当前位置:网站首页>Interview for postgraduate entrance examination of Baoyan University - machine learning
Interview for postgraduate entrance examination of Baoyan University - machine learning
2022-06-26 07:53:00 【moluggg】
Ashore some midstream 985, The following is my summary of the important and difficult knowledge of machine learning , To understand ( recite ) The main topic is , Thank you for bringing up the wrong words :
Indicates difficult knowledge points , It can be combined with zhouzhihua's understanding of the machine learning textbook
Basic concepts :
hyperplane :
n In the Euclidean space n-1 Dimensional linear subspace
Explain it. ROC Curve and PR curve
ROC True rate and false positive rate
PR Accuracy and recall

If a learner's PR curve Wrapped up another , be
It can be said that A Better performance than C

Define it prediction Accuracy 、recall Recall rate
!、
| Example | Counter example | |
|---|---|---|
| Example | TP( Real examples ) | FN( False negative example ) |
| Counter example | FP( False positive example ) | TN( What a negative example ) |
Accuracy :P = TP/(TP+FP) Indicates how many samples are predicted to be positive .
Recall rate :R =TP/(TP+FN) Indicates how many positive samples have been retrieved
Take an example to explain : The merchant has produced a batch of goods with problems , It has been put into the market , You can judge whether there is a problem according to some characteristics , If you appear, you will find
Accuracy : Among the retrieved samples, the samples with actual problems
Recall rate : How many samples with problems are found in the total samples with problems
Real interest rates = Recall rate
False positive interest rate :FP/(FP+TN)
What is? F1 Count , How to use it
F1 Number is a measure of the performance of a model . It's a weighted average of model accuracy and recall ,1 Best ,0 It means the worst . In the classification problem, sometimes the accuracy rate and recall rate will not be high at the same time , Then we can use F1 Count .
F 1 = 2 × P × R P + R = 2 × T P Total number of samples + T P − T N F 1=\frac{2 \times P \times R}{P+R}=\frac{2 \times T P}{\text { Total number of samples }+T P-T N} F1=P+R2×P×R= Total number of samples +TP−TN2×TP
Fourier transformation ?
Fourier transform means : A function satisfying some conditions can be expressed as a trigonometric function or a linear combination of their integral forms .
What is deep learning , What's the connection between it and machine learning algorithms ?
machine learning : Use algorithms to parse data , Learn the internal distribution law of data or data and data 、 The connection and difference between data and labels , Make decisions and predictions about new data .
Deep learning : A subfield of machine learning , It is concerned with the construction of neural networks with reference to the theories of Neurology , Back propagation is used to model large amounts of unlabeled or semi-structured data .
What is the difference between generative model and discriminant model
The generation model learns about the distribution of data ; Discriminant models learn the difference between different types of data , Do not learn the internal characteristics of data . On the issue of classification , The discriminant model is better than the generative model .
The idea of solving the discriminant model is : Conditional distribution ------> The posterior probability of model parameters is the largest ------->( Likelihood function \cdot Parametric prior ) Maximum -------> maximum likelihood
The solution idea of the generation model is : Joint distribution -------> Solve the category prior probability and category conditional probability
The common generation methods are Gaussian mixture model 、 Naive Bayes method and hidden Markov model , Common discrimination methods are SVM、LR etc.
How to use cross test on time series data
And standard k-folds Different cross tests , The data is not randomly distributed , It's sequential . If the pattern appears later , The model still needs to select the data of the previous time , Although the early stage has no impact on the model . We can do this as follows :
fold1:training[1], test[2];
fold2:training[1 2], test[3];
fold3:training[1 2 3], test[4];
fold4:training[1 2 3 4], test[5];
fold5:training[1 2 3 4 5], test[6];
Over fitting and under fitting :
Over fitting : The specific performance is that the final model has a good effect on the training set ; The effect is poor on the test set . The generalization ability of the model is weak .
The reason for over fitting :
Too much noise interference in training data , Make the learner think that part of the noise is a feature, thus disturbing the learning rules .
Wrong modeling sample selection , For example, there is too little training data , Wrong sampling method , sample label Errors, etc , As a result, the sample cannot represent the whole .
The model is unreasonable , Or the assumption is not consistent with the actual conditions .
Feature dimension / Too many parameters , The model complexity is too high .
Over fitting solution :
Add data , Reduce model complexity , Data dimension reduction ,dropout layer ,early stopping , Add regularization term
Under fitting : It means that the general nature of the training sample has not been learned well . The performance in training set and test set is not good .
The reason for the lack of fit
Model complexity is too low , Too few features
terms of settlement :
Increase the number of features , Increase model complexity , Reduce the regularization coefficient
Unbalanced data sets : Processing mode
① Collect more data, less data
② Random oversampling : Copy more copies of the less
③ Random undersampling : Multiple classes only extract part of them
④ Over sampling based on clustering : Group a certain class of samples into several classes
for instance , It shows that using ensemble learning can be very useful .
How do you make sure your model doesn't fit ?
① The model should be as simple as possible
② Using regularization techniques
③ Use cross validation
How to evaluate the effectiveness of your machine learning model ?
① Validity of dataset segmentation , How to divide training set and test set
② Performance indicators
What is nuclear technology , What's the use ?
https://blog.csdn.net/hellocsz/article/details/91904967
Kernel function : Because data is linearly nonseparable in low dimensional space , Mapping to high dimensional space can distinguish , Kernel function is to solve the problem of too much computation in mapping to high-dimensional space , At the same time, it can reduce the interference of noise data .
The essence : The square of the inner product of the eigenvector
Common kernel functions : Linear kernel 、 Gaussian kernel 、 Laplace core
The core idea of nuclear technology is : First , The original data is embedded into a suitable high-dimensional feature space through some nonlinear mapping ; then , Using a general linear learning machine to analyze and process patterns in this new space .
What is reinforcement learning , Reinforcement learning 、 Multi task learning ?
Reinforcement learning is reinforcement learning : The external environment only gives evaluation information to the output rather than correct information .
Now most machine learning tasks are single task learning . For complex problems , It can also be decomposed into simple and independent subproblems to solve alone , And then merge the results , Get the result of the initial complex problem . But many problems in the real world can not be decomposed into an independent sub problem , The subproblems are also interrelated , Multi task learning is born to solve this problem . Make multiple connections (related) The task of (task) Put it together to learn . Sharing factors among multiple tasks , They can be in the learning process , Share what they learn , Related multi task learning is better than single task learning (generalization) effect .

https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/348873723
Integrated learning :
Integrated learning By integrating multiple weak classifiers , Make them complete the learning task together , Build a strong classifier

Understand examples :
https://blog.csdn.net/blank_tj/article/details/82229322?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant_t0.none-task-blog-2%7Edefault%7EBlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2%7Edefault-1.essearch_pc_relevant&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant_t0.none-task-blog-2%7Edefault%7EBlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2%7Edefault-1.essearch_pc_relevant
Activation function
comparison sigmoid Activation function ReLU What are the advantages of activating functions ?
(1) Prevent the gradient from disappearing ( sigmoid The derivative of is only in 0 There is better activation near , The gradients in the positive and negative saturation regions are close to 0)
(2) ReLU The output of is sparse ;
(3) ReLU Simple function and fast calculation
What is the role of attention mechanism in deep learning ? Which scenarios will use ?
The attention mechanism in deep learning is essentially similar to the selective visual attention mechanism of human beings , The core goal is to selectively select a small amount of important information from a large amount of information and focus on these important information , Ignore most of the unimportant information . Currently in Neural machine translation (Neural Machine Translation)、 Image understanding (Image caption) And other scenarios are widely used .
For multi classification problems , Why do neural networks generally use cross entropy instead of Euclidean distance loss ?
In general, the cross entropy is easier to converge to a better solution .
What functions can be used as activation functions ?
nonlinear , Almost everywhere , monotonous
Machine learning algorithm
CNN
The effect of pooling layer :
Reducing the image size means reducing the data dimension , Ease of overfitting , Maintain a certain degree of rotation and translation invariance .
Dropout The role of :
Prevent over fitting . Every time you train , For each neural network unit , Discard temporarily with a certain probability .
What is the function of hole convolution ?

Expansion convolution , Keep the number of parameters unchanged The receptive field of convolution kernel is increased , At the same time, it can guarantee the output feature mapping (feature map) The size of the remains the same . An expansion rate is 2 Of 3×3 Convolution kernel , Feel wild and 5×5 The convolution kernel of is the same , But the number of parameters is only 9 individual .
1x1 What is the use of convolution ?
Channel dimension reduction or dimension increase , Ensure that the convolutional neural network can accept any size of input data
The original plane structure of the picture is preserved , Regulation depth, So as to complete the function of dimension elevation or dimension reduction .
If you use 1x1 Convolution kernel , This operation implements multiple feature map The linear combination of , Can achieve feature map Changes in the number of channels . Thus, the nonlinearity is increased
Why do we now tend to use convolution kernels of small size ?
Using multiple small convolution kernels in series can have the same ability as large convolution kernels , And there are fewer parameters , In addition, there are more activation functions , Enhanced nonlinearity .
Explain the principle and application of deconvolution
Deconvolution is called transpose convolution , The forward propagation is multiplied by the transpose matrix of the convolution kernel , Back propagation times convolution kernel matrix
The input data is approximately reconstructed from the convolution output results , On the sampling
Deconvolution is also called transpose convolution , If the convolution operation is realized by matrix multiplication , Tiling convolution kernels into matrices , be ** Transpose convolution left multiplies the transpose of this matrix in the forward calculation [ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-cbgcsQiT-1643367003784)(https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=W%5E%7BT%7D)] , Multiply left in back propagation W, Just the opposite of convolution ,** It should be noted that , Deconvolution is not the inverse operation of convolution .
What are the uses of deconvolution ?
Realize up sampling ; Approximate reconstruction of the input image , Convolution layer visualization
Gradient descent algorithm :
Batch gradient descent :
θ j ′ = θ j + 1 m ∑ i = 1 m ( y i − h θ ( x i ) ) x j i \theta_{j}^{\prime}=\theta_{j}+\frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m}\left(y^{i}-h_{\theta}\left(x^{i}\right)\right) x_{j}^{i} θj′=θj+m1i=1∑m(yi−hθ(xi))xji
What it gets is a global optimal solution , But every iteration step , All the data in the training set , Stochastic gradient descent :
Randomly shuffle dataset;
repeat{
for i=1, … , 99{
θ j ′ = θ j + ( y i − h θ ( x i ) ) x j i \theta_{j}^{\prime}=\theta_{j}+\left(y^{i}-h_{\theta}\left(x^{i}\right)\right) x_{j}^{i} θj′=θj+(yi−hθ(xi))xji
}
}
Small batch random :
θ j : = θ j − α 1 10 ∑ k = i i + 9 ( h θ ( x ( k ) ) − y ( k ) ) x j ( k ) \theta_{j}:=\theta_{j}-\alpha \frac{1}{10} \sum_{k=i}^{i+9}\left(h_{\theta}\left(x^{(k)}\right)-y^{(k)}\right) x_{j}^{(k)} θj:=θj−α101k=i∑i+9(hθ(x(k))−y(k))xj(k)
advantage : Fast training ;
shortcoming : Decreased accuracy , It's not the global best ; Not easy to implement in parallel .
Using gradient descent method to train neural network , Discover the model Loss unchanged , What are the possible problems ? How to solve ?
It is very likely that the gradient has disappeared , It means that when the neural network is updated iteratively , Some weights are not updated .
Change the activation function , Change the initialization of the weight .
The solution of gradient explosion ?
For the gradient explosion problem , The solution is to introduce Gradient Clipping( Gradient cut ). adopt Gradient Clipping, Constrain the gradient to a range , This will not make the gradient too large .
Gradient clipping method : Given the selected vector norm ( vector norm) To rescale the gradient ; And clipping the gradient value beyond the preset range .
Random forests
Integrated thought : Every decision tree is a classifier ( Let's say we're dealing with classification ), So for an input sample ,N A tree will have N A classification result . And the random forest integrates all the voting results , Specify the category with the most votes as the final output , This is one of the simplest Bagging thought .
Bayes theorem : How it is used in machine learning ?
Bayesian theorem will tell you its posterior probability based on the prior knowledge of an event .
Its basic idea is as follows : For the given items to be classified , Solve the probability of each category under this condition , Which is the biggest , Which category do you think the item to be classified belongs to . The reason for adding the word simplicity is : This classification algorithm is based on the idea of Bayesian probability , Suppose the attributes are independent of each other , for example A and B,A and B They are independent of each other , Whether it happens or not does not affect each other . This assumption is relatively simple , So it is called simple .https://blog.csdn.net/u013206066/article/details/54381182
Naive Bayes classifier
Data dimension reduction PCA LDA
After feature selection , Maybe because the characteristic matrix is too large , Resulting in large amount of calculation 、 Long training time , therefore Reduce the dimension of characteristic matrix It's also essential .
thought :
PCA: take The original feature space is mapped to the feature vector space which is orthogonal to each other , Use SVD decompose To construct eigenvectors .

LDA: Find a projection direction , Within class variance is the smallest , Maximum variance between classes
say concretely : The covariance between the same species should be as small as possible 、 The distance between the class centers of is as large as possible .
(1) Calculate the intra class scatter matrix S b S_{b} Sb
(2) Compute the divergence matrix between classes S w S_{w} Sw
(3) Calculation of matrix S w − 1 S b S_{w}^{-1} S_{b} Sw−1Sb
(4) The matrix S w − 1 S b S_{w}^{-1} S_{b} Sw−1Sb Do feature decomposition , Calculate the biggest d d d The largest eigenvalue corresponds to the eigenvector W W W .
(5) Calculate the data points after projection Y = W T X Y=W^{T} X Y=WTX
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/51769969
Multiple classification problem , At this time, the inter class divergence matrix is :
S b = ∑ j = 1 k N j ( u j − u ) ( u j − u ) T S_{b}=\sum_{j=1}^{k} N_{j}\left(u_{j}-u\right)\left(u_{j}-u\right)^{T} Sb=j=1∑kNj(uj−u)(uj−u)T
among u Average all data points .
The intraclass divergence matrix is :
S W = ∑ j = 1 k ∑ x ∈ X j ( x − u j ) ( x − u j ) T S_{W}=\sum_{j=1}^{k} \sum_{x \in X_{j}}\left(x-u_{j}\right)\left(x-u_{j}\right)^{T} SW=j=1∑kx∈Xj∑(x−uj)(x−uj)T
Scatter matrix is also called divergence matrix , Multiply the covariance matrix by the coefficient (n-1) So we get the scatter matrix , All scatter matrices have the same effect as covariance matrices , Understanding the covariance matrix means understanding the dispersion matrix , They have only one coefficient, only difference
The same thing :
1) Both can reduce the dimension of data .
2) Both of them use the idea of matrix eigendecomposition in dimension reduction .
3) Both assume that the data is Gaussian 【 Normal distribution 】.
Difference :
1)LDA It's a supervised dimension reduction method , and PCA It's an unsupervised dimension reduction method
2)LDA Dimension reduction can be reduced to category number at most k-1 Dimension of , and PCA There is no such restriction .
3)LDA Besides, it can be used for dimensionality reduction , It can also be used to classify .
4)LDA Choose the projection direction with the best classification performance , and PCA Select the direction where the sample point projection has the maximum variance .
Dimension disaster
Dimensional disasters are used to describe when ( mathematics ) As the spatial dimension increases , Analyze and organize high dimensional space ( It's usually hundreds of dimensions ), Various problem scenarios due to volume index increase . Such a problem will not be encountered in low dimensional space , For example, physical space is usually modeled only in three dimensions .
The calculation of Euclidean distance is invalid in high dimensional space
Kmeans
KNN and k-means What makes clustering different ?
k-Nearest Neighbors It's a supervised learning algorithm , and k-means It's unsupervised .
k Starting point
1) Choose as far away from each other as possible K A little bit
2) First, the hierarchical clustering algorithm is used for the data , obtain K After a cluster , Select a point from each class cluster , This point can be the central point of this kind of cluster , Or the point closest to the center of the cluster .
curse of dimensionality
k The determination of :
Contour coefficient method
Contour coefficient is a very common clustering effect evaluation index . The index combines two factors of cohesion and separation . The specific calculation process is as follows :
Suppose that the data to be classified has been clustered by the clustering algorithm , And finally we get a cluster . For each sample point in each cluster , Calculate their contour coefficients respectively . In particular , The following two indicators need to be calculated for each sample point :
The following two indicators need to be calculated for each sample point :
a ( i ) : Sample points i The average value of the distance to other sample points belonging to the same cluster . a ( i ) The smaller it is , Explain the sample i The more likely you are to fall into this category . b ( i ) : sample Ben spot i To Its He cluster C j in Of the Yes sample Ben Of flat all distance leave Of flat all value b i j , b ( i ) = m i n ( b i 1 , b i 2 , ⋯ , b i k ) \text { } a(i) \text { : Sample points } i \text { The average value of the distance to other sample points belonging to the same cluster . } a(i) \text { The smaller it is , Explain the sample } i \text { The more likely you are to fall into this category . }\\ b(i): Sample points i To other clusters C_{j} Average of the average distance of all samples in b_{ij} ,b(i)=min(b_{i1},b_{i2},\cdots ,b_{ik}) a(i) : Sample points i The average value of the distance to other sample points belonging to the same cluster . a(i) The smaller it is , Explain the sample i The more likely you are to fall into this category . b(i): sample Ben spot i To Its He cluster Cj in Of the Yes sample Ben Of flat all distance leave Of flat all value bij,b(i)=min(bi1,bi2,⋯,bik)
Then the contour coefficient of the sample point is :
s ( i ) = b ( i ) − a ( i ) max ( a ( i ) , b ( i ) ) s(i)=\frac{b(i)-a(i)}{\max (a(i), b(i))} s(i)=max(a(i),b(i))b(i)−a(i)
Kmeans What are the advantages and disadvantages
advantage : Method is simple 、 Easy to operate , Less parameter adjustment
shortcoming :K Selection of 、 It is greatly influenced by the initial value 、 Sensitive to noise
Density clustering and hierarchical clustering , Spectral clustering
The algorithm examines the connectivity between samples from the perspective of sample density , Based on the connectable samples, the cluster is expanded to get the final clustering results .
Hierarchical clustering : first , Each object acts as a cluster , Determine the similarity according to the data points with the shortest distance between clusters , Determine according to the similarity . If the distance between two clusters exceeds the threshold value given by the user, it will terminate . Repeat until all clusters meet the above conditions .
Density clustering :
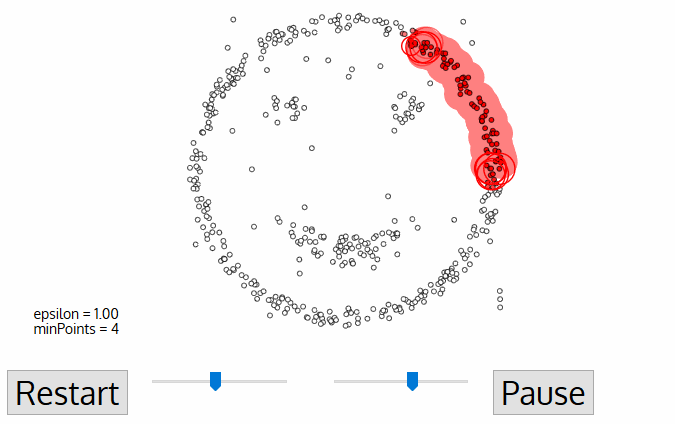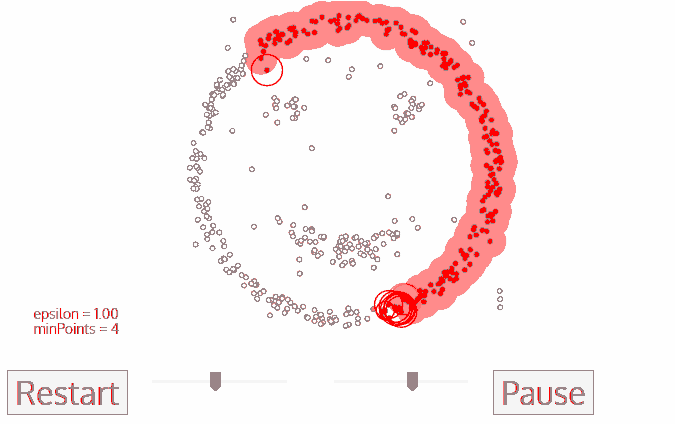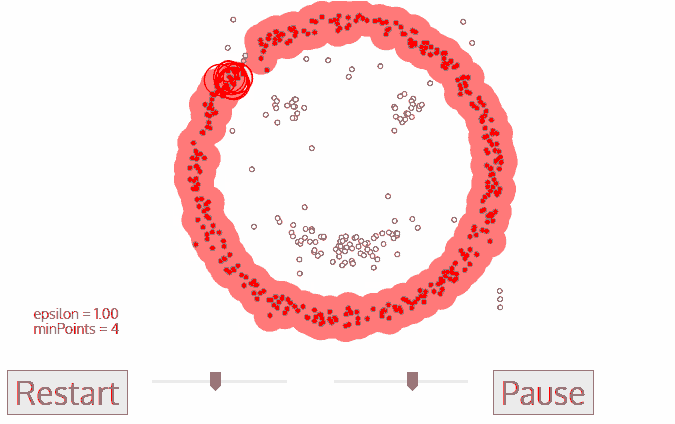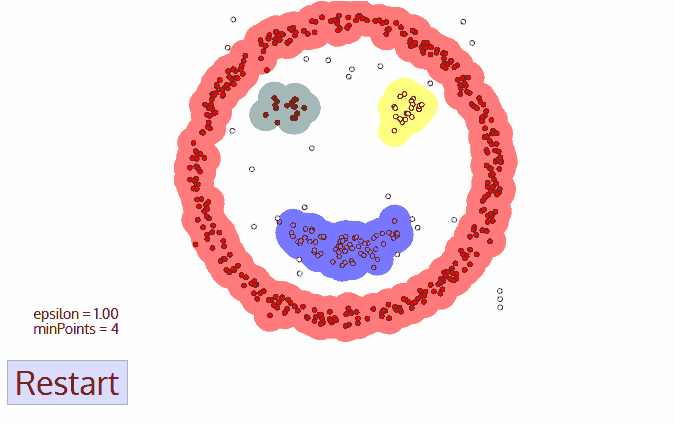
** Example :** Initial value :① Neighborhood parameters ε ② Minimum number of points MinPts
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-TVKJdFez-1643367003787)(mindmaster_image/20210210023731.png)]
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-TSqBiWVm-1643367003787)(mindmaster_image/20210210024227.png)]

Spectral clustering (Spectral Clustering, SC) It is a clustering method based on graph theory , Draw the weighted undirected graph Divided into two or more optimal subgraphs , Make the subgraphs as similar as possible , The distance between subgraphs should be as far as possible , To achieve the purpose of common clustering .
Decision tree :
You can choose :ID3 Information gain 、,
C4.5 Gain rate ( It solves the problem that information gain has a preference for those with more attributes )
CART gini index ( Gini The smaller the index is, the less likely the selected sample in the set will be misclassified , That is to say, the higher the purity of the set , conversely , The more impure the collection .)
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-1vT1P8cD-1643367003789)(mindmaster_image/1217155-20200204153304802-1069293659.png)]
prune , pre-pruning 、 After pruning
The principle of logical regression
Linear regression + sigmoid function ( Logarithmic probability function )
The loss function is : Cross loss entropy
LR The basic idea of is the maximum likelihood idea . therefore , It is easy to follow this path .

️ SVM : How to classify multiple tasks ?
SVM thought : Maximizes the distance from the point closest to the hyperplane to the hyperplane
Hard spacing 、 Soft space
SVM It's a binary algorithm , You can convert a multi category task into a two category task , Specifically, there are one to many , One to one algorithm :
If I had four categories ( That is to say 4 individual Label), They are A、B、C、D. So when I was extracting the training set , Separate extraction
(1)A The corresponding vector is a positive set ,B,C,D The corresponding vector is a negative set ;
(2)B The corresponding vector is a positive set ,A,C,D The corresponding vector is a negative set ;
(3)C The corresponding vector is a positive set ,A,B,D The corresponding vector is a negative set ;
(4)D The corresponding vector is a positive set ,A,B,C The corresponding vector is a negative set ;
One on one :
Permutation and combination , The category with the most statistics output
Hidden Markov ,CRF
hidden Markov model (Hidden Markov model, HMM) It is a generation model of dynamic Bayesian network with the simplest structure , It is also a famous directed graph model . It is a typical statistical machine model to deal with annotation problems in natural language , This paper will focus on this classical machine learning model .
Hidden Markov models do not directly discuss state sequences , Is to determine the state sequence by observing the state
https://blog.csdn.net/lrs1353281004/article/details/79417225
Hidden Markov model consists of Initial probability distribution 、 State transition probability distribution as well as Observation probability distribution determine .
Hidden Markov model consists of π、A、B decision .π and A Determine the sequence of States ,B Determine the observation sequence .
hidden Markov model λ=( A, B,π),A,B,π It is called the three elements of hidden Markov model **.**
Two assumptions :
① t The state of the moment just depends on the state of the previous moment
② The observation at any time only depends on the state at that time
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-iKJdBb94-1643367003790)(mindmaster_image/image-20210827155516631.png)]
Three basic questions :
You can search
The problem of probability calculation :
Given the model λ = ( A , B , π ) \lambda=(A, B, \pi) λ=(A,B,π) And the observation sequence O = ( o 1 , o 2 , … , o T ) \mathrm{O}=\left(o_{1}, o_{2}, \ldots, o_{T}\right) O=(o1,o2,…,oT) . The calculation is in the model λ \lambda λ Next observation sequence O Probability of occurrence P ( O ∣ λ ) \mathrm{P}(\mathrm{O} \mid \lambda) P(O∣λ) .
The solution to this problem is forward 、 Backward algorithm .

Learning problems ( model training ):
Known observation sequence O = ( O 1 , o 2 , … , o T ) \mathrm{O}=\left(\mathrm{O}_{1}, \mathrm{o}_{2}, \ldots, \mathrm{o}_{T}\right) O=(O1,o2,…,oT), Estimation model Λ = ( A , B , π ) \mathrm{\Lambda}=(\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{B}, \pi) Λ=(A,B,π) Parameters , Under this model, the observed sequence is approximately
rate P ( O ∣ λ ) (\mathrm{O} \mid \lambda) (O∣λ) Maximum .
When the observation sequence and the corresponding state sequence are given at the same time , The maximum likelihood estimation method is used to estimate the parameters .
When only the observation sequence is given , When there is no corresponding state sequence , be based on EM Algorithm for parameter estimation . (Baum-Welch Algorithm )
Log likelihood function maximization , structure Q Function and maximize Q function ( Using Lagrangian algorithm )
Prediction problem ( Sequence generation ):
Also known as decoding problem . Known models λ = ( A , B , π ) \lambda=(\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{B}, \pi) λ=(A,B,π) And the observation sequence O = ( o 1 , o 2 , … , o T ) \mathrm{O}=\left(o_{1}, \mathrm{o}_{2}, \ldots, \mathrm{o}_{T}\right) O=(o1,o2,…,oT)
Find the conditional probability of a given observation sequence P(I|O) The largest sequence of States . That is, given the observation sequence O = ( o 1 , o 2 , … , o T ) O=\left(o_{1}, o_{2}, \ldots, o_{T}\right) O=(o1,o2,…,oT) Find the most likely corresponding state sequence I = ( i 1 , i 2 , … , i T ) \mathrm{I}=\left(i_{1}, i_{2}, \ldots, i_{T}\right) I=(i1,i2,…,iT)
The method to solve this problem is Viterbi algorithm .
Also learned
边栏推荐
- 4 best practices for wireless (OTA) updates
- arduino——ATtiny85 SSD1306 + DHT
- Informatics Orsay all in one 1354: bracket matching test
- WiFi-802.11 2.4G频段 5G频段 信道频率分配表
- Jemter 壓力測試 -基礎請求-【教學篇】
- Opencv鼠标事件+界面交互之绘制矩形多边形选取感兴趣区域ROI
- Google Earth engine (GEE) 02 basic knowledge and learning resources
- Technology sharing | mysql:caching_ sha2_ Password quick Q & A
- Basic use of swiperefreshlayout, local refresh of flutterprovider
- Open a file at line with'filename:line'syntax - open a file at line with'filename:line' syntax
猜你喜欢

Median segmentation (find rules) - Niuke

Solution to the problem of multi application routing using thinkphp6.0
What is Wi Fi 6 (802.11ax)? Why is Wi Fi 6 important?

Opencv鼠标事件+界面交互之绘制矩形多边形选取感兴趣区域ROI
Flutter (III) - master the usage of dart language in an article

Detailed explanation of the generate go file command of import in golang (absolute detail)

数据中心灾难恢复的重要参考指标:RTO和RPO

Jemter 压力测试 -基础请求-【教学篇】

What are the characteristics of digital factory in construction industry

Junit
随机推荐
45. jumping game II dynamic planning DP
Data governance: from top project to data culture!
Es performance tuning and other features
技术分享 | MySQL:caching_sha2_password 快速问答
Apache InLong毕业成为顶级项目,具备百万亿级数据流处理能力!
Project management learning
ASP. Net and Net framework and C #
How to define a digital factory and what is the relationship with smart factory and industry 4.0
Detach an entity from jpa/ejb3 persistence context
Google Earth engine (GEE) 01- the prompt shortcut ctrl+space cannot be used
Common uniapp configurations
手机开户哪个证券公司佣金最低?网上开户是否安全么?
[UVM basics] TLM common data receiving and sending and data receiving examples
Jemter 压力测试 -可视化工具-【使用篇】
Ping An technology's practice of migrating from Oracle to ubisql
Google Earth Engine(GEE) 02-基本了解和学习资源
Leetcode topic [array] -11- containers with the most rainwater
Which securities company has the lowest Commission for opening a mobile account? Is it safe to open an account online?
Flutter (III) - master the usage of dart language in an article
JS Date object