当前位置:网站首页>Understanding of "dbdnet: a deep boosting strategy for imagedenoising"
Understanding of "dbdnet: a deep boosting strategy for imagedenoising"
2022-07-26 00:16:00 【RrS_ G】
translate :DBDnet: Depth enhancement strategy for image denoising
-- IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MULTIMEDIA -- 2021
Catalog
3、 ... and 、 experimental result
One 、 introduction
In the learning based denoising method , Residual learning is the most commonly used denoising method . This method can generate a noise map from noisy observations , Then we can get a noiseless image , Pictured 1 Shown .

However , The method based on residual learning is difficult to obtain accurate noise map even if using complex networks , That is, the noise graph always contains some noise . The author calls this kind of noise the noise of noise graph (NoN). Intuitively ,NoN The more , The lower the denoising performance , Find an effective way to reduce NoN Influence , It is very important to obtain high-quality images .
Previous methods based on deep learning rarely consider this problem . In the field of traditional image denoising , Based on boosting Methods , And designed some good boosting Module to solve this problem . This module can iteratively eliminate NON, Extract a clean noise map . Therefore, the author developed boosting Algorithm , And make full use of their advantages to eliminate NoN.
Let's introduce boosting Algorithm :
In recent years , People have proposed a variety of methods based on boosting Methods ,“twicing” Technology is a very early research , Its boosting The process is described as follows :

among f It is a de-noising operator , The left side of the equation represents the first n Sub iteration .
be based on “twicing” technology ,Bregman Iteration adopts an iterative regularization method , This method is based on Bregman The concept of distance , Add the residual noise back to the observation signal .Bregman Iterative boosting The process can be written as :

In recent years ,boosting The algorithm is introduced into the field of deep learning , To improve the performance of the network . Here is the author's method .
Two 、 Method
A、 motivation
The basic problem of image denoising is from noise observation y Restore clean images in x, It can be expressed as :
![]()
among v Represents additive noise mapping , Gaussian white noise usually modeled as zero mean . The main goal of the residual learning network is to observe from noise y Generate noise mapping v Approximation of , This process can be expressed as :
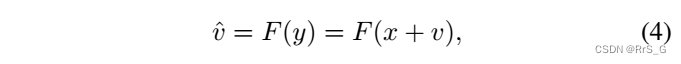
among F Represents the algorithm for generating noise residuals , The leftmost side of the equation is the generated noise signature (GNFM).
Besides , Noiseless image x The approximate calculation of is :
![]()
The left side of the equation is the final denoising result . From this formula , It has a great impact on the final result , However, due to the capacity limitations of general Networks ,
It has a great impact on the final result , However, due to the capacity limitations of general Networks , Will contain some noise ( namely NoN), That is to say v and
Will contain some noise ( namely NoN), That is to say v and  It's not equal , Suppose there is a gap u, That is, both meet :
It's not equal , Suppose there is a gap u, That is, both meet : .
.
The author thinks that u Affected by two parts , The first is the original image x High frequency information ( That is, boundary information and detail information ), Especially when generating  In the process of , original image x Some high-frequency information
In the process of , original image x Some high-frequency information  Will be recognized as noise , Introduced to the
Will be recognized as noise , Introduced to the  in , As a result
in , As a result  False identification part of . Besides , Noise observation y Although some pixels of are polluted by noise , But it will still be recognized as clean pixels . therefore , Noise map cannot be completely extracted from noise observation ,
False identification part of . Besides , Noise observation y Although some pixels of are polluted by noise , But it will still be recognized as clean pixels . therefore , Noise map cannot be completely extracted from noise observation , It will contain some unrecoverable noise information
It will contain some unrecoverable noise information  .
.
under these circumstances ,u It can be used  To express . in other words , The unrecovered noise information
To express . in other words , The unrecovered noise information  add , Subtract the misidentified high-frequency information
add , Subtract the misidentified high-frequency information  , You can start from
, You can start from  Get a clean noise map v. The process can be expressed as :
Get a clean noise map v. The process can be expressed as :
![]()
therefore , stay boost In the process , You can update :
You can update :

among  and
and  It's network simulation
It's network simulation  and
and  Generated feature mapping .
Generated feature mapping .
Through this operation ,NoN Can gradually reduce .
B、NoN Eliminate modules
stay Eq.(7) Inspired by , eliminate NoN The process can be decomposed into generating characteristic graphs  、 Generate feature map
、 Generate feature map  The process of . So , The author puts forward two different NoN Eliminate the module to generate these two feature maps . Next , The specific implementation of these two non elimination modules will be introduced in detail .
The process of . So , The author puts forward two different NoN Eliminate the module to generate these two feature maps . Next , The specific implementation of these two non elimination modules will be introduced in detail .
(1)、 modular A: modular A It can be downloaded from  Simultaneous generation
Simultaneous generation  and
and  , The overall structure is shown in the figure 2(A) Shown .
, The overall structure is shown in the figure 2(A) Shown .

A convolution block is used to extract the unrecovered noise map  And a dense attention block to extract false high-frequency information
And a dense attention block to extract false high-frequency information  . Be careful ,
. Be careful , It's noise mapping v Part of , It's easy to get from
It's noise mapping v Part of , It's easy to get from  Extract it from . however
Extract it from . however  Is the original image x Part of, not v Of , So in order to extract it accurately , The author uses the dense attention block ( Strong ability to capture information ). In order to improve the complexity of dense attention blocks and the ability of information capture , The author introduces two advanced deep learning technologies ( Dense connection and attention mechanism ), Pictured 2(d) Shown .
Is the original image x Part of, not v Of , So in order to extract it accurately , The author uses the dense attention block ( Strong ability to capture information ). In order to improve the complexity of dense attention blocks and the ability of information capture , The author introduces two advanced deep learning technologies ( Dense connection and attention mechanism ), Pictured 2(d) Shown .
The whole process can be described as :

CB It's a convolution block ,DAB Indicates a dense attention block .
(2)、 modular B: The author found that from  It's extracted directly from
It's extracted directly from  and
and  It's not accurate , Because they will affect each other in the process of being extracted , modular B That's the solution , See the picture for details 2(b) Shown . modular B First generate
It's not accurate , Because they will affect each other in the process of being extracted , modular B That's the solution , See the picture for details 2(b) Shown . modular B First generate  , Then subtract it as the input of the next module . The whole process is shown as follows :
, Then subtract it as the input of the next module . The whole process is shown as follows :

C、 Network structure
After obtaining the above two NoN After eliminating the module , Plug them into the network , Generate DBDnet. The network structure is shown in the figure 3 Shown .

Take the noise observation value y For input , Convolution layer extraction  , experienced n individual NoN Eliminate modules , Finally, the final predicted noise map is obtained through a convolution layer . The specific algorithm is as follows :
, experienced n individual NoN Eliminate modules , Finally, the final predicted noise map is obtained through a convolution layer . The specific algorithm is as follows :
 among
among  It means the first one n individual NoN Eliminate modules .
It means the first one n individual NoN Eliminate modules .
The optimization objectives are as follows :

3、 ... and 、 experimental result
Here are some experimental results .
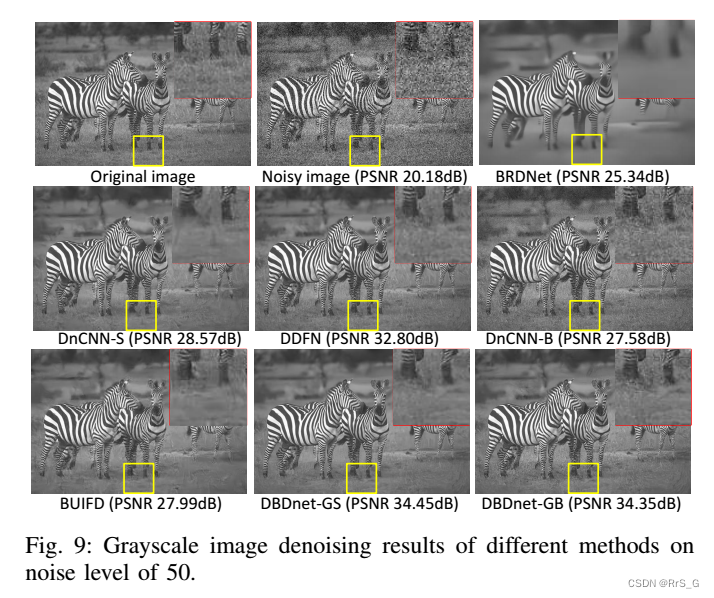
grayscale :
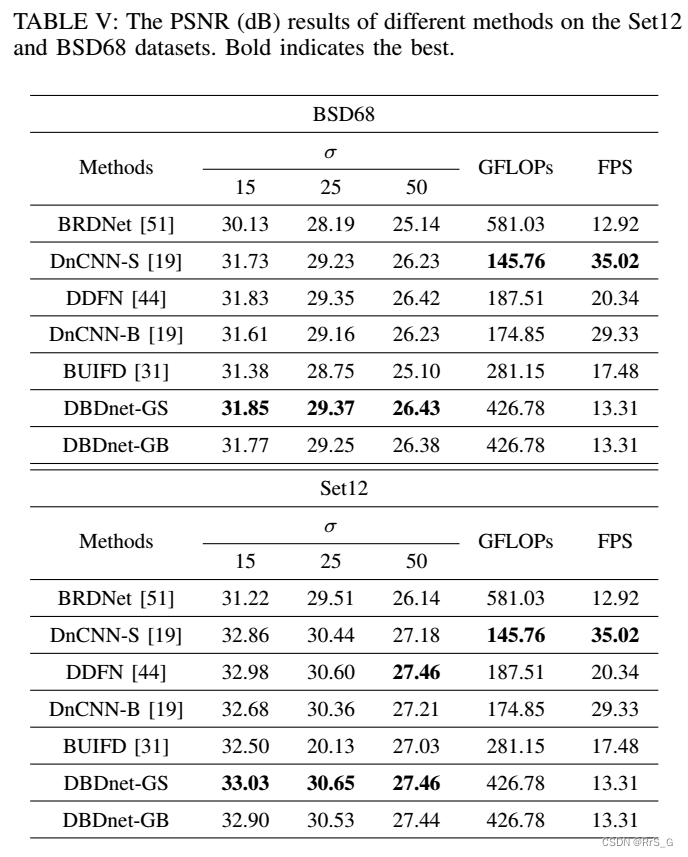
among GFLOPs For computational complexity ,FPS To infer speed .

Real images :
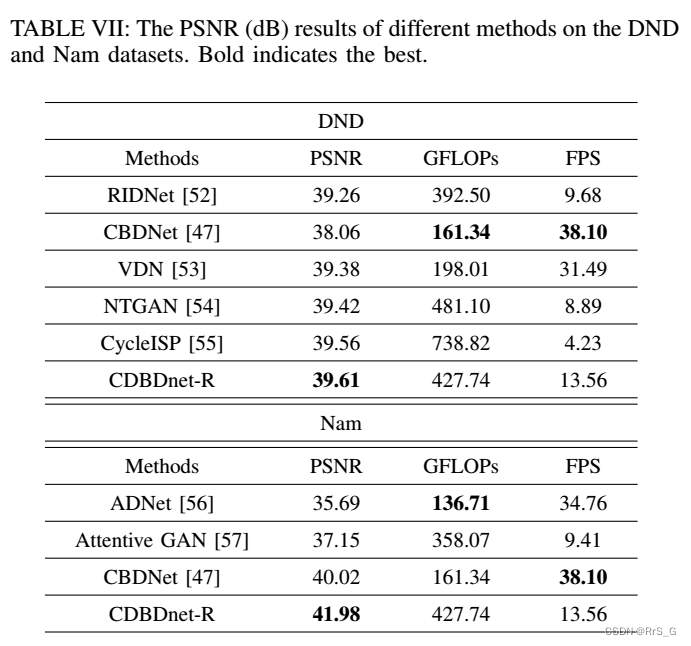

Code :
pcl111/DBDNet: Code of "DBDnet: A Deep Boosting Strategy for Image Denoising" (github.com)
边栏推荐
- 06_ue4进阶_使用地形工具设置大地图
- 痞子衡嵌入式:MCUXpresso IDE下将源码制作成Lib库方法及其与IAR,MDK差异
- 【目录】Nodejs、npm、yarn、BUG
- What does it mean that the web server stops responding?
- 07_ UE4 advanced_ MP value of firing fireball and mechanism of attacking blood deduction
- Js理解之路:Js常见的6中继承方式
- LeetCode 刷题系列 -- 931. 下降路径最小和
- Stm32- analyze latency based on assembly
- 服务器如何搭建虚拟主机?
- FreeRTOS个人笔记-互斥量
猜你喜欢
Binary tree 101. Symmetric binary tree

Leetcode169 detailed explanation of most elements
Binary tree - 617. Merge binary tree

Getaverse, a distant bridge to Web3
Bond network card mode configuration

NVIDIA可编程推理加速器TensorRT学习笔记(三)——加速推理

“动物币”凶猛,陷阱还是机遇?2021-05-12
![Niuke / Luogu - [noip2003 popularization group] stack](/img/95/871b1c6f492b467bffd25912304b44.gif)
Niuke / Luogu - [noip2003 popularization group] stack

Piziheng embedded: the method of making source code into lib Library under MCU Xpress IDE and its difference with IAR and MDK

【一库】mapbox-gl!一款开箱即用的地图引擎
随机推荐
Piziheng embedded: the method of making source code into lib Library under MCU Xpress IDE and its difference with IAR and MDK
Nest.js 用了 Express 但也没完全用
Leetcode question brushing series -- 931. Minimum sum of descent path
Solve the problem of rapid index bar extrusion
This time, thoroughly understand promise principle
FreeRTOS个人笔记-消息队列
NVIDIA programmable reasoning accelerator tensorrt learning notes (III) -- Accelerating reasoning
FreeRTOS个人笔记-互斥量
J9 number theory: what is Dao mode? Obstacles to the development of Dao
MySQL - database log
06_ UE4 advanced_ Set up a large map using the terrain tool
06_ue4进阶_使用地形工具设置大地图
After using MQ message oriented middleware, I began to regret
Redirection and request forwarding
MySQL——多版本并发控制(MVCC)
计算物理期刊修改
OPENCV学习DAY6
Sort fake contacts
Getaverse,走向Web3的远方桥梁
Jd.com API for obtaining recommended product list