当前位置:网站首页>没错,请求DNS服务器还可以使用UDP协议
没错,请求DNS服务器还可以使用UDP协议
2022-07-26 00:00:00 【flydean】
简介 之前我们讲到了如何在netty中构建client向DNS服务器进行域名解析请求。使用的是最常见的TCP协议,也叫做Do53/TCP。
事实上除了TCP协议之外,DNS服务器还接收UDP协议。这个协议叫做DNS-over-UDP/53,简称(“Do53”)。
本文将会一步一步带领大家在netty中搭建使用UDP的DNS客户端。
搭建netty客户端 因为这里使用的UDP协议,netty为UDP协议提供了专门的channel叫做NioDatagramChannel。EventLoopGroup还是可以使用常用的NioEventLoopGroup,这样我们搭建netty客户端的代码和常用的NIO UDP代码没有太大的区别,如下所示:
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); b.group(group) .channel(NioDatagramChannel.class) .handler(new Do53UdpChannelInitializer()); final Channel ch = b.bind(0).sync().channel(); 这里的EventLoopGroup使用的是NioEventLoopGroup,作为client端Bootstrap的group。
因为要使用UDP协议进行传输,所以这里的channel使用的是NioDatagramChannel。
设置好channel之后,传入我们自定义的handler,netty client就搭建完毕了。
因为是UDP,所以这里没有使用TCP中的connect方法,而是使用bind方法来获得channel。
Do53UdpChannelInitializer中包含了netty提供的UDP DNS的编码解码器,还有自定义的消息处理器,我们会在后面的章节中详细进行介绍。
在netty中发送DNS查询请求 搭建好netty客户端之后,接下来就是使用客户端发送DNS查询消息了。
先看具体的查询代码:
int randomID = (int) (System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000); DnsQuery query = new DatagramDnsQuery(null, addr, randomID).setRecord( DnsSection.QUESTION, new DefaultDnsQuestion(queryDomain, DnsRecordType.A)); ch.writeAndFlush(query).sync(); boolean result = ch.closeFuture().await(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); if (!result) { log.error("DNS查询失败"); ch.close().sync(); } 查询的逻辑是先构建UDP的DnsQuery请求包,然后将这请求包写入到channel中,然后等待消息处理完毕。
DnsQuery之前我们已经介绍过了,他是netty中所有DNS查询的基础类。
public interface DnsQuery extends DnsMessage DnsQuery的子类有两个,分别是DatagramDnsQuery和DefaultDnsQuery。这两个实现类一个表示UDP协议的查询,一个表示TCP协议的查询。
我们看下UDP协议的DatagramDnsQuery具体定义:
public class DatagramDnsQuery extends DefaultDnsQuery implements AddressedEnvelope<DatagramDnsQuery, InetSocketAddress> 可以看到DatagramDnsQuery不仅仅继承自DefaultDnsQuery,还实现了AddressedEnvelope接口。
AddressedEnvelope是netty中UDP包的定义,所以要想在netty中发送基于UDP协议的数据包,就必须实现AddressedEnvelope中定义的方法。
作为一个UDP数据包,除了基本的DNS查询中所需要的id和opCode之外,还需要提供两个额外的地址,分别是sender和recipient:
private final InetSocketAddress sender;private final InetSocketAddress recipient;所以DatagramDnsQuery的构造函数可以接收4个参数:
public DatagramDnsQuery(InetSocketAddress sender, InetSocketAddress recipient, int id, DnsOpCode opCode) { super(id, opCode); if (recipient == null && sender == null) { throw new NullPointerException("recipient and sender"); } else { this.sender = sender; this.recipient = recipient; }}这里recipient和sender不能同时为空。
在上面的代码中,我们构建DatagramDnsQuery时,传入了服务器的InetSocketAddress:
final String dnsServer = "223.5.5.5"; final int dnsPort = 53; InetSocketAddress addr = new InetSocketAddress(dnsServer, dnsPort); 并且随机生成了一个ID。然后调用setRecord方法填充查询的数据。
.setRecord(DnsSection.QUESTION, new DefaultDnsQuestion(queryDomain, DnsRecordType.A)); DnsSection有4个,分别是:
QUESTION,ANSWER,AUTHORITY,ADDITIONAL;这里是查询操作,所以需要设置DnsSection.QUESTION。它的值是一个DnsQuestion:
public class DefaultDnsQuestion extends AbstractDnsRecord implements DnsQuestion 在这个查询中,我们传入了要查询的domain值:www.flydean.com,还有查询的类型A:address,表示的是域名的IP地址。
DNS消息的处理 在Do53UdpChannelInitializer中为pipline添加了netty提供的UDP编码解码器和自定义的消息处理器:
class Do53UdpChannelInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<DatagramChannel> { @Override protected void initChannel(DatagramChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline(); p.addLast(new DatagramDnsQueryEncoder()) .addLast(new DatagramDnsResponseDecoder()) .addLast(new Do53UdpChannelInboundHandler()); } } DatagramDnsQueryEncoder负责将DnsQuery编码成为DatagramPacket,从而可以在NioDatagramChannel中进行传输。
public class DatagramDnsQueryEncoder extends MessageToMessageEncoder<AddressedEnvelope<DnsQuery, InetSocketAddress>> { DatagramDnsQueryEncoder继承自MessageToMessageEncoder,要编码的对象是AddressedEnvelope,也就是我们构建的DatagramDnsQuery。
看一下它里面最核心的encode方法:
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, AddressedEnvelope<DnsQuery, InetSocketAddress> in, List<Object> out) throws Exception { InetSocketAddress recipient = (InetSocketAddress)in.recipient(); DnsQuery query = (DnsQuery)in.content(); ByteBuf buf = this.allocateBuffer(ctx, in); boolean success = false; try { this.encoder.encode(query, buf); success = true; } finally { if (!success) { buf.release(); } } out.add(new DatagramPacket(buf, recipient, (InetSocketAddress)null));}基本思路就是从AddressedEnvelope中取出recipient和DnsQuery,然后调用encoder.encode方法将DnsQuery进行编码,最后将这些数据封装到DatagramPacket中。
这里的encoder是一个DnsQueryEncoder实例,专门用来编码DnsQuery对象。
DatagramDnsResponseDecoder负责将接受到的DatagramPacket对象解码成为DnsResponse供后续的自定义程序读取使用:
public class DatagramDnsResponseDecoder extends MessageToMessageDecoder<DatagramPacket> 看一下它的decode方法:
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, DatagramPacket packet, List<Object> out) throws Exception { try { out.add(this.decodeResponse(ctx, packet)); } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException var5) { throw new CorruptedFrameException("Unable to decode response", var5); }}上面的decode方法实际上调用了DnsResponseDecoder的decode方法进行解码操作。
最后就是自定义的Do53UdpChannelInboundHandler用来进行消息的读取和解析:
private static void readMsg(DatagramDnsResponse msg) { if (msg.count(DnsSection.QUESTION) > 0) { DnsQuestion question = msg.recordAt(DnsSection.QUESTION, 0); log.info("question is :{}", question); } for (int i = 0, count = msg.count(DnsSection.ANSWER); i < count; i++) { DnsRecord record = msg.recordAt(DnsSection.ANSWER, i); if (record.type() == DnsRecordType.A) { //A记录用来指定主机名或者域名对应的IP地址 DnsRawRecord raw = (DnsRawRecord) record; System.out.println(NetUtil.bytesToIpAddress(ByteBufUtil.getBytes(raw.content()))); } }}自定义handler接受的是一个DatagramDnsResponse对象,处理逻辑也很简单,首先读取msg中的QUESTION,并打印出来。
然后读取msg中的ANSWER字段,如果ANSWER的类型是A address,那么就调用NetUtil.bytesToIpAddress方法将其转换成为IP地址输出。
最后我们可能得到下面的输出:
question is :DefaultDnsQuestion(www.flydean.com. IN A) 49.112.38.167 总结 以上就是在netty中使用UDP协议进行DNS查询的详细讲解。
本文的代码,大家可以参考:
learn-netty4
更多内容请参考 http://www.flydean.com/55-netty-dns-over-udp/
最通俗的解读,最深刻的干货,最简洁的教程,众多你不知道的小技巧等你来发现!
欢迎关注我的公众号:「程序那些事」,懂技术,更懂你!
边栏推荐
- LeetCode_55_跳跃游戏
- The mobile version of Duoyu security browser will add new functions to make users browse more personalized
- Compile live555 with vs2019 in win10
- Part 66: monocular 3D reconstruction point cloud
- Binary tree - 226. Flip binary tree
- What is multithreading
- 06_ue4进阶_使用地形工具设置大地图
- What is parity? How to use C language?
- Binary tree - 404. Sum of left leaves
- Practical experience of pair programming
猜你喜欢

Getaverse,走向Web3的远方桥梁

The mobile version of Duoyu security browser will add new functions to make users browse more personalized

最近随感,关于牛市和DeFi 2021-05-17

二叉树——226. 翻转二叉树

复盘:推荐系统—— 负采样策略

调用钉钉api报错:机器人发送签名过期;solution:签名生成时间和发送时间请保持在 timestampms 以内
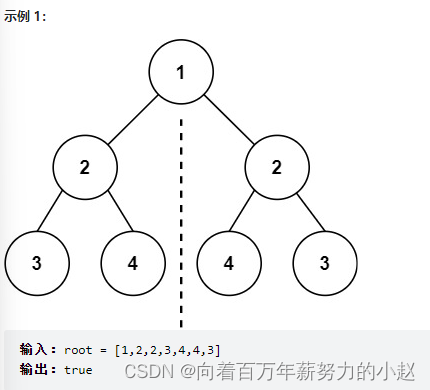
Binary tree 101. Symmetric binary tree

Binary tree - 530. Minimum absolute difference of binary search tree
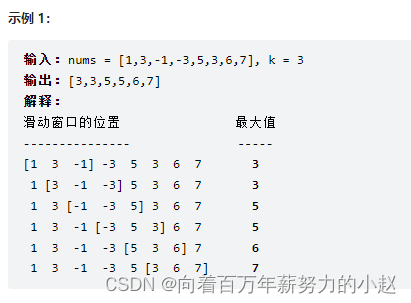
栈与队列——239. 滑动窗口最大值

Sequence traversal II of leetcode107 binary tree
随机推荐
MySQL的DDL、DML和DQL的基本语法
SHIB(柴犬币)一月涨幅数百倍,百倍币需具备哪些核心要素?2021-05-09
What is parity? How to use C language?
最近随感,关于牛市和DeFi 2021-05-17
Binary tree -- 257. All paths of binary tree
Part 66: monocular 3D reconstruction point cloud
Programming password guessing game
LeetCode_55_跳跃游戏
Leetcode107-二叉树的层序遍历II详解
Iterator pattern of behavioral pattern
回溯——77. 组合
Binary tree 101. Symmetric binary tree
Key features and application trends of next generation terminal security management
Song of statistics lyrics
Android solves the risk of database injection vulnerability
行为型模式之迭代器模式
Exercise (3) create a list set (both ArrayList and LinkedList)
如何用yolov5 做个闯红灯监控的智能交通系统(1)
Solve the problem of rapid index bar extrusion
Stack and queue - 347. Top k high frequency elements