlight the matching strings; WHEN is 'always', 'never', or 'auto' -U, --binary do not strip CR characters at EOL (MSDOS/Windows) -u, --unix-byte-offsets report offsets as if CRs were not there (MSDOS/Windows)Query system commands
uname -a # View kernel / operating system /CPU The information of linux system information head -n l /etc/issue # View operating system version cat /proc/cpuinfo # see CPU Information hostname # Check the linux System information command lspci -tv # List all PCI equipment lsusb -tv # List all USB The equipment linux System information command lsmod # List loaded kernel modules env # View environment variable resources free -m # View memory usage and swap usage df -h # View the usage of each partition du -sh # View the size of the specified directory grep MemTotal /proc/meminfo # View total memory grep MemFree /proc/meminfo # View the amount of free memory uptime # View system running time 、 The number of users 、 load cat /proc/loadavg # View system load disks and partitions mount | column -t # View attached partition status fdisk -l # View all sections swapon -s # View all swap partitions hdparm -i /dev/hda # View disk parameters ( Only applicable to IDE equipment ) dmesg | grep IDE # View on startup IDE Device detection status network ifconfig # View properties of all network interfaces iptables -L # View firewall settings route -n # View routing table netstat -lntp # View all listening ports netstat -antp # View all established connections netstat -s # View network statistics process ps -ef # View all processes top # Real time display of process status users w # view active user id # View specified user information last # View user login log cut -d: -f1 /etc/passwd # View all users of the system cut -d: -f1 /etc/group # View all groups in the system crontab -l # View the scheduled task service for the current user chkconfig –list # List all system services chkconfig –list | grep on # List all started system services rpm -qa # View all installed packages cat /proc/cpuinfo : see CPU Of related parameters linux System commands cat /proc/partitions : see linux System information command for hard disk and partition information cat /proc/meminfo : see linux System memory information linux System commands cat /proc/version : View version , similar uname -r cat /proc/ioports : View device io port cat /proc/interrupts : View interrupt cat /proc/pci : see pci Device information cat /proc/swaps : View all swap Partition information
sql Optimize and supplement
explain
If it is mysql Words , We can learn about Use How to view the execution plan 
-- see SQL Use index or not , prefix explain that will do
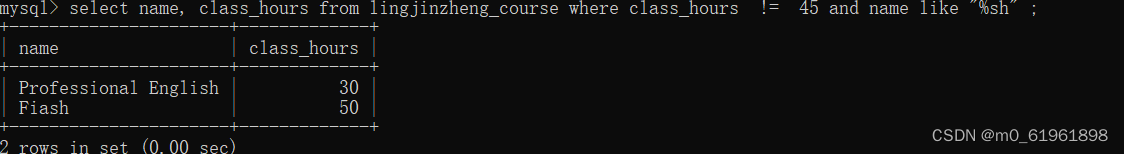
explain select * from emp where name = 'Jefabc';
-- expain The information coming out is 10 Column , Namely id、select_type、table、type、possible_keys、key、key_len、ref、rows、Extra
One 、 id
SELECT Identifier . This is a SELECT The query serial number of
My understanding is that SQL Identification of the order of execution ,SQL From big to small execution
id Phase at the same time , The order of execution is from top to bottom
If it's a subquery ,id The serial number of will increase ,id The higher the value, the higher the priority , The first to be executed
id If the same , It can be thought of as a group , From top to bottom ; In all groups ,id The bigger the value is. , The higher the priority , Execute first
Two 、select_type
Each select The type of clause
(1) SIMPLE( Simple SELECT, Don't use UNION Or subquery, etc )
(2) PRIMARY( The outermost query in the subquery , If the query contains any complex sub parts , The outermost select Marked as PRIMARY)
(3) UNION(UNION The second or later of SELECT sentence )
(4) DEPENDENT UNION(UNION The second or later of SELECT sentence , Depends on external queries )
(5) UNION RESULT(UNION Result ,union The second... In the sentence select Start all the back select)
(6) SUBQUERY( First in subquery SELECT, The results don't depend on external queries )
(7) DEPENDENT SUBQUERY( First in subquery SELECT, Depends on external queries )
(8) DERIVED( Derived from table SELECT, FROM A subquery of a clause )
(9) UNCACHEABLE SUBQUERY( The result of a subquery cannot be cached , The first line of the outer link must be reevaluated )
3、 ... and 、table
Show the table names in the database accessed in this step ( Show which table this row's data is about ), Sometimes it's not a real name , It may be abbreviated as , For example, above e,d, It may also be the abbreviation of the result of the step
Four 、type
How to access the table , Express MySQL How to find the desired row in the table , also called “ Access type ”.
Common types are : ALL、index、range、 ref、eq_ref、const、system、NULL( From left to right , Performance from poor to good )
ALL:Full Table Scan, MySQL Will traverse the entire table to find the matching rows
index: Full Index Scan,index And ALL The difference for index Type only traverses the index tree
range: Retrieve only rows in the given range , Use an index to select rows
ref: Indicates the join matching condition of the above table , That is, which columns or constants are used to find values on index columns
eq_ref: similar ref, The difference is that the index used is the only index , For each index key value , Only one record in the table matches , Simply speaking , It is used in multi table connection primary key perhaps unique key As a condition of Association
const、system: When MySQL Optimize some part of the query , And convert to a constant , Use these types to access . For example, place the primary key in where In the list ,MySQL You can convert the query to a constant ,system yes const Special case of type , When the query table has only one row , Use system
NULL: MySQL Decompose statements during optimization , Execute without even accessing tables or indexes , For example, selecting the minimum value from an index column can be done through a separate index search .
5、 ... and 、possible_keys
Pointed out that MySQL Which index can be used to find records in the table , If there is an index on the field involved in the query , Then the index will be listed , But not necessarily used by queries ( The index that this query can utilize , If there is no index display null)
This column is completely independent of EXPLAIN Output the order of the table shown . This means that possible_keys Some of the keys in cannot actually be used in the order of the generated tables .
If the column is NULL, There is no relevant index . under these circumstances , It can pass the inspection WHERE Clause to see if it references certain columns or columns suitable for indexing to improve your query performance . If so , Create an appropriate index and use it again EXPLAIN Check query
6、 ... and 、Key
key Columns show MySQL Actually decide which key to use ( Indexes ), Must be included in possible_keys in
If index is not selected , The key is NULL. To coercive MySQL To use or neglect possible_keys Index in column , Use in query FORCE INDEX、USE INDEX perhaps IGNORE INDEX.
7、 ... and 、key_len
Represents the number of bytes used in the index , You can use this column to calculate the length of the index used in the query (key_len The displayed value is the maximum possible length of the index field , It's not the actual length , namely key_len It is calculated according to the table definition , It is not retrieved from the table )
Without loss of accuracy , The shorter the length, the better
8、 ... and 、ref
Comparison of columns and indexes , Indicates the join matching condition of the above table , That is, which columns or constants are used to find values on index columns
Nine 、rows
Estimate the number of rows in the result set , Express MySQL According to table statistics and index selection , Estimated number of rows to read to find the required record
Ten 、Extra
This column contains MySQL Solve query details , There are several situations :
Using where: Don't read all the information in the table , Just index to get the data you need , This happens when all the request columns of the table are part of the same index , Express mysql The server will filter the rows after the storage engine retrieves them
Using temporary: Express MySQL You need to use temporary tables to store result sets , Common in sorting and grouping queries , common group by ; order by
Using filesort: When Query Contained in the order by operation , And sorting operations that can't be done with indexes are called “ File sorting ”
sing join buffer: The change emphasizes that no index is used to get the connection conditions , And you need to connect buffers to store intermediate results . If this value appears , That should pay attention to , Depending on the specific situation of the query, you may need to add indexes to improve the performance .
Impossible where: This value emphasizes where Statement will result in no eligible rows ( There can be no results by collecting statistics ).
Select tables optimized away: This value means only by using the index , The optimizer may only return one line from the aggregate function result
No tables used:Query Use in statement from dual Or without any from Clause
sql Optimize
① SQL Optimize
avoid SELECT *, Just query the required fields .
Small tables drive large tables , That is, small datasets drive large datasets :
When B The data set ratio of the table A Watch hour , use in Optimize exist The execution order of the two tables is to check first B Check the table again A Table query statement :SELECT * FROM tb_dept WHERE id in (SELECT id FROM tb_dept) ;
When A The data set ratio of the table B Watch hour , use exist Optimize in , The execution order of the two tables is to check first A surface , check B surface , Query statement :SELECT * FROM A WHERE EXISTS (SELECT id FROM B WHERE A.id = B.ID) ;
Try to use joins instead of subqueries , Because use join when ,MySQL No temporary tables are created in memory .
② Optimize the use of indexes
Try to use primary key query , Not other indexes , Because the primary key query does not trigger a back table query .
Don't do column operations , Put the calculation into each business system to realize
The query statement is as simple as possible , Big sentences split small ones , Reduce lock time
or The query is rewritten into union Inquire about
No functions and triggers
avoid %xx Inquire about , have access to :select * from t where reverse(f) like reverse('%abc');
To use less join Inquire about
Use same type comparison , such as '123' and '123'、123 and 123
Try to avoid where Used in clauses != perhaps <> The operator , The query reference discards the index and performs a full table scan
The list data uses paging query , The amount of data per page should not be too large
Avoid using... On index columns is null and is not null
③ Table structure design optimization
Use the smallest data type that can hold data .
Use as much as possible tinyint、smallint、mediumint As an integer type instead of int.
Use as much as possible not null Define fields , because null Occupy 4 Byte space . Numbers can be defaulted 0 , String default “”
Use less as far as possible text type , When you have to use it, you'd better make a separate table .
Use as much as possible timestamp, Instead of datetime.
Don't have too many fields in a single table , It is suggested that 20 Within fields .
The class loading mechanism complements

Class loading time
encounter new、getstatic、putstatic or invokestatic These four bytecode instructions , If the type has not been initialized
turn , You need to trigger the initialization phase first .
Use java.lang.reflect When a package's method makes a reflection call on a type , If the type is not initialized , Then
First trigger its initialization
When initializing a class , If it is found that its parent class has not been initialized , You need to trigger the initialization of its parent class first .
When the virtual machine starts , The user needs to specify a main class to execute ( contain main() Method type ), Virtual opportunity first
Initialize this main class .
When using JDK 7 New dynamic language support , If one java.lang.invoke.MethodHandle The final solution of the example
The analysis result is REF_getStatic、REF_putStatic、REF_invokeStatic、REF_newInvokeSpecial There are four types of method sentences
Handle , And the class corresponding to this method handle has not been initialized , You need to trigger its initialization first .
When an interface defines JDK 8 New default method added ( By default Keyword decorated interface method ) when , If there is
The implementation class of this interface is initialized , The interface must be initialized before it .
For the six scenarios that trigger type initialization ,《Java Virtual machine specification 》 A very strong qualifier is used in
——“ Yes and only ”, The behavior in these six scenarios is called active reference to a type . besides , For all reference types
Expressions do not trigger initialization , It's called passive reference
The class loading mechanism has five main stages
load
“ load ”(Loading) The stage is the whole “ Class loading ”(Class Loading) A stage in the process , There is no hope that readers will be confused
These two nouns look very similar . In the loading phase ,Java There are three things virtual machines need to do :
1) Get the binary byte stream that defines this class by using the fully qualified name of a class .
2) Convert the static storage structure represented by the byte stream into the runtime data structure of the method area .
3) Generate a representation of this class in memory java.lang.Class object , As the access to various data of this class in the method area
mouth .
in general , Virtual machine get class file ( Or some other form ) Convert to class objects and store them in the method area .
verification
- File format validation
- Metadata validation
- Bytecode verification
- Symbol reference validation
Get ready
The preparation phase is formally defined for variables in the class ( That is, static variables , By static Decorated variable ) Allocate memory and set class variables
Initial value stage .
analysis
The parsing phase is Java The process of virtual machine replacing symbolic reference in constant pool with direct reference .
· Symbol reference (Symbolic References): A symbolic reference describes the referenced target with a set of symbols , The symbol can be any
The literal quantity of form , As long as it can be used to locate the target unambiguously . Symbol references are independent of the memory layout of the virtual machine implementation , lead
The target used is not necessarily what has been loaded into the virtual machine memory . The memory layout of various virtual machines can be different ,
But the symbol references they can accept must be consistent , Because the literal form of symbolic reference is clearly defined in 《Java Virtual machine specification
Fan 》 Of Class In file format .
· Direct reference (Direct References): A direct reference is a pointer that points directly to the target 、 A relative offset or an energy
Handle to indirectly locate the target . Direct reference is directly related to the memory layout of the virtual machine , The same symbol is referenced in different virtual
Direct references translated from pseudo machine instances are generally not the same . If there is a direct quote , The target of the reference must already be in the virtual machine
There is... In your memory .
initialization
The initialization phase is to execute the class constructor () Method process
·() The compiler automatically collects the assignment actions and static statement blocks of all class variables in the class (static{} block ) Medium
Statement merge , The order in which the compiler collects is determined by the order in which statements appear in the source file , Only... Can be accessed in a static statement block
To variables defined before a static statement block , Define the variable after it , In the previous static statement block, you can assign values , But you can't visit
ask
边栏推荐
- Problems encountered in the application and development of Hongmeng and some roast
- 8-图文打造LeeCode算法宝典-最小栈与LRU缓存机制算法题解
- Reshape a two-dimensional array with 3 rows and 3 columns to find the sum of the diagonals
- 指南针软件买股票进行交易安全吗?怎么开户买股票
- AIX basic operation record
- 量化投资学习——经典书籍介绍
- 二叉树常见面试题
- 近期工作汇报
- JWT (SSO scheme) + three ways of identity authentication
- CentOS安装Redis多主多从集群
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
[online simulation] Arduino uno PWM controls the speed of DC motor
Redis knowledge mind map
Pit record_ TreeSet custom sorting results in less data loss
Mysql 30条军规
MySQL 8th job
Global and Chinese market of aluminum sunshade systems 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
二叉树常见面试题
Update mysql5.6 to 5.7 under Windows
六月集训(第26天) —— 并查集
工程数学概率论统计简明教程第二版复习大纲
Under the double reduction, the amount of online education has plummeted. Share 12 interesting uses of webrtc
Blog post index summary --c #
Moore vote, leetcode169, leetcode229
Reasons for "unresolved external symbols" during vs or QT compilation link:
Vscode environment setup: synchronous configuration
RDB持久化验证测试
Quantitative investment learning - Introduction to classic books
SQL Server 基础介绍整理
JWT (SSO scheme) + three ways of identity authentication
Oracle sqlplus 查询结果显示优化