当前位置:网站首页>Chapter 13 IO flow
Chapter 13 IO flow
2022-07-27 12:14:00 【Haha's tea】
Catalog
1. Character stream FileReader and FileWriter Use
2. Byte stream FileInputStream and FileOutputStream Use
3. One of the processing streams : The use of buffer streams
4. Treatment flow 2 : The use of conversion streams
5. Standard input 、 Output stream
6. Print stream :PrintStream and PrintWriter
Custom classes implement serialization and deserialization operations
10. NIO.2 in Path、Paths、Files The use of the class
File The use of the class
1.File An object of class , Represents a file or a file directory ( Be commonly called : Folder )
2.File Class declaration in java.io It's a bag
3.File Class involves the creation of files or file directories 、 Delete 、 rename 、 Modification time 、 File size, etc , It does not involve writing or reading the contents of the file . If you need to read or write the contents of the file , You have to use IO Flow to complete .
4. follow-up File The object of the class is often passed as an argument to the constructor of the stream , To indicate read or write to “ End ”

1. How to create File Class
File(String filePath)
File(String parentPath,String childPath)
File(File parentFile,String childPath)2. Relative paths : Compared with the path indicated under a certain path . Absolute path : The path to the file or file directory that contains the drive letter

3. Path separator : windows:\\ unix:/
Common methods
public String getAbsolutePath(): Get absolute path
public String getPath(): Get path
public String getName(): Get the name
public String getParent(): Get the upper file directory path . If there is no , return null
public long length(): Get file length ( namely : Number of bytes ). Cannot get the length of the directory .
public long lastModified(): Get the last modification time , Millisecond value
The following method applies to file directories :
public String[] list(): Get the name array of all files or file directories in the specified directory
public File[] listFiles(): Get all the files in the specified directory or file directory File Array
public boolean renameTo(File dest): Rename the file to the specified file path
such as :file1.renameTo(file2) For example
To ensure return true, need file1 It exists in the hard disk , And file2 Can't exist in the hard disk .
public boolean isDirectory(): Determine whether it is a file directory
public boolean isFile(): Determine if it's a document
public boolean exists(): Judge whether it exists
public boolean canRead(): Judge whether it is readable
public boolean canWrite(): Judge whether it is writable
public boolean isHidden(): Determine whether to hide
Create the corresponding file or file directory in the hard disk
public boolean createNewFile(): create a file . If the file exists , Do not create , return false.
public boolean mkdir(): Create file directory . If this file directory exists , We won't create . If the upper directory of this file directory does not exist , It doesn't create .
public boolean mkdirs(): Create file directory . If the upper file directory does not exist , Exist together
Delete a file or file directory from the disk
public boolean delete(): Delete files or folders
Delete notes :java Delete in does not go to the recycle bin . To delete successfully ,io4 There can't be subdirectories or files in the file directory I/O yes Input/Output Abbreviation ,I/O Technology is a very practical technology , be used for Data transmission between processing devices . As read / Writing documents , Network communication, etc .Java In the program , For data input / Output operation to “ flow (Stream)” By .java.io A variety of “ flow ” Classes and interfaces , To get different kinds of data , And pass Standard method Input or output data .
One 、 Classification of flows
1. Operating data units : Byte stream 、 Character stream
2. The flow of data : Input stream 、 Output stream
3. The role of flow : Node flow 、 Processing flow
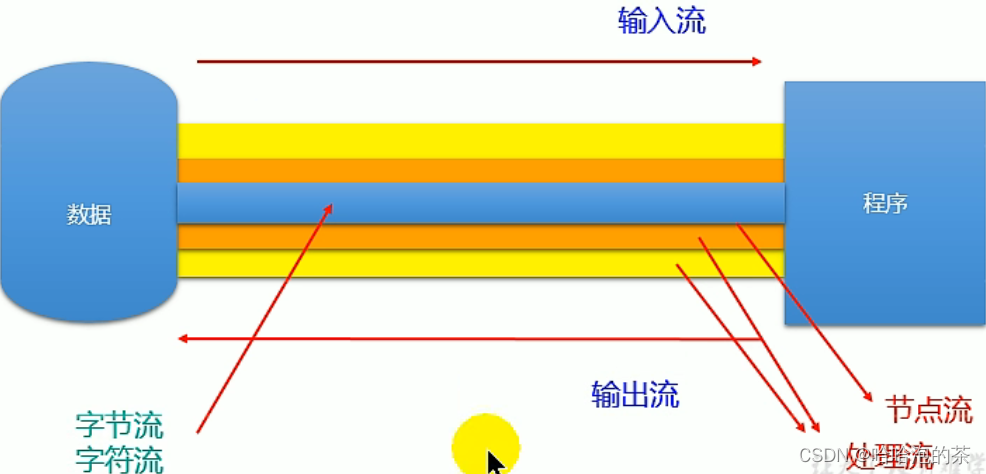
Two 、 Flow architecture
Abstract base class Node flow ( Stream or file ) Buffer flow ( One kind of processing flow )
InputStream FileInputStream (read(byte[] buffer)) BufferedInputStream (read(byte[] buffer))
OutputStream FileOutputStream (write(byte[] buffer,0,len)) BufferedOutputStream (write(byte[] buffer,0,len)) / flush()
Reader FileReader (read(char[] cbuf)) BufferedReader (read(char[] cbuf) / readLine())
Writer FileWriter (write(char[] cbuf,0,len)) BufferedWriter (write(char[] cbuf,0,len)) / flush()1. Character stream FileReader and FileWriter Use
take day09 Under the hello.txt The contents of the file are read into the program , And output to the console
explain : 1.read(): Returns a character read in . If the end of the file is reached , return -1 read(char[] cbuf): Return every read in cbuf The number of characters in the array . If the end of the file is reached , return -1
2. Exception handling : In order to ensure that the stream resource can be closed . Need to use try-catch-finally Handle
3. The file read in must exist , Otherwise it will be reported FileNotFoundException.
Write data from memory to a file on the hard disk
explain :1. Output operation , Corresponding File Can not exist . No exception will be reported
2. File If the file in the corresponding hard disk does not exist , In the process of output , This file will be created automatically .
File If the file in the corresponding hard disk exists :
If the constructor used by the stream is :FileWriter(file,false) / FileWriter(file): Overwrite the original file
If the constructor used by the stream is :FileWriter(file,true): The original file will not be overwritten , Instead, the contents are added on the basis of the original documents
2. Byte stream FileInputStream and FileOutputStream Use
Conclusion :1. For text files (.txt, .java, .c, .cpp), Use character stream FileReader、FileWriter Handle
2. For non text files (.jpg, .mp3, .mp4, .avi, .doc, .ppt, ...), Use byte stream FileInputStream、FileOutputStream Handle
3. One of the processing streams : The use of buffer streams
1. Buffer flow :BufferedInputStream BufferedOutputStream BufferedReader BufferedWriter
2. effect : Improve the read speed of the stream 、 The speed of writing The reason to improve the speed of reading and writing : Internally, a buffer is provided , By default 8kb
3. Processing flow , Namely “ Socket joint ” On the basis of existing flows .
explain : While closing the outer laminar flow , The inner layer flow will be automatically closed . Therefore, the closing of inner laminar flow can be omitted .
4. Treatment flow 2 : The use of conversion streams
1. Converted flow : Belongs to the character stream
InputStreamReader: Convert a byte input stream to a character input stream
OutputStreamWriter: Convert the output stream of one character to the output stream of bytes 2. effect : Provides conversion between byte stream and character stream
3. decode : byte 、 Byte array ---> A character array 、 character string code : A character array 、 character string ---> byte 、 Byte array
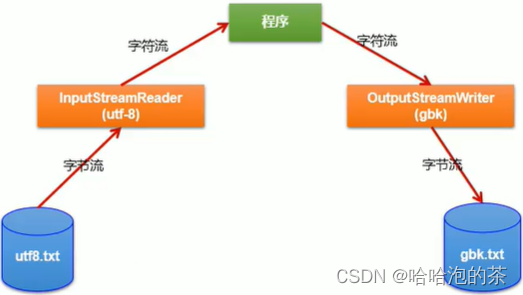
4. Character set
ASCII: American standard information interchange code . Use a byte of 7 Bits can represent .
ISO8859-1: Latin code table . European Code watch Use a byte of 8 Who said .
GB2312: Chinese code table of China . Up to two bytes encode all characters .
GBK: China's Chinese coding table upgrade , It integrates more Chinese characters and symbols . Up to two text encodings
Unicode: International Standard Code , It's a fusion of all the characters currently used by humans . Assign a unique character code to each character . All the text is represented in two bytes .
UTF-8: Variable length encoding , You can use 1-4 Bytes to represent a character .5. Standard input 、 Output stream
(1) System.in: Standard input stream , Input from the keyboard by default System.out: Standard output stream , Output from the console by default
(2) adopt System Class setIn(InputStream is) / setOut(PrintStream ps) Method to specify the input and output streams
(3) practice : Enter a string from the keyboard , Request to read the whole line of string into uppercase output . Then proceed with the input operation , Until you type “e” perhaps “exit” when , Exit procedure .
Method 1 : Use Scanner Realization , call next() Returns a string
Method 2 : Use System.in Realization .System.in ---> Converted flow ---> BufferedReader Of readLine()
6. Print stream :PrintStream and PrintWriter
(1) Provides a series of overloaded print() and println()
(2) practice : Like the one below test1()

7. Data flow
(1)DataInputStream and DataOutputStream
(2) effect : A variable or string used to read or write basic data types

practice : Put the string in memory 、 The variables of the basic data type are written out to the file . Read the basic data type variables and strings stored in the file into memory , Save in variable .
Be careful :① When handling exceptions , You should still use try-catch-finally.
② Read different types of data in the same order as when the file was originally written , Keep the data in the same order !
8. Object flow
1.ObjectInputStream and ObjectOutputStream
2. effect : A processing stream used to store and read basic data type data or objects . His strength is that he can put java Write the object in to the data source , It can also restore objects from the data source .
3. Think of one java Objects are serializable , Need to meet the corresponding requirements . see Person.java
4. Serialization mechanism : The object serialization mechanism allows the java Object to platform independent binary stream , This allows this binary stream to be permanently stored on disk , Or transfer this binary stream over the network to another network node . When other programs get this binary stream , It can be restored to the original java object .
Serialization process : Put... In memory java Objects are saved to disk or transmitted over the network Use ObjectOutputStream Realization
Deserialization : Restore the object in the disk file to one in memory java object Use ObjectInputStream Realization
Custom classes implement serialization and deserialization operations
Person The following requirements need to be met , To serialize
1. Need to implement interface :Serializable
2. The current class provides a global constant :serialVersionUID
3. Except for the present Person Class needs to be implemented Serializable Beyond the interface , You must also ensure that all its internal properties must also be serializable .( By default , Basic data types are serializable )
Add :ObjectInputStream and ObjectOutputStream Cannot serialize static and transient Modified member variables
9. Random access file stream
RandomAccessFile Use
1.RandomAccessFile Directly inherited from java.lang.Object class , Realized DataInput and DataOutput Interface
2.RandomAccessFile It can be used as an input stream , It can also be used as an output stream
3. If RandomAccessFile As an output stream , If the written file does not exist , Is automatically created during execution ; If the file written to exists , The contents of the original file will be overwritten .( By default , Ab initio coverage )
4. You can use related operations , Realization RandomAccessFile“ Insert ” The effect of data


10. NIO.2 in Path、Paths、Files The use of the class

Path、Paths、Files The core API


Path Interface

Files class


边栏推荐
- deeplab系列详解(简单实用年度总结)
- 基于bolt数据库实现简单的区块链 day(2)
- 图像分割 vs Adobephotoshop(PS)
- In the first half of the year, the number of fires decreased by 27.7%. Guangdong will improve the fire safety quality of the whole people in this way
- Sword finger offer notes: T53 - ii Missing numbers from 0 to n-1
- Leetcode 03: t58. Length of the last word (simple); Sword finger offer 05. replace spaces (simple); Sword finger offer 58 - ii Rotate string left (simple)
- Newticker uses
- N ¨UWA: Visual Synthesis Pre-training for Neural visUal World creAtionChenfei
- B 站 713 事故后的多活容灾建设|TakinTalks 大咖分享
- Leetcode 02: sword finger offer 58 - I. flip the word order (simple); T123. Verify palindrome string; T9. Palindromes
猜你喜欢

Analysis of the use of JUC framework from runnable to callable to futuretask

npm踩坑
![[untitled] multimodal model clip](/img/f0/8ae72ae0845372b6fe2866fae83f52.png)
[untitled] multimodal model clip

解决方案:Can not issue executeUpdate() or executeLargeUpdate() for SELECTs
Unexpected harvest of epic distributed resources, from basic to advanced are full of dry goods, big guys are strong!

go入门篇 (4)

Why is ack=seq+1 when TCP shakes hands three times

【机器学习-白板推导系列】学习笔记---概率图模型和指数族分布
Iptables firewall

Newton Raphson iterative method
随机推荐
Introduction to box diagram
基于bolt数据库实现简单的区块链 day(2)
LNMP architecture setup (deploy discuz Forum)
Leetcode 03: t58. Length of the last word (simple); Sword finger offer 05. replace spaces (simple); Sword finger offer 58 - ii Rotate string left (simple)
[网摘][医学影像] 常用的DICOM缩略图解释以及Viewer converter 转换工具
V-show失效问题
Pytorch shows the summary like tensorflow
Unity Shader 一 激光特效Shader[通俗易懂]
查看系统下各个进程打开的文件描述符数量
Sword finger offer notes: T53 - ii Missing numbers from 0 to n-1
Can you really write binary search - variant binary search
Database cli tool docker image
How to make a graph? Multiple subgraphs in a graph are histogram (or other graphs)
Arduino常见供电问题与解决
Sword finger offer notes: t58 - ii Rotate string left
Makefile template
硬刚甲方后:中国移动 4908 万大单被废
【机器学习-白板推导系列】学习笔记---条件随机场
Do you really understand the underlying data structure skip list of Zset in redis?
Summary of leetcode SQL exercises (MySQL Implementation)
