当前位置:网站首页>509. 斐波那契数、爬楼梯所有路径、爬楼梯最小花费
509. 斐波那契数、爬楼梯所有路径、爬楼梯最小花费
2022-07-04 05:30:00 【贪睡的蜗牛】
509. 斐波那契数
斐波那契数 (通常用 F(n) 表示)形成的序列称为 斐波那契数列 。该数列由 0 和 1 开始,后面的每一项数字都是前面两项数字的和。也就是:
F(0) = 0,F(1) = 1
F(n) = F(n - 1) + F(n - 2),其中 n > 1
给定 n ,请计算 F(n) 。
输入:n = 2
输出:1
解释:F(2) = F(1) + F(0) = 1 + 0 = 1
输入:4
输出:3
解释:F(4) = F(3) + F(2) = 2 + 1 = 3
给你个4,4是需要3和2,3需要2和1,2需要1和1
从1遍历到该数 用数组保存遍历的值
class Solution {
public:
int fib(int n) {
if(n<=1) return n;
vector<int> temp(n+1);
temp[0]=0;
temp[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
temp[i]=temp[i-1]+temp[i-2];
}
return temp[n];
}
};
不用维护从1到n整个数字,用两个数值保存
class Solution {
public:
int fib(int n) {
if(n<=1) return n;
vector<int> temp(2);
temp[0]=0;
temp[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
temp[i%2]=temp[(i-1)%2]+temp[(i-2)%2];
}
return temp[n%2];
}
};
递归的方式
终点是返回1和0
class Solution {
public:
int fib(int n) {
if(n<=1) return n;
return fib(n-1)+fib(n-2);
}
};
70. 爬楼梯
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
输入:n = 3
输出:3
解释:有三种方法可以爬到楼顶。
- 1 阶 + 1 阶 + 1 阶
- 1 阶 + 2 阶
- 2 阶 + 1 阶
确定递推式(动态规划)
1、确定dp数组以及下标的含义和递推式
dp[i]=dp[i-1]+dp[i-2];
表示爬到当前层有从下一层和下下层两者方法的加和
2、dp数组初始化
dp[1]=1;
dp[2]=2;
3、确定遍历的顺序
迭代的方式 用数组保存从前到后
递归的方式 从后往前,但是也是从前开始计算的
1、迭代的方式,用数组保存(动态规划)
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n<=2) return n;
vector<int>dp(n+1);
dp[1]=1;
dp[2]=2;
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++)
{
dp[i]=dp[i-1]+dp[i-2];
}
return dp[n];
}
};
2、不用维护从1到n整个数字,用两个数值保存(动态规划)
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n<=2) return n;
vector<int>dp(n+1);
dp[0]=2;
dp[1]=1;
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++)
{
dp[i%2]=dp[(i-1)%2]+dp[(i-2)%2];
}
return dp[n%2];
}
};
3、递归的方式(动态规划)
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n<=2) return n;
return climbStairs(n-1)+ climbStairs(n-2);
}
};
4、回溯法
下面这个代码结果是正确的,用我的电脑运行了快十五秒,但是用其他的代码只用了几秒。
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
int count = 0;
dfs(n, 0, count);
return count;
}
int dfs(int n, int index, int& count) {
if (n == index)count++;
if (index > n) return -1;
//当前状态可以选择爬一步,也可以选择爬两步
//爬一步
dfs(n, index + 1, count);
//爬两步
dfs(n, index + 2, count);
return -1;
}
};
5、对于递归和回溯出现超时的原因
递归法出现了大量重复计算,比如我爬上10层,如下图有两个分支,一个是直接8层,一个是从9层延续到8层,这样就会出现大量的重叠。如果递归树继续往下画,重叠就会更多,递归法计算了大量的重叠子问题而导致效率低下。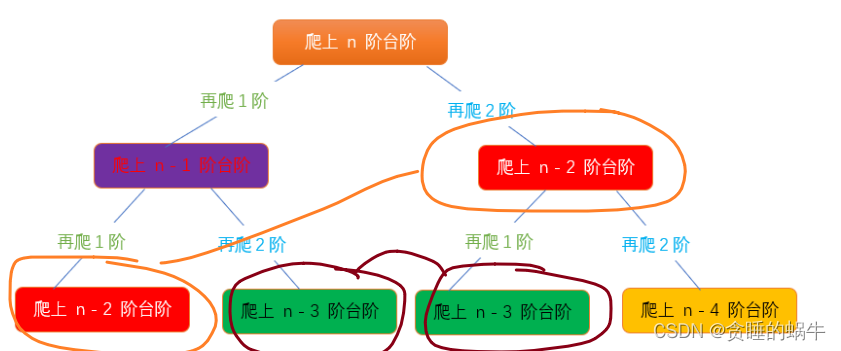
对于回溯法同样也是,此时的我是在楼梯中的一层,有很多分支会通过我,但是当第一个分支通过我已经计算了从我到达顶点的有多少种方法,但是其余的分支经过我竟然还进行了重复计算,这就造成了浪费。
解决方法:增加一个全局容器,存储信息
对于回溯而言。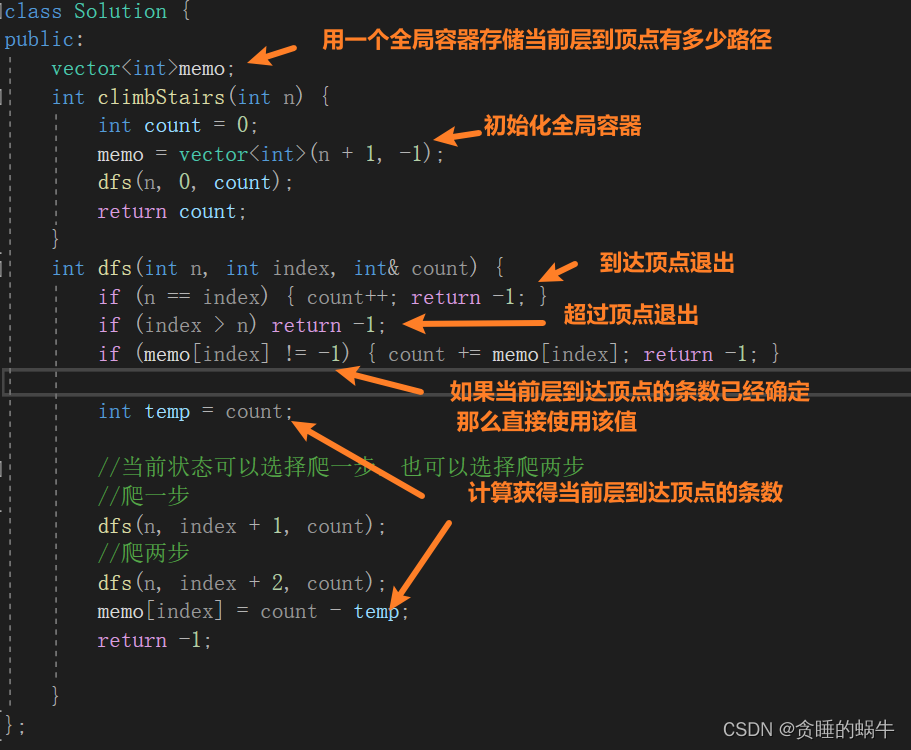
class Solution {
public:
vector<int>memo;
int climbStairs(int n) {
int count = 0;
memo = vector<int>(n + 1, -1);
dfs(n, 0, count);
return count;
}
int dfs(int n, int index, int& count) {
if (n == index) {
count++; return -1; }
if (index > n) return -1;
if (memo[index] != -1) {
count += memo[index]; return -1; }
int temp = count;
//当前状态可以选择爬一步,也可以选择爬两步
//爬一步
dfs(n, index + 1, count);
//爬两步
dfs(n, index + 2, count);
memo[index] = count - temp;
return -1;
}
};

class Solution {
public:
vector<int>memo;
int climbStairs(int n) {
memo = vector<int>(n + 1, -1);
return dfs(n);
}
int dfs(int n) {
if (n <= 2) return n;
if (memo[n] != -1) return memo[n];
int count= dfs(n - 1)+ dfs(n - 2);
memo[n] = count;
return count;
}
};
746. 使用最小花费爬楼梯
给你一个整数数组 cost ,其中 cost[i] 是从楼梯第 i 个台阶向上爬需要支付的费用。一旦你支付此费用,即可选择向上爬一个或者两个台阶。
你可以选择从下标为 0 或下标为 1 的台阶开始爬楼梯。
请你计算并返回达到楼梯顶部的最低花费。
输入:cost = [1,100,1,1,1,100,1,1,100,1]
输出:6
解释:你将从下标为 0 的台阶开始。
- 支付 1 ,向上爬两个台阶,到达下标为 2 的台阶。
- 支付 1 ,向上爬两个台阶,到达下标为 4 的台阶。
- 支付 1 ,向上爬两个台阶,到达下标为 6 的台阶。
- 支付 1 ,向上爬一个台阶,到达下标为 7 的台阶。
- 支付 1 ,向上爬两个台阶,到达下标为 9 的台阶。
- 支付 1 ,向上爬一个台阶,到达楼梯顶部。
总花费为 6 。
确定递推式
1、dp数组以及下标的含义
dp[i]表示到达第i层的最小花费
2、确定递推公式
到达i层有两种方式,一种是dp[i-1],一种是dp[i-2],那么选最小的
dp[i]=min{
dp[i-1],dp[i-2]}+cost[i];
为什么是cost[i],由于题目意思是上到i需要那些体力,因此就应该到哪就要花费到那的体力
3、dp数组初始化
dp[0] = cost[0];
dp[1] = cost[1];
4、确定遍历的顺序
从前到后遍历一遍就可以了
代码
class Solution {
public:
int minCostClimbingStairs(vector<int>& cost) {
vector<int>dp(cost.size());
dp[0] = cost[0];
dp[1] = cost[1];
for (int i = 2; i <cost.size(); i++) {
dp[i] = min(dp[i - 1],dp[i - 2] ) + cost[i];
}
return min(dp[cost.size() - 1], dp[cost.size() - 2]);
}
};
边栏推荐
- Just do it with your hands 7 - * project construction details 2 - hook configuration
- What are the reasons for the frequent high CPU of ECS?
- Solar insect killing system based on single chip microcomputer
- ETCD数据库源码分析——初始化总览
- What is MQ?
- JS string splicing
- How much computing power does transformer have
- KMP match string
- 光模塊字母含義及參數簡稱大全
- BUU-Crypto-[HDCTF2019]basic rsa
猜你喜欢

Zhanrui tankbang | jointly build, cooperate and win-win zhanrui core ecology

2022 t elevator repair operation certificate examination question bank and simulation examination
![[Excel] 数据透视图](/img/45/be87e4428a1d8ef66ef34a63d12fd4.png)
[Excel] 数据透视图

RSA加密应用常见缺陷的原理与实践
ansys命令
![BUU-Crypto-[GUET-CTF2019]BabyRSA](/img/87/157066155e8d3a93e30a68eaf1781b.jpg)
BUU-Crypto-[GUET-CTF2019]BabyRSA

BUU-Pwn-test_ your_ nc

VB.net 简单的处理图片,黑白(类库——7)

Letter meaning and parameter abbreviation of optical module Daquan

卸载Google Drive 硬盘-必须退出程序才能卸载
随机推荐
BUU-Reverse-easyre
BUU-Real-[PHP]XXE
c语言经典指针和数组笔试题解析
BUU-Pwn-test_ your_ nc
Evolution of system architecture: differences and connections between SOA and microservice architecture
Remote desktop client RDP
Simulated small root pile
2022年R2移动式压力容器充装复训题库及答案
How to configure static IP for Kali virtual machine
2022 a special equipment related management (elevator) examination questions simulation examination platform operation
fastjson
Thinkphp6.0 middleware with limited access frequency think throttle
JS string splicing
LC weekly 300
Ping port artifact psping
left_ and_ right_ Net normal version
Just do it with your hands 7 - * project construction details 2 - hook configuration
谷歌 Chrome 浏览器将支持选取文字翻译功能
Online shrimp music will be closed in January next year. Netizens call No
拓扑排序和关键路径的图形化显示