当前位置:网站首页>Opencv Learning Notes 6 -- image feature [harris+sift]+ feature matching
Opencv Learning Notes 6 -- image feature [harris+sift]+ feature matching
2022-07-01 14:55:00 【Cloudy_ to_ sunny】
opencv Learning Notes 6 -- Image features [harris+SIFT]+ Feature matching
Image features (SIFT-Scale Invariant Feature Transform)
Image scale space
To a certain extent , Whether the object is big or small , The human eye can tell , But it's hard for computers to have the same capabilities , So let the machine be able to have a unified understanding of objects at different scales , We need to consider the characteristics of images in different scales .
The scale space is usually obtained by Gaussian blur


Different σ The Gaussian function determines the smoothness of the image , The bigger σ The more blurred the image is .
Multiresolution pyramid
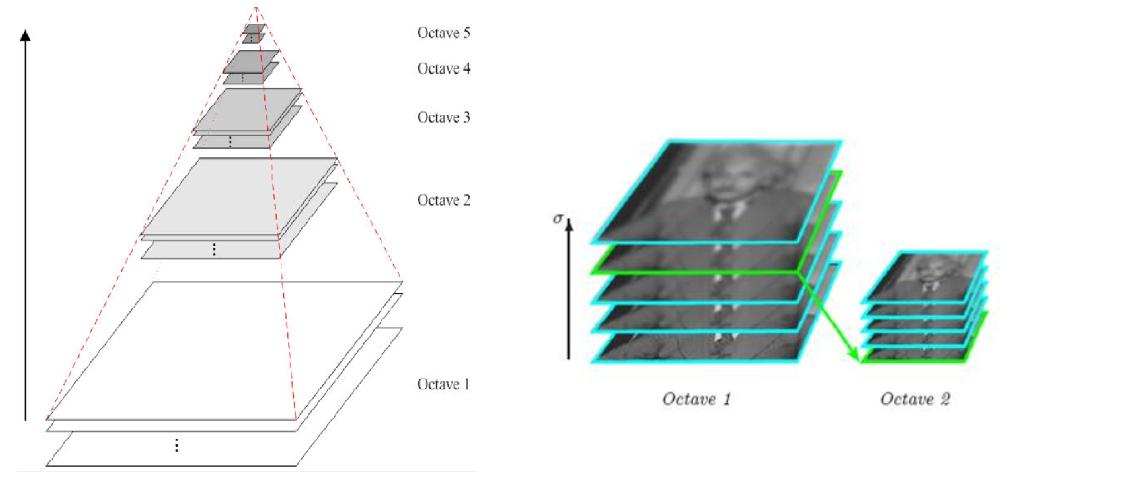
Gaussian difference pyramid (DOG)


DoG Spatial extremum detection
In order to find the extremum of scale space , Each pixel and its image domain ( The same scale space ) And scale domain ( Adjacent scale space ) Compare all the adjacent points of , When it is greater than ( Or less than ) At all adjacent points , This point is the extreme point . As shown in the figure below , In the middle of the detection point and its image of 3×3 Neighborhood 8 Pixels , And its adjacent upper and lower floors 3×3 field 18 Pixels , common 26 Compare pixels .

Precise positioning of key points
The key points of these candidates are DOG The local extremum of a space , And these extreme points are discrete points , One way to accurately locate the extreme point is , For scale space DoG Function for curve fitting , Calculate its extreme point , So as to realize the precise positioning of key points .


Eliminate boundary response

The main direction of the feature point

Each feature point can get three information (x,y,σ,θ), I.e. location 、 Scale and direction . Keys with multiple directions can be copied into multiple copies , Then the direction values are assigned to the copied feature points respectively , A feature point produces multiple coordinates 、 The scales are equal , But in different directions .
Generating feature descriptions
After finishing the gradient calculation of the key points , Use histogram to count the gradient and direction of pixels in the neighborhood .

In order to ensure the rotation invariance of the feature vector , Focus on feature points , Rotate the axis in the neighborhood θ angle , That is, the coordinate axis is rotated to the main direction of the feature point .

The main direction after rotation is the center 8x8 The window of , Find the gradient amplitude and direction of each pixel , The direction of the arrow represents the direction of the gradient , The length represents the gradient amplitude , Then the Gaussian window is used to weight it , At the end of each 4x4 Draw on a small piece of 8 Gradient histogram in three directions , Calculate the cumulative value of each gradient direction , A seed point can be formed , That is, each feature is represented by 4 It is composed of seed points , Each seed point has 8 Vector information in three directions .

It is suggested that each key point should be used 4x4 common 16 A seed point to describe , Such a key point will produce 128 Dimensional SIFT Eigenvector .

opencv SIFT function
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt#Matplotlib yes RGB
img = cv2.imread('test_1.jpg')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
def cv_show(img,name):
b,g,r = cv2.split(img)
img_rgb = cv2.merge((r,g,b))
plt.imshow(img_rgb)
plt.show()
def cv_show1(img,name):
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
cv2.imshow(name,img)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
cv2.__version__ #3.4.1.15 pip install opencv-python==3.4.1.15 pip install opencv-contrib-python==3.4.1.15
'3.4.1'
Get the feature point
sift = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create()
kp = sift.detect(gray, None)
img = cv2.drawKeypoints(gray, kp, img)
cv_show(img,'drawKeypoints')
# cv2.imshow('drawKeypoints', img)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()

Calculating characteristics
kp, des = sift.compute(gray, kp)
print (np.array(kp).shape)
(6827,)
des.shape
(6827, 128)
des[0]
array([ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 21., 8., 0.,
0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 157., 31., 3., 1., 0., 0.,
2., 63., 75., 7., 20., 35., 31., 74., 23., 66., 0.,
0., 1., 3., 4., 1., 0., 0., 76., 15., 13., 27.,
8., 1., 0., 2., 157., 112., 50., 31., 2., 0., 0.,
9., 49., 42., 157., 157., 12., 4., 1., 5., 1., 13.,
7., 12., 41., 5., 0., 0., 104., 8., 5., 19., 53.,
5., 1., 21., 157., 55., 35., 90., 22., 0., 0., 18.,
3., 6., 68., 157., 52., 0., 0., 0., 7., 34., 10.,
10., 11., 0., 2., 6., 44., 9., 4., 7., 19., 5.,
14., 26., 37., 28., 32., 92., 16., 2., 3., 4., 0.,
0., 6., 92., 23., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=float32)
Image features -harris Corner detection

The basic principle






cv2.cornerHarris()
- img: The data type is float32 Into the image of
- blockSize: The size of the specified area in corner detection
- ksize: Sobel Window size used in derivation
- k: The value parameter is [0,04,0.06]
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt#Matplotlib yes RGB
img = cv2.imread('chessboard.jpg')
print ('img.shape:',img.shape)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# gray = np.float32(gray)
dst = cv2.cornerHarris(gray, 2, 3, 0.04)
print ('dst.shape:',dst.shape)
img.shape: (512, 512, 3)
dst.shape: (512, 512)
def cv_show(img,name):
b,g,r = cv2.split(img)
img_rgb = cv2.merge((r,g,b))
plt.imshow(img_rgb)
plt.show()
def cv_show1(img,name):
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
cv2.imshow(name,img)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
img[dst>0.01*dst.max()]=[255,255,255]
cv_show(img,'dst')
# cv2.imshow('dst',img)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()

Feature matching
Brute-Force Brute force match
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
img1 = cv2.imread('box.png', 0)
img2 = cv2.imread('box_in_scene.png', 0)
def cv_show(img,name):
b,g,r = cv2.split(img)
img_rgb = cv2.merge((r,g,b))
plt.imshow(img_rgb)
plt.show()
def cv_show1(img,name):
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
cv2.imshow(name,img)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
cv_show1(img1,'img1')

cv_show1(img2,'img2')

sift = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create()
kp1, des1 = sift.detectAndCompute(img1, None)
kp2, des2 = sift.detectAndCompute(img2, None)
# crossCheck It means that two feature points should match each other , for example A No i Characteristic points and B No j The nearest feature point , also B No j Feature points to A No i The feature points are also
#NORM_L2: Normalized array of ( Euclid distance ), If other feature calculation methods need to consider different matching calculation methods
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(crossCheck=True) # Brute force match
1 Yes 1 The matching of
matches = bf.match(des1, des2)
matches = sorted(matches, key=lambda x: x.distance)# Sort
img3 = cv2.drawMatches(img1, kp1, img2, kp2, matches[:10], None,flags=2)
cv_show(img3,'img3')

k For the best match
bf = cv2.BFMatcher()
matches = bf.knnMatch(des1, des2, k=2)#1 Yes K matching
good = []
for m, n in matches:
if m.distance < 0.75 * n.distance:
good.append([m])
img3 = cv2.drawMatchesKnn(img1,kp1,img2,kp2,good,None,flags=2)
cv_show(img3,'img3')

If you need to complete the operation more quickly , You can try to use cv2.FlannBasedMatcher
Random sampling consistency algorithm (Random sample consensus,RANSAC)

Select the initial sample points for fitting , Given a tolerance range , Keep iterating

After each fitting , There are corresponding data points within the tolerance range , Find out the situation with the largest number of data points , Is the final fitting result

Homography matrix

边栏推荐
- [zero basic IOT pwn] reproduce Netgear wnap320 rce
- Hidden rules of the workplace that must be understood before 30
- 炎炎夏日,这份安全用气指南请街坊们收好!
- Don't want to knock the code? Here comes the chance
- [zero basic IOT pwn] reproduce Netgear wnap320 rce
- Demand prioritization method based on value quantification
- leetcode:329. 矩阵中的最长递增路径
- It's settled! 2022 Hainan secondary cost engineer examination time is determined! The registration channel has been opened!
- 建立自己的网站(14)
- 音乐播放器开发实例(可毕设)
猜你喜欢
![[leetcode 324] 摆动排序 II 思维+排序](/img/cb/26d89e1a1f548b75a5ef9f29eebeee.png)
[leetcode 324] 摆动排序 II 思维+排序

Official announcement: Apache Doris graduated successfully and became the top project of ASF!
![[15. Interval consolidation]](/img/6c/afc46a0e0d14127d2c234ed9a9d03b.png)
[15. Interval consolidation]

微服务追踪SQL(支持Isto管控下的gorm查询追踪)

竣达技术丨室内空气环境监测终端 pm2.5、温湿度TVOC等多参数监测

cmake 基本使用过程
![[zero basic IOT pwn] reproduce Netgear wnap320 rce](/img/f7/d683df1d4b1b032164a529d3d94615.png)
[zero basic IOT pwn] reproduce Netgear wnap320 rce
![[dynamic programming] interval dp:p1005 matrix retrieval](/img/c9/2091f51b905d2c0ebc978dab3d34d3.jpg)
[dynamic programming] interval dp:p1005 matrix retrieval

111. Minimum depth of binary tree

JVM第二话 -- JVM内存模型以及垃圾回收
随机推荐
竣达技术丨室内空气环境监测终端 pm2.5、温湿度TVOC等多参数监测
Official announcement: Apache Doris graduated successfully and became the top project of ASF!
[Verilog quick start of Niuke series] ~ multi function data processor, calculate the difference between two numbers, use generate... For statement to simplify the code, and use sub modules to realize
Basic operations of SQL database
微信网页订阅消息实现
Salesforce、约翰霍普金斯、哥大 | ProGen2: 探索蛋白语言模型的边界
It's suitable for people who don't have eloquence. The benefits of joining the China Video partner program are really delicious. One video gets 3 benefits
【锁】Redis锁 处理并发 原子性
适合没口才的人做,加入中视频伙伴计划收益是真香,一个视频拿3份收益
How to view the state-owned enterprises have unloaded Microsoft office and switched to Kingsoft WPS?
[stage life summary] I gave up the postgraduate entrance examination and participated in the work. I have successfully graduated and just received my graduation certificate yesterday
一波三折,终于找到src漏洞挖掘的方法了【建议收藏】
微服务开发步骤(nacos)
JVM second conversation -- JVM memory model and garbage collection
What if you are always bullied because you are too honest in the workplace?
The data in the database table recursively forms a closed-loop data. How can we get these data
Build your own website (14)
深度分析数据在内存中的存储形式
[零基础学IoT Pwn] 复现Netgear WNAP320 RCE
博文推荐 | 深入研究 Pulsar 中的消息分块