当前位置:网站首页>Pleasant and burden free cross process communication
Pleasant and burden free cross process communication
2022-06-11 23:51:00 【I'm Wong Tai Sin】
List of articles
1. background
A recent requirement involves cross process communication , The common practice of cross process communication is to define AIDL Interface , Then start a service , Get the binding service binder object , Then you can start communicating .
With more and more business modules , Each module needs to define its own AIDL Interface , This may lead to more and more interfaces , More and more difficult to manage .
Is there any elegant way to communicate across processes ?
I think of it. EventBus. At the beginning of learning Android When , This framework is used , I thought it was really easy to use , It can realize the decoupling between modules very gracefully .
Is it possible to refer to EventBus , Implement a cross process version of EventBus Well ? I've been referring to these days EventBus Design idea , Rolled up a framework ProcessBus, It is very convenient to realize cross process communication .
Welcome to build together .
Address :https://github.com/bearhuang-omg/ProcessBus
2. Usage mode
The interface provided is very simple :
| Interface | Parameters | Return value | remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| init( Not necessary ) | context:Context | nothing | initialization , Pass in context Used for binding Service, If no incoming , Then, the components will be internally reflected context, Then bind Service |
| register | cmd:String // Listening instructions block: (Event)→Unit // Callback method for receiving instructions | Releasable // Pass in lifecycle You can automatically de register , Avoid memory leaks | Listen for an instruction |
| unRegister | observerKey:String // The only one returned during registration key | nothing | Anti registration |
| post | event:Event // Events sent | nothing | Send an event |
Example :
// Monitoring events , And automatically de register
Bus.register("testCmd2") {
event ->
Log.i(TAG, " Received the incident ")
}?.autoRelease(lifecycle)
// Send events
Bus.post(Event("testCmd2", " The message sent "))
// Manually de register
val key = Bus.register("testCmd1") {
event ->
Log.i(TAG, " Received the incident ")
}?.key!!
Bus.unRegister(key)
As can be seen from the example ,ProcessBus It's very simple to use , And it can realize decoupling between different modules , Replace most of AIDL Interface .
ProcessBus Has the following characteristics :
- Simple interface ;
- There is no need to actively call the initialization method , Can be used anywhere ( Actively calling initialization methods can avoid reflection , Be efficient );
- Event Can carry accessories , For transferring large files .
3. The basic principle
chart
ProcessBus The structure diagram of is as follows :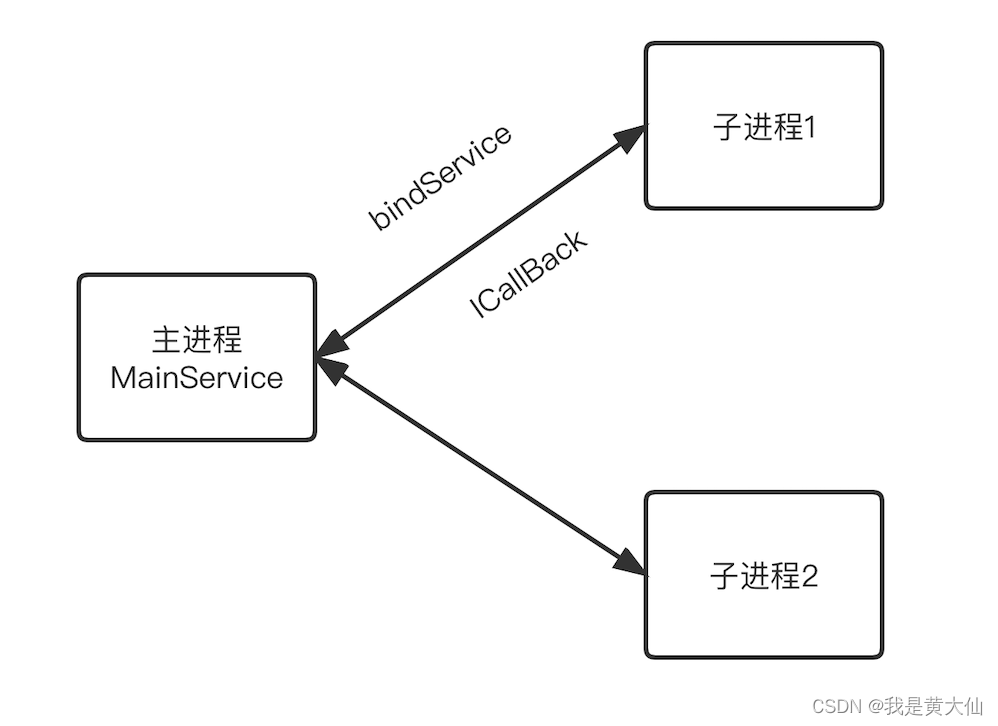
sdk Internally, a service will be started in the main process , Designed for cross process communication , When a child process registers or sends a message , Will automatically bind the service ,
After binding the service , At this time, the subprocess will replace the current ProcessKey and ICallBack Pass to the main process , among ProcessKey Is a string that uniquely marks a process ,ICallBack It's a binder object , The main process gets this binder After object , You can send messages to the child process .
technological process
The specific flow chart is as follows :
| step | remarks | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | bindService | The child process is bound to the main process service , Get the... That communicates with the main process binder |
| 2 | bind | The child process passes through the binder take ProcessKey and ICallBack Pass to the main process , After the main process receives it, it saves it in map among |
| 3 | reigster | Subprocesses will focus on cmd Tell the main process , After the main process receives , Save in map among |
| 4 | post | Other child processes send a Event To main process , The main process will match after receiving cmd, Then get the corresponding one ICallBack |
| 5 | ICallBack | The main process gets the corresponding ICallBack after , perform ICallBack Method , take Event To the corresponding child process |
About Event
Event The data structure of is as follows :
| data | remarks |
|---|---|
| cmd:String( must ) | Instructions , The main process will send the command to the listening object |
| content:String ( must ) | The content carried by the event |
| fromProcess:String ( sdk Inside filling ) | Sent process name , from sdk Inside filling |
| attachmentBinder:IBinder ( Not necessary ) | The attachment , It's a binder object , Suitable for transferring large files , The target process passes directly through binder Get attachments |
4. summary
At present, only the most basic functions have been realized , You can consider adding comments later , Give Way sdk More convenient to use .
Welcome to build together .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

思科私有动态路由协议:EIGRP

Graph and graph traversal

Flex flexible layout tutorial and understanding of the main axis cross axis: Grammar

How many steps does it take for C language to become Fibonacci number

图及图的遍历
![将数组分成和相等的三个部分[问题分析]](/img/0b/856fcceb0373baa8acb46e9ae2c861.png)
将数组分成和相等的三个部分[问题分析]

CVPR 2022 | meta learning performance in image regression task

sonarqube介绍和安装步骤

Ar helps brand stores achieve global data growth

Simulated examination question bank and simulated examination of 2022 crane driver (limited to bridge crane)
随机推荐
SF14 | supertrend "super trend" indicator magic change and upgrade (source code)
2022 high place installation, maintenance and removal of simulated examination platform for operation certificate examination question bank
swiper
Live broadcast preview | featurestore meetup V3 is coming!
Jenkins of the integrate tool
Mingdeyang FPGA development board xilinx-k7 core board kinex7k325 410t industrial grade
2022 operation of simulation examination platform for safety officer C certificate
Dblink operation in Oracle
【delphi】判断文件的编码方式(ANSI、Unicode、UTF8、UnicodeBIG)
(dp+ longest common subsequence) acwing 897 Longest common subsequence
抗原產品進入家庭,中國醫療器械企業迎來新藍海
Custom font settings
In order to stimulate inspiration and creativity, Shanghai daoning united with XMIND to bring you full-featured mind mapping and brainstorming software
[signals and systems] (XXII) Laplace transform and complex frequency domain analysis - s-domain analysis
04 automatic learning rate - learning notes - lihongyi's in-depth learning 2021
El scrollbar display horizontal scroll bar
A new product with advanced product power, the new third generation Roewe rx5 blind subscription is opened
Handwritten simple promise
On the knowledge points of cookie attributes and the differences between webstorage and cookies?
平衡二叉树(AVL 树)