当前位置:网站首页>[Part 13] source code analysis and application details of completabilefuture class [key]
[Part 13] source code analysis and application details of completabilefuture class [key]
2022-06-11 21:21:00 【__ Struggling Kaka】
1.1 summary
From the last article we know , Use Future When you get the result of asynchronous execution , Or call the blocking method get(), Or polling isDone() Is it true, Neither method is very good , Because the main thread will also be forced to wait .
from Java 8 It's starting to introduce CompletableFuture, It's for Future Improvements have been made. , You can pass in the callback object , When an asynchronous task completes or an exception occurs , Automatically call the callback method of the callback object . When the task is finished , The calling thread is notified to execute the callback method . Before calling the callback method , The calling thread can perform other tasks , It's non blocking .
CompletableFuture It also provides Serial 、AND polymerization 、OR Aggregate calls multiple tasks , And support exception handling .
1.2 Principle analysis
1.2.1 CompletionStage
- CompletionStage Represents a stage in the asynchronous computing process , After one phase is completed, another phase may be triggered
- A phase of computation execution can be a Function,Consumer perhaps Runnable. such as :stage.thenApply(x -> square(x)).thenAccept(x -> System.out.print(x)).thenRun(() -> System.out.println())
- The execution of a phase may be triggered by the completion of a single phase , It can also be triggered by multiple phases together
1.2.2 CompletableFuture
- stay Java8 in ,CompletableFuture Provides a very powerful Future Extension of , Can help us Simplify the complexity of asynchronous programming , And it provides Functional programming The ability of , The calculation result can be processed by callback , There are also transformations and combinations CompletableFuture Methods .
- It may represent a clearly accomplished Future, It could also represent a completion phase (CompletionStage), It supports triggering some functions or performing some actions after the calculation is completed .
- It has achieved Future and CompletionStage Interface

1.2.3 CompletableFuture in API
1、CompeletableFuture< Void > runAsync(Runnable r)
Asynchronous execution Runnable, By default, the public ForkJoinPool
2、CompeletableFuture< Void > runAsync(Runnable r,Executor e)
And methods 1 The difference is that the thread pool is specified .
3、CompeletableFuture< U > supplyAsync(Supplier supplier)
Perform tasks asynchronously , And methods 1 The difference is Runnable no return value , and Supplier Can return value .
4、CompeletableFuture< U > supplyAsync(Supplier supplier,Executor e)
And methods 3 The difference is , You can specify a thread pool
The above four methods are to execute tasks asynchronously .
1.2.4 CompletableFuture Serial call to
CompletableFuture A serial call interface is provided to ensure two CompletableFuture Serial calls between , The function of callback method can be realized in disguise .
CompletableFuture Provides 8 A serial function :
1、CompeletableFuture< U > thenApply(Function<T,R> f)
Function<T,R> Incoming parameters required , And it will return the value
2、CompeletableFuture< U > thenCompose(Function<T,R> f)
and thenApply The difference is , Incoming Function The code in the needs to contain CompletableFuture, Incoming parameters required , And it will return the value
3、CompeletableFuture< Void > thenAccept(Consumer< T > c)
Consumer Incoming parameters required , No return value Synchronous execution
4、CompeletableFuture< Void > thenRun(Runnable r)
Runnable Neither parameters can be passed in , Nor can it return parameters
5、CompeletableFuture< U > thenApplyAsync(Function<T,R> f)
6、CompeletableFuture< U > thenComposeAsync(Function<T,R> f)
7、CompeletableFuture< Void > thenAcceptAsync(Consumer< T > c)
8、CompeletableFuture< Void > thenRunAsync(Runnable r)
Method 5-8 And methods 1-4 The difference between , Namely Async That is, it will asynchronously call the later CompeletableFuture
CompletableFuture<String> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("this is f1");
return "this is f1";
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> f2 = f1.thenApplyAsync((s)->{
System.out.println(s+","+s);return 1;});
CompletableFuture<Void> f3 = f1.thenAccept((s)->{
System.out.println(s+"、"+s);});
CompletableFuture<Void> f4 = f1.thenRun(()->System.out.println("runable"));
CompletableFuture<String> f5 = f1.thenCompose(s->CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(s);return "Compose";}));

As can be seen from the above code ,f1.thenApplyAsync I just created one CompletableFuture f2, Its task is
(s)->{
System.out.println(s+","+s);return 1;}
f2 Is in f1 Called after execution .
1.2.5 CompletableFuture Of AND Aggregate call
In addition to the previous and subsequent call relationships ,CompletableFuture It also provides 6 Aggregate call method ,AND The meaning of aggregate call now has three CompletableFuture, Only when two CompletableFuture When they're all done , Will execute the third CompletableFuture.
1、CompletableFuture< U > thenCombine(Completable other,Function< T, R> f)
Third CompletableFuture yes Function Type of .
2、CompletableFuture< Void > runAfterBoth(Completable other,Runnable r)
Third CompletableFuture yes Runnable Type of .
3、CompletableFuture< Void > thenAcceptBoth(CompletableFuture other,Consumer c);
Third CompletableFuture yes Consumer Type of .
4、CompletableFuture< U > thenCombineAsync(Completable other,Function< T, R> f)
5、CompletableFuture< Void > runAfterBothAsync(Completable other,Runnable r)
6、CompletableFuture< Void > thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletableFuture other,Consumer c);
Method 4-6 Compared to the method 1-3 The difference is that the third... Is executed asynchronously CompletableFuture.
CompletableFuture<String> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("this is f1");
return "f1 return";
});
CompletableFuture<String> f2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("this is f2");
return "f2 return";
});
CompletableFuture<String> f6 = f1.thenCombine(f2,(s1,s2)->{
System.out.println(s1+"--thenCombine--"+s2); return "this is f6";});
CompletableFuture<Void> f7 = f1.runAfterBoth(f2,()->{
System.out.println("runnable");});
CompletableFuture<Void> f8 = f1.thenAcceptBoth(f2,(s1,s2)->{
System.out.println(s1+"consumer"+s2);});

1.2.6 CompletableFuture Of OR Aggregate call
CompletableFuture Provides 6 individual OR Aggregate call .OR Aggregate calls mean , Now there are three CompletableFuture, When one of the two calls is completed , A third... Will be triggered CompletableFuture Implementation .
1、CompletableFuture< U > applyToEither(CompletableFuture other,Function<T,R> f);
Third CompletableFuture yes Function Type of .
2、CompletableFuture< U > acceptEither(CompletableFuture other,Consumer< T > c);
Third CompletableFuture yes Consumer Type of .
3、CompletableFuture< U > runAfterEither(CompletableFuture other,Runnable r);
Third CompletableFuture yes Runnable Type of .
4、CompletableFuture< U > applyToEitherAsync(CompletableFuture other,Function<T,R> f);
5、CompletableFuture< U > acceptEitherAsync(CompletableFuture other,Consumer< T > c);
6、CompletableFuture< U > runAfterEitherAsync(CompletableFuture other,Runnable r);
Method 4-6 Compared to the method 1-3 The difference is that the third... Is executed asynchronously CompletableFuture.
CompletableFuture<String> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(4000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("this is f1");
return "f1 return";
});
CompletableFuture<String> f2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("this is f2");
return "f2 return";
});
CompletableFuture<String> f9 = f1.applyToEither(f2,(s1)->{
System.out.println(s1+"--applyToEither--");return s1+"**";});
CompletableFuture<Void> f10 = f1.acceptEither(f2,(s1)->{
System.out.println(s1+"--accept--");});
CompletableFuture<Void> f11 = f1.runAfterEither(f2,()->{
System.out.println("Runnable");});
f1.join();

1.2.7 CompletableFuture Exception handling in
CompletableFuture Also provided catch finally The mechanism of
1、Catch
CompletableFuture< R > exceptionally(Function<T,R> f)
When something goes wrong , Would call f.
2、finally
CompletableFuture< R > whenComplete(BiConsumer< T > c)
Only receive parameters
CompletableFuture< R > handler(BiFunction<T,R> f)
Both receive parameters , Return value again
about whenComplete、handler There are corresponding asynchronous calling methods , The corresponding method is whenCompleteAsync()、handlerAsync().
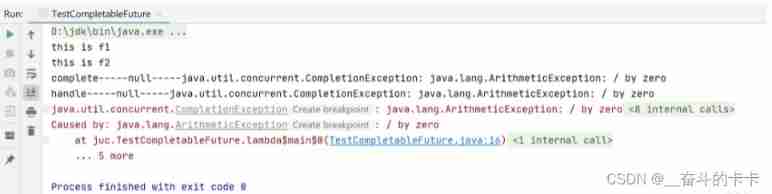
CompletableFuture<String> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("this is f1");
int a = 0/0;
return "f1 return";
});
f1.exceptionally(e->{
e.printStackTrace();return e.toString();});
f1.whenComplete((r1,r2)->{
System.out.println("complete-----"+r1+"-----"+r2);});
f1.handle((r1,r2)->{
System.out.println("handle-----"+r1+"-----"+r2);return r1 +"--"+r2;});
1.3 summary
CompletableFuture Compare with Future, Support serial calls between tasks 、AND Aggregate call 、OR Aggregate call 、 Exception handling and other functions . Serial calls can implement callback functions .
边栏推荐
- [nk] 牛客练习赛100 C 小红的删数字
- Release of version 5.6 of rainbow, add multiple installation methods, and optimize the topology operation experience
- ASCII码对照表
- Release of version 5.6 of rainbow, add multiple installation methods, and optimize the topology operation experience
- Add personal statement for go file in file template in Golan
- Serval and Rooted Tree(CF1153D)-DP
- In idea, run the yarn command to show that the file cannot be loaded because running scripts is disabled on this system
- Application scenario: wide application of Poe network card in NDI technology for live broadcast program production
- New product release: lr-link Lianrui launched the first 25g OCP 3.0 network card
- Implement AOP and interface caching on WPF client
猜你喜欢
One article to show you how to understand the harmonyos application on the shelves

【数据可视化】使用 Apache Superset 可视化 ClickHouse 数据
![[nk] deleted number of 100 C Xiaohong in Niuke practice match](/img/f1/a99600e1800c087aceb60a559dee39.png)
[nk] deleted number of 100 C Xiaohong in Niuke practice match

新品发布:LR-LINK联瑞推出首款25G OCP 3.0 网卡

Use float to create a page header, footer, left content, and main content.

ORA-04098: trigger ‘xxx. xxx‘ is invalid and failed re-validation

New product release: lr-link Lianrui launched the first 25g OCP 3.0 network card
Compilation process of program

The secret of derating - don't challenge Datasheet

BCC tool tool usage
随机推荐
[Game Theory - introduction]
Live broadcast with practice | 30 minutes to build WordPress website with Alibaba cloud container service and container network file system
bzoj3188 Upit
Field queryIndexFieldnameService in xxxImpl required a single bean, but 19 were found:
可综合RTL代码设计方法和注意事项
[index system] the latest modeling method of data warehouse index system
RANSAC extraction plane (matlab built-in function)
Notes on the preload method of Gorm
New product release: domestic single port Gigabit network card is officially mass produced!
应用场景:现场直播节目制作NDI技术中PoE网卡的广泛应用
Why should I use iwarp, roce V2, nvme of and other protocols for 100g network transmission
为什么需要微服务
MySQL add adds multiple new fields and specifies the field location
技术交流|网络安全设备为什么要用Bypass功能
【博弈论-绪论】
Weekly 02 | to tell you the truth, I am actually a student of MIT
Work assessment of spectral analysis of Jilin University in March of the 22nd spring -00079
Serval and Rooted Tree(CF1153D)-DP
【C语言进阶】整型在内存中的存储
Solve the problem of img 5px spacing