当前位置:网站首页>Luogu p4047 [jsoi2010] tribal division solution
Luogu p4047 [jsoi2010] tribal division solution
2022-07-03 14:27:00 【q779】
Luogu P4047 [JSOI2010] Tribal Division Answer key
Topic link :P4047 [JSOI2010] Tribal Division
The question :
Congcong's research found that , Wild islanders always live in groups , however , Not all the savages on the whole desert island belong to the same tribe , Wild people are always ganging up to form their own tribes , There are often fights between different tribes . It's just , It's all a mystery —— Congcong doesn't know how the tribes are distributed .
But the good news is , Congcong gets a map of the desert island . The map is marked n n n A place where savages live ( It can be regarded as coordinates on the plane ). We know , Savages of the same tribe always live nearby . We put the distance between the two tribes , It is defined as the distance between the two nearest settlements in the tribe . Congcong also got a meaningful message —— These savages are divided into k k k Tribes ! That's good news . Congcong hopes to mine the details of all tribes from this information . He is trying such an algorithm :
For any method of tribal division , Can find the distance between the two tribes , Congcong hopes to find a way to divide tribes , Keep the two nearest tribes as far away as possible .
for example , The left figure below shows a good division , The picture on the right is not . Please program to help Congcong solve this problem .
about 100 % 100\% 100% The data of , Guarantee 2 ≤ k ≤ n ≤ 1 0 3 2 \leq k \leq n \leq 10^3 2≤k≤n≤103, 0 ≤ x , y ≤ 1 0 4 0 \leq x, y \leq 10^4 0≤x,y≤104.
The minimum distance is the maximum , One eye and two points
But here is a kruskal Solution method
Let's put the O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2) The edge is built
Then find the minimum spanning tree
Greedily divide the minimum spanning tree into k k k A connecting block
Concrete , We just merge the smallest edges of the tree in turn
Finally, a total of ( n − 1 ) − ( k − 1 ) = n − k (n-1)-(k-1) = n-k (n−1)−(k−1)=n−k side
So the answer is n − k + 1 n-k+1 n−k+1 The edge weight of the edge
Mouth paste a proof of correctness ( Maybe not very rigorous )
Consider counter evidence
Set an edge on the minimum spanning tree w 1 ( u , v ) w_1(u,v) w1(u,v) , Replace it with w 2 ( u , v ′ ) w_2(u,v^{\prime}) w2(u,v′) ( w 2 > w 1 w_2>w_1 w2>w1)
If w 1 w_1 w1 Will be merged and we merged w 2 w_2 w2 , It seems that there is no change
If w 1 w_1 w1 Will be merged and we didn't merge w 2 w_2 w2 ,
Then we must merge a ratio w 1 w_1 w1 Big side , And it is the edge on the minimum spanning tree
So the answer will be too big
If w 1 w_1 w1 Will not be merged and we merged w 2 w_2 w2 , There is no such situation .
If w 1 w_1 w1 Will not be merged and we did not merge w 2 w_2 w2 , No influence .
Time complexity O ( n 2 log n ) O(n^2 \log n) O(n2logn)
Code :
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f
#define N (int)(1e3+15)
#define M (int)(1e6+15)
#define pf(x) ((x)*(x))
struct Edge{
int u,v,w;}e[M];
int n,k,f[N],x[N],y[N],c[N],pos;
int find(int x){
return f[x]==x?x:f[x]=find(f[x]);}
void merge(int u,int v){
f[find(u)]=find(v);}
void addEdge(int u,int v,int w){
e[++pos]={
u,v,w};}
int dis(int i,int j){
return pf(x[i]-x[j])+pf(y[i]-y[j]);}
void kruskal()
{
sort(e+1,e+1+pos,[](Edge a,Edge b)
{
return a.w<b.w;
});
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1; i<=pos&&cnt<n; i++)
{
int u=e[i].u,v=e[i].v;
if(find(u)!=find(v))
{
merge(u,v);
c[++cnt]=e[i].w;
}
}
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
// freopen("check.in","r",stdin);
// freopen("check.out","w",stdout);
cin >> n >> k;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
f[i]=i,cin >> x[i] >> y[i];
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
for(int j=1; j<i; j++)
addEdge(i,j,dis(i,j));
kruskal();
cout << fixed << setprecision(2);
cout << sqrt((double)c[n-k+1]) << '\n';
return 0;
}
Reprint please explain the source
边栏推荐
- Common commands for getting started with mongodb database
- Too many files with unapproved license
- Sub-GHz无线解决方案Z-Wave 800 系列ZG23 soc和ZGM230S模块
- 7-14 sum integer segments (C language)
- Exercise 10-8 recursive implementation of sequential output of integers
- Strategy, tactics (and OKR)
- js 2023. String pair equal to the target string after connection
- Exercise 8-8 moving letters
- Learn to punch in today
- 超简单手机地图开发
猜你喜欢
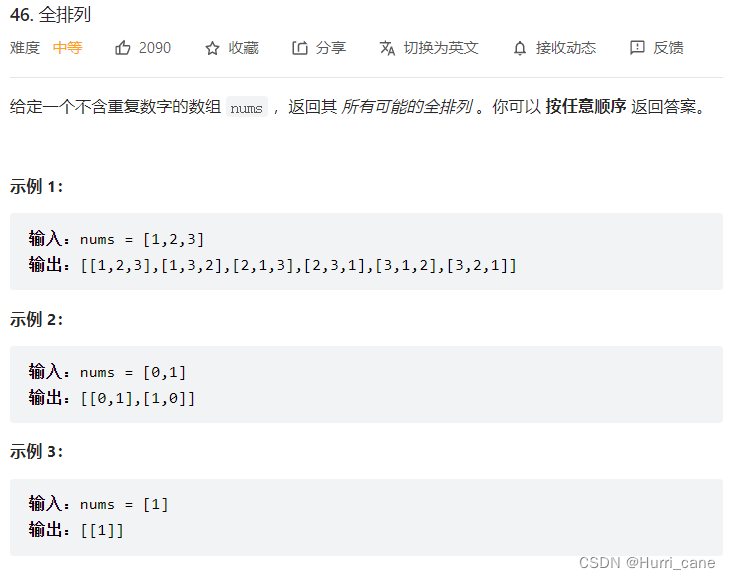
Thinking about the arrangement problem in the backtracking problem (leetcode questions 46 and 47)
protobuf与grpc

Protobuf and grpc

JS input number and standard digit number are compared. The problem of adding 0 to 0

Leetcode(4)——寻找两个正序数组的中位数
![洛谷P4047 [JSOI2010]部落划分 题解](/img/7f/3fab3e94abef3da1f5652db35361df.png)
洛谷P4047 [JSOI2010]部落划分 题解
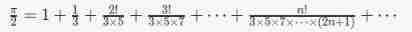
7-15 calculation of PI
Exercise 9-1 time conversion
TS code automatically generates JS

Doris学习笔记之数据表的创建
随机推荐
Sendmail can't send mail and it's too slow to send. Solve it
Preliminary summary of structure
JS matrix zero
TS code automatically generates JS
剑指 Offer 28. 对称的二叉树
7-14 sum integer segments (C language)
556. The next larger element III
Stop asking yourself if you are suitable for software testing
ConstraintLayout 的使用
7-6 mixed type data format input
7-4 BCD decryption (10 points)
Leetcode(4)——寻找两个正序数组的中位数
MongoDB数据库入门的常用命令
7-2 and then what time (15 minutes)
Accelerating strategy learning using parallel differentiable simulation
Sub-GHz无线解决方案Z-Wave 800 系列ZG23 soc和ZGM230S模块
天图投资冲刺港股:资产管理规模249亿 投了小红书与奈雪
7-24 reduction of the simplest fraction (rolling Division)
NFT new opportunity, multimedia NFT aggregation platform okaleido will be launched soon
好看、好用、强大的手写笔记软件综合评测:Notability、GoodNotes、MarginNote、随手写、Notes Writers、CollaNote、CollaNote、Prodrafts、Noteshelf、FlowUs、OneNote、苹果备忘录