当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode force buckle (Sword finger offer 31-35) 31 Stack push pop-up sequence 32i II. 3. Print binary tree from top to bottom 33 Post order traversal sequence 34 of binary search tree The path with a
Leetcode force buckle (Sword finger offer 31-35) 31 Stack push pop-up sequence 32i II. 3. Print binary tree from top to bottom 33 Post order traversal sequence 34 of binary search tree The path with a
2022-07-01 12:03:00 【Wood White CPP】
The finger of the sword Offer 31. Pressure into the stack 、 Pop-up sequence
Answer key :
It is most suitable to use stack to assist this problem .
First , Create a stack , In turn pushed The elements in the container are pushed onto the stack .
During pressing , Discover top stack elements and popped The elements in the container are equal , Pop up the top element of the stack , Continue traversing popped, See whether the element behind it is an element in the stack . If not , Keep pressing the stack .
Last , Judge popped Is the traversal complete , Return after traversing true, Otherwise return to false.
Code :
class Solution {
public:
bool validateStackSequences(vector<int>& pushed, vector<int>& popped) {
stack<int> st;
int j=0;
for(auto i:pushed){
st.push(i);
while(!st.empty()&&st.top()==popped[j]){
st.pop();
++j;
}
}
return j==popped.size()?true:false;
}
};result :

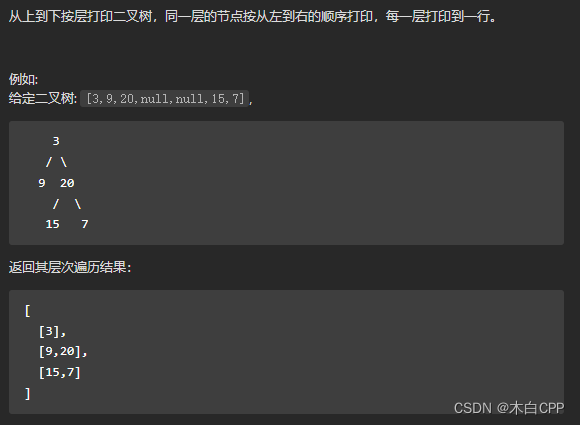
The finger of the sword Offer 32 - I. Print binary tree from top to bottom
Answer key :
Using queues for hierarchical traversal .
First , Exclude the special case of empty trees , Create a queue , The node used to store the tree . First push the root node from the queue head into the queue .
Step one : Get the first element at the end of the team temp, And pop it up .
Step two : Judge temp Whether the node has left and right subtrees , If there are, push them into the queue .
Cycle the above steps , Until the queue is empty .
Code :
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(root==NULL) return res;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
TreeNode* temp=que.front();
que.pop();
if(temp->left!=nullptr) que.push(temp->left);
if(temp->right!=nullptr) que.push(temp->right);
res.push_back(temp->val);
}
return res;
}
};result :

The finger of the sword Offer 32 - II. Print binary tree from top to bottom II
Answer key :
Using queues for hierarchical traversal .
First , Exclude the special case of empty trees .
then , Create a queue , And push the root node into the queue .
Step one : Create a container , The value used for the storage node . Temporarily store the size of the current queue .
Step two : Pop up all values in the queue , Be careful , Pop up , Push the left and right subtrees of the pop-up node into the queue , Step 1 records the length , So the nodes pushed later ( Next level node ) Will not be ejected .
Repeat the above steps , Until the queue is empty .
Code :
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return{};
queue<TreeNode*> que;
vector<vector<int>> res;
int sz=0;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
res.push_back(vector<int>());
int sz=que.size();
for(int i=0;i<sz;++i){
TreeNode* node=que.front();
res.back().push_back(node->val);
que.pop();
if(node->left!=nullptr) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right!=nullptr) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return res;
}
};result :
The finger of the sword Offer 32 - III. Print binary tree from top to bottom III
Answer key :
Method 1 : queue + Stack
Using queues for hierarchical traversal , Use stack for reverse storage .
The train of thought is the same as the previous question , Is to add a judgment bit flag, If true Just press it into the stack first , Then pop it up to the array .
Code :
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return {};
vector<vector<int>> res;
queue<TreeNode*>que;
stack<int>st;
bool flag=false;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
res.push_back(vector<int>());
int sz=que.size();
for(int i=0;i<sz;++i){
TreeNode* node=que.front();
if(flag)
st.push(node->val);
else
res.back().push_back(node->val);
que.pop();
if(node->left!=nullptr) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right!=nullptr) que.push(node->right);
}
while(!st.empty()){
res.back().push_back(st.top());
st.pop();
}
flag=!flag;
}
return res;
}
};result :

Method 2 : queue + An array of reverse
I think this question is about the use of stacks and queues , But from the perspective of problem solving , Method one is not necessarily the best , Adopting method 2 can reduce double complexity .
And the sword finger Offer 32 - II. Print binary tree from top to bottom II The idea of this question is exactly the same
Add judgment as flag,, If true Inversion array . It's that simple !
Code :
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return {};
vector<vector<int>> res;
queue<TreeNode*>que;
bool flag=false;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
res.push_back(vector<int>());
int sz=que.size();
for(int i=0;i<sz;++i){
TreeNode* node=que.front();
res.back().push_back(node->val);
que.pop();
if(node->left!=nullptr) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right!=nullptr) que.push(node->right);
}
if(flag)
reverse( res.back().begin(), res.back().end());
flag=!flag;
}
return res;
}
};result :

The finger of the sword Offer 33. The post order traversal sequence of binary search tree
Answer key :
Using recursive methods
We need to know , The last node of post order traversal is the root node , Its left subtree is in the first half and the second half of the array respectively .
First , Find the left subtree of the current root node [start,j-1] This part , Then find the right subtree of the current root node [j,end-1] This part .
Judge whether these two parts meet the requirements of the search tree ( The left subtree is all smaller than the root node , The right subtree is all larger than the root node ), Unsatisfied return false; If satisfied, continue to recurse the left and right subtrees .
Code :
class Solution {
public:
bool recursion(vector<int>& postorder,int start,int end){
if(end<=start) return true;
int i=start;
while(postorder[i]<postorder[end]) ++i;
int j=i;
while(postorder[i]>postorder[end]) ++i;
return i==end&&recursion(postorder,start,j-1)&&recursion(postorder,j,end-1);
}
bool verifyPostorder(vector<int>& postorder) {
return recursion(postorder,0,postorder.size()-1);
}
};result :

The finger of the sword Offer 34. The path of a value in a binary tree
Give you the root node of the binary tree root And an integer target and targetSum , Find out all From the root node to the leaf node The path sum is equal to the given target sum .
Leaf node A node without children .
Answer key :
The idea of this question is actually quite simple , Is to use depth first search , Record the value of the node while traversing , Until the leaf node judges whether the sum of nodes is the target value target
This is the result ... Unsatisfactory hahaha
Code :
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>&res,vector<int> row,TreeNode* root, int target){
if(root==nullptr) return;
target-=root->val;
row.push_back(root->val);
if(root->left==nullptr&&root->right==nullptr){
if(target==0) res.push_back(row);
return;
}
dfs(res,row,root->left,target);
dfs(res,row,root->right,target);
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int target) {
vector<int> row;
vector<vector<int>> res;
dfs(res,row,root,target);
return res;
}
};result :

The finger of the sword Offer 35. Replication of complex linked list
Answer key : Hash
First , Copy the old linked list into the hash table .
In the hash table, the nodes are linked according to the order of the old table , Form a new table .
Code :
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
unordered_map<Node*,Node*> map;
Node* h=head;
while(h!=nullptr){
map[h]=new Node(h->val);
h=h->next;
}
h=head;
while(h!=nullptr){
map[h]->next=map[h->next];
map[h]->random=map[h->random];
h=h->next;
}
return map[head];
}
};result :

边栏推荐
- C summary of knowledge points 1
- The Missing Semester
- Botu V15 add GSD file
- 8 best practices to protect your IAC security!
- Xiaomi mobile phone unlocking BL tutorial
- Neo4j Chinese developer monthly - issue 202206
- C#依赖注入(直白明了)讲解 一看就会系列
- 消息队列之监控退款任务批处理过程
- Joint Time-Frequency and Time Domain Learning for Speech Enhancement
- 指纹浏览器工作原理、使用场景以及重要性简单讲解
猜你喜欢

Redis configuration environment variables

Computer graduation project asp Net hotel room management system VS development SQLSERVER database web structure c programming computer web page source code project

Comment Cao définit la décimale de dimension

LeetCode力扣(剑指offer 31-35)31. 栈的压入弹出序列32I.II.III.从上到下打印二叉树33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径35. 复杂链表的复制

Learning summary on June 30, 2022
S7-1500PLC仿真

Exposure: a white box photo post processing framework reading notes

Y48. Chapter III kubernetes from introduction to mastery -- pod status and probe (21)

【单片机】【数码管】数码管显示

Acly and metabolic diseases
随机推荐
Golang des-cbc
Exposure: a white box photo post processing framework reading notes
谈思生物直播—GENOVIS张洪妍抗体特异性酶切技术助力抗体药物结构表征
Talk about the pessimistic strategy that triggers full GC?
Istio, ebpf and rsocket Broker: in depth study of service grid
自组织是管理者和成员的双向奔赴
Want to ask, is there a discount for opening a securities account? Is it safe to open a mobile account?
如何看懂开发的查询语句
Value/sortedset in redis
How to set decimal places in CAD
Software project management 9.2 Software project configuration management process
How to understand the developed query statements
博途V15添加GSD文件
Neo4j Chinese developer monthly - issue 202206
Golang des-cbc
Impressive bug summary (continuously updated)
Explore the contour detection function findcontours() of OpenCV in detail with practical examples, and thoroughly understand the real role and meaning of each parameter and mode
Adjacency matrix undirected graph (I) - basic concepts and C language
指定的服务已标记为删除
Kernel synchronization mechanism